The structure of the skin
The skin is the largest integral multifunctional organ, interconnected with all other organs and systems of the body. In direct contact with the external environment, it performs a barrier-protective function. On the surface of the skin there is a complex pattern in the form of triangular and rhombic fields, formed by numerous grooves. Coarser grooves form folds in the palms, soles, scrotum, and facial wrinkles.
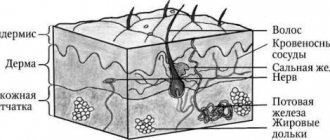
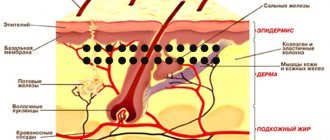
Histologically, three layers of skin are distinguished (Fig. 1):
- epidermis;
- derm (dermis);
- subcutaneous fatty tissue (subcutis), or hypodermis (hypodermis).
Rice. 1. Skin structure
The epidermis is the epithelial part of the skin, and the dermis and hypodermis are connective tissue. The border zone between the epidermis and dermis has the appearance of a wavy line due to the presence of outgrowths in the dermis - papillae, which cause the formation of ridges and furrows on the surface of the skin, forming a skin pattern. The connective tissue part of the skin (dermis and hypodermis) contains nerves, blood and lymphatic vessels, and muscles. In addition, the skin has its own appendage structures, which include hair, sebaceous and sweat glands, as well as nails.
Treatment and removal
Treatment of hemangiomas in children includes the use of one of the modern methods (treatment with liquid nitrogen, laser, etc.), drug therapy with the prescription of antitumor and hormonal drugs, or surgical excision.
The initial stage of diagnosing vascular wall pathology involves asking the patient (in the case of a child, his parents) about the manifestation of symptoms and the dynamics of the development of the defect. Next, the doctor examines the tumor in detail. If necessary, (depending on its location) it is referred to a specialist for a more in-depth examination (ENT specialist, ophthalmologist, etc.).
The structure, size and depth of growth of the anomaly are clarified during an ultrasound examination. During an ultrasound, blood flow in the affected area is studied.
Important! The diagnostic method of ultrasound examination will not be informative for all forms of hemangioma.
Removal of hemangioma in children is mandatory if it bleeds, itches, causes discomfort, or is located in areas rubbed by clothing.
Pigment formations
All pigmented formations on the skin can be divided into two groups: non-dangerous (melanoma-non-dangerous) and dangerous (melanoma-dangerous) pigmented nevi (Table).
Table 1. Classification of skin tumors of melanocytic origin
| Skin tumors of melanocytic origin | |
Melanomic nevi
| Melanoma-dangerous nevi
|
Melanomic nevi
Congenital melanocytic nevus
All congenital nevi are harmless. Among them there are small, medium and giant formations:
1. Congenital small melanocytic nevus (Fig. 2).
Elements of the rash. A spot or plaque raised above the skin measuring up to 1.5 cm. The shape of the nevus is round or oval, the boundaries are clear or blurred. The surface of the nevus is smooth or wrinkled, lumpy, folded, lobed.
Color. Light and dark brown. In rare cases, a depigmented rim is noted.
Localization. Any.
Course and prognosis. The risk of developing melanoma before puberty is virtually non-existent; in later life it ranges from 1 to 5%.
Rice. 2. Congenital small melanocytic nevus
2. Congenital medium melanocytic nevus (Fig. 3).
Elements of the rash. A round or oval plaque raised above the skin from 1.5 to 20 cm. The surface of the formation is smooth or wrinkled, lumpy, folded, lobulated, covered with papillae or polyps.
Color. Light or dark brown, there may be small dark inclusions on a lighter background.
Localization. Any.
Course and prognosis. There is virtually no risk of developing melanoma before puberty. Average congenital nevi change slightly throughout life. Due to the growth of the child, there is a proportional increase in education. It is advisable to remove the nevus before reaching puberty.
Rice. 3. Congenital medium melanocytic nevus
3. Congenital giant melanocytic nevus (Fig. 4).
Elements of the rash. A plaque raised above the skin level measuring more than 20 cm in diameter. There may be satellite lesions along the periphery of the main lesion. A disorder of the skin pattern is characteristic. On the surface of the formation there are nodules, papules and, as a rule, coarse dark hair. The boundaries can be either smooth or uneven.
Color. Darkly pigmented formation.
Localization. Any.
Course and prognosis. According to various sources, the risk of transformation of congenital giant melanocytic nevus into malignant melanoma reaches 5%. Surgical excision of the formation followed by plastic correction should be carried out as early as possible, however, often the operation is not possible due to the size or location of the formation.
Rice. 4. Congenital giant melanocytic nevus
Acquired melanocytic nevus
Acquired melanocytic nevus can be represented by a borderline (transitional) or complex (mixed) nevus. The transition from borderline nevus to complex nevus to intrademal nevus over time demonstrates the normal evolution of neogenesis.
1. Borderline nevus
Elements of the rash. A round or oval spot, sometimes slightly raised above the surface of the skin, up to 1 cm in size, with clear, even boundaries.
Color. Homogeneous (various shades of brown).
Localization. Any.
Course and prognosis. Borderline nevus, which arose in early childhood, becomes mixed as a result of the proliferation of nevus cells and their advancement into the dermis. This usually occurs during puberty. After the disappearance of the borderline component, the nevus becomes intradermal. This natural transformation usually occurs before the age of 30. In some cases, common borderline nevi remain unchanged throughout a person's life.
Rice. 5. Borderline nevus
2. Complex nevus
Elements of the rash. A formation in the form of a papule or node, usually up to 1 cm in size. The surface is smooth, less often warty, often with the growth of bristly hair. In shape, complex nevi are predominantly formations that rise evenly above the skin.
Color. Generally uniform: dark brown.
Localization. Any.
Rice. 6. Complex nevus
Dermal (intradermal, “resting”) nevus
Elements of the rash. A round, dome-shaped formation, usually up to 1 cm in size, rising above the surface of the skin. Over time, the nevus may develop a stalk and may take on the appearance of a warty (papillomatous) nevus. This phenomenon is most typical for formations localized in the torso area.
Color. Yellow-brown, brown or with brown spots, telangiectasias may be observed.
Localization. The most common are the face and neck. Formations of this group on the trunk and limbs are less common.
Course and prognosis. In most cases, intradermal nevi are not treated. Indications for removal of the formation are: localization in which there is permanent injury to the lesion.
Rice. 7. Dermal nevus
Prevention of the occurrence of acquired nevomelanocytic nevi is to reduce exposure to sunlight (especially in the early period of a person’s life). This is achieved by reducing the time spent in the sun (especially during the peak solstice period from 11 a.m. to 4 p.m.) and using sunglasses.
Blue nevus
Blue nevus can be either congenital or acquired; it most often appears in childhood or adolescence. These skin lesions are much less common than nevi of epidermal melanocytic origin. A blue nevus develops from ectopic melanocytes of the dermis. The coloring characteristic of a blue nevus is due to the Tyndall phenomenon - the refraction of light by the pigment of tumor cells located deep in the dermis.
Currently, several types of dermal melanocytic nevi are considered in the nosological form of “blue nevus”: simple blue nevus, cellular, cellular non-pigmented, combined and deeply penetrating.
Rice. 8. Blue nevus
1. Simple blue nevus (blue nevus, Jadassohn–Tiche nevus
Elements of the rash. The nodule, usually up to 1 cm in size, is sharply demarcated from the surrounding skin, round in shape, hemispherically protruding above the skin level, with a smooth surface.
Color. Blue, light blue, dark blue, gray, bluish - black.
Localization. Any type is possible, but the typical location for blue nevi is the dorsum of the hands and feet. A rare arrangement – soft and hard palate.
Course and prognosis. This formation grows quite slowly, often remaining unnoticed for several years. Over time, a blue nevus may acquire a flatter shape and lose pigment. Transformation of a blue nevus into melanoma is extremely rare.
2. Blue cell nevus (proliferating)
Elements of the rash. The development of a nevus begins with the formation of a spot or compaction in the dermis, which then transforms into a node or plaque up to 2.5 cm in diameter.
Color. Blue.
Localization. Any is possible. Quite often the localization of nevus in this group is the gluteal, lumbosacral region, less often on the dorsum of the hands and feet. Rare tumor localizations have been described - the conjunctiva and the scalp.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical and histological signs; immunohistochemical studies are necessary.
Course and prognosis. Depending on the clinical picture, pathomorphological signs, course and prognosis of the process, two forms of blue cell nevus are distinguished: typical (classical) and atypical with uncertain biological potential. Malignant transformation usually occurs over a long period of time in mature or elderly people and is manifested by rapid tumor growth, ulceration and discoloration. With a cellular blue nevus, cells similar to this formation may be observed in the regional lymph nodes. This process is called “benign metastasis.” Treatment is surgical excision with pathological examination.
Spitz nevus (atypical spindle cell, juvenile, benign juvenile melanoma)
Elements of the rash. A small single dome-shaped hairless node measuring up to 1 cm in diameter. Education, as a rule, is singular.
Color. Pink-red with abundant vascularization, yellow-brown, dark brown, uneven coloring possible.
Localization. Any is possible. In children and adolescents, the most common location is the scalp and face.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of histological examination. A quickly growing dome-shaped formation in a child allows one to suspect a Spitz nevus.
Course and prognosis. Spitz nevus is characterized by a sudden appearance. From the moment it appears, the formation is characterized by rapid growth, then it flattens and remains unchanged for years. Some nevi may undergo morphological transformation into dermal melanocytic nevi, and transformation into melanoma is also possible. The risk of malignant tumor degeneration occurs during puberty. Malignant degeneration is rare, but such formations require careful monitoring. This formation must be removed before the end of puberty. Then, in the postoperative period, dynamic observation is advisable.
Rice. 9. Spitz nevus
Halo nevus (Sutton's nevus)
Elements of the rash. A slightly elevated, slightly infiltrated reddish-brown nodule of round or oval shape, with an average diameter of 4-5 mm. The halo nevus is surrounded by a halo of depigmentation. The diameter of the rim, as a rule, is 2-3 times larger than the size of the hyperpigmented nodule. Characterized by multiple skin lesions.
Localization. Any type is possible, but the most common is the back.
Course and prognosis. There are several stages in the course and resolution of halo-nevus:
- melanocytic nevus with a surrounding rim,
- the central element loses pigmentation and acquires a pink color,
- disappearance of the central element,
- complete repigmentation of the entire nevus over several months or years.
No treatment required.
Rice. 10. Halo nevus
Hemangioma of internal organs
Minor tumors that have developed on internal organs, as a rule, do not appear. They are discovered by chance, during a medical examination carried out for another violation.
For an internal anomaly to manifest itself, its size must be impressive (up to 5–10 cm). If the formation arose inside the spinal column, it will not have manifestations. But as soon as the growth touches the ligaments or the periosteal membrane, pain will appear. By compressing the nerve roots, it can cause sensory disturbances in the upper and lower extremities.
In some cases, the development of pathology in internal organs may immediately manifest itself as symptoms. It depends on the location of the tumor. Its growth can quickly lead to disruption of the organ. A large hemangioma poses a danger to the eyes, throat and trachea. Liver hemangioma in a child rarely causes negative symptoms.
Melanoma-dangerous nevi
Phenotypically, these nevi do not reveal clinical signs of malignancy, but are distinguished by melanocyte dysplasia and a tendency to malignancy, thus giving reason to consider them as premalignant or borderline formations. These are the only tumors that require mandatory prophylactic removal with morphological verification of the pathological process. If it is multiple in nature, it is advisable to classify this group of patients as a risk group and subject them to mandatory clinical examination with dynamic monitoring by an oncologist.
Dysplastic nevus
Elements of the rash. A spot with a separate slightly raised area, usually in the center, above the skin level. The shape is round, oval or irregular with “ragged” edges. The boundaries are irregular and blurred.
Color. Various shades of black, brown, reddish, light red.
Localization. The most common are the torso, arms, buttocks, dorsum of the feet, and less commonly, the face.
Course and prognosis. A dysplastic nevus may not undergo any transformations throughout a person’s life, but may transform into a superficial melanoma; Complete regression of education is also possible. Against the background of a dysplastic nevus, melanoma develops in 9% of cases. It differs in clinical, histological, and biological manifestations from the known forms of melanoma, and is considered by some authors as “minimal melanoma.” The appearance of these nevi in young patients is not an alarming syndrome; they, as a rule, do not transform into melanoma.
With dysplastic nevus syndrome, the prognosis is unfavorable, and the risk of developing malignant melanoma increases significantly.
Treatment. Not all dysplastic nevi require immediate removal. Dynamic observation with photography and measurement of the size of the formation is necessary. Changing, suspicious, and traumatizing nevi are subject to excision.
Rice. 11. Dysplastic nevus
For what reasons does hemangioma appear?
Modern science has not fully elucidated the causes of pathological proliferation of endothelial cells. According to one version, hemangioma begins to grow during intrauterine development of the fetus under conditions of chronic oxygen starvation. According to another, the overgrown cells are residual embryonic cells. Another theory suggests that the neoplasm is formed under the influence of maternal infections in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. But these are just guesses, since the formation of hemangioma also occurs in babies who were born during a normal pregnancy, not complicated by infectious diseases.
It has been noted that pathology is observed more often in multiple pregnancies and in premature newborns.
Risk factors for the development of a benign tumor of this type include the mother’s age exceeding 40 years, as well as medical indicators: preeclampsia (protein in the urine, high blood pressure, swelling), threat of miscarriage, entanglement of the umbilical cord, inflammatory processes of the placenta, its abruption and presentation (when the embryonic organ is located as low as possible in the uterus, which makes childbirth difficult).
hemangioma on a child's face