An alcohol solution of iodine is often used at home to treat wounds and other injuries, but the use of such liquids is not always justified. In the West, iodine has long been abandoned, as this disinfectant was noticed to have a negative effect on the skin. Iodine solutions are very dangerous when treating mucous membranes. Young children are able to drink dark liquid in the absence of their parents. Then a chemical burn from iodine is inevitable. Let's consider what to do in such cases.
Features and degrees of iodine burns
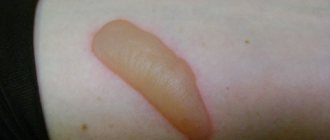
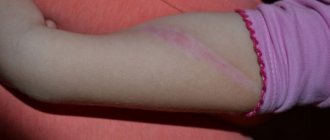
The iodine burn itself looks like a dark spot at first. The extent of the injury directly depends on the area of treatment. In people with a fair skin type, the spot takes on a light brown tint, while in people with dark skin, a darker, richer, brown color appears. After a while, the skin begins to peel off because iodine has a drying effect.
You can get a burn with iodine for several reasons, but more often such injuries occur due to intensive treatment of wounds, applying an alcohol solution to mucous membranes, or ingesting liquid. Also, people who are allergic to iodine can also become victims of improper use. A person often does not even realize that he has an allergy.
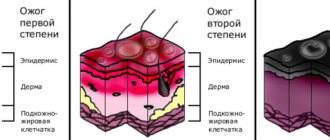
Chemical damage, as it affects the skin, is divided, like thermal burns, into degrees:
- Stage 1 is characterized by redness of the tissues, a burning sensation and slight pulsation.
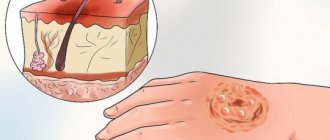
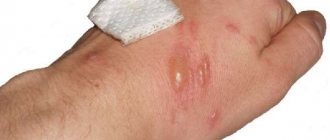
- Stage 2 damage is manifested by blisters with clear liquid inside.
- 3rd and 4th degree burns with iodine solutions practically do not occur.
A burn is accompanied by unpleasant sensations: pain, tightness of the skin, and local temperature may rise.
An alcohol solution of iodine, which is sold in any pharmacy, can cause a burn if it is used incorrectly, stored in improper conditions, or basic safety measures are not followed during use. We are talking about the composition getting into the mucous membrane of the eyes or mouth.
The familiar iodine network is also the cause of burns, because many people use an excessive amount of alcohol solution. Fans of traditional medicine are sure: the more, the better. In this case, this principle does not work. This approach to treatment will only worsen the patient’s condition.
Causes of burns
The free sale of iodine tincture in pharmacies creates a false impression of its harmlessness. Like any drug, it has its side effects, and if used incorrectly, it can cause serious damage. The main errors are caused by violation of the rules for use and storage of the drug.
The most common of them:
- long-term exposure to the substance, use of iodine tincture for lotions;
- applying iodine directly to the wound;
- treatment of mucous membranes (tonsils, eyes, gums, oral cavity);
- repeated treatment of the same area of skin without observing a time interval;
- the use of iodine tincture for the prevention and treatment of iodine deficiency;
- storage in a place accessible to children;
- storing the drug near food products, or in containers without appropriate labeling;
- using a medicine without first testing for sensitivity to its components.
When purchasing the drug, be sure to read the instructions for use. This can avoid negative consequences and mistakes arising due to lack of knowledge.
What to do in case of an iodine burn: first aid
Iodine burn belongs to the class of chemical injuries. If the damage by iodine is insignificant, then the darkening of the skin will disappear within 2-3 days. In case of serious damage where blisters are present, you should consult a doctor.
Regardless of the degree of damage, you should consult a doctor if the patient’s condition does not improve within 3 days and the temperature persists.
It is important for people who are close to the victim to remember that his further condition depends on the speed of their actions. Algorithm of action for iodine burns:
- Rinse or rinse the damaged area with running water for at least 10-20 minutes.
- Once the injury site has been washed, the removal of the chemical begins. Tooth powder or toothpaste will come to the rescue in this matter. The powder is applied directly to the skin if there are no blisters. Toothpaste is diluted with a small amount of water and also applied with light movements to the skin. If such products are not at hand, then ordinary soapy water will do.
- For deep and severe burns, in order to relieve the victim of discomfort, he is given a painkiller tablet like Ibuprofen.
Iodine neutralization for burns of the mouth and eyes can only be carried out in a medical facility. Doctors use specialized tools.
If there are blisters on the skin, then a visit to the doctor is necessary. The situation is especially dangerous when the clear liquid inside the bubble becomes cloudy or gel-like. This change indicates that the wound has become infected.
The effects of iodine cannot be neutralized by ice or thermal burn sprays.
Symptoms
Burns from iodine usually do not appear immediately, but only after some time. This injury is similar in its symptoms to chemical injuries, but has its own characteristics:
- A dark spot forms on the treated area. Usually the trace of iodine disappears quite quickly - within a day. But if the drug damages the skin, the marks remain for a long time.
- Mucous membranes, if iodine gets on them, can become deformed and change their normal color.
- The skin on the affected area peels off.
- Discomfort occurs. Most often, such a burn does not cause pain, but may cause burning and itching.
- Contact of iodine in the eyes leads to severe burning, pain and watery eyes. The whites of the eyes become red.
If the burn is minor, then the listed signs are observed for a short time and disappear after a couple of days. However, longer contact with iodine can result in extremely unpleasant consequences, requiring targeted treatment and even seeking medical help.
Further treatment
You can treat burns from iodine on your own, but only in case of minor damage. At home, various medications, ointments, creams, and folk recipes come to the rescue. To speed up healing, all recommended methods must be applied comprehensively. It is important not to delay visiting a doctor, as if the wound is treated incorrectly, an infection can get into the damaged tissue. The protective barrier of the skin at the burn site is broken, so microbes have an open path to colonization. Further treatment in this case will be based on the use of antibacterial creams, ointments or sprays.
Medications
To restore a damaged area of skin that was burned with iodine, doctors recommend using the following drugs:
- antiseptics;
- painkillers;
- wound healing ointments and creams;
- decongestants.
The antiseptic and wound-healing effect is especially important in the presence of blisters. For home treatment, classic burn remedies Panthenol and Olazol are suitable. The compositions must be applied to the skin up to 3-4 times a day. The spray must be sprayed at a distance of 20 cm from the wound.
When the foam subsides after applying the spray, it is appropriate to apply a wound-healing cream or ointment with an antiseptic effect:
- Bepanten;
- Rescuer;
- Dermazin;
- Sulfadimethoxine;
- Levomekol.
If an infection joins the wound, treatment with ointments and fatty creams is stopped. Further therapy consists of treating the wound with an antiseptic like Chlorhexidine. This drug should be applied to a sterile cloth and applied to the wound until completely dry. Furacilin is prescribed as an alternative composition. Applications with an antiseptic must be applied until purulent masses cease to form.
If you get a burn from iodine on your face, use Panthenol. It is first applied to clean skin of the hands, and only then with light, massage movements on the damaged area.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is considered a good addition to therapy, but only auxiliary. Traditional recipes cannot cure a burn as quickly as modern drugs.
Several effective methods:
- Starch paste. To prepare, simply mix 1/2 cup hot water with a tablespoon of starch. Stir the finished mixture until completely homogeneous. Cool the prepared jelly completely. Apply to damaged skin for 20-30 minutes, then rinse off the residue under running water.
- Application from oatmeal porridge. For the procedure, just boil a glass of rolled oats in water. Apply the cooled mixture to the burn and secure with a sterile bandage. Keep on the skin for 1 hour, remove any residue with water.
- Mashed potatoes. Rinse 2-3 medium potatoes thoroughly under water, peel and grate. Place the finished mixture on the wound and tie it with a bandage, but not too tightly. Leave the application on for an hour, remove any residue under running water. The same procedure is carried out from pumpkin pulp.
- Tea compress. Skin burns with iodine cause discomfort and pain. To relieve these sensations, it is enough to apply a compress of black tea to the skin. The liquid should be cool and well filtered.
- Sea buckthorn oil. The herbal product regenerates the skin well, so it can be used both in pure form and as part of lotions. When using sea buckthorn essential oil, it is important to consider its concentration (it is better to dilute it with water in a 1:1 ratio).
- Aloe leaf compress. Before use, the leaf is washed well and the top film is removed to allow access to the pulp. Apply to the affected area on the skin until the mucus dries. For convenience, the sheet is fixed with a sterile bandage.
- Oak bark decoction. 1 tbsp. oak bark, pour 200 ml of boiling water and boil for 5 minutes. Then leave for 15 minutes, strain and cool. Wash the wound with the prepared decoction 2-3 times a day.
If there are burst blisters on the skin, then traditional methods cannot be used.
The final choice towards a folk remedy for treating a burn is best made together with your doctor. It is important to regularly carry out all prescribed procedures so that there is no scar or scar left after the injury.
Folk remedies
If, after exposure to the medication, the skin begins to look dry and wrinkled, then you can use the following remedies:
- Sea buckthorn fruit oil. This product of natural origin helps to quickly restore damaged skin. This effect is achieved due to the high content of vitamins A and E. During the treatment process, it is necessary to lubricate the skin several times a day. Treatment is continued until complete healing. Sea buckthorn oil is recommended for use when the skin on the face is affected.
- Egg white. It is necessary to beat this ingredient until foam forms. Then the affected areas of the body are treated with this product and left to act for a short period of time.
- Oatmeal. This folk remedy helps neutralize all manifestations of a burn in a minimum period of time. Chilled porridge is used for treatment. Apply to the skin several times a day.
- Grated potatoes. A raw tuber is used, which is previously peeled. Rubbed and applied to the painful area and left for a few minutes.
- St. John's wort oil. Oil extract is prepared by mixing raw materials with vegetable oil. The medicine is used to treat a variety of wounds.
- Welding. Use natural tea of any kind. The resulting tea leaves are cooled and used as a poultice.
Features of the treatment of burned mucous membranes
A burn with iodine on the skin is much easier to cure than on the mucous membrane. Such an injury is especially dangerous if the throat, tonsils, gums or eyes are affected. Due to lack of child supervision, there are cases of throat burns when the baby drinks iodine. What to do in such cases?
The first thing you need to pay attention to is the symptoms. If a child has swallowed a large amount of iodine, this condition is accompanied by:
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased salivation;
- pain when swallowing;
- cough;
- hiccups;
- voice change.
The child may also complain of chest pain. This condition occurs due to damage to the esophagus. In such a situation, you should immediately seek medical help. The child needs to drink a lot of water, it is advisable to organize plenty of milk or jelly. It is impossible to induce vomiting, as it is possible that iodine may re-expose the esophagus.
When an iodine burn to the eyes is diagnosed, it is imperative to rinse the eyeballs under clean water. It is important to rinse your eyes well (blinking 10-20 times under water is enough). The further course of treatment is based on the use of eye drops:
- Tsiprolet;
- Phloxal;
- Tsipromed;
- Gentamicin.
After initial treatment, the whites of the eyes become red. In this case, a visit to the doctor is carried out immediately after the washing procedure.
It is forbidden to neutralize eye damage yourself; this is done in medical institutions. The first aid that can be provided at home is only rinsing under running water.
When the tonsils or gums are burned, the mucous membrane loses its smoothness; it may wrinkle and change color. In this case, it is important to rinse your throat with cool water for 15 minutes and then visit a doctor. Further self-medication will only worsen the patient’s condition.
What to give preference, brilliant green or iodine?
Everyone's favorite brilliant green (from the French "brilliant"), originally from Latin and meaning "brilliant", was used as a dye for silk, wool and other fabrics. As it turned out, according to the method of exposure, iodine and brilliant green have great distinctive features. To effectively use both tools, you need to understand exactly how they differ from each other.
Did you know that iodine successfully dries the skin, but if used in excess it can burn it? Now you know! To avoid this, you need to apply the basic rule: under no circumstances apply iodine to open wounds - this can cause severe burns to the surface of the skin, unlike brilliant green. If you cut your finger, get an abrasion, bruise or cut, do not immediately run for iodine - you can aggravate the injury. It is much more logical to use Iodine in cases of sprains, bruises or joint diseases to improve blood circulation. In these cases, the “iodine grid” is the most effective way to recover faster.
Physiological and immunological aspects
Iodine is an essential trace element necessary for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. In the intestines, iodine is converted to iodide, the ionized form of iodine. Food sources of iodine include fish, iodized salt, and iodates used as preservatives in bread.
Fish is a good source of iodine, as iodine has been leached from the soil and into the ocean over thousands of years. Iodine in fish can be free, as a substitute for chlorine, or bound to proteins.
Allergy to iodine is a form of drug tolerance and is not very common. The toxic effect of iodine on the body is caused by an overdose of drugs containing this substance. Additional factors may include chronic diseases of organs and systems.
Clinical significance
Patients with a history of allergy to iodine or seafood should be questioned in more detail regarding the severity of the previous allergic reaction. If possible, you need to separate seafood allergies from other causes of seafood intolerance. A history of seafood allergy increases the risk of side effects when a contrast agent is administered threefold. As with any allergy, the nature and severity of the reaction should be considered when choosing the type of contrast agent and when determining the need for premedication. Allergy to seafood in itself should not be considered an absolute contraindication to intravenous contrast.
There is no reason to believe that an allergy to iodine, indicated by skin reactions when using antiseptics, will be of particular importance during the intravenous administration of contrast media.
Author of the article: Vorobets K.Yu.
Allergy to iodine and use of contrast media
Contrast agents are derivatives of triiodobenzoic acid and contain small amounts of free iodine. Adverse reactions to these substances can be classified as idiosyncratic or non-idiosyncratic.
The mechanisms of idiosyncratic reactions are unknown. Among the theories that explain them is the allergy theory, which suggests that either the contrast agent or iodine itself acts as a hapten, causing a specific immune response. An antigen-antibody reaction then occurs when the patient is re-injected with iodine-containing contrast agent. These drugs can lead to the formation of antigenic iodine proteins in vitro. However, the same researchers were subsequently unable to demonstrate a significant relationship between hypersensitivity to contrast agents and the presence of lymphocytes that specifically react to these substances or to iodide. Additionally, attempts to induce antibody production in vivo in animals have been unsuccessful despite optimal conditions.
Therefore, it is unlikely that the mechanism of idiosyncratic reactions to contrast media is based on a specific immune response (i.e., a true allergy), and, more likely, such reactions occur due to the activation of complement and other mediators of nonspecific immunity. Therefore, idiosyncratic reactions to contrast agents are best referred to as anaphylactoid, pseudoallergic, but not allergic. In addition, activation almost certainly occurs in response to the appearance of a whole molecule of contrast agent rather than free iodine. For example, none of the 23 patients with documented hypersensitivity to contrast agents had a similar reaction to subcutaneous sodium iodide.
Non-idiosyncratic reactions are due to direct toxic or osmolar effects. The only adverse effect of a contrast medium that can be intelligibly explained by free iodine is “iodine pig” and other manifestations of iodism. “Iodine mumps” is manifested by swelling of the submandibular, sublingual and parotid salivary glands after intravenous administration of an iodine-containing contrast agent. It is part of a group of non-idiosyncratic reactions due to impaired iodide metabolism due to iodine overload. All this is called iodism; it can also manifest itself as swelling of the lacrimal glands, runny nose, and skin rashes. Most of these cases occur in patients with weakened renal function (possibly due to decreased renal excretion, iodide concentrations in the body increase).