The body reacts to environmental stimuli in completely different ways. The ambiguity and variety of effects can even confuse a person.
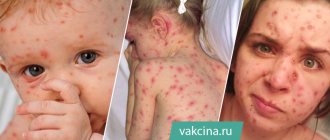
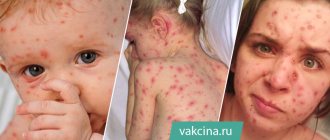
Urticaria is a large group of allergic diseases with similar symptoms. It is not contagious and affects a significant part of the world's population. Characterized by spontaneous eruption of blisters, redness, or angioedema1. symptoms of allergic urticaria and causes
Urticaria appears quickly and clearly, so it can be diagnosed using the following parameters:
- at the first manifestation of an allergy, the skin becomes blistered;
- the rash is accompanied by burning and itching;
- Externally, the affected area of the epithelium looks as if it were a burn from contact with nettles, hence the name.
The mechanism of allergy development is based on immediate hypersensitivity. Upon repeated contact with even a small dose of the allergen, the response appears quickly.
Experts identify several of the most common causes of the disease:
- stress;
- infections;
- use of medications;
- parasitic infestations;
- insect bites;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- ultra-violet rays;
- flower pollen;
- dust indoors and outdoors;
- some types of sweets;
- citrus.
There are two main types of illness:
- urticaria of an immune nature;
- non-immune urticaria.
In the acute form, fever always has an immunological basis for the manifestation of rashes. The chronic form is different and has a wider list of activation mechanisms:
- exogenous factors (influence of processes from outside);
- endogenous factors (the influence of processes occurring inside the body).
Food provocateurs, along with drugs and temperature, are considered exogenous factors. The second group is diseases of a somatic nature and associated with various internal pathological processes. These include:
- gout (a chronic disease characterized by metabolic disorders of certain substances);
- diabetes;
- lupus erythematosus;
- chronic cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder, which is characterized by a violation of its motor function, accompanied by changes in the physical and chemical properties of bile);
- pancreatitis (inflammatory processes in the pancreas), etc.2,3
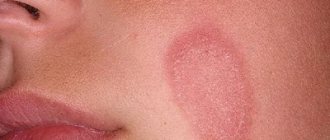
The rapid spread of an itchy rash, which occurs at the slightest interaction with the substance that caused the allergy, is characteristic of acute urticaria. Externally, the rash looks like many bubbles of different sizes with a clear border of bright color. The rash is often local in nature. The rashes are concentrated on the skin, but there are cases when they appear on the mucous membranes. As usual, symptoms that appear up to 6 weeks characterize spontaneous urticaria; if the blisters do not go away for more than 6 weeks, we are talking about a chronic form of the disease4.
The recurrent (chronic) form of urticaria is an allergic-type disease, which is characterized by the appearance of a rash in the form of papules and itchy blisters. This allergic reaction lasts over 6 weeks. Occurs in 25% of patients. After a long period of remission, repeated manifestations of the rash are possible. Such symptoms are more common in women.
There are two types of chronic urticaria:
- persistent - there is a constant renewal of the rash;
- recurrent – periodic exacerbations of the disease occur.
Pseudo-form is a symptom indicating disorders in the digestive system. It appears when:
- hepatitis;
- helminthiasis;
- chronic gastritis;
- poisoning;
- infectious diseases.
However, there is no relationship between the immune system and the appearance of the pseudo-form5.
Allergic urticaria in adults
The disease has a number of features when it occurs in an adult. Fever may present as follows:
- Spicy. Rashes appear on the body and limbs, they are accompanied by itching, which increases in warmth. Redness occurs 15-20 minutes after contact with the allergen substance. The blisters disappear quickly and leave no marks or scars.
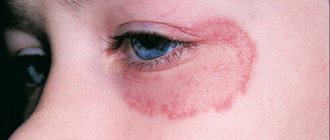
- Quincke's edema. It is characterized by swelling and larger rashes, appearing on the face near the eyes or mouth. A rash appears on the nasal mucosa and on the conjunctiva of the eyes. In exceptional cases, it is accompanied by swelling of the genitals and limbs. It often causes difficulty breathing and can even be life-threatening.
- Persistent papular. It develops due to long-term treatment of any type of disease and is characterized by the formation of papular blisters (nodules that are located above the skin level). The blisters are noticeably raised above the skin. The patient has to fight the disease for a long time – up to several months. The entire period is accompanied by itching.
- Chronic. It is characterized by wave-like increases and decreases in the level of severity of symptoms. Periods of recovery are followed by exacerbations with severe itching. The time period of the disease is calculated in decades. In rare cases, skin lesions become papular. This form of urticaria is characterized by the manifestation of Quincke's edema. When scratching itchy areas, the disease may be accompanied by an infection, which significantly complicates the course of the disease.
- Solar. The main cause is UV radiation, but the development of allergies is also associated with chronic diseases (for example, chronic liver disease). The appearance of urticaria lesions varies among patients. The rash can be mild or severe; the size of the lesion and blisters, color saturation, shape and location will differ. The severity of the disease is determined by the severity of itching. The most severe form is accompanied by the development of neurotic disorder and insomnia6,7.
Which hives are contagious?
Patients should know which hives are contagious and which are not. The cause of the development of pathology can be both diseases of an infectious nature and internal malfunctions in the body. The disease can be triggered by food, medications, toxins and other irritants.
The development of a severe infectious disease in a person is not always accompanied by the appearance of urticaria. Infectious urticaria can develop under the influence of viruses that enter the body. In such a situation, infection is possible, but it all depends on the individual characteristics of the organism.
If a patient has an infectious disease, then his body may not start the mechanism for producing antibodies to allergens and a skin reaction will not occur.
Allergic urticaria in children
Children are very susceptible to skin rashes, and this is the most common reaction in the case of allergies. Children under 3 years of age most often suffer from manifestations of nettle fever. But older children can also experience trouble in the form of itchy rashes.
The location of blisters is similar to adults - on the extremities (most often in folds and places of close contact with clothing), around the mouth or eyes.
The mechanism of manifestation of the rash is the formation of a large amount of histamine due to the penetration of an allergen substance into the body. The surface of the skin becomes swollen and blisters form. The skin lesion disappears quite quickly and without a trace if the child does not scratch the sore spot. But then it can appear again, in another part of the body.
The doctor can quickly diagnose the cause that provoked the hives if the parents determine the time and place of the first appearance of the spots. Accurate diagnosis involves taking the following samples: skin scraping and blood test.
Diet for urticaria
During the treatment of urticaria caused by food intolerance, it is necessary to avoid eating foods that stimulate the release of histamine. These include:
- coffee, chocolate, honey;
- citrus fruits, nuts;
- products containing dyes, emulsifiers, preservatives;
- milk, chicken eggs;
- baking, mayonnaise, mushrooms, peas;
- chicken, spices, vinegar;
- soybeans, beans, pineapples and some others.
Strong tea, coffee and alcohol should also be avoided. Procedures such as freezing, cooking, and peeling help to slightly reduce the allergenicity of products.
The basis of the diet for allergic urticaria should be porridge cooked in water, vegetarian and cereal soups, baked apples, olive oil, compotes, kefir.
If the patient does not know what foods he has an allergic reaction to in the form of urticaria, he can act as follows:
- After eliminating the symptoms of the disease, do not eat anything for one day.
- From the second day, start eating one product at a time. At the same time, keep a food diary and monitor your condition.
When treating urticaria, it is important to drink a lot - at least two to three liters of water per day. This helps remove allergens from the body faster.
Treatment of allergic urticaria
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out in 4 stages:
- a specialist conducts an initial examination;
- anamnesis, possible causes, etc. are collected;
- after this, diagnostic samples are taken;
- tests are prescribed.
The treatment procedure occurs step by step:
- eliminating the influence of a provocateur (allergen) and cleansing the body;
- pharmacotherapy (course of taking medications);
- diet prescription.
The drugs used in specific cases will be different. In the case of the endogenous nature of fever, the main task is to eliminate the root cause and prescribe effective treatment.
Often, a severe form of the disease requires the prescription of corticosteroids (Prednisolone) and antihistamines (Cetrin®). The drug Cetrin® copes with all symptomatic manifestations of allergic reactions. The effect of taking it is noticeable already 20 minutes after taking the tablet. The product is non-addictive and suitable for long-term use.
Cetrin® belongs to the second generation antihistamines, which eliminates the manifestation of a number of negative symptoms8.
Self-medication for both adults and children can be hazardous to health. A timely visit to a specialist will help you quickly cope with hives and identify the causes of its occurrence.
Bibliography
- Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of urticaria / Russian Association of Allergists and Clinical Immunologists: approved by the President of the RAACI on December 23, 2013 - Moscow, 2013. - 9 p.
- Mukhin, N. A. Gout: Faces of the disease / N. A. Mukhin // Modern rheumatology. – 2007. – No. 1. – 5 s.
- Ivashkin, V.T. Gastroenterology. National leadership / V. T. Ivashkin, T. L. Lapina. – M.: Iz-vo GEOTAR-Media, 2008. – 754 p.
- Vasilyeva, A.A. Acute urticaria and angioedema in the practice of a family doctor / A. A. Vasilyeva, R. F. Khakimova // Bulletin of modern clinical medicine, vol. 4 – 2011. – No. 4. – 54-58 s.
- Revyakina V. A. Urticaria in pediatric practice / V. A. Revyakina // Emergency Medicine - 2007. - No. 4. – 93-96 p.
- Hives. Atopic dermatitis: guidelines for students of medical, pediatric and dental faculties / Ed. ed. V. M. Chervenets. – M.: Alquist Publishing House, 2012. – 22 p.
“Oh, I’m blushing all over!..” But why?
Urticaria, or nettle fever, is an allergic disease. Hives can be either a direct reaction to an allergen or one of the manifestations of a wide range of diseases of a very different nature.
Hives are not contagious, and therefore you should not be afraid of people who are “showered” with red blisters.
However, there is one “but”... Often, urticaria occurs together with Quincke’s edema, which is its most dangerous feature.
The fact is that this swelling can spread to the mucous membrane of the larynx, which without urgent medical help can lead to respiratory arrest and death. Urticaria is divided into acute and chronic.
Acute nettle fever
It occurs suddenly and does not last long - from several hours to a couple of weeks. Acute urticaria can be caused by allergies to insect bites, food, or an infection that has affected the human body. This form of the disease is most common in children.
Causes of acute urticaria include allergic reactions to:
- food products (the most common cause of the disease);
- medications;
- insect bites (especially bees and wasps);
- weather and physical conditions (cold, heat, sun rays, vibration, pressure changes, etc.);
- other substances and materials that can act as an allergen (latex, animal saliva).
Infectious diseases can also cause acute urticaria.
Experts note that sometimes acute nettle fever becomes chronic, which requires longer and more complex treatment.
Chronic urticaria
As its name suggests, it lasts a long time. It can be observed for several months. The causes of this type of illness are more serious. These include disturbances in the functioning of various organs - the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, chronic infections, and toxicosis of pregnant women. Doctors say that chronic urticaria is an autoimmune pathology (this is the name for the phenomenon when the body mistakes its own cells for foreign ones and begins to fight them). It affects mostly adults, and women are especially susceptible to it.
However, a significant proportion of chronic urticaria does not have a clearly identified cause. In other words, this pathology has not yet revealed all its secrets, and therefore its danger, expressed in the likelihood of developing Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock, has not decreased to this day.
Stages of rash treatment
Is this disease dangerous? The disease does not pose a particular danger to humans. However, it requires care and adherence to the rules of therapy. In severe cases, it can cause Quincke's edema, which can be fatal. Treatment of urticaria includes certain stages.
Stages:
- Making a diagnosis, identifying the cause of the allergic reaction.
- The use of various medications - antihistamines, sedatives. External agents are used - creams, ointments, gels, solutions.
- The use of traditional medicine is allowed.
- In certain cases, it is advisable to use physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Be sure to prescribe a suitable diet during the treatment process, excluding foods that can cause allergies.
Treatment is carried out until complete recovery; the prescribed diet is followed for at least six months.
Transmission of rash from mother to child
During childbirth, the baby can become infected with various diseases from the mother. However, urticaria is not one of them. In a child under the age of six months, this phenomenon is diagnosed quite rarely. The reasons may be cosmetics, products consumed by the mother and ingested by the baby with milk.
One type of urticaria is miliaria. It appears as a result of irritation on the skin from sweat and mechanical damage.
Thus, a child cannot catch hives from the mother, but there may be other factors that influence this.
You can't get infected
Is urticaria always dangerous for people? There are certain factors that cause rashes, but do not pose a danger to humans.
Factors:
- Medicines,
- Toxic substances,
- Natural phenomena (frost, sun),
- Food,
- Hormonal imbalances
- Malignant tumors.
Such factors are not contagious and cannot be transmitted from one to another. If hives arose as a result of a reaction to such irritants, then there is nothing to be afraid of - you cannot become infected with it.
The disease can occur during severe stress and depression. In such a situation, it is also not contagious to others.
Clinical picture
The development of the disease is acute. Against the background of complete well-being, red spots suddenly appear on the face or chest, or anywhere else, protruding above the skin and accompanied by itchy skin. Such zones of hyperemia can merge and cover the entire surface of the skin.
Children are characterized by an increase in body temperature to hectic levels, accompanied by a headache. Severe itching of the skin precedes the appearance of blisters, so it is very important not to miss the moment and to be in the reliable hands of doctors in time.
How is urticaria transmitted?
Experts have proven that skin rashes themselves do not pose a danger to others. The disease cannot be transmitted through the skin, since urticaria is the body’s reaction to an allergen or a sign of an infectious pathology. At the same time, urticaria is one of those diseases that are inherited. Only if the cause of the skin lesion is an infectious disease, then its transmission from a sick person to a healthy person by airborne droplets cannot be ruled out.
Skin rashes due to urticaria can be either single or multiple, and this depends on the state of the person’s immunity. If you have such a rash, you should definitely consult a doctor and ask questions about the disease, since urticaria is dangerous due to its very serious consequences. If there are indications, he will conduct a thorough examination and prescribe anti-allergy medications.