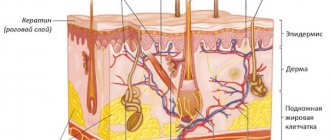
Scabies is a microscopic mite (of the arachnid family) that is capable of penetrating under human skin, creating colonies there, and feeding on skin tissue. The scabies mite penetrates into the thinnest and most delicate areas of the skin, which are easily injured. The entry points for infection are most often the spaces between the fingers, in children - the elbows, face, armpits, in women - the mammary glands.
The Russian version of the name of the disease, “scabies,” is clear: the main symptom of scabies is itchy skin.
The severe itching that occurs with scabies is a type of allergic reaction to the presence of a mite in the body. Itching may intensify and subside depending on the activity of the mite under the skin.
Focal and extrafocal forms of scabies spread
The scabies mite that causes the disease can be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person through various types of contact: through direct (family or sexual) contact or indirectly through shared objects (clothing, bedding, shower accessories).
Doctors warn that scabies is an extremely contagious (contagious) disease and is more common than other parasitic skin diseases.
About 300 million cases of scabies are registered annually; the density of the disease is especially high in countries with a low level of hygienic culture of the population. An increase in diseases is recorded during wars, social and natural shocks, and economic downturns. At the same time, outbreaks of scabies are observed in relatively prosperous countries when the living conditions of certain social groups deteriorate.
Today, scabies is such a common disease in Russia that we can talk about an epidemic. This is facilitated by hotbeds of military action in various regions of the country and neighboring states, an increase in the number of migrants from Central Asian countries, including illegal ones, an increase in the number of people without a fixed place of residence, street children, and socially vulnerable citizens.
It should be noted that the spread of scabies is also facilitated by the development of crime, an increase in the number of people who drink alcohol and drugs, and practice promiscuous sexual relations.
In modern Russia, there is a weakening of the immune system in the vast majority of residents, which also affects the progressive spread of scabies. There are experts who believe that there is a connection between periods of increased solar activity and an increase in the number of cases of scabies.
These factors contribute to the creation of spontaneous foci of the disease. The focus of scabies can be considered a group of people in which there is a patient who can infect others. A focus in which there is only one infected person is considered potential, and if there are two or more patients in the group, then such a focus is classified as a radiating or active focus of scabies.
Infection with scabies mites most often occurs within a family, where the mite was brought by one of the family members - this is the most common route of transmission of scabies and is recorded in 90% of registered cases. In such cases, medical workers identify a family outbreak of scabies infection. Somewhat less common are cases of infection of relatives or acquaintances who are not constantly in the family, which is a hotbed of scabies.
Half of the people who are the primary sources of family scabies infection are in the age group of 17–35 years. In a family, most often these are children of different ages, husbands. Infection occurs both sexually and through common objects. Within a family, one spouse infects the other, children can become infected through household means (the indirect route of infection is no more than 13%).
Experts identify another possible way for scabies to spread—foci of infection in organized communities. There are invasive contagious organized groups - those in which the conditions for transmission of the scabies pathogen are similar to the family focus, and groups in which such conditions are absent.
- The first group is groups that have common places of residence and recreation (bedrooms in orphanages, camps, boarding schools, dormitories). Pseudo-irrigation is often recorded - two (or more) sick people may appear in one outbreak, who became infected from different sources of the spread of the disease (independent of each other).
- The second group is non-invasive contact groups. This is the name given to teams whose members live or are located within the same building, and their contacts occur during the daytime. These are groups in kindergartens, classes in schools, groups in secondary and higher educational institutions, various labor collectives of enterprises and organizations. These groups do not pose a threat of epidemic spread; scabies manifests itself as a separate case of the disease.
Along with focal ones, there are also extrafocal forms of scabies mite spread. The pathogen is transmitted in such cases in a bath or sauna, on long-distance trains, and hotels. Such cases of tick transmission are recorded quite rarely.
Scabies is more common in the younger population. College students, vocational schools, and universities hold first place in the frequency of scabies infection. Young men can become infected through sexual contact, or while staying in a collective outbreak (the outbreak can be military training, internship, or in a dormitory). Second place is occupied by teenagers and children of secondary school age - they are also at high risk of infection, in third place are younger schoolchildren who became infected within the family or in preschool institutions. Persons over 26 years of age rank last in terms of the number of diseases and the intensity of the spread of scabies.
Therapeutic course
Clinical guidelines call for treating all patients' skin with emulsions or sprays. The exception is the scalp. Antiscabiotic drugs have low toxicity and do not cause discomfort during treatment. Before the first application of a benzyl benzoate-based product, the patient should take a shower. Repeated treatment of the skin is carried out after 48 hours - ticks in the larval stage die. If the symptoms are completely eliminated, a new cycle of application of the drug is not carried out. After completion of treatment, the patient should use an antiseptic to treat furniture, household items and clothing.
The crusted form of scabies requires a different approach to treatment. Antiscabiosis therapy is preceded by the stage of softening and removing crusts using soap and soda baths or keratolytic ointments. After removing all the stratum corneum, the patient can begin applying the benzyl benzoate solution to the affected areas.
Types of scabies
There are several types of the disease:
- Typical scabies is a disease that occurs classically, that is, it is easily diagnosed (a pronounced clinical picture). Specific skin lesions are characterized by the presence of scabies mite passages. A rare type of scabies is a disease without visible mite passages; the disease develops as a result of damage to the subcutaneous tissues by mite larvae (not adult individuals). This disease lasts no more than two weeks - this is the minimum time required for a tick larva to transform into an adult that can infect the skin and reproduce. During this period, typical signs of scabies appear.
- In 1848, it became known for the first time that a person was infected with Norwegian scabies. This case was recorded in medical sources.
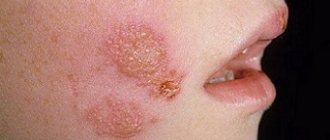
- Norwegian scabies (other names: crusted or crustose scabies) is a disease that is quite rare. The disease can affect people with weakened immune systems, patients with tuberculosis, AIDS, cancer patients, and also develops in people undergoing chemotherapy, taking hormonal drugs, and in those who suffer from vitamin deficiency. This is an aggressive form of scabies, which in most cases is very severe. A characteristic symptom of Norwegian scabies is a rash on the skin. The surface of weeping ulcers and erosions acquires a dirty yellow color and is covered with dark crusts that resemble a shell in appearance. It is in the lower layers of the cortical formation that the scabies tracts are located. In the intercortical space, when examining the material under a microscope, mites are found in various stages of development - a colony of 200 mites can be located on one square centimeter of skin. Also typical signs of Norwegian scabies are damage to the nails, soles, and skin of the palms. The patient exudes a heavy sour odor, and his temperature often rises.
- There are facts when ticks are transmitted to humans from domestic animals - dogs, pigs, horses, rabbits and goats. This disease is called pseudoscabies, pseudosarcoptosis or tick-borne dermatitis. If contact with the source of infection is avoided, pseudoscabies goes away on its own, and this is explained by the fact that mites that cause diseases in animals cannot reproduce in human skin tissue. Pseudoscabies is transmitted from person to person.
- There is another type of typical form of the disease - low-symptomatic, or “incognito scabies”, “clean scabies”.
- The disease affects people who shower frequently; during this procedure, most of the scabies mite population is removed. That is why the disease occurs with mild symptoms. In this case, complications such as dermatitis, pyoderma or, in rare cases, microbial eczema and urticaria may occur. Thus, typical manifestations turn out to be blurred and not expressed.
Incubation period
It is not entirely appropriate to talk about the incubation period for scabies, since a person is considered sick from the moment of first contact with scabies. However, symptoms of mite parasitism on the body can occur for different periods of time, depending on what stage of development the scabies itch is at.
So, if a sexually mature female gets on the skin of a person, the incubation period can be 2-5 hours, since the parasite immediately begins its active life activity - it gnaws through passages in the epidermis and lays eggs (3-4 eggs per day) from which larvae hatch.
In cases where scabies larvae get on the skin, the time until the first symptoms appear is about 12-14 days - this is how long it takes for the larvae to turn into sexually mature individuals.
Diagnosis and treatment
Symptoms of scabies are often similar to those of other diseases transmitted during sexual intercourse.
Differential diagnosis with syphilis is carried out. To exclude a diagnosis of syphilis, serological tests should be performed.
In children, it is necessary to differentiate the disease from urticaria or infantile prurigo. You should also distinguish scabies from dermatitis, eczema, pityriasis rosea, inflamed insect bites, and allergic rashes.
Scabies, like many skin diseases, can serve as a kind of sign indicating the presence of other sexually transmitted infections. There is an explanation for this - the body affected by one infection cannot cope with other diseases. Skin affected by mites is an open “entry gate” for STDs (sexually transmitted infections).
Scabies itself is a disease that a specialist can easily diagnose and prescribe treatment that will quickly relieve the patient of unpleasant symptoms. Skin irritation and itching cannot be ignored.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Read further:
Types of scabies in humans and animals: what are they, symptoms and treatment
What do mosquitoes eat, besides blood, females and males, in the swamp and in nature?
Scabies during pregnancy: symptoms, how to treat, the best ointments
Sulfur ointment for scabies: how to use and treat scabies in children and adults
Parasites in children's bodies: signs, medications, treatments, how to identify them
Signs of worms in children aged 2 years: how to determine the presence of parasites in a baby