Last update: 03/03/2021
With the onset of spring, many of us notice a deterioration in our health - weakness, fatigue, irritability appear, mood decreases, and sleep is disturbed. Changes also affect appearance - hair becomes dull and brittle, skin becomes dry and often flaky, rashes and redness appear. All these unpleasant symptoms signal to us about the development of a common seasonal disease - hypovitaminosis or vitamin deficiency.
Vitamin deficiency on the skin of the hands
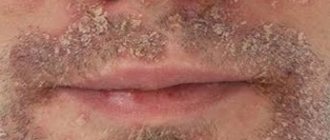
One of the most unpleasant forms of vitamin deficiency is vitamin deficiency of the skin of the hands. It manifests itself as dryness, peeling, itching, cracking of the skin, causing a lot of discomfort. In addition, cracks that appear on the hands increase the risk of various skin infections.
It is important to understand that vitamin deficiency in the hands of children and adults is not an aesthetic problem, but a serious disease. It occurs due to a lack of vitamins in the body, usually of groups A, B or E. Often the signs of vitamin deficiency are similar to allergies or fungal skin lesions, so people who try to independently diagnose and treat the disease often use drugs that do not improve the condition at all. , but on the contrary, aggravating their condition.
What vitamin deficiency is most common in children?
Vitamin D
The child's body is most vulnerable to hypovitaminosis - a mild but still significant manifestation of vitamin deficiency. Signs of hypovitaminosis in children can be observed at any time of the year, most often in the spring.
A significant number of children have a lack of vitamin D. At the age of 7 to 14 years, no more than 10% of children in the Central and Northwestern regions of Russia are provided with vitamin D. The reason for the deficiency is rare exposure to the sun.
Preventive measures to prevent vitamin D deficiency are divided into primary and secondary. Primary measures include the prevention of deficiency in the mother during pregnancy. The level of vitamin D in the blood of a newborn is ~80% of the maternal level. Secondary prevention includes prescribing vitamin D supplements to the child after birth.
The main manifestation of hypovitaminosis D in children is rickets - a disease accompanied by deformation of the bones of the skull and chest, long tubular bones due to their softening, curvature of the spine, delay in the formation of the static and motor functions of the child. Sometimes there is an enlargement of the abdomen.
Hypovitaminosis D during pregnancy increases the risk of congenital rickets in the child. For preventive purposes, pregnant women and young children can take vitamin D. Completing the deficiency reduces the risk of acute respiratory infections by modulating the immune response.
Vitamin A
Lack of vitamin A, which is responsible for the normal functioning of the organs of vision, mucous membranes and skin, usually manifests itself in preschool children. Symptoms may include:
- excessive dryness and flaking of the skin, cracks on the pads of the fingers and soles;
- periodic itching in the buttocks, abdomen, elbows and knees;
- inflammation of the eyes and ocular membranes.
When the first symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a pediatrician.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) enters our body mainly with plant foods. Its shortage may be associated with two problems: a decrease in consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits and a high degree of technological processing of food.
Add fresh vegetables and fruits to your diet, and steam foods instead of long-term cooking. Vitamin C increases the body's resistance to infections and is involved in the formation and maintenance of healthy bones, cartilage, and teeth. If there is a deficiency, the following symptoms are observed:
- rapid fatigue of the child and general weakness;
- gum inflammation and bleeding;
- anemia (decreased hemoglobin level in the blood).
Vitamin E
Hypovitaminosis of vitamin E negatively affects the condition of the child’s skin - it becomes dry, nails break, and vision deteriorates. Vitamin E is present in fats and oils, eggs, liver, milk and in the germ of cereal plants. Vitamin E deficiency is common in premature babies.
In Russia, less than half of children under 13 years of age take multivitamin complexes. Among teenagers, this proportion is even smaller.
Meanwhile, it has been proven that additional intake of vitamins leads not only to an improvement in the vitamin status of children and a reduction in the frequency of anemia, but also reduces the incidence of acute respiratory infections, especially in children from the group of frequently ill children, and is also accompanied by an improvement in cognitive functions.
Causes of vitamin deficiency
The causes of this form of vitamin deficiency may be the following factors:
- unbalanced diet;
- abuse of refined foods;
- monotonous diet;
- stress, emotional turmoil;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- physical inactivity;
- prolonged physical and mental fatigue;
- improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- chronic lack of sleep;
- use of antibiotics.
Treatment of vitamin deficiency in the skin of the hands
If such a nuisance as vitamin deficiency of the hands happens to you, there is no need to panic. A timely diagnosed disease responds well to treatment, and improvement occurs quite quickly.
To quickly treat vitamin deficiency in the skin of the hands, it is necessary, first of all, to identify the cause of the disease. If it is a disturbance in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, you should consult a specialist and undergo a course of treatment. But in most cases, it is enough to simply review and adjust your diet, enriching it with essential vitamins. In the treatment of vitamin deficiency, several methods can be distinguished, which often should be combined:
- Balanced diet.
- Taking pharmaceutical medications containing vitamins.
- The use of external agents for local help with vitamin deficiency of the hands.
- Traditional methods of obtaining vitamins.
- Correct daily routine.
- Walks in the open air.
- Sports activities.
- Rejection of bad habits.
Nutrition for vitamin deficiency of the hands
Proper, balanced nutrition is the key to the prevention and rapid treatment of vitamin deficiency. Since this form of the disease, such as vitamin deficiency of the hands, speaks primarily of a lack of vitamins of groups A, B and E in the body, doctors recommend consuming foods rich in these particular vitamins.
The diet must include:
- meat, fish, seafood, eggs;
- legumes, grains, fermented milk products (cottage cheese, cheese, fermented baked milk, yogurt, sour cream);
- fresh fruits and vegetables, nuts.
It is better to replace refined drinks with a high sugar content with juices, fruit drinks and compotes, preferably homemade, without preservatives.
What is a dietary supplement
A dietary supplement is a biologically active food additive. A dietary supplement is not a medicine!
Accordingly, there are no standards for the production of dietary supplements.
Their quality control consists only of assessing their safety as food products. Unfortunately, in our country there is no system and regulatory framework for control in the field of dietary supplements. It is worth noting that all classifications are conditional. Dietary supplements are a fairly large group of substances, which includes vitamins, minerals, amino acids, essential fatty acids, and probiotics. Vitamins
are organic compounds. The body cannot synthesize them on its own, so they must come from food.
Minerals
- chemical elements that are contained in soil and water, from where they are extracted by the root system of plants. (A balanced diet covers the body’s daily needs for vitamins and minerals).
Amino acids
- a constituent element of protein. The body needs 20 amino acids for protein synthesis. Of these, eight amino acids are essential, meaning they are not produced in the body.
Essential fatty acids
- These are complex compounds of glycerol and fatty acids. The most famous of which are: omega 3 and omega 6. These fatty acids are not synthesized in the body and are found mainly in flaxseed oil and fatty fish.
Probiotics
- preparations that contain bacteria beneficial to the intestinal microflora. Contained in pickled vegetables, yogurt, kefir, some cheeses, and kombucha.
Taking a multivitamin complex
Taking multivitamin complexes can provide quick help in the fight against vitamin deficiency. Today the market offers a huge number of high quality and effective products. These complexes are pure synthetic chemical compounds containing the necessary balanced set of vitamins and microelements. A specialist should recommend such drugs to each individual individually.
Application of external skin care products
Skin care products that moisturize, nourish and protect the skin of the hands experiencing stress and discomfort will help to significantly alleviate and quickly improve the condition of the skin with vitamin deficiency on the hands.
One of the most effective products in this spectrum can rightfully be called La Cree cream for dry skin. It is intended to eliminate the causes and consequences of dry skin, including vitamin deficiency. The cream moisturizes the skin and restores its water-lipid balance. The product also protects the skin from loss of its own moisture and negative environmental influences in cold and windy weather. By carefully caring for your hands, the cream will have a healing effect, because nutrients will be delivered locally to problem areas of the skin.
The product contains jojoba, shea and wheat germ oils, rich in vitamins A and E, which help normalize the water-lipid balance of the skin, soften and nourish it, protecting it from peeling and drying.
Beeswax, another component of the healing cream, is a real natural resource of vitamin A. It has excellent nourishing, softening, healing and anti-inflammatory properties and has a restorative effect on dry and very dry damaged skin of the hands.
Seed and licorice extracts, rich in vitamins A and C, flavonoids and essential oils, relieve inflammation and itching, eliminate redness and flaking of skin injured by vitamin deficiency.
Vitamins in dermatology. Review article
Vitamins include a group of organic compounds that are present in small quantities in cells and catalyze various chemical reactions. It is known that almost all hypovitaminosis is accompanied by certain changes in the skin and its appendages. In dermatovenerology, vitamins and their various complexes are used for nonspecific immunomodulatory therapy, which changes the body’s relationship with etiopathogenetic factors and drugs used to treat this disease.
Vitamins are divided into two classes:
- water-soluble: thiamine, riboflavin, nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid, pyridoxine, folic acid, cobalamin, ascorbic acid, biotin,
- fat-soluble: retinol, calciferol, tocopherol, phylloquinone.
Water-soluble vitamins
Thiamine (vitamin B1) controls the most important processes of energy production and biosynthesis of living cell substances. This vitamin is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids. The action of thiamine is characterized as hyposensitizing, analgesic, antipruritic, anti-inflammatory; it stimulates the detoxification function of the liver and has a beneficial effect on the state of the central nervous system. Thiamine stimulates melanogenesis, as well as the synthesis of connective tissue elements. Changes in lipid peroxidation in the body of thiamine have been reported; in particular, an increase in the permeability of lysosomal and plasma membranes of leukocytes has been established. There are observations about the participation of thiamine in immunological reactions. The action of this vitamin is realized by activating the biosynthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, which underlies the proliferation of both thymocytes and bone marrow cells. With thiamine deficiency, both cellular and humoral immunity are inhibited.
Thiamine is recommended for eczema, psoriasis, lupus erythematosus, for diseases with photosensitivity - photodermatoses: porphyrin disease, lupus erythematosus, pellagra; as well as neurodermatitis, pruritus, chronic urticaria, skin itching, seborrhea, lichen planus, when the peripheral nervous system is involved in the pathological process in patients with herpes zoster, leprosy, as well as in the complex treatment of vitiligo, circular and seborrheic hair loss, chills, cheilitis , acne vulgaris, pyoderma, candidiasis.
On the other hand, a dermatologist in his practice may encounter negative effects of vitamin B1 caused by allergic reactions: urticaria, skin itching, Quincke's edema, erythroderma. A manifestation of increased sensitivity to thiamine under conditions of its production is contact dermatitis.
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) is involved in energy metabolism processes. It is part of tissue respiration enzymes and affects the metabolism of nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. This vitamin has a beneficial effect on the processes of growth, regeneration and trophism of tissues, is closely related to the metabolism of a number of other vitamins, and stimulates phagocytosis and melanogenesis.
If there is a deficiency of riboflavin in the body, wounds and trophic ulcers do not heal well.
Riboflavin preparations are effective in combination with other drugs for cheilitis, angular and aphthous stomatitis, glossitis, cracked lips, seborrheic dermatitis, alopecia, rosacea, photodermatoses, psoriasis, eczema, neurodermatitis, prurigo, acne vulgaris, streptoderma. Vitamin B2 is indicated for long-term use of antibiotics, sulfonamides, hormones, and antimalarial drugs, which are often used in dermatology. The stimulating effect of riboflavin in trophic disorders in tissues, as well as its participation in the regeneration process, make it possible to use this vitamin for the treatment of burns.
Nicotinic acid (vitamin PP or B3) is part of the enzymes of redox reactions, affects the metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, reduces blood glucose, improves the functional state of the central nervous system, liver and stomach, and participates in the reparative processes of the skin.
With a lack of nicotinic acid, pellagra develops (Italian pelle - skin, agro - rough). The main manifestations of pellagra are photodermatitis and inflammatory lesions of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tongue. Dermatitis is located mainly in open areas. Erythematous in the acute period, it is accompanied by itching or burning. Then, within 2 - 3 weeks, it becomes dry and scaly, and the skin thickens. Collar of Kasal is a term used to describe sharply defined skin lesions that form around the neck, resembling a necklace. Skin lesions also occur on areas of bony prominences and on the face. When nicotinic acid is added to the diet, the skin symptoms of pellagra quickly disappear centrifugally. A decrease in the content of nicotinic acid in the body has been established in psoriasis, eczema, and photodermatoses.
Due to the vasodilating effect of nicotinic acid, it is successfully used to treat chills, chronic acrodermatitis atrophicus, Raynaud's disease and scleroderma, and due to its beneficial effect on the nervous system and liver function, it is used to treat eczema, neurodermatitis, prurigo, lichen planus, and psoriasis. The photodesensitizing effect of vitamin PP allows it to be used for photodermatoses, and its beneficial effect on the functional state of the digestive tract allows it to be used for erythematosus. Due to the ability of this vitamin to prevent and reduce toxic effects, it is recommended to prescribe it for long-term use of high doses of antibiotics, sulfonamides, antimalarial drugs, as well as in combination with other drugs - for cheilitis, stomatitis. The use of nicotinic acid gives a good effect on sluggishly healing wounds and ulcers. Nicotinic acid is prescribed to obtain the phenomenon of inflammation in the diagnosis of syphilitic roseola and erythema leprosum.
Patients suffering from allergic dermatoses during periods of severe allergic conditions (allergic dermatitis, eczema, urticaria) should not be prescribed the drug. Side effects include redness of the skin of the face and upper half of the body, increased skin temperature, sometimes itching and urticarial elements.
Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5). It has been established that pantothenic acid takes part in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and participates in redox processes and in melanogenesis.
Pantothenic acid is used in dermatological practice as a dermatoprotector, because it has a regenerating and anti-inflammatory effect. It is used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis, eczema, trophic ulcers, burns, herpes, alopecia and dermatoses of various etiologies.
Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) catalyzes processes that regulate the metabolism of nucleic acids, proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Pyridoxine deficiency leads to the development of anemia, functional changes in the central nervous system, seborrheic dermatitis, glossitis, cheilitis, and hair loss.
Vitamin B6 is used to treat dermatoses in which there is a significant lack of pyridoxine in the body - seborrhea, stomatitis, psoriasis, scleroderma, herpes zoster, photodermatoses, atopic dermatitis.
The drug is indicated for patients suffering from neurodermatitis and eczema. Pyridoxine prevents and reduces toxic effects in people taking high doses of antibiotics, antimalarial and antituberculosis drugs for a long time.
A positive clinical effect was established in patients with acne vulgaris, for the treatment of which a cosmetic cream containing 0.5% pyridoxal phosphate was used.
The use of the drug in dermatological practice for psoriasis, eczema, and neurodermatitis is associated with its ability to stimulate metabolic processes in the skin and mucous membranes. In patients with psoriasis, the use of pyridoxal phosphate is pathogenetically justified by a deficiency of pyridoxine and a violation of tryptophan metabolism at the level of the B6-dependent enzyme.
Allergic reactions to pyridoxine are possible - skin itching, urticaria, toxicoderma.
Folic acid (vitamin B9). Folic acid plays an important role in the metabolism of serine, glycine, histidine, and the biosynthesis of DNA and RNA molecules. It is also essential for the normal course of the processes of growth, development, tissue proliferation, and melanogenesis.
The administration of folic acid is accompanied by a clinical effect for psoriasis, solar urticaria, pruritus, porphyria cutanea tarda, rosacea, cheilitis, hyperkeratosis, dermatitis herpetiformis, pyoderma, acne, radiation damage to the skin, as well as with prolonged use of cytostatics, antibiotics, sulfonamides. Thus, the combination of methotrexate with folic acid in the treatment of patients with psoriasis significantly reduces the incidence of such serious side effects as anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Folic acid is classified as a vitamin that is characterized by severe toxicity, since even a single administration of it to a person in a dose of more than 100 mg causes symptoms reminiscent of histamine poisoning - severe redness of the face, an itchy maculopapular rash, etc. Positive skin tests in some cases indicate about the allergic nature of such phenomena.
Cobalamin (vitamin B12). The ability of cobalamin to increase nonspecific resistance to bacterial infections has been established. One of the basis of the mechanism of the immunomodulatory action of this vitamin is considered to be its effect on the exchange of nucleic acids and proteins.
Vitamin B12 is successfully used for psoriasis, photodermatoses, dermatitis herpetiformis, and neurodermatitis.
When cobalamin is administered, allergic reactions in the form of urticaria and Quincke's edema are possible. The combined use of cobalamin with thiamine more often causes the development of allergic reactions than separate use. In case of a pronounced hyperergic state during the period of exacerbation of eczema and neurodermatitis, the administration of cobalamin can enhance allergic reactivity, therefore, in the acute stage of dermatoses, the use of this vitamin should be avoided. A similar tactic is advisable for the progressive stage of psoriasis, psoriatic erythroderma and its arthropathic form.
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is involved in the formation of connective tissue, the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, the synthesis of adrenal hormones, nucleic acids, has a beneficial effect on regenerative processes, regulates pigment metabolism in the skin, stimulates the antitoxic function of the liver, the activity of the endocrine glands, promotes adaptive abilities of the body. Ascorbic acid preparations are characterized by antitoxic, hyposensitizing, anti-inflammatory, and antihyaluronidase effects. In vitro, the bacteriostatic and bactericidal role of vitamin C in relation to staphylococcus and streptococcus was revealed.
Vitamin C deficiency leads to disruption of the T-immune system and less significant deviations of humoral immunity. The fact of melasma due to vitamin C deficiency is widely known. Violation of collagen synthesis with vitamin deficiency is reflected in poor wound healing.
The positive effect of ascorbic acid has been noted in inflammatory, degenerative and other pathological processes of the skin. The administration of ascorbic acid is advisable for toxicoderma, allergic dermatitis, eczema, neurodermatitis, prurigo, chronic urticaria, lichen planus, photodermatoses, vasculitis, pemphigus, stomatitis, glossitis, chronic atrophic acrodermatitis, chronic pyoderma, acne vulgaris, alopecia alopecia, mycoses of the feet, a also with prolonged use of corticosteroid drugs and antimalarials. In the treatment of diseases manifested by vascular pathology of the skin, the effectiveness increases with the combination of ascorbic acid and rutin.
Biotin (vitamin H) is an organic acid that participates in numerous carboxylation reactions. Biotin deficiency is accompanied by alopecia, dryness, scaly skin (seborrhea), skin hyperesthesia, swelling and atrophy of the tongue papillae.
Used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, alopecia, seborrhea. A good clinical effect was obtained when treating acne vulgaris with high doses of biotin.
Fat-soluble vitamins
Vitamin A (retinol). In terms of the variety of reactions in which retinol is involved, it ranks first among vitamins. Retinol affects the processes of reproduction and growth, redox processes, the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, the synthesis of corticosteroids and sex hormones, nucleic acids. Retinol is involved in the regeneration of epithelial tissues and regulates the processes of keratogenesis. The important function of retinol has been established as maintaining the stability of plasma and subcellular membranes. At the same time, retinol hypervitaminosis leads to shifts in the activity of phospholipases, which play an important role in changes in the composition of biomembranes. The antioxidant properties of retinol have been established. The ability of the vitamin to have an immunomodulatory effect is noted. This vitamin causes a relative and absolute increase in the content of B-lymphocytes in the peripheral blood. With retinol deficiency, antibody formation is inhibited. The ability of this vitamin to relieve the immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids is known.
Retinol deficiency in the body naturally manifests itself as a violation of the processes of keratinization of the skin and mucous membranes, especially the oral cavity; brittle nails, hair loss, phrynoderma (Greek Phrynos - toad) - follicular keratosis, in which areas of keratinization are surrounded by a zone of depigmentation on the skin of the upper arms and legs, are noted. Then it moves to the torso, back, stomach and neck. Lesions on the face may resemble comedones due to inflammation of the sebaceous glands of the hair follicles.
The beneficial effect of retinol in inflammatory, degenerative and other pathological processes of the skin serves as the basis for its widespread use in dermatological practice. This vitamin is effective for diseases accompanied by hypertrophy of the stratum corneum of the epidermis (all forms of ichthyosis, follicular keratosis, hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles). It is used in the treatment of dermatoses, which are characterized by disturbances in the processes of keratinization (psoriasis), the secretory function of the sebaceous glands (seborrhea, seborrheic alopecia, acne vulgaris), with damage to the mucous membranes (leukoplakia), nail dystrophy, hair growth disorders (dryness and increased fragility, monilethrix (Latin monile necklace + Greek thrix hair; - hereditary hair dystrophy, manifested by alternating spindle-shaped thickenings of the hair shaft with areas of thinning, dryness, fragility and hair loss. In combination with other agents, retinol is useful in the treatment of eczema, chronic ulcerative pyoderma, trophic ulcers, Raynaud's disease. Taking into account the pronounced antioxidant properties of retinol, its combination with tocopherol acetate and 0.5% selenium ointment has been successfully used in the treatment of psoriasis and baldness.
Hypervitaminosis A is also characterized by dermatological manifestations: rash, itching, pigmentation, yellow discoloration of the skin of the palms and soles, delayed wound healing, hair loss. Seborrheic rashes and bleeding of the mucous membranes of the mouth may be observed on the skin.
Retinoids, being synthetic derivatives of vitamin A, have significantly expanded therapeutic options for a number of dermatoses, including severe ones and those resistant to other medications. Synthetic retinol derivatives - aromatic retinoids - are hundreds of times less toxic than their natural predecessor, so they can be used in the clinic in fairly large doses for a long time. Etretinate (tigazone) and 13-cis-retinoic acid (isotretioin) have found use in clinical practice.
The influence of retinoids is characterized by an amazing variety of biological effects. In practical terms, the most significant is their antitumor and immunostimulating effect; When these drugs are prescribed in patients, the total number of lymphocytes in the blood and the number of T cells significantly increases.
Isotretinoin (the commercial name of the drug is “Roaccutane”), which has a sebostatic effect (inhibits the secretion of the sebaceous glands), is used in the treatment of various forms of acne. Among the side effects during the period of taking maximum doses of Roaccutane, in some cases, increased dryness of the skin is observed, especially around the mouth, mucous membranes of the oral cavity, as well as dermatitis of the facial skin, weeping, itching, and reversible alopecia.
Another retinoid, tigazone, due to its antiproliferative effect, has been effective in the treatment of psoriasis. The effectiveness of treatment increases significantly when etretinate is combined with photochemotherapy. The authors recommend such an integrated approach in the treatment of patients with widespread, often recurrent psoriasis.
There is evidence of a favorable clinical result of the use of tigazon in the treatment of patients with lichen planus of the oral mucosa, subacute lupus erythematosus, hyperkeratotic eczema of the hands and feet, palmoplantar hyperkeratosis, pustulosis of the palms and soles, and ichthyosis of various forms.
The most common complications of taking tigazone include dry mucous membranes, itching, hair loss, and excessive peeling of the palms and soles.
Calciferol (vitamin D). The skin plays a major role in the production of vitamin D, where it can be actively synthesized by keratinocytes, fibroblasts and macrophages under the influence of UV rays.
The action of the vitamin is realized by regulating phosphorus-calcium metabolism; it also has a regulating effect on the state of the autonomic nervous and vascular systems, increases sweating and sebum secretion, improves hair growth, and normalizes water metabolism in the skin. Many tissues have receptors for calcitriol, so it is thought to have a variety of functions that are not yet understood. Thus, its active influence on cell differentiation in normal and tumor tissues has recently been established.
Due to the wide range of biochemical activity of calciferols, they are used in the treatment of tuberculous lupus, scrofuloderma, and chromomycosis. The literature describes a case where the administration of vitamin D for senile osteoporosis led to regression of concomitant psoriasis in the patient, which served as the basis for the use of vitamin D in the treatment of this disease.
Calciferol can cause acute poisoning with symptoms of hemorrhagic vasculitis. With prolonged use of high doses of the vitamin, pustular and acne-like rashes and general sweating may occur. These phenomena are reduced with the combined use of calciferol with retinol, thiamine and ascorbic acid.
Tocopherol (vitamin E) affects the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids and steroids, promotes the accumulation of retinol and other fat-soluble vitamins in the body, exhibits anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic effects, reduces the permeability of the vascular wall, and acts as an antioxidant. Protecting lipids from peroxidation is one of the most studied functions of vitamin E. Since unsaturated lipids are a component of biological membranes, this function of tocopherol is very important for maintaining the structural integrity and functional activity of lipoprotein cell membranes and subcellular structures. The immunostimulating properties of tocopherol are realized by inhibiting the activity of T-suppressors. At the same time, vitamin E significantly increases the activity of natural killer cells.
The use of vitamin E is indicated for ichthyosis, dermatomyositis, scleroderma, Raynaud's disease, photodermatoses, psoriasis, ulcerative stomatitis, poorly healing leg ulcers, X-ray ulcers, acne vulgaris, seborrhea, nested hair loss, as well as for dermatoses associated with dysfunction of the gonads. Good clinical results have been established with the combined administration of tocopherol acetate, retinol and 0.5% sodium selenite ointment to patients suffering from psoriasis and alopecia alopecia.
Vitamin E is also used externally in dermatology - in the form of an oil concentrate or an ointment containing 3% tocopherol acetate.
Vitamin K (phylloquinone) is involved in blood clotting, enhances the anti-inflammatory effect of steroid hormones, affects tissue regeneration, increases resistance to infections, and has an analgesic effect. Vitamin K deficiency leads to the development of hemorrhagic syndrome.
The use of vitamin K is indicated for burns and frostbite, radiation injuries, dermatoses with a hemorrhagic component, ulcerative stomatitis, gingivitis, and dermatomyositis.
Vitamin-like compounds
Lipoic acid (vitamin F) is part of a multienzyme complex involved in the decarboxylation of pyruvic acid, exhibits a pronounced hepatotropic and weak hypoglycemic effect, activates the consumption of glucose and pyruvate by tissues, reduces the content of cholesterol and total lipids in the blood serum, stimulates phosphorylation and protein biosynthesis in the liver.
The effectiveness of lipoic acid in psoriasis and dermatoses accompanied by impaired liver function and lipid metabolism has been established.
With prolonged use of lipoic acid, allergic skin reactions are possible.
Calcium pangamate (vitamin B15) affects lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, increases the activity of respiratory chain enzymes, and therefore significantly increases the absorption of oxygen by tissues. Due to the lipotropic effect of the vitamin, the total content of lipids in the liver, as well as cholesterol, decreases, the production of glucocorticoids increases, and a detoxifying effect is observed.
Calcium pangamate is successfully used for psoriasis, pruritus, skin itching, toxicoderma, as well as to improve the tolerability of corticosteroid and sulfonamide drugs.
Rutin (vitamin P). The vitamin P group includes a number of substances - bioflavonoids, which have the ability to reduce the permeability and fragility of capillaries.
The physiological effect of the vitamin is realized through the endocrine glands, through its influence on the enzyme systems involved in tissue respiration. Vitamin P preparations exhibit antihistamine effects and antioxidant properties. Rutin regulates free radical homeostasis through several mechanisms. Firstly, it neutralizes the most dangerous radicals (peroxynitrite and hydroxyl), and secondly, it controls the production of physiologically important radicals (superoxides) by cells. In addition, rutin stimulates the release of nitric oxide, the main stimulator of relaxation of the muscles of the vascular wall.
With vitamin P deficiency in the body, characteristic changes are noted in the form of small intradermal hemorrhages (petechiae), which occur spontaneously, especially in areas of pressure, and disappear after the administration of bioflavonoids.
The use of vitamin P is advisable in case of increased permeability of blood vessels and their fragility (hemorrhagic diathesis, capillary toxicosis). The effectiveness of vitamin P has been noted for toxicoderma, allergic dermatitis, eczema, urticaria, vasculitis, exudative form of psoriasis, erythroderma, Dühring's dermatosis, and radiation dermatitis.
Along with vitamin P, it is advisable to prescribe ascorbic acid.
Methylmethionine sulfonium chloride (vitamin U), being a donor of methyl groups, is involved in the biotransformation of various xenobiotics, as well as the methylation of histamine, which provides an antihistamine effect. When studying the autoflora of workers involved in the production of methylmethionine sulfonium chloride, a significant increase in the number of microbes was found, an increase in the number of hemolytic forms of microorganisms and yeast-like fungi. Such changes are regarded as evidence of the possibility of a nonspecific effect of vitamin production products on the general reactivity of the body.
Vitamin U has proven to be somewhat effective in the complex treatment of patients with psoriasis, especially patients with concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The material was prepared by dermatocosmetologist S.N. Lyshkanets
Traditional methods of obtaining vitamins
Traditional medicine offers us many effective remedies to combat vitamin deficiency in the skin of the hands. They can be divided into two groups - local and taken orally.
Fruit masks
Applications made from fruit mass are very useful for vitamin deficiency in the hands. To prepare a vitamin fruit porridge, take a mixture of chopped apple, banana and peach (you can replace it with kiwi or pear), add 1 teaspoon of unrefined olive or flaxseed oil, mix, apply to inflamed areas. After 25 minutes, rinse the mixture with warm water.
Mask with yolk
The following mask is perfect for renewing skin cells: mix one yolk of a chicken egg (preferably homemade or farm), 1 tbsp. a spoonful of wheat germ oil and 1 tbsp. a spoonful of honey. Apply the mixture to the skin of your hands, gently massaging them until completely absorbed. After 15 minutes, wash off excess mask with warm water without soap.
Herbal infusions
In case of severe irritation, peeling and cracking of the skin of the hands, you can use baths of herbal infusions. Take 1 teaspoon each of dried chamomile, string, linden and sage flowers, pour boiling water and let it brew for 20 minutes. Place your hands in the warm infusion and hold until it cools. It is better to use thick ceramic dishes for such baths, so the herbal infusion will remain warm longer, this will enhance the effect of the procedure.
Potato decoction
Potato decoction baths are also useful. After preparing potatoes for dinner, do not pour the broth into the sink, but, after cooling it a little, make a bath for your hands - they will thank you!
Just remember that you should not wash your hands immediately after such a procedure, just gently pat them dry with a soft towel.
Folk recipes for decoctions and drinks for the treatment of vitamin deficiency in the hands
Homemade vitamin cocktails will provide you with effective help in the fight against such an unpleasant ailment as vitamin deficiency of the skin of the hands. Honey is a mandatory component of these medicinal drinks.
Here are some examples of recipes:
- Dilute 200 g of honey in 500 ml of warm boiled water. Add pureed currants to the resulting liquid and stir the mixture until smooth. Take half a glass of the prepared drink several times a day.
- Dissolve 50 g of honey in one glass of warm water. Add freshly squeezed juice of one lemon and juice of 1 kg of carrots. Drink this tasty drink several times a day, and you will quickly cope with vitamin deficiency in your hands.
Herbal decoctions are also an effective remedy for vitamin deficiency in the hands. They contain raspberry leaves, lingonberries, black currants and dried rose hips.
To prepare a healing infusion, take 1 teaspoon of each component, pour into a thermos and pour 2 cups of boiling water. Let the drink steep overnight (at least 8 hours), then you can drink it throughout the day instead of tea.
Daily regimen for vitamin deficiency
Compliance with the daily regimen for a disease such as vitamin deficiency, in any form, is of great importance. Getting enough sleep, walking in the fresh air, playing sports, sunbathing - all these factors will help prevent the disease or cope with it if it already exists.
Giving up bad habits will also help overcome vitamin deficiency, improve overall health, increase immunity and resistance to seasonal respiratory diseases.
Benefits and harms of dietary supplements
Benefit can only be obtained when a dietary supplement is prescribed in the presence of a clinical picture of the disease (where dietary supplements can provide support), laboratory-confirmed deficiencies and in certain physiological conditions (pregnancy).
As an example:
in most of Russia, from October to March, vitamin D is not synthesized due to the angle of incidence of sunlight, therefore, taking a preventive dosage of vitamin up to 2000 IU is allowed. During pregnancy and lactation, additional iodine intake of 250-300 mcg is indicated. When planning pregnancy and up to 12 weeks inclusive - folic acid 400-800 mcg.
If you have Crohn's disease or celiac disease, you may need extra calcium, folic acid, and vitamin B12. For anemia - iron, vitamin B12. Vegetarians are also included in a special group, who also have deficiencies.
Taking dietary supplements should not be a willful decision; consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Among the disadvantages, it is worth noting:
inadequate control in the field of dietary supplements, the difference in composition, chemical formula and effect of synthetic dietary supplements from natural ones obtained from food. Taking dietary supplements (which are not drugs) gives a false sense of security: there is no desire to improve nutrition and eating habits.
Many are convinced that modern food products do not contain enough vitamins and minerals, and that supplements help cope with ARVI and even COVID-19. Although it has already been proven that additional intake of vitamin C and vitamin D does not reduce the incidence of ARVI and does not in any way affect treatment or prognosis. Uncontrolled use of supplements can not only be financially costly, but also often worsen health conditions and lead to toxic liver damage.
In conclusion, I would like to note that the best alternative to dietary supplements is a variety of food products. A balanced diet containing the necessary macro- and micronutrients is the key to your health. Dietary supplements are justified only if certain substances do not enter the body, but this situation also requires mandatory consultation with a specialist before prescribing such seemingly safe substances.
Vitamin deficiency on the skin of the hands in children
Unfortunately, such an unpleasant disease as vitamin deficiency of the skin of the hands is quite common in children, causing them a lot of suffering and anxiety. The child becomes capricious and irritable, appetite and sleep deteriorate, and this is not surprising, because the delicate baby skin is so sensitive, and the manifestations of the disease on it cause pain and itching for the baby.
If vitamin deficiency is accompanied by rashes, ulcers, irritation, cracking of the skin on the hands and other parts of the body, then parents need to be especially vigilant and in every possible way protect the baby from infection, which can aggravate the course of the disease.
The baby’s diet should also be enriched with food containing vitamins A and B. Of course, if vitamin deficiency appears on the child’s skin, it is necessary to consult a doctor, who should individually select a comprehensive treatment. It will probably include taking multivitamin preparations, a special diet enriched with vitamin products, and local treatment of inflamed areas of the skin.
What can be done at home if the problem is vitamin deficiency on the skin of a child’s hands? Traditional medicine offers many recipes for treating this disease.
- Bathing in herbal decoctions of chamomile and string will be effective. They will help relieve itching and irritation, and soothe the baby's inflamed skin. It is not difficult to prepare such a decoction: pour 1 tablespoon of dried chamomile and chamomile flowers into a thermos, pour boiling water over it, and let it brew for several hours. Pour into bathing water.
- All kinds of vitamin cocktails from different fruits, fruit drinks and juices can help children. When prescribing them, you must remember that many products, such as some fruits and honey, can cause severe allergies, so they should be used very carefully and only on the recommendation of a specialist. The younger the child, the greater the risk of allergic reactions to various foods.
Of course, it is easier to prevent the development of vitamin deficiency in a child than to treat the disease. Therefore, it is very important to understand in time whether there are not enough vitamins in the baby’s body. Remember, timely diagnosis by a specialist will help you quickly and effectively cope with vitamin deficiency and prevent it from harming the child’s health.
Symptoms of vitamin deficiencies
Manifestations of vitamin deficiency (hypovitaminosis) depend on which particular vitamin is missing.
A
deficiency manifests itself primarily in the form of ophthalmological and dermatological pathologies. “Twilight vision” – the ability to confidently navigate in the absence of insufficient lighting – is impaired. Bright daylight is poorly perceived. The conjunctiva is affected (conjunctivitis develops) and the cornea (it softens, perforation becomes possible). The skin becomes dry and vulnerable to infection (typical manifestations are pyoderma and furunculosis). A lack of vitamin A also increases the likelihood of developing respiratory diseases (rhinitis, bronchitis).
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) deficiency
manifests itself in the form of a complex of symptoms called
beriberi disease
. The most typical neurological disorders are: headache, fatigue, intolerance to mental stress, general weakness, uncertainty when walking, sensations of numbness and tingling. Pain in the heart area, tachycardia, nausea, constipation and some other manifestations are also possible.
B2
deficiency is manifested by damage to the lips (lips crack, pockets appear in the corners of the mouth), and the oral mucosa (stomatitis develops). Dry skin is also observed; Possible weight loss and anemia.
Vitamin
B6
has skin and neurological manifestations. The most typical symptoms are dry skin, seborrheic dermatosis (scalp, face, neck), redness of the tongue, cracks in the corners of the mouth, numbness and tingling sensations (hands and feet), anemia, and seizures are possible in young children.
Vitamin
B12
is one of the common causes of anemia, which most often results in symptoms such as general weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, tachycardia, tinnitus, and dizziness.
Vitamin
C
(ascorbic acid) deficiency is historically known as
scurvy
. Characteristic symptoms: redness, swelling and bleeding of the gums (in severe cases, teeth may fall out), muscle weakness, painful legs when walking, bruising may appear on the skin.
D
deficiency can cause rickets and osteoporosis, as it leads to changes in bone tissue. Children may experience bone deformation; adults (especially older people) often suffer from fractures. Other manifestations: weakness, increased fatigue, muscle cramps in the arms and legs, insomnia, weight loss and loss of appetite.
Vitamin E deficiency
causes hemolysis (decomposition of red blood cells), leading to reproductive dysfunction. Main manifestations: muscular dystrophy, impaired coordination of movements, blurred vision. The skin loses elasticity, hair becomes dull and begins to break.
K
deficiency leads to impaired blood clotting and increased bleeding (nasal, subcutaneous and gastrointestinal hemorrhages are possible).
Clinical researches
Conducted clinical studies prove the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of the products. The products are suitable for daily care of adult and children's skin with mild to moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
The brand's products are recommended by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
Sources:
- Yukhtina N.V., Modern ideas about atopic dermatitis in children
- Kamasheva G.R., Khakimova R.F. Valiullina S.A., Methods for assessing the severity of atopic dermatitis in young children, Dermatology journal, 2010
- Kovyazina N.A., Fedosimova N.A., Illek Ya. Yu. Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in young children, Vyatka Medical Bulletin, 2007