Diseases that begin with the letter “L”: Lactostasis, Laryngitis, Laryngotracheitis, Cor pulmonale, Pulmonary fibrosis, Leukemia, Leukemia in children, Leukoplakia, Leucinosis, Leprosy, Dental treatment, Lymphadenitis, Lymphangitis, Lymphogranulomatosis, Lymphoma, Lymphostasis, Lipoma, Listeriosis , Lichen, Pediculosis pubis.
Ringworm belongs to the group of dermatological diseases of the fungal and viral type. It is characterized by the appearance of dry or weeping areas of skin that periodically itch severely. Ringworm is a fairly common disease and it is customary to distinguish several varieties depending on:
- causes of occurrence (causative agent);
- type of change in the structure of the skin;
- location;
- degree of infectiousness to others.
The disease has a long development period and a high risk of relapse.
Why does lichen appear?
It is difficult to name with 100% certainty the exact causes of infection and the method of formation of the lichen patch on the skin. However, there are a number of factors that provoke the appearance of the disease:
- low level of immunity;
- constant exposure to stressful situations;
- chronic emotional and physical fatigue;
- infections;
- genetic predisposition to skin diseases.
Even the gender and age category of the patient can influence the form of the disease.
The causes of lichen also depend on its type.
Shingles appears due to contact with the Herpes zoster virus. The causative agent of the disease is the Herpesviridae virus. The disease is activated when there is a herpetic infection in the patient’s body.
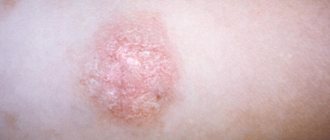
Pityriasis or “pink lichen” has an infectious and allergic cause.
Lichen versicolor or pityriasis versicolor is located in the stratum corneum of the skin. A person can become infected with it through close contact with a carrier of the disease, as well as through the use of household items (towels, bed linen, dishes) of a sick person. The main causes of this type of disease are excessive sweating, hot weather and inflammatory processes on the skin. The causative agent of lichen versicolor is a fungus.
Flat red fungus is directly related to disturbances in the patient’s body’s metabolic processes and low level of immune properties. Contact with certain medications and chemicals can become an irritant. This type of lichen has a genetic predisposition, that is, if close relatives often suffer from lichen planus, then the risk of the disease in this case is maximum.
Trichophytosis is one of the most common types of disease and affects children and adults who come into contact with a sick animal or household items carrying fungal spores.
Lichen ruber planus
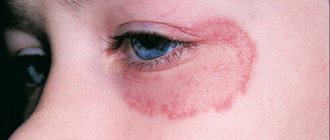
Flat multi-colored (from pale pink to purple) nodules of lichen red often appear on the mucous membranes, nails (they crumble), and delicate skin of the chest and abdomen. Their appearance is accompanied by severe itching, which, as a result of scratching, leads to the rapid growth of foci of skin damage.
Dermatologists find it difficult to determine the cause of the appearance of lichen red, but note that it is quite common in patients with diabetes, as well as those suffering from diseases of the stomach, liver, and biliary tract. Moreover, women over 40 years of age are primarily at risk.
Symptoms
Each type of fungus manifests itself differently on the skin.
The girdling appearance is characterized by the following features:
- a feeling of numbness in the affected area;
- lymph nodes increase in size;
- painful sensations in muscles and joints;
- swelling of the affected area of the skin;
- formation of small bubbles;
- burning and soreness of the skin.
The name of the species of lichen is directly related to its appearance. The disease seems to surround the body. As a rule, the lesion is located on the head, in the chest or abdomen in the direction from the chest to the spine.
Shingles begins its manifestation with the formation of small blisters with liquid on the skin. After a few days, the color of the bubbles becomes more cloudy and they “dry out.” A dry crust forms at the site of the lesion, which gradually peels off. After it disappears, the area of the skin becomes covered with pigment. There is a high risk of bubbles reappearing. The period during which the patient can infect other people is 2 weeks.
Pityriasis manifests itself as follows:
- a bright pink spot with a diameter of about 5 cm appears at the site of the lesion;
- within 2 weeks the skin peels off.
Most often, this fungus is located in the abdomen, back and upper torso. Small lesions may merge into one large area as they spread.
Symptoms of pityriasis versicolor are severe itching, peeling and burning sensation, and the formation of light pink spots on the skin. Without treatment, the duration of this type of disease can be several years. Pityriasis usually occurs in the area of the shoulders, neck and back, much less often on the lower extremities, head and genital area.
Lichen planus is a dark burgundy-colored swelling or bump on the skin. This place is very itchy. The patient's legs, torso and genitals are mainly affected. Also, the fungus can cover the nail plates, feet, palms and mouth. In this case, the fungus appears as whitish spots. The nail subsequently splits.
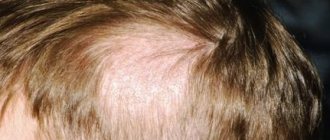
Trichophytosis affects large areas of the skin. Mainly found on the scalp. It is characterized by unpleasant itching and pink spots that do not have clear boundaries. The spots may become covered with small cloudy blisters or a flaky crust. The infection period can last from 5 to 7 days.
Lichen rosea (or Zhibera)
A little-studied type of disease that usually develops against the background of a weakened immune system in the autumn or spring season. The risk group in this case consists of girls who have a hormonal imbalance in their body.
The manifestation of lichen is the appearance of round or oval pink and light brown spots on the chest, shoulders, back, sides, and skin folds. Dermatological changes, accompanied by itching and flaking of the skin, may go away on their own within a few weeks, however, when the first signs of the disease appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor to rule out the presence of syphilis similar in symptoms.
Diagnostic methods for determining the type of lichen
The main ways to determine fungus are the following:
- visual examination of the patient, where the color, shape and location of the rash are determined;
- collection of complaints and analysis of symptoms.
Each species is determined by different methods. First of all, a sick patient should seek advice from a dermatovenerologist.
Shingles is difficult to determine by simple visual inspection, so additional diagnostic procedures will be required:
- searching for the presence of antibodies to viral pathogens;
- bubble content analysis;
- using the hybridization method to determine the genome of the virus.
If pityriasis is suspected, the doctor will send the patient for blood and urine tests, and will also conduct a microscopic examination of the scales to exclude the diagnosis of syphilis. Pityriasis can be diagnosed better than other types of disease through visual examination.
Lichen versicolor can be identified by the results obtained from the following procedures:
- Examination of the lesion site with a Wood's ultraviolet lamp. The doctor “examines” the fungal spores, which turn yellow or brown.
- At the appointment, the doctor drops a few drops of iodine onto the affected area of the skin and immediately wipes it with a cotton swab moistened with alcohol. If it is a multi-colored fungus, the skin will turn brown.
- Taking a sample by scraping the skin for microscopic examination in a laboratory.
To diagnose lichen planus, the patient will be referred for general blood and urine tests, as well as a skin sample for histological examination.
Trichophytosis can be determined using the following methods:
- “X-raying” of the skin using a Wood's ultraviolet lamp. This form of fungus will turn green.
- Submission of biochemical blood and urine tests.
- Determining the degree of sensitivity of the pathogen to selected antibiotics by inoculating the sample taken on nutrient media.
- Taking a sample by scraping the skin for microscopic examination in a laboratory.
Prevention of relapse and infection of others
The absence of itchy spots and new formations on the skin indicates that the lichen has passed. To prevent relapses, several preventive measures must be followed within 7-10 days after treatment:
- take a shower at least once every 2 days using tar soap or shampoo;
- after visiting public places, wash your hands with fungicidal soap;
- daily wet cleaning of the house with antiseptic solutions;
- refuse to use other people's hygiene products - towels, combs, washcloths, etc.
A systematic examination of children and pets using a Wood's lamp will help identify the disease in the early stages and begin treatment in a timely manner. Avoiding contact with stray animals, rational nutrition and timely treatment of infectious diseases will reduce the risk of infection with fungal pathogens.
Treatment options for lichen depending on its type
Just like the causes and symptoms, treatment regimens differ depending on the type of fungus.
If shingles fungus is diagnosed at the very beginning of the disease, the doctor may prescribe the following medications: Acyclovir, Zovirax. According to individual indicators, drugs such as “Curantil” and “Furosemide” can be prescribed. If the immune system is particularly weakened, intravenous drips with immunoglobulin may be prescribed.
The treatment regimen for advanced shingles consists of taking the following medications:
- analgesics;
- antipyretic drugs in the presence of high fever;
- B vitamins, which help strengthen the body’s protective functions;
- sedatives for insomnia;
- prescribing diuresis when signs of intoxication appear;
- the skin at the site of the lesion can be treated with a solution of brilliant green, metacil ointment, "Solcoseryl".
Pityriasis in most cases goes away on its own and does not require treatment. The exception is severe itching, for which you can use antihistamines and hormonal creams.
During the course of the disease it is recommended:
- wear underwear made from natural fabrics;
- limit bathing and interaction of the affected area with water;
- exclude the use of cosmetics.
Treatment of versicolor versicolor is possible using the following medications: 5% salicylic ointment, Cycloperox, 5% sulfur ointment, Bifazol, Miconazole, Lamisil. If foci of the disease have spread throughout the body, then it is recommended to take Orungal or Itraconazole.
The flat red fungus causes significant discomfort to the patient due to severe itching and burning sensation. Suprastin, Tavegil and Zyrtec will help cope with itching. In addition, corticosteroids and antimalarial medications may be prescribed.
If lichen planus affects the mucous membrane, then treatment with Solcoseryl is necessary. If this type of disease recurs, antibiotics are prescribed.
If trichophytosis affects areas of the skin without the presence of hair, then the area can be treated with iodine and antifungal ointment (Exoderil, Microspor).
If there is hair in the area of the focus of trichophytosis, it is better to shave it off. In advanced cases, it is necessary to take antifungal drugs orally (for example, Irunin).
The course of the disease must be accompanied by taking a vitamin complex to maintain immunity.
Diet for fungal diseases
When the skin is affected by fungal diseases, it is important to maintain proper nutrition. In this case, it is useful to use the following products:
- breakfast with cereal porridge;
- dairy products;
- greens and green vegetables;
- honey;
- still mineral water;
- foods containing iron.
If you have pityriasis, you need to switch to dairy and plant foods. For other types of fungus, you should include in your menu:
- rose hips, viburnum and sea buckthorn;
- peanuts, hazelnuts and nuts;
- squid and salmon;
- seeds and vegetable oil;
- apples, apricots, cherries, blueberries, cherries;
- prunes and raisins;
- green bell peppers and carrots.
Along with the list of healthy foods, there is also a prohibited food group:
- dishes using spices and hot additives;
- alcoholic products;
- tangerines.
The following categories of drinks and food are subject to restrictions:
- coffee, tea and hot chocolate;
- cheeses that are too salty;
- broths cooked with meat and mushrooms;
- confectionery sweets with butter creams;
- canned food;
- fatty fish.
What is microsporia and trichophytosis
Ringworm is most often diagnosed in young children. This is due to the immaturity of the immune system and frequent contact with animals. The fungal disease progresses quickly and therefore requires timely treatment. Delayed therapy is fraught not only with the spread of lesions throughout the body, but also with hair loss.
The causative agents of dermatological diseases are pathogenic fungi of the following types:
- Microsporum ferrugineum - parasitizes only humans and affects hair and skin;
- Microsporum canis/lanosum – infects people and animals, affecting the scalp and skin;
- Trichophyton - found in both animals and humans, affecting not only hair and skin, but also nails.
Trichophytosis in humans can be diagnosed at any age. Fungal (mycotic) disease is provoked by both zoophilic and anthropophilic fungi. Carriers of Trichophyton are most often children under the age of 12-13 years. The disease can be severe when the body's immune defenses are greatly reduced.
Microsporia affects not only pets, but also rabbits, goats, sheep, deer, pigs, etc. In infected cats and dogs, ringworm can occur in a latent form, so it is almost impossible to visually distinguish a healthy animal from a sick one. To reduce the risk of contracting the disease, it is recommended to limit contact with stray animals.
What consequences can lichen cause?
The most common and harmless type of lichen is pink. The course of the disease passes without complications.
Shingles can cause the following complications:
- inflammatory process in the membrane of the spinal cord and brain;
- partial or complete loss of vision;
- dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system;
- viruses that infect the respiratory organs and liver;
- postherpetic neuralgia.
Ringworm and versicolor often provoke the appearance of a secondary infection, which complicates the treatment process. In most cases, antibiotics are necessary. In addition, trichophytosis often leaves bald patches at the site of the fungal infection, which can remain forever.
A flat red fungus contributes to the manifestation of bacterial infections and the development of an inflammatory process in the patient’s oral cavity.
More often than others, the following categories of patients suffer from various types of lichen:
- pregnant and lactating women;
- people who do not care about their health and do not observe personal hygiene rules;
- children;
- pet owners;
- people with a low level of protective properties of the body.
Measures to prevent the disease
Since there can be many causes of lichen infection, it is impossible to completely exclude the possibility of the disease. However, compliance with preventive measures will reduce the risks. Prevention of lichen includes:
- timely treatment of acute respiratory diseases;
- compliance with hygiene procedures;
- taking a vitamin complex;
- increasing the level of immunity;
- use of shampoos with antifungal gels;
- hardening of the body;
- providing quality oral care, treatment of caries, gums and throat diseases;
- proper nutrition;
- avoiding contact with people infected with the fungus;
- vaccination of pets and periodic examinations at a veterinary clinic;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- preventing hypothermia of the body.
When diagnosing a chronic form of lichen, it is recommended to periodically visit a dermatologist’s office in order to identify possible foci of the disease.
How to treat ringworm in humans
The principles of therapy depend on the type of microsporia and trichophytosis. Effective treatment involves the use of both local and systemic antifungal drugs. If only the superficial layers of the skin are affected, doctors advise limiting the use of ointments, liniments and creams.
In case of rapid progression of the disease, systemic antimycotics - tablets, suspensions, capsules - are included in the treatment regimen.
Drug therapy
At the initial stage of development of dermatophytosis, local treatment can be carried out with antifungal ointments, shampoos, gels and sprays. Effective medications against ringworm include:
- Ketoconazole is an ointment based on imidazoledioxolane derivatives, which quickly eliminates itching and flaking of the skin.
- Terbinafine is a fungicidal ointment that improves skin condition by healing foci of inflammation and accelerating regenerative processes in the epidermis.
- Clotrimazole is a fungicidal antifungal cream that not only eliminates the symptoms of dermatophytosis, but also prevents the development of secondary pyoderma.
Before getting rid of ringworm using pharmaceutical products, you should consult your doctor. Additionally, he may prescribe treatment of plaques with salicylic acid or sulfur-tar ointment.
In severe cases of dermatophytosis, systemic medications are used - Griseofulvin, Exifin, Oronazole. In addition to antifungal agents, therapy may include immunostimulants and drugs that improve blood microcirculation in the affected areas.
Additional treatments
Treatment of microsporia on the head should begin with hair removal in the affected areas. To speed up recovery, a dermatologist may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures:
- UV irradiation;
- electrophoresis;
- microwave therapy;
- UHF therapy;
- photophoresis.
If nails are damaged, local treatment is carried out using antiseptics - iodine solution or Yoddicerin. It is necessary to limit contact with water to prevent further spread of infection.
Folk remedies and recipes
Treatment of trichophytosis in humans does not exclude the use of folk remedies that have antifungal properties. Among folk recipes, there are many options for treating ringworm on the skin. To destroy pathogens of dermatomycosis, raisins, honey with garlic, birch tar, apple cider vinegar, lemon, etc. can be used. The most effective remedies include:
- Garlic with lemon - a mixture of grated products is applied to the lesions and bandaged for 2 hours daily at least 2 times a day.
- Birch tar with butter - the products are mixed in equal proportions and applied to the skin 3 times a day.
- Raisins – softened seedless raisins are rubbed daily on pink spots and the skin around them 3-4 times a day.
Skin care
During the treatment, special attention is paid to hair and body care. It is recommended to wash your hair only with antifungal shampoos, which inhibit the proliferation of fungal flora. The procedure must be performed at least once every 2 days.
To prevent the disease, we do not recommend washing in public places, strengthening the immune system, vaccinating pets, and maintaining personal hygiene.
To treat affected areas, use fungicidal soap based on tar, turpentine or tea tree oil. To prevent the spread of infection, all underwear should be washed daily at 90°C.