Scabies is a microscopic mite (of the arachnid family) that is capable of penetrating under human skin, creating colonies there, and feeding on skin tissue. The scabies mite penetrates into the thinnest and most delicate areas of the skin, which are easily injured. The entry points for infection are most often the spaces between the fingers, in children - the elbows, face, armpits, in women - the mammary glands.
The Russian version of the name of the disease, “scabies,” is clear: the main symptom of scabies is itchy skin.
The severe itching that occurs with scabies is a type of allergic reaction to the presence of a mite in the body. Itching may intensify and subside depending on the activity of the mite under the skin.
Reasons for appearance
The lesions are caused by the parasite Sarcoptes scabiei. Any living creature that has been infected can carry it. And the more lesions on the patient’s body, the higher the risk that he can infect someone.
what does a scabies mite look like?
Infection is carried out by females and larvae. The female lives in the skin. During the daytime it is inactive, but in the evening it actively gnaws through passages, reproduces, feeds and secretes waste products. Consequently, the greatest risk of infection appears precisely in the evening and night time, when the tick is more active.
Everyone who comes into contact with the infected person is at risk. For example:
- family member
- roommate
- roommate
However, you can also become infected through indirect contact. For example in the following places:
- bathhouse
- public shower
- crowded places
Interesting. Outside a living organism, the female can live up to 3 days.
The disease spreads quickly due to the fact that the female lays eggs from which larvae hatch. After maturation, the latter crawl out to mate. The male dies and the female burrows back into human skin to continue the cycle of reproduction and spread.
Prevention of scabies in the groin
The main rule in the prevention of groin scabies in men and women is maintaining hygiene in intimate places. Daily change of underwear and washing, absence of promiscuity will protect against scabies infection.
To destroy ticks in the house, they disinfect it, change bed linen more often, and wash clothes at high temperatures.
If you notice any symptoms of scabies in the groin, penis and labia, photos of which you can view, contact a specialist immediately.
Classification of the disease and symptoms
There is a typical form of the rash with its inherent scabies, as well as apathetic forms. The latter include:
- Scabies that has no passages Appears if the cause of infection is larvae. Patients are tormented by itching due to parasites entering the body, but there are no passages because the larvae are not able to gnaw through them. However, scabies only last a couple of weeks until the insects mature and grow.
- Disease of clean people (incognito) It is distinguished by an unclear clinical picture. This disease develops in a person who washes very often, thereby washing away most of the parasites from the body.
- Scabious lymphoplasia is characterized by the formation of small dense nodes of a purple hue near the affected areas. They are very itchy. The nodes often merge into plaques, forming a dry crust. The rash remains on the skin for 2-6 weeks from the moment scabies appears. This is considered a complication, since lymphoid tissue suffers most from such damage.
- Scabious erythroderma Develops in those who develop scabies while simultaneously using antiallergic or hormonal medications. Patients do not suffer from itching and therefore do not scratch or abrade the skin, leaving most of the parasites unharmed. Consequently, their population increases faster than usual, and mites begin to spread even in places with an increased number of sebaceous glands. There are more moves than usual. The skin is dry, red and thick around the joints.
- Norwegian form Very rare. It occurs against the background of immune suppression, for example, taking drugs that enhance the production of hormones, cytostatics, or immunodeficiency. The disease is similar to erythroderma, but the number of parasites in the body is greater than with any other form of the disease. Thick gray and brown crusts (3 mm thick) appear on the affected areas. Ticks live underneath them. The entire epidermis is affected, as well as the nails. The disease becomes systemic - a person’s temperature rises, and the lymph nodes also enlarge.
- The peculiarity of children is that it spreads throughout the child’s body more strongly than through the body of an adult. In a child, lesions can be found even on the face, head, feet and palms. In infants, nails may be affected. A lot of vesicles and red bumps appear on the skin.
scabies in children - In the elderly Scabies in the elderly is characterized by few symptoms. There are fewer scabies than usual, but the number of scratches and crusts is very large.
Scabies of the elderly
The incubation period appears or disappears depending on whether a person is exposed to infection through a larva or through a female. In the latter case, there is practically no incubation period; symptoms appear immediately. If it is a larva, 2 weeks will pass from the moment of infection until the first symptoms appear (this time is necessary for the larva to grow).
Itching is the main symptom that those infected suffer from. It indicates the activity of the parasite. It can either be present only in certain areas of the skin or spread throughout the entire body (except for the face and places on the head covered with hair). One of the most basic symptoms indicating that a person is infected with scabies is that itching occurs mainly in the evening and at night.
With typical scabies, an itch also appears. It is a white stripe, 5 to 7 mm long. Scabies burrow rises above the epidermis. Most often it forms in the following places:
- folds between fingers
- wrist or elbow joint
- flexion surfaces
- front or sides of the abdomen
- armpits
- in the chest area (in females)
- near the genitals (in males)
With a standard disease, passages do not form in the following places:
- back (upper part)
- neck
- face
- scalp
The reason is that these places contain the largest number of sebaceous glands. The latter produce fat, which clogs the ventilation passages, depriving the parasites of access to oxygen.
Another symptom is when small dense tubercles appear on the body around the follicles, the so-called papules. It is in them that the larvae live until they mature. They prefer the following places:
- front and side parts of the body
- hips
- buttocks
There are other manifestations:
- Vesicles. They are bubbles with transparent contents. Formed on the hands, feet and wrists.
- Pustules. Same as vesicles, but differ in the presence of pus. This indicates bacterial infection.
- Bloody crusts.
- Scratching.
All these symptoms represent a side (allergic) reaction to parasites, their metabolic products, tissue damage and the proliferation of bacteria there.
Scabies in the groin in men
In men, itching appears mainly due to neglect of the rules of intimate hygiene. Dirt and sweat lead to inflammation, which causes itching and burning.
Urine becomes a strong irritant; after emission, itching, burning, burning of the skin, and sometimes redness appear. When using underwear made from low-quality fabric, the same symptoms are possible.
If the cause of itching is a scabies mite, then scabies in the groin in men is localized in the scrotum and pubic area, at night, when the itching intensifies, the affected area turns red, swells, and symptoms appear.
The rash forms on the penis, pubis, scrotum, glans and foreskin, and buttocks.
Diagnostics
To determine the clinical picture, you need to do the following:
- Explain your symptoms to your doctor in detail. For example, itching only bothers you at certain times
- get tested
- examine the patient's body
- determine the source of infection
- find traces of the tick itself or its larvae
Typically, the disease is determined by the following criteria:
- purulent blisters
- dry crust
- redness on the buttocks
- scabies (the most important criterion)
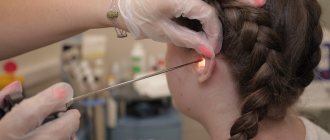
To determine the itch, the lesion can be stained with iodine, oil containing minerals, or simply pressed on the epidermis with a glass slide. This will block blood from reaching the affected area and allow you to clearly see the affected area. It can also be detected using dermatoscopy (during the procedure the tick itself is detected).
Ticks can be detected using lactic acid. One drop (40%) should be applied to any lesion and wait 5 minutes. The loosened skin can then be scraped off with a sharp spoon until capillary bleeding appears. The resulting epidermis must be applied to a glass slide and looked at under a microscope. The method will allow you to identify most parasites and the products of their activity.
Treatment of scabies in the groin
Before prescribing medications, the doctor examines the patient and makes a diagnosis. Scabies in the groin has similar symptoms to sexually transmitted diseases, viral and fungal infections. When diagnosing, pay attention to the presence of dermatitis (when scratching, there is a possibility of introducing a bacterial infection into microtraumas).
A number of symptoms that indicate the development of scabies:
- Itching that gets worse at night.
- The presence of scabies (white thin strips up to 1 cm long rising above the skin), rash.
- Using antihistamines does not relieve symptoms.
Experts can easily diagnose scabies in the groin. Difficulties may arise if the first parasite was a scabies mite larva, then it does not form burrows. This requires other ways to determine the disease:
- Skin biopsy. A scraping is taken from the affected area and examined under a microscope. This method allows you to exclude and confirm various diseases.
- With the help of iodine, tracts are determined in people and medicine. When applied to the affected areas, the scabies darken.
- To determine the type of scabies mite, the female is removed from under the skin with a needle and examined under a microscope.
- They examine the skin without taking scrapings; a binocular microscope is used for this.
After this, medications are prescribed. It is recommended to apply all products during tick activity, that is, in the evening and at night, for at least 12 hours. The entire family and team in which the person is located should undergo the course of therapy. An aerosol product is best because it is convenient to use and has the same effectiveness as ointments.
Before starting treatment, the patient washes to wash off some of the mites. After the course, he washes all things, changes bed linen, and disinfects the house.
Treatment of scabies in the groin in men and women should be comprehensive, under the supervision of a doctor.
Treatment of scabies in the groin with folk remedies
Treatment for scabies in the groin is not recommended by doctors. Medications are the most effective and safe; they quickly (sometimes even with one use) destroy all ticks and their larvae, and have side effects known to the patient. Using self-made products can cause complications.
Some herbal preparations are harmless and hypoallergenic. Birch tar can be purchased at any pharmacy; it actively destroys ticks. Lavender oil, in addition to its pleasant smell, has the ability to destroy parasites, celandine and other plants, but you may be allergic to them.
Treatment of scabies in the groin with medications
It is best to treat scabies in the groin with medications. Scabies in the groin most often affects adult men and women (men account for half of the cases of scabies infection).
It is possible to use both strong agents, for example, sulfur ointment, and soft ones.
Sulfur ointment has a high effect, but is known for its bad odor and leaving marks on clothes.
Mild products (Benzyl benzoate, Zinc ointment, Permethrin ointment) take longer to kill ticks, but are odorless and do not leave marks. They have many benefits, such as relief of symptoms, absence of allergens.
When undergoing a course of treatment in a large group, it is most convenient to use aerosol agents. For example, Spregal.
How to treat
For proper treatment, specific therapy must be carried out to confirm scabies. If the doctor was unable to identify the mite and scabies, a trial treatment will be prescribed. In addition, preventive treatment is prescribed to all family members and people in contact with the patient.
The doctor will prescribe medications that kill ticks. Most often they are:
- aerosols
- ointments
- creams
- suspensions
- emulsions
The prescribed drugs will be based on the following substances:
- benzyl benzoate
- permitrina
- sulfur
- piperonyl butoxide
- esbiola
Sometimes treatment includes washing with soap or treating the skin with emollient ointments before using the drug.
Only a doctor can prescribe a medicine and treatment method. It is based on the following criteria:
- clinical picture
- complications
- person's age
- pregnancy
Self-medication can cause complications, apathetic forms of infection or a protracted course of the disease.