Anti-cellulite, nourishing, moisturizing creams for face, hands and feet; tonics, scrubs, makeup removers and sun protection products, shampoos and conditioners - almost every modern woman has all this in her arsenal. To them you can add perfumes and all kinds of products from the group of decorative cosmetics. So it turns out that every day a modern woman, in order to look attractive, applies a huge amount of cosmetics to herself. But sometimes cosmetics can play a cruel joke and create an effect opposite to what was expected. For example, instead of masking skin imperfections or highlighting its advantages, cosmetics provoke the appearance of pimples, ulcers, inflammation, blemishes or itchy rashes. This could be an allergic reaction to cosmetics.
What is a cosmetic allergy?
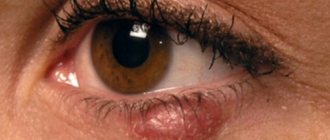
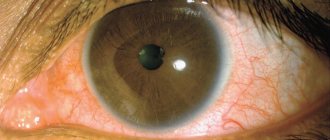
Many women are familiar with the condition when, after applying makeup, their eyelids suddenly swell and their face begins to burn or itch. The reason for this may be cosmetics, or more precisely one or more ingredients included in the cosmetic product. Most are a complex mixture of perfumes, emulsifiers, sunscreens, pigments, metals, resins and preservatives. Many contain extracts of exotic plants and essential oils, which can also cause an allergic reaction. Allergies to cosmetics can appear at any age, but are most often diagnosed in women between the ages of 20 and 60.
Cost of skin tests
| Skin tests | ✕| |
| Carrying out a skin allergy test using the scarification method | 1500 |
| Carrying out a skin allergy test using the prick test method | 2000 |
Skin prick tests with 6 household allergens:
| 1500 |
Skin prick tests with 4 epidermal allergens:
| 1000 |
Skin prick tests with 6 tree pollen allergens:
| 1500 |
Skin prick tests with 8 meadow grass allergens:
| 2000 |
Skin prick tests with 5 weed allergens:
| 1250 |
Skin prick tests with 6 household allergens:
| 900 |
Skin prick tests with 4 epidermal allergens:
| 600 |
Skin prick tests with 6 tree pollen allergens:
| 900 |
Skin prick tests with 8 meadow grass allergens:
| 1200 |
Skin prick tests with 5 weed allergens:
| 750 |
Allergological scratch tests and prick tests are carried out by an allergist-immunologist after an initial consultation.
During one procedure, the treatment is performed with no more than 15 allergens.
Clinical signs
Content:
- What is a cosmetic allergy?
- Clinical signs
- What can cause allergies
- Hypoallergenic cosmetics
- How to prevent allergies to cosmetics
- What to do if you have an allergy
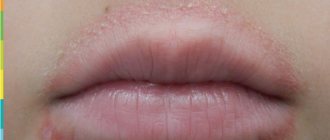
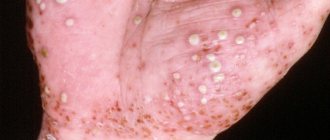
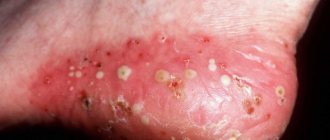
Allergies to cosmetics can manifest themselves in a variety of symptoms. Some of them may occur immediately after applying the cosmetic product, others - after a few days. Frequent signs of allergies are burning, itching and tingling of the skin. If you continue to use inappropriate products, symptoms may also include redness and flaking of the skin, pimples, watery blisters, and severe irritation. However, the first and most common symptom of a makeup allergy is redness and irritation of the eyes, as well as a rash. But identifying these symptoms as an allergic reaction can be problematic.
For example, women who spend a lot of time at the computer may attribute an unpleasant sensation in the eyes and redness to the consequences of working at the monitor. In fact, a similar reaction can occur to unsuitable mascara, eye shadow or cream.
The manifestation of allergic contact dermatitis (a reaction that occurs as a result of contact with an allergen) is in many ways similar to eczema - red, dry, itchy patches on the skin or a scaly rash that appears in the area where a cosmetic product is applied. In rare cases, allergies to cosmetics can cause a watery rash or even large blisters, much like those that appear after contact with Sosnowski's hogweed. Also, an allergy to cosmetics can manifest itself in the form of urticaria, acne, folliculitis and darkening of certain areas of the skin.
It is difficult to distinguish between allergic and non-allergic (caused by irritation) contact dermatitis. A reaction caused by cosmetics may manifest as irritant contact dermatitis or a specific allergy.
In the case of irritant contact dermatitis, signs of a reaction appear directly on the area of the body where the cosmetic was applied and, as a rule, do not spread beyond its boundaries. The intensity of the reaction depends on the concentration of the irritant substance.
A specific allergic reaction, also known as allergic cosmetic dermatitis, usually occurs in people with a genetic predisposition to allergies. Skin changes may spread to other areas of the body. The intensity of the reaction, as in the previous case, depends on the concentration and amount of cosmetics used.
The skin barrier - what is the danger of damaging it?
Sensitive skin has a damaged protective physical barrier, which allows unfriendly dust particles, toxins, allergens, microorganisms and cosmetic ingredients to penetrate the skin.
The immune resistance of damaged skin is significantly reduced. Inflammatory mediators trigger the inflammatory response. From a dermatological point of view, this is an asymptomatic period - the skin reacts sharply, but without visible manifestations.
After some time, dry skin, erythema, rashes and telangiectasia appear. This is the symptomatic period of sensitive skin disease.
Paradoxically, barrier damage is caused by too frequent use of aggressive cosmetics, as well as improper care, when cosmetics are used too sparingly or not at all for fear of irritation.
What can cause allergies
It should be noted that an allergic reaction can be caused not only completely, but also by products that a woman has been using for quite a long time. This can be explained as follows.
First, everyone experiences allergy symptoms at different rates. The adverse reaction occurs most quickly in people suffering from seasonal allergies, asthma or eczema.
Secondly, the skin does not necessarily immediately signal an intolerance to a new cosmetic product. This primarily applies to people with strong immune systems. But over time, their immune system loses the ability to resist the inappropriate component in cosmetics and a severe allergic reaction occurs. That is, you can use the same lipstick every day for several months without any unpleasant symptoms, and then suddenly it causes an allergy.
In addition, expired cosmetics can cause an allergic reaction. But a more common cause of allergies is a new cosmetic product. In this case, signs may appear either within a few minutes after using cosmetics, or after several days or even weeks. But most often, allergies to makeup appear after about 24 hours. That is, a reaction to the shadows or primer used in make-up on Saturday evening may very well appear on Monday morning. This often happens the very first time you use a new cosmetic product. The second time, the reaction may occur almost immediately or according to the same principle as the first time.
One clear sign that a cosmetic product is causing an allergy is the fact that the rash or other unwanted symptoms go away after you stop using the product. But even if the allergy has passed and you have probably already understood which product caused it, this is not all that should be done in such a situation. At the next stage, you need to figure out which component in the cream, eye shadow, lipstick or other product caused the undesirable reaction. This knowledge will help you avoid foods that contain the allergen in the future.
Dangerous components in cosmetics
If a certain cosmetic product causes an allergy, the reason should always be sought in its chemical composition. The most common culprits for adverse reactions are metals found in certain types of cosmetics. Typically these are nickel and cobalt. They can be found in many eye shadows, antiperspirants and hair dyes.
The second most common cause of allergies to cosmetics is preservatives, which are added to many products to extend their shelf life. The most powerful allergens from this group are parabens, formaldehydes, and methylisothiazolinone. Preservatives are found in almost everything: from wet wipes to hair products.
Another dangerous ingredient is fragrances added to cosmetics and personal care products. Although additives in this group are generally not harmful to health, they can cause severe reactions in those with sensitive skin.
Also among the potentially dangerous substances for allergy sufferers are propylene glycol, which is used in cosmetics to maintain its moisture, and lanolin, a fat obtained from sheep’s wool.
And one more important point. An allergic reaction can occur not only after contact with synthetic components. The fact that the label of a cosmetic product says that it is natural does not guarantee protection against potential allergies. Many organic ingredients and essential oils are also strong allergens. It should also be remembered that extracts of some plants (especially citrus fruits and St. John's wort) can cause photoallergic reactions.
Or maybe the reason is not cosmetics?
Sometimes symptoms that resemble a makeup allergy may not be caused by cosmetic products at all. This may be a manifestation of increased skin sensitivity, which can appear for various reasons. Most often they are hidden inside the body, or more precisely, in substances obtained from food. Modern food contains many preservatives, pesticides and other components hazardous to health. According to a study by a cosmetics company, increased skin sensitivity can be caused by both internal factors (unhealthy food, parasitosis, helminthic infestations, persistent infections, alcohol and spice abuse, hormonal imbalance) and external factors (wind, sun, poor environment, dust, conditioned air , detergents). But experts call stress the most important enemy of the skin. In a state of chronic stress, the rate of cellular metabolism decreases, which in turn causes the accumulation of toxins in skin cells, giving it jaundice. And constantly high levels of adrenaline increase the risk of eczema.
Proper care for sensitive skin
Cosmetics for sensitive skin are subject to strict evaluation. Tests are carried out in dermatological clinics on a group of people strictly with this skin type.
Patients with sensitive skin should use products from the same series, where the number of ingredients is limited. The main task is to restore the epidermal barrier. The composition of the products should include substances that compensate for defects in the hydrolipid chain, for example, vegetable oils, butters, waxes, which create an occlusive film on the skin. Moisturizing substances that act both on the surface and deep in the skin are important.
Restoring the epidermal barrier
Facial cleansing should be done carefully and with appropriate measures. It is good to use gentle cleansing cosmetics that will not disturb the natural surface of the skin. Avoid medications containing alcohol.
Hypoallergenic cosmetics
People who are familiar with the problem of allergies to cosmetics often buy products from the hypoallergenic group in the future. Do they really protect against allergies?
If a cosmetic product states that it is hypoallergenic, this only means that during testing it was found that this product causes allergic reactions much less frequently than a similar one from the regular series.
However, buyers also need to understand that in most cases there is nothing behind the labels “hypoallergenic”, “natural”, “pure”, “organic” other than a marketing ploy. But not all manufacturers carry out real laboratory tests confirming the hypoallergenicity of products.
Delicate skin – sensitive skin
In dermatology, there is a term “sensitive skin”, which refers to the sum of subjective and objective sensations. Sensitive skin is characterized by increased neurosensory sensitivity and an overreaction of the immune system.
In Europe, 1/3 of children born suffer from allergies; this is a genetically determined disease. It is predicted that in 2022 the number of allergy sufferers will exceed the number of healthy people. In addition to genetic sensitivity, there is also acquired sensitivity, depending on the degree of damage to the epidermal barrier by environmental factors.
Delicate skin – sensitive skin
How to prevent allergies to cosmetics
There are recommendations by following which you can avoid hypersensitivity to substances contained in cosmetics.
- Do not use cosmetics after the expiration date. Any cosmetics can be used only for a limited time. The packaging of each product indicates the production date and expiration date. In addition, many cosmetics have a pictogram in the form of an open container and numbers. So these numbers indicate how many months after opening the package you can use the product. After this period has expired, in order to avoid an allergic reaction, it is better to throw away the cosmetic product.
- Store correctly. Proper storage of cosmetics helps prevent their premature deterioration and thereby reduce the risk of allergies. Proper storage of cosmetics involves protecting them from exposure to excessive heat, direct sunlight and increased dampness.
- Keep clean. Applicators and makeup brushes can quickly accumulate dirt and bacteria, which can cause an unwanted reaction. Therefore, they should be washed frequently and dried thoroughly. It is best to place makeup brushes in a glass or other container with the bristles facing up, this helps to ventilate them and prevents the growth of bacteria.
- Pencil is safer than liquid eyeliner. Fans of liquid eyeliners should know that such products are much more likely to cause allergies than regular eye and eyebrow pencils. The fact is that wax is used in cosmetic pencils, and this eliminates the need to add preservatives, which cannot be said about liquid products. In addition, liquid cosmetic products may contain latex, which can also cause allergies in some people.
- Avoid waterproof cosmetics. And the point here is not so much in the cosmetics themselves (they may not cause any unwanted reaction), but in the products for removing them. Waterproof makeup removers are usually more aggressive and often contain ingredients that cause irritation to the skin and mucous membranes.
Powder forms instead of creams. Practical observations show that cosmetics in crumbly form (for example, powder, eye shadow, blush) are much less likely to cause allergies than similar products in creamy or liquid form. The whole point, again, is the difference in the chemical composition of dry and liquid products.- Always remove your makeup at night. The most common cause of irritation or allergic dermatitis is the reluctance to remove makeup before bed. Many girls and women believe that nothing bad will happen if yesterday’s makeup is washed off in the morning. But the longer cosmetics come into contact with the skin, the higher the risk of irritation, inflammation of the eyelids and redness of the eyes. Even if there was no decorative cosmetics on the skin, you should definitely rinse your face with clean water before going to bed. If it is necessary to remove makeup, then special products are used for this, and then experts also advise rinsing the skin with clean water. And only after that you can apply a nourishing night cream.
- Pay attention to the composition of cosmetics. Buy cosmetics that do not contain fragrances, preservatives and other potentially dangerous ingredients. It is important to remember that all ingredients on the product label are indicated in descending order of their quantity.
- Review your menu. This point may seem inappropriate to some: what do nutrition and allergies to cosmetics have in common? Do not forget that any allergy is the result of a malfunction of the immune system. To strengthen your immune system, you need to eat healthy and balanced every day. In addition, fresh fruits and vegetables contain many substances that are beneficial for the skin. We must not forget about the invaluable role of water in maintaining the beauty and youth of the skin. And the younger and more beautiful the skin looks, the less cosmetic products you will have to use, which means the risk of an allergic reaction is also minimal.
- Go through a laboratory test of stool for intestinal dysbiosis with sensitivity to antibiotics or phages, for antigens to Giardia, opisthorchid, toxocara, ostica, roundworms, blood for persistent infections: Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, herpes virus subtype B, toxoplasma, mycoplasma and chlamydia .