A mole or nevus is a pigmented formation on the skin. It contains melanin and melanocyte cells. Moles appear on the body as a person grows older and depend on solar activity. Nevi can develop on any part of the body, become more voluminous or increase in size, causing some aesthetic inconvenience. In addition to their external beauty, nevi can degenerate into malignant melanoma through the process of metastasis. Can this be avoided? Yes, it is enough to remove the mole surgically in a trusted clinic. How exactly does the removal take place, what are the risks/consequences, and how often should I visit a dermatologist?
General characteristics of formations
A mole is a pigment formation of one of the shades of the brown palette. The base contains melanin and the melanocyte cells that produce it. Melanins are high molecular weight pigments. They are characterized by a heterogeneous structure and complex chemical composition. Pigments are found not only in moles, but also in all skin, hair, iris, inner ear and even some parts of the brain.
Content:
- General characteristics of formations
- Indications/contraindications for the procedure
- What you need to know about melanoma?
- How to properly prepare for mole removal
- Technique of the operation
- Possible complications and side effects
- Features of rehabilitation
It is important not to confuse nevi and birthmarks. Moles do not form in the prenatal period, but as a person grows older and are closely related to his lifestyle. The cause of the formation of pigment spots can be a hereditary factor, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, or hormonal changes.
Each mole is a separate formation with a unique life cycle. At first it is a flat spot, which can increase and rise slightly above the skin as it grows and develops. The size and location of the formation depends on the level of melanocytes. If they are in the epidermis (top layer of skin), the mole will be flat. The deeper the melanocyte is immersed in the dermis, the higher the formation is located on the surface of the human body.
Convex nevi, which rise slightly above the skin, should not frighten their owners. This condition has no negative consequences and is considered a variant of the norm. The main thing is that the mole is miniature, round and uniform (in terms of color and structure) throughout its life cycle.
Can a mole disappear on its own and how safe is it? Yes, the formation can disappear without the influence of mechanical factors. This happens gradually and can alert a person. First, a white outline is formed around the formation, which resembles an orbit. This contour begins to increase and gradually covers the surface of the entire formation. The nevus disappears, and a small white spot remains in its place. Most often this occurs after severe sunburn. The disappearance of moles can also be a harbinger of the rare disease vitiligo.
If you notice changes in a mole (increase/decrease, uneven edges, change in shade or structure), be sure to consult a specialist.
Laser removal
Modern cosmetology allows using a laser to eliminate any mole without a trace on the surface of the skin. The practical benefit of the laser is that under its influence the visible area of the mole is destroyed , leaving virtually no marks on the skin. High-precision treatment of nevus does not affect the surrounding skin. As a result, the duration of the recovery course is reduced. If we talk about other advantages of the mentioned technology, they look like this:
pros
- jeweler precision of the beam;
- short duration of the operation;
- rapid regeneration of damaged skin areas;
- no bleeding;
- the patient does not need special care after completion of the procedure;
- no restrictions throughout the rehabilitation course.
Minuses
- It is impossible to obtain material for further histological examination in order to identify oncological processes, which endangers the patient’s life.
- Possible allergic reactions to ultraviolet radiation.
- If the patient suffers from other skin diseases such as herpes, dermatitis, etc., drug treatment is necessary after the procedure.
- If the tumor is large, it is impossible to remove it completely in one session.
Indications/contraindications for the procedure
The surgical method is most often used when malignant degeneration of a nevus is suspected. Doctors recommend removing formations that are constantly in contact with clothing or located on the scalp, which increases the risk of damage. Moles in the groin, neck, chin, back or in the folds of the skin are most often damaged - consult a dermatologist to decide whether to remove them. Large formations on “legs” also pose a colossal danger. They can come off or become twisted, which can cause pain and infection.
Excision covers not only the affected area, but also healthy tissue, which prevents recurrence of skin growths. The main advantage over more modern laser removal or cryodestruction is the obtaining of material for histological examination. The excised tissue is sent for diagnostics in order to better understand the causes of the disease, understand the possible risks and create a preventive course for the patient.
Surgical procedures can only be performed in specialized medical institutions. Beauty salons or home procedures are not suitable for this and can cause irreversible consequences for the body.
| Indications | Relative contraindications |
| Increasing the size of education | Infectious diseases regardless of stage |
| Deep penetration of the mole under the skin | Acute inflammatory processes |
| Bleeding, change in color or texture | Chronic pathologies in the acute stage |
| Frequent injury to the mole, the formation causes pain or inconvenience | Pregnancy and breastfeeding period |
| Aesthetic discomfort |
There are no direct contraindications to surgical removal of nevi. In case of relative contraindications, the patient must undergo additional tests and consult a specialist.
The doctor will determine the advisability of removal, indicate possible complications and features of rehabilitation. In some cases, surgery will have to be postponed until the patient fully recovers.
Who is contraindicated for
Surgical removal of a nevus is contraindicated in the presence of the following diseases:
- exacerbation of chronic inflammatory diseases;
- infectious disease - viral, fungal, bacterial;
- fever of unknown origin, increased body temperature and other symptoms of intoxication.
Also, surgery may be postponed during pregnancy or breastfeeding - in each case, the doctor makes a decision taking into account the symptoms and condition of the formation.
What you need to know about melanoma?
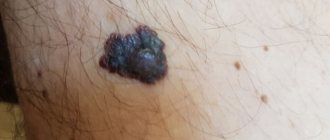
Every mole on the human body can degenerate into a malignant melanoma. What it is? Melanoma is one of the types of malignant tumors. It also contains melanocyte cells (producing melanin), but in melanoma the cells are more aggressive.
They constantly divide, displace healthy cells, enter the vascular bed and spread throughout the body. As soon as the first aggressive cell approaches the brain or, for example, the lungs, it settles inside the organ and begins to rapidly divide. This process is called metastasis.
Melanomas are extremely dangerous because they quickly metastasize and divide at an incredible rate. The main thing is to detect the pathology in time. Surgical removal of melanoma will prevent the process from spreading throughout the body and guarantee a complete cure. Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner or complete refusal of treatment can result in death.
Diagnostics
A visual examination allows you to determine the type of birthmark. At the first appointment, the doctor asks the patient a number of questions:
- how often does one take sunbathing or tan in a solarium?
- were there any burns from ultraviolet radiation;
- whether there were cases of malignant moles in the family;
- whether the patient took hormonal medications;
- whether he works in a specific industry related to the processing of toxic substances and investment;
- suffers from chronic diseases of internal organs;
- were there any cases of injury?
After this, dermatoscopy is performed - a method for examining suspicious pigmented formations. The specialist applies immersion oil to the spot, then uses a magnifying device to carefully examine the condition of the nevus. Using a three-point rating system, the dermatologist checks the following parameters:
- asymmetry of structure;
- coloring;
- the presence of an atypical pigment network;
- presence of light blue areas.
Dermatoscopy is considered an effective technique that gives a completely reliable result - up to 95%. But in some cases, this research method is not enough, so the question of whether large springs can be removed is decided after additional tests:
- biopsy - analysis of tissue particles of the formation;
- cytology - a test for the growth of malignant cells;
- histology – determination of the degree of pathological processes, assessment of the condition and structure of cells;
- epiluminescence microscopy is a clarifying technique for benign formations.
In some cases, an additional examination using ultrasound, radiography, or MRI is prescribed. If necessary, the doctor sends the patient for clinical urine and blood tests to assess the general health before surgery to excise the tumor.
How to properly prepare for mole removal
No specific preparation is provided before removal. The patient just needs to come to the medical center and follow the necessary instructions from the specialist. Before the operation, a painkiller must be administered to make the procedure as comfortable as possible. In most cases, drugs with lidocaine are used. If there is an increased risk of bleeding, the doctor selects a medication and administers it intravenously after pain relief.
Immediately before the procedure, the doctor conducts a short consultation. He explains the essence of the method, possible complications and skin care rules.
As soon as the nuances are agreed upon, the doctor begins work. The patient is placed on a couch and the skin is treated with a special solution. It disinfects the area so that pathogenic bacteria do not enter the open wound. At this stage, the preparation ends, and the specialist proceeds directly to the surgical intervention.
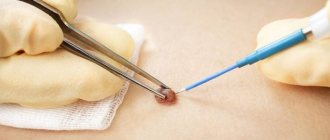
Technique of the operation
The removal technique depends on the location and size of the formation. The mole must be excised within healthy tissue. The area of excision is determined by the doctor, warning the patient about it. For example, if the nevus is located on the face, the specialist must remove a minimum amount of epidermis. On other parts of the body, the result of the intervention will be less noticeable, so the doctor can capture more healthy tissue.
There are two main methods of surgical removal. One of them is cutting off the mole without suturing. The doctor uses a scalpel to cut off the growth slightly below the skin level. If bleeding occurs during the procedure, the wound is cauterized and a local antibiotic is applied. A bandage is applied to the affected area and skin care rules are explained. Most often, the surgical area is prohibited from getting wet or subjected to mechanical or ultraviolet influence. Based on the individual characteristics of the patient, the doctor draws up a list of necessary medications, care products and sets a date for the next visit to assess the body’s reaction.
The second method is removal with sutures. Most often, the method is used in the treatment of dark or flat moles. The doctor cleanses the skin, injects an anesthetic, and excises the formation and its surrounding surface.
During the operation, the deep layers of the skin are affected, so suturing is a mandatory procedure.
The healing rate of the area is 7-14 days and depends on the individual characteristics of the patient. The operated area should be cleaned periodically, protected from damage, and ointments or oral medications should be regularly applied.
The main thing is not to self-medicate, but strictly follow the doctor’s instructions. After some time, you need to make an appointment with a dermatologist again. He will evaluate the condition of your skin, possible side effects/complications, and your overall body response to surgery.
Large moles on the body
Moles appear in the first year after birth or throughout life.
The size also varies, and the location on the body can be anywhere. There are several types of large moles:
- fibroepithelial - benign formations up to one and a half centimeters in size;
- Sutton's or halonevus - characterized by the presence of a colorless ring;
- melanocintar – flat moles that appear during hormonal changes;
- Becker - are more often observed in men, consist of epidermal cells;
- blue – nevus is bluish in color and small in size;
- basal – characterized by inactive pigmentation, colorless;
- warty - have a bumpy surface, consisting of tiny nodules;
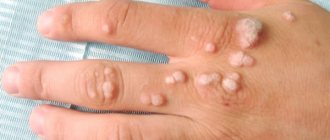
- papillomatous – formed by the papilloma virus;
- red – associated with the growth of the capillary network;
- nevus of the sebaceous glands - formed due to an embryonic anomaly of tissue development;
- Port-wine stains are a vascular pathology inherent in newborns.
Some springs are completely harmless, while others can pose a danger, which is expressed in the risk of malignancy. Most of the formations must be removed. But only a doctor can determine what to do with a large mole.
Possible complications and side effects
The main disadvantage of surgical removal is the postoperative scar. It will be noticeable even with a cosmetic stitch, despite the fact that over time the skin will lighten and restore its structure. The surgeon’s task is to make the scar as invisible as possible, so choose a medical institution and doctor responsibly.
There is a risk of developing a keloid scar. This is a tumor-like growth of rough fibrous connective tissue. It is formed in people with a corresponding predisposition. Most often occurs when suturing large wounds.
Another risk is relapse. A repeat process is possible provided that the doctor has partially removed the mole, which is a gross violation of the surgical technique.
Immediately after excision, redness of the skin, itching, and a feeling of discomfort are possible. All these symptoms go away on their own after a few days. If something worries you, be sure to tell your doctor about it.
Prevention of degeneration
In order to prevent the transformation of an ordinary nevus into a malignant one, it is important to promptly contact a specialist with a request for diagnosis. The question of whether large moles are removed will be clarified at the first appointment. Doctors usually recommend getting rid of pigment formation as early as possible from the point of view of aesthetics and safety.
But measures to prevent degeneration are still worth taking:
- do not get carried away with tanning;
- in the hot season, go outside, applying cream with SPF 30 - 50 to areas of the skin not protected by clothing;
- protect yourself from injury;
- Do not take hormonal drugs uncontrollably.
And most importantly, do not ignore scheduled examinations by specialists. Especially during periods of hormonal changes in the body, it is necessary to constantly see a doctor.
The specialists at the Desir clinic specialize in various areas of medicine. We have some of the best dermatologists and highly specialized specialists: dermatologists-oncologists. Make an appointment and get your moles examined. If you are concerned about the presence of a large mole, we will provide qualified assistance. Our innovative equipment allows us to conduct research as accurately as possible and use the latest techniques to remove formations of various types.