Every person panics when he discovers lichen on his eye or other parts of his body. This disease appears after infection with the Varicella Zoster virus. The pathogen causes chickenpox when first infected, and subsequently herpes zoster. It is this type of lichen that is most often found in ophthalmology, the treatment of which requires detailed examination and long-term therapy.
Causes and routes of infection
The virus enters the body through airborne droplets. Ringworm can appear in both adults and children. Pathogenic microorganisms live in the peripheral and central nervous system. Under favorable conditions, they begin to develop and reproduce. Viral cells can remain in the human body in the sleep phase for several years, and manifest themselves in other pathologies or against the background of severe immunodeficiency.
Common causes of virus activation:
- the presence of a latent form of herpes in the body;
- disorders in the central nervous system;
- exacerbation of diseases that have become chronic;
- long-term therapy with immunostimulating drugs;
- presence of HIV infection;
- leukemia, mycosis.
What does ringworm look like on the face and what can cause it?
The first signs, common to all types of lichen, are the appearance of flaky spots that have a color different from the main shade of the skin. The rash is accompanied by irritation and itching. Spots can appear in several locations at once. There are a number of main reasons that provoke the occurrence of the disease:
- weakened immune system;
- stressful situations;
- tendency to allergies;
- contacts with people and animals showing signs of infectious dermatoses;
- lack of necessary vitamins in the body;
- insect bites;
- problems with digestion and the endocrine system;
- hereditary predisposition.
The main carriers of fungal infections that cause lichen are animals, people, and soil.
Due to a weak immune system, children are most susceptible to the disease. Ringworm in children is common. To avoid unpleasant situations, you should limit your child’s contact with stray animals and regularly examine the skin for spots.
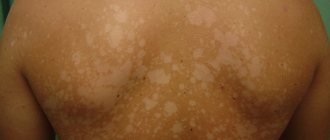
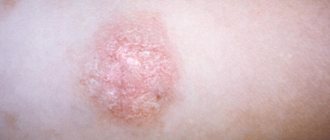
Each type of lichen looks different. The photo shows pityriasis rosea.
In order to make a correct diagnosis, you need to know what types of lichen on the face there are, their symptoms and causes:
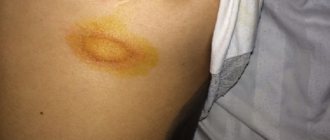
- Ringworm (microsporia, trichophytosis) is accompanied by the appearance of a flaky pigmented spot, itching and pain. It often appears at the beginning of the hairline. This type of dermatosis can be contracted from an animal or person through contact with soil containing a fungal infection.
- Pink (Giber's disease) - pink spots with a rich border and flaky scales. This type of dermatosis can be caused by hypothermia, by rubbing the skin, or during stressful situations.
- Lichen ruber has a chronic form. Elderly people are more susceptible to it. It looks like bright red raised spots with a depressed center. It can be localized in the mouth, in this case it looks like tubercles, and at the last stage ulcers appear.
- Psoriasis scaly (psoriasis) is a chronic disease that manifests itself in the form of small, pigmented, dry spots, usually affecting large areas of the skin.
- Pityriasis appears as slightly raised yellow-brown spots. It occurs as a result of the activity of normal skin microflora (fungus) as a concomitant disease with excessive sweating or endocrine diseases.
- Herpes zoster, or herpes zoster, has a specific cause. Only people who have had chickenpox get sick from it: particles of the virus remain in the body. Under the influence of unfavorable conditions, it appears in the form of pink spots with the further appearance of bubbles. It can occur on the face along the trigeminal nerve, on the cheeks, forehead, nose and eyes. The rash is accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes.
What types of lichen are there?
| Disease | Stimulus | How is it transmitted? |
| Pityriasis versicolor | Mushroom | Not contagious |
| Pityriasis rosea (Tinea Zhibera) | Viral herpes | Airborne |
| Shingles | Transmission by tactile and airborne droplets | |
| Ringworm | Mushroom | Infection through tactile contact |
| Red flat | Virus or neurology | Not getting through |
| Feline ringworm | Mushroom | Transmitted by airborne droplets and tactile contact |
| Solar | Pathogenic mushrooms | Not getting through |
| Nodular (Piedra's lichen) | Mushroom | Airborne and tactile method of infection |
| Weeping | Pathological form of chronic disease | Not contagious |
Symptoms of lichen
Similar rashes can occur in the forehead area of a person.
When lichen occurs in the eye area, the herpes virus is localized in the trigeminal nerve and affects its fibers, while the inflammatory process occurs in the following places of the skin:
- upper and lower eyelid;
- separate areas on the forehead;
- dorsum and wings of the nose;
- parietal region of the head.
When herpes is localized in the maxillary nerve, the lower eyelid is affected. A more acute form of the disease is characterized by damage to the ocular and maxillary nerve endings. In the case of an advanced form of lichen, the inflammation spreads to the cornea and sclera of the eye. With poor quality treatment, pathogenic microflora can spread throughout the face and affect large areas of the skin.
Lichen on the eyelid is accompanied by fever, pain when walking and severe migraine. At the very beginning of the lesion, severe swelling forms in the eyelid area. Soon the symptoms worsen, itching, burning appears, the skin becomes tense and acquires a bluish tint. Within 2-3 days, a large number of small vesicles filled with clear liquid form on the affected eyelid. If the eye is not treated for ringworm, the blisters will enlarge and tighten, which will eventually lead to their rupture. The released fluid, in turn, will also affect the inflamed skin around the eye and contribute to the formation of erosions. The vesicles will grow and coalesce into large areas of location, which will lead to the accumulation of purulent masses under the crust of the vesicular lesion.
Dermatologists and ophthalmologists have found that approximately 10 days before the formation of a rash, infected patients experience neuralgic symptoms, reflected by burning, tingling and twitching in the area where pathogenic herpes microorganisms are localized.
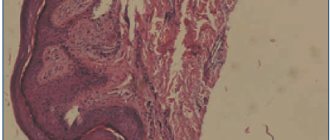
Oral lichen planus
The selection of medications is made based on the cause, severity of the process and associated pathologies. With an asymptomatic course and single papular elements, sometimes no medical intervention is even required. Erosive and ulcerative lesions, on the contrary, require timely treatment, otherwise there is a high risk of deterioration of the patient’s condition and infection. To stop the inflammatory process, topical corticosteroids are used. Oral forms are used only in extremely severe cases. At the first signs of improvement, the dosage of the drug must be reduced and subsequently discontinued to avoid side effects. In addition to topical steroids, local treatment of the disease includes pain relief (anesthetic solution or pyromecaine) and acceleration of regeneration (methyluracil, vitamin E in oil). To prevent candidiasis while using steroid hormones, it is recommended to take antifungal agents orally (fluconazole, Nystatin) or in the form of ointments (Griseofulvin, Ketoconazole). In some cases, topical calcineurin inhibitors (Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus) may be prescribed for local immunosuppression. To speed up tissue regeneration, it is recommended to take multivitamins.
All patients with nervous disorders require sedative therapy (tincture of valerian and motherwort, Phenazepam, Sibazon). Patients with a burdened allergic history require hyposensitizing therapy (Claritin, Zyrtec, Erius). If the disease is accompanied by immunodeficiency, immunomodulatory therapy (Likopid, Myelopid, Interferon) is prescribed. To improve enzyme activity and accelerate the synthesis of nucleic acids, antimalarial drugs (Delagil, Rezokhin) are used.
Physiotherapeutic methods (electrical and phonophoresis) are also effective, and for some patients with long-term non-healing erosions, surgical intervention is recommended if there is a possibility of malignancy. In addition, all patients, without exception, need to undergo a complete sanitation of the oral cavity and eliminate all irritating factors (sharp edges of teeth, overhanging fillings, traumatic orthopedic structures) and foci of chronic inflammation (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis). It is necessary to give up smoking, alcohol, hot and spicy foods and adhere to a gentle diet. It is important to avoid nervous tension and avoid stress if possible.
Prognosis and prevention of oral lichen planus
Timely diagnosis and identification of causes make it possible to select pathogenetic therapy and carry out successful treatment. In this case, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. But since lichen planus of the oral cavity is a chronic dermatoses, the patient must be registered at a dispensary and regularly undergo examination by a dermatologist and dentist. The absence of the necessary medical intervention leads to aggravated course and complications. Prevention of lichen planus consists of following the requirements of oral hygiene, undergoing dental examinations once every six months, treating dental and somatic diseases, quitting smoking and other bad habits.
Diagnostic methods
After presenting complaints, the patient undergoes biomicroscopy procedures.
At the first signs of illness, the patient should immediately seek help from an ophthalmologist. At an early stage, an accurate diagnosis can be made through a detailed examination of the medical history and current symptoms. In advanced forms, the virus can be detected by fluorescent antibodies. The following ophthalmological procedures will help determine the extent of the damage:
- Visometry is a method for studying visual acuity.
- Tonometry is a test to determine eye pressure.
- Diagnostics of light projection - determines the state of the visual-nervous analyzer of the eye.
- Biomicroscopy - performed with a slit lamp to examine the structure of the eye organ.
- Electrophysiological examination is a series of modern techniques that are used to study the functions of the optic nerve, retina, sclera and areas of the cerebral cortex responsible for visual functions.
Clinical course
Typically, ophthalmoherpes is the result of the awakening of the virus, and not of primary infection. In this case, eye damage can be expressed to varying degrees.
Ophthalmologists distinguish several clinical forms of the disease:
- Damage to the anterior part of the eye (conjunctivitis, keratitis, recurrent corneal erosion, blepharoconjunctivitis, episcleritis);
- Damage to the posterior part of the eyeball (uveitis, perivasculitis, central serous retinopathy, acute retinal necrosis syndrome, anterior ischemic retinopathy, neonatal retinochorioretinitis).
Treatment and prevention
When lichen in a child or adult, drug therapy should be carried out strictly under medical supervision. The first stage of treatment is the administration of antiviral drugs to combat Varicella Zoster. These may be drugs such as Valtrex, Vidarabine and Acyclovir. Ophthalmologists give particular preference to the latter medicine, since the drug has a wide spectrum of action, which contributes to the rapid defeat of pathogenic microorganisms. Pharmaceutical organizations offer medicines in the form of drops, ointments and tablets. Medications containing interferons are also prescribed.
Levamisole can be used when the pathological process is chronic.
Herpetic pathologies that have become chronic are treated with immunocorrective and antiviral medications, such as Amiksin, Levamisole, Tactivin. Such medications promote faster treatment and have pain-relieving and wound-healing effects.
Processing agents
In case of a mild form of the disease or at the initial stage of development, ophthalmologists advise treating the affected areas with the following means:
- methylene alcohol 2%;
- iodine;
- antiviral ointment (tetracycline, oxolinic ointment or Zovirax).
Ophthalmic lichen often provokes the formation of vesicular structures on the conjunctiva and cornea, which can lead to severe infectious pathologies with a severe decrease in visual acuity, including loss.
When carrying out the procedure, the first stage includes treating the affected area with methylene alcohol, then cauterizing with iodine and applying ointment. Repeat the procedure every 2-3 hours. For a faster effect, take immunostimulants; intramuscular injections, such as “Interferon”, which includes 5 to 10 injections, or “Cycloferon” - 10-14 injections, are considered more effective.
Features of facial skin care during illness
When using the wrong soap, a newborn's face may develop pityriasis alba - small light spots. In this case, the hygiene product should be replaced. The face must be wiped with herbs, while avoiding excessive moisture.
During illness, in addition to drug treatment, it is worth providing proper skin care for an adult. You should not use cosmetics for camouflage purposes - the lichen on the skin of the face will become even more inflamed. Tar soap is used as a cleanser. Additional care will be provided by masks made from natural ingredients: cranberries, raisins, propolis.