Blue or blackening of gangrenous areas is associated with the active synthesis of iron sulfide produced during the destruction of hemoglobin. Gangrene affects any tissue and organs - the skin, subcutaneous fat, muscle structures, smooth muscles of internal organs.
Gangrene of the limbs is an irreversible process, the spread of which can only be stopped through surgical intervention (vascular shunting). Such manipulations make it possible to avoid complete amputation of a limb, limiting itself only to the removal of necrotic (dead) tissue.
What symptoms precede blackening of the toes?
Some people wonder why the big toe turns black and what such alarming symptoms may indicate. It is worth noting that darkening of the skin of the lower extremities does not occur suddenly. Often this phenomenon is preceded by other signs that are worth paying attention to.
Symptoms that precede a change in skin tone on the legs:
- toenails become deformed and their shape changes noticeably;
- constant pain in the lower extremities with varying intensity;
- legs become less or, conversely, very sensitive;
- the general condition worsens, which manifests itself in the form of weakness and fever;
- areas of the skin on the legs become red and very flaky;
- legs swell;
- the feet become too cold or, conversely, too warm.
All these symptoms appear, as a rule, before the legs turn black and increase gradually. It is important to seek help from a specialist when blackheads first appear on your legs, as this may indicate tissue death.
Diabetes mellitus: the leg turned black, pain and other symptoms appeared
Black spots on the legs with diabetes rarely appear suddenly.
As a rule, darkening of the skin color is preceded by the following symptoms:
- change in the shape of the nail bed on the toes;
- gradually increasing painful sensations;
- decreased sensitivity or, conversely, hypersensitivity of the skin;
- deterioration in general health (weakness, low-grade fever);
- redness, peeling, keratinization of the skin area;
- the appearance of swelling of the limbs;
- your feet become hot or, conversely, too cold.
All these symptoms appear before the blackening of the fingers and legs, developing gradually. Please note that lightning-fast blackening of any part of the limb indicates tissue necrosis.
In this case, it is necessary to urgently contact a surgeon to find out the cause of the blackening of the skin and prescribe therapy.
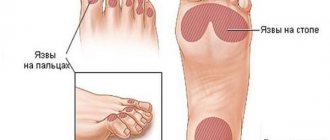
Why do my feet turn black?
Most often, such an alarming symptom as a blackened toe is associated with gangrene. But this pathology is not the only reason for changes in skin color.
Common causes of blackening of the skin on the legs:
- Fungal infection. Here we are not talking about ordinary candidiasis, but about an atypical and dangerous form called trichophyton. It often manifests itself as blackening of not only the fingers, but also the nails. The disease is accompanied by severe itching and numbness of the lower extremities. The infection spreads quickly and treatment is difficult.
- Problems with blood vessels. This is often the cause of darkening of the skin in diabetes mellitus. With an increased level of glucose in the blood, the formation of blood clots is activated, which adhere to the walls of blood vessels, narrowing the lumen for the passage of blood. In the absence of therapy, thromboembolism occurs, which leads to tissue death and the only treatment here is amputation.
- Mechanical damage. What should I do if I stubbed my toe and it turned black? In this case, the cause of blackening may be a fracture of the phalanges or a severe bruise. If the hematoma does not spread to adjacent areas of the skin, it should not cause concern. The swelling and blackening will go away over time, like a regular bruise. If, on the contrary, this area enlarges or begins to bleed, it is worth undergoing examination by a specialist.
- Tight shoes or being on your feet for a long time. Frequent formation of calluses and corns, which leads to darkening of skin areas, can be caused by improperly sized shoes, as well as heavy load on the lower limbs.
- Acanthosis nigricans. It most often occurs in diabetics due to insulin resistance. In this case, itching, thickening and darkening of the skin gradually leads to cell death or the formation of tumors.
- Hereditary predisposition. It is rare and is primarily associated with the peculiarity of skin pigmentation. In this case, there is no painful sensation, except for aesthetic discomfort. No therapy required.
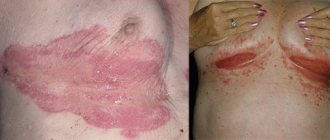
Causes of gangrene development
Gangrene is classified as dry or wet. A pathological condition develops against the background of various factors. For the extremities, the most common ischemic causes are acute and persistent disruption of blood supply against the background of occlusive vascular lesions. An infectious process, an allergic reaction, or exposure to toxins can contribute to the development of gangrene. Among external factors, the first most common place is occupied by frostbite and burns.
Gangrene is always caused by a disorder of tissue nutrition and destruction of cellular structures. It develops mainly in areas of the body remote from the heart, but sometimes it can even affect internal life-supporting organs (with ischemia of the intestines or lungs).
Wet gangrene is considered the most life-threatening because it progresses quickly and has a severe course.
The causes of necrotic tissue damage include:
- Physico-chemical and temperature irritations (injuries, frostbite, burns - thermal or acid);
- Infectious processes;
- Diabetes mellitus (and related disorders, including diabetic micro- and macroangiopathy);
- Cardiac decompensation (severe forms of heart failure);
- Progressive atherosclerosis and other occlusive vascular lesions;
- Emboli;
- Obliterating endarteritis;
- Mechanical compression of large blood vessels or their injury (for example, during injury with a cold weapon or firearm).
The most common catalyst for gangrene is cardiovascular pathologies that provoke disorders of the central and peripheral circulation.
The process of gangrene development is irreversible, so if you have specific symptoms, it is important to urgently seek professional medical help.
Features of the development and speed of spread of gangrene depend on the following factors:
- Region of residence (especially the presence of epidemics in it);
- General condition of the body (necrosis progresses most quickly in persons with exhaustion, hypovitaminosis, intoxication, chronic pathologies, anemia and diseases associated with metabolic and hemostasis disorders);
- Climatic conditions (both excessive cooling and intense heating catalyze the rapid spread of necrosis);
- Anatomical disorders of the structure of tissues and organs;
- Habits and lifestyle (smoking and alcohol abuse in the presence of vascular pathologies significantly increase the risk of developing the disease).
- Therapy for gangrene is carried out only in a hospital setting, often with emergency hospitalization of the patient.
How to distinguish diabetes from gangrene due to darkening of the toes?
A symptom such as blackened toes in diabetes mellitus occurs when iron sulfide is formed from hemoglobin cells under the influence of air. In 95% of cases, diabetics experience so-called dry gangrene. The pathology does not cause acute intoxication and is not accompanied by tissue decay. This has little effect on the general condition.
Dry gangrene also requires appropriate therapy, but develops gradually. The disease can progress from 3 weeks to several years. Amputation and disability can be avoided by seeking treatment in the early stages of the disease. It is important not to confuse the pathology with ordinary gangrene, which is accompanied by tissue death.
Symptoms of gangrene are as follows:
- pain when walking;
- increased swelling of the legs;
- the shade of the skin changes quickly, moving from pink to black;
- the boundaries of infection are clearly visible;
- there is no unpleasant odor or it is quite insignificant.
Gangrene, regardless of the type, is also curable, especially if treatment is organized in the first stages. During therapy, attention is paid to restoring normal blood circulation, as well as eliminating infections that led to tissue death. Surgical intervention is possible, during which muscle tissue affected by necrosis is removed.
Symptoms of gangrene
The symptoms of gangrene are extremely specific and cannot be confused with manifestations of other diseases and disorders.
Dry gangrene, which is most characteristic of vascular etiology, is not life-threatening. The affected tissues do not disintegrate, but become mummified - they dry out, losing fluid. Toxic substances are released in moderate quantities, and the body manages to inactivate them. The focus of necrotic lesion is clearly organic and distinguishable. Wet gangrene is characterized by intense and aggressive coverage of tissue structures, very rapid progression, and infection of the systemic bloodstream by poisons released during necrosis. This condition often becomes a consequence of an infectious process and poses a direct threat to the patient’s life.
Common symptoms of gangrene of the hands or feet:
- A sharp and severe attack of pain in the affected limb;
- Fading of the cover and its subsequent coloring in a marble shade;
- Reduction (in the dry form) or increase (in the wet form) of the limb in size;
- Complete loss of sensitivity in the affected tissues;
- Dyeing fabrics dirty gray (when wet) or blue-black (when dry);
- The appearance of a persistent putrid odor (in the wet form) / clear limitation of dead tissue (in the dry form).
The difference lies in the general well-being of the patient. With the wet form of gangrene, it rapidly worsens - symptoms of extensive intoxication appear, the pulse weakens, and chills are observed. With dry gangrene, such symptoms do not occur. The affected limb often detaches on its own.
How to treat black toes with diabetes?
When blackening appears on the lower extremities, especially in diabetes mellitus, diagnostics are carried out to determine the cause of the development of the pathology. First of all, the condition of the blood vessels is checked using ultrasound. It is important that the blood flow is not impaired. Neurological reflexes, artery scanning, arteriography and diagnostics of changes in pressure on the fingers are also carried out. It is mandatory to measure the pulse in the lower extremities by palpation.
Often patients at an appointment ask the question, what to do: did you stub your toe and it turned black? Most often, an x-ray is taken to identify a fracture, which can cause a change in skin color. In this case, plaster is applied. If there is no fracture, then other diagnostic methods can be used to identify the root cause of the blackening.
Most often, drug treatment is carried out, which is aimed at restoring normal blood flow and the condition of blood vessels in case of blockage. It is important during therapy to pay attention to the shoes a person wears. It should be comfortable. This will prevent the damaged limb from inflammatory and purulent processes.
Surgery (bypass surgery, angioplasty) is also performed if a too narrowed area inside the large arteries is detected.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of gangrene is not difficult and includes:
- Inspection of the affected area (visual);
- Arterio- or phlebography;
- Ultrasound Doppler examination of blood vessels;
- Rheovasography;
- CT and MRI;
- Duplex scanning with contrast agent;
- General blood analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- Bacteriological examination of biomaterial taken from the affected area.
A correct diagnosis can be made in all cases.
Folk remedies
Wondering if there are any natural remedies or traditional methods used to treat a black toe? There are, and they are used in combination with traditional therapy.
For treatment at home you can use:
- burdock leaves - a paste is made from them and applied to the blackened area;
- new potatoes (pink) - pieces of the vegetable with peel are applied to the sore spot for a couple of hours.
Doctors note that not a single folk remedy can cope with a blackened nail or finger alone. It is important to approach therapy comprehensively.
Prevention
In order to prevent your toe from turning black, especially with diabetes, you should adhere to certain preventive measures.
Doctors give the following recommendations:
- Regular use of special ointments for diabetic feet and proper care of the lower extremities.
- It is important not to overheat, not to allow your feet to sweat, and not to overcool this area.
- You should not walk outside without shoes, even on the beach.
- All microtraumas on the foot are immediately treated.
- It is worth monitoring your diet.
- Shoes should be comfortable.
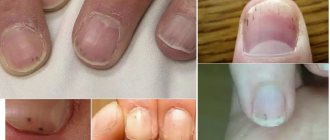
Why do nails turn black?
If your toenails turn black, you should immediately consult a specialist, as this may indicate various diseases. The cause of blackening of the nail plate can be both pathological and non-pathological factors.
Pathological causes include:
- disturbances in the functioning of the heart and circulatory system (in this case, the nails turn blue, all at once);
- improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- lack of iron in the body;
- thrombosis, varicose veins, diabetes;
- wearing shoes that are too tight.
Non-pathological causes include injuries to the nail plate of varying degrees. In this case, blood accumulates under the nail plate, which looks like a blackened nail. Medicinal herbs, lotions and even low-quality dark-colored varnish can also lead to a change in the color of the nail.
Frostbite of the lower extremities
Frostbite on the feet, which is accompanied by burning and tingling, requires immediate medical attention. When cold, blood vessels constrict and blood flow may even stop in certain areas. At this moment, cell destruction occurs. Frostbite can be either mild or severe, resulting in tissue necrosis. In this case, the leg becomes dark in color.
If frostbite occurs on the lower extremities, which can occur even at slightly sub-zero temperatures, it is important to place your feet in a warm place. This can be a pleasant, not hot bath. You should not use warming ointments; they can only stop the frostbite area. Massaging the legs also helps, but the movements should be smooth and light so as not to damage the skin.