Cones (tubercles, nodules) on the body are compactions of a predominantly round or oval shape in the form of a subcutaneous bulge, in most cases having clear contours. Lumps on the back can appear for various reasons, for example, as a result of injury or inflammation in the spine or surrounding soft tissues. Less commonly, compactions are of a tumor nature and are neoplasms or cystic protrusions in the form of sac-like cavities filled with exudate.
Lump on the back
If lumps or dense balls appear on your back, you should show the formation to a specialist, even if it does not cause discomfort or pain . Emergency medical attention is required in cases where the lump itches, hurts when pressed or touches clothing, has a mobile structure, or the skin around the lump is covered with scales or changes color.
Lump under the skin on the back
Lumps on the back due to injuries
Spinal injuries and bruises of paravertebral soft tissues (muscles, ligaments, tendons) are one of the most common causes of lumps and lumps on the back. Spinal injuries are divided into two groups: fractures and bruises. Dislocations and subluxations, as well as damage to joint capsules and ligaments without signs of vertebral displacement, can also be classified as a separate category. Provoking factors for spinal injury can be not only falls and blows, but also sudden lifting of heavy objects, various accidents, unsuccessful diving into water and other traumatic situations.
Signs of a spinal injury
The following signs indicate that a lump on the back appeared as a result of physical or mechanical impact:
- a history of any traumatic impact of external factors on a given area of the body (for some types of injuries, clinical manifestations may be noticeable only after several days or even months);
- pain in the area of the damaged segment (may intensify during any physical activity);
- swelling and redness of the tissues around the lump;
- the presence of hematomas, bruises and hemorrhages;
- muscle spasm.
Causes of spinal injuries
Neurological disorders (numbness, paralysis, tic, tremor, paresis) are typical for closed fractures with damage to the spinal cord, which is located in the central spinal canal, along the spinal tube. Pain during fractures has a very high intensity and often provokes the development of traumatic shock - a life-threatening condition that occurs against the background of heavy blood loss.
Immobilization for spinal contusion
What to do in case of injuries and bruises?
Even if a person is able to move independently and does not experience pain when moving, it is important to show the lump on the back to a traumatologist, since pain with some types of fractures has a reflected course and may appear only a few days after the injury. If a patient is diagnosed with a bruise, treatment will consist of applying cold compresses for 2-3 days (5-6 times a day for 10-15 minutes), as well as using local anti-inflammatory drugs that have angioprotective, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. Such drugs include ointments and gels from the NSAID group (Diclofenac, Nise, Ibuprofen), venotonic and venoprotective agents (Troxerutin, Troxevasin), complex preparations (for example, Dolonit gel with dimexide and sodium heparin in the composition).
Ointments for back bruises
Treatment for fractures includes surgical methods, immobilization of the spine (plaster splints, special beds), the use of corsets and fixing splints, drug therapy aimed at relieving pain and correcting the consequences of heavy blood loss.
"Troxevasin"
How to treat
The treatment method is selected exclusively by a specialist after diagnosis. Therapy is aimed mainly at eliminating the cause of the disease, due to which the condition of the lymph nodes is quickly restored. Of course, in case of severe pain, at the first stage of treatment, means are used to relieve pain, relieve inflammation and swelling in order to make the patient feel better. Depending on the cause of the enlarged nodes, drug therapy may include:
- antibiotics;
- antiviral agents;
- NSAIDs.
If inflammation of the lymph nodes is caused by a bacterial infection, the patient is prescribed antibiotics, for example, Amoxicillin tablets.
With the development of lymphadenopathy due to back diseases, the use of exercise therapy and massage as therapeutic therapy is contraindicated, because any impact on the inflamed areas provokes an increase in symptoms and threatens even greater complications. In such cases, the pain syndrome is first relieved, compression of the nerve endings is eliminated, and when the lymph node shrinks to normal size, standard treatment is prescribed.
Rheumatic bumps
Painless bumps in the form of subcutaneous nodules can be a manifestation of erythema nodosum, characteristic not only of rheumatism, but also of some severe infectious diseases, for example, erysipelas or tick-borne borreliosis. Rheumatism is a connective tissue disease in which mainly the membranes of the heart become inflamed, as well as large joints, such as the joints of the legs, knees or hip joints. Rheumatism of the back is diagnosed quite rarely and accounts for no more than 8.4% of the total number of patients with this diagnosis.
Clinical signs of erythema nodosum
Cones with rheumatic inflammation of the spine are painless, have a dark red, purple or burgundy color and clear contours. The structure of the formations is dense, motionless (less often, inactive). The size of the nodules can range from a few millimeters to a chicken egg, and their occurrence is preceded by high fever and other symptoms, which may include:
- intense aching pain in the back (mainly in the area where the nodules are located);
- progressive curvature of the spine;
- numbness, trembling in the limbs;
- pale pink rash;
- minor hemorrhages against the background of increased pallor of the skin;
- increased sweating.
Nodules on the skin
The disease is caused by an infectious pathogen - group A β-hemolytic streptococcus - and often develops after illnesses of the oropharynx (sore throat, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, pharyngitis).
Causes
If we talk about specific diagnoses that a doctor can make after diagnosis, these include:
- Lipomas;
- Hematomas;
- Atheromas;
- Osteochondrosis;
- Hemangiomas.
Lipoma is a benign tumor formed from human adipose tissue. The formation is not solid to the touch, is well mobile, and no pain is observed on palpation. The development of lipoma can be rapid and relatively slow. The reasons for the appearance are a violation of fat metabolism or improper functioning of the gallbladder. Sizes vary individually, as they can reach very large sizes, but are usually up to four centimeters.
Hematomas also become a common diagnosis when a lump occurs in the lumbar region. They are benign formations that are formed from proliferated blood vessels. It is dangerous because it destroys healthy tissue and can grow to enormous sizes.
Atheromas (cysts) are tumors formed due to blockage of the sebaceous gland ducts. The formation is painless, round in shape, contains epithelial cells and fatty substances. Sizes from centimeter to seven. The danger is infection of the contents, which leads to swelling and fever.
Osteochondrosis (salt deposition) is a common factor for the development of cones. The main reasons for the development may be sedentary work, low physical activity, metabolic disorders in the body, poor nutrition and various traumatic actions.
Hemangiomas are characterized, like hematomas, by pathological proliferation of blood vessels
To determine the nature of the formation, it is important to consult a doctor in time, who is obliged to prescribe diagnostic procedures
Women going through menopause also become more susceptible to these symptoms. The stress and hormonal imbalance that the body experiences during menopause affects the formation of benign tumors. A person who leads a sedentary lifestyle (especially after the age of 35) is most at risk of developing a tumor. Spinal injuries, incorrect back posture when walking and scoliosis, as well as too little physical activity put a person at risk for the disease.
We advise you to read: hemangioma of the cervical spine.
Trigger points for myogelosis
Myogelosis (Schade-Lange disease) is a pathology of muscle tissue in which painful lumps called trigger points form in the muscles. These compactions provoke myofascial pain, which is significantly aggravated by mechanical irritation, such as pressure. There are four types of trigger points, classified according to the degree of pain response to external influence.
Myogelosis of the neck and back
Table. Types of myofascial trigger points on the back.
| Variety | Conditions preceding the onset of pain |
| Active | Pain is chronic and can occur both under the influence of negative and provoking factors, and in the absence of visible and significant stress (at rest). |
| Passive (latent) | Pain syndrome is detected only with physical irritation of the trigger point, for example, during palpation. |
| Primary | The cause of the primary trigger syndrome is chronic muscle overload or a single power or dynamic load that does not correspond to the degree of training of the muscle fiber. |
| Secondary (associative) | The mediator of pain is usually trigger points from nearby muscles or excessive loads of the compensatory type (compensate for the insufficient functioning of another muscle). |
Clinically, myofascial syndrome with myogelosis is manifested by painful sensations in the back associated with physical, static or dynamic load, as well as the appearance of small subcutaneous lumps in the area of the affected muscle. Lumps with myogelosis are not painful, have clear boundaries, and do not have mobility.
Danger to humans
A person who risks his health and does not seek medical help on time must understand the consequences this can lead to. Despite the fact that at first glance the tumor may seem benign, there is a risk of its degeneration into oncology. This is the most dangerous of all factors and requires double-checking in any case.
We should not exclude the development of complex complications of a purulent type: phlegmon, acute paraproctitis, and, of course, sepsis (blood poisoning). Sepsis can be fatal! With osteochondrosis, for example, possible consequences may be abnormal development and deformation of the spinal column. For example, hematomas, which destroy healthy tissue surrounding them, can significantly affect a person. Their rapid growth can damage the spinal cord, large arteries and nerve roots.
If we talk about smaller problems, a tumor of any size will become a defect in cosmetic terms, if you do not seek help. As a rule, after “advanced” cases, scars and spots remain. This can be completely avoided if you receive treatment on time.
Inflammatory processes
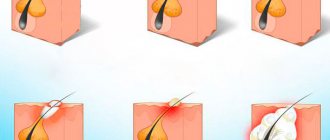
Pus-filled, painful bumps on the back can also be boils or carbuncles. These are purulent-necrotic inflammatory processes in the hair follicles, sebaceous and sweat glands, which often involve the surrounding connective tissue. One of the main reasons for the occurrence of boils and carbuncles is lack of personal hygiene (irregular showering) and microtrauma of the skin, through which microbes and bacteria enter the hair follicle. In 60-70% of cases of furunculosis, the causative agent of the inflammatory process is Staphylococcus aureus, so treatment of boils and carbuncles may include antibiotic therapy.
What does a boil look like?
You can understand that a purulent lump on the back is the result of an inflammatory process by the following signs:
- the presence of red erythema around the formation and a purulent core in its center;
- severe pain even with mild exposure to external irritants (for example, upon contact with clothing);
- Predominant localization - on the back, back of the head and neck;
- rejection of necrotic tissue with subsequent scarring.
"Flemoxin"
Boils are treated comprehensively. To eradicate the infectious pathogen, penicillin antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Flemoxin) are used. If the abscess has opened, a bandage with a hypertonic solution is applied on top. This is the name of a solution with a higher concentration of dissolved substances and a higher osmotic pressure. After draining the wound, dressings with tetracycline or erythromycin ointment are used topically. If the boil has just appeared, the use of physiotherapeutic methods (dry heat, ultra-high frequency therapy) and ichthyol ointment, which has an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and disinfectant effect, is indicated.
Erythromycin ointment
If you want to know in more detail what types of pain-relieving ointments for the back there are, and also consider the composition and application, you can read an article about this on our portal.
Treatment options
It is impossible to remove a lump at home without corresponding consequences. Because in most cases surgery is required. The basis of effective therapy is a correct diagnosis. Without it, applying any treatment regimen is dangerous and can lead to serious complications.
Today, the following methods for eliminating lumps are used:
- Laser. After it there are practically no scars or scars left.
- A liquid nitrogen. A modern, highly effective technique with a minimum number of contraindications and side effects.
- Puncture. It involves a puncture in a certain place and squeezing out the contents from the cone. It is carried out using special tools and antiseptics.
- Surgical excision. Local or general anesthesia is used.
Fibroma, lipoma and hemangioma are in most cases treated without the use of a scalpel. Patients are prescribed vitamins, a follow-up examination, and their diet and lifestyle are adjusted. Additionally, the doctor prescribes various medications aimed at suppressing the inflammatory process and increasing immunity. To prevent complications, you should carefully follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Could the lump be a herniated disc?
Lumps localized along the spine may well be a large intervertebral hernia or protrusion. These are protrusions and protrusions of the jelly-like core, which fills the intervertebral disc and is held in place by a fibrous membrane in the form of a ring. The pathogenetic factor in the formation of a hernia is dehydration and degeneration of the intervertebral disc, which develop against the background of impaired blood circulation, a sedentary lifestyle, chronic diseases of the spine and musculoskeletal system (osteochondrosis, osteosclerosis, osteoporosis, etc.).
Formation of intervertebral hernia
Clinically, the hernia may not manifest itself in any way for a long time, but if the size of the protrusion exceeds 5-7 mm, the patient begins to notice pronounced pain and neurological disorders. With large hernias, the clinical picture usually consists of the following symptoms:
- stiffness in the muscles and joints of the spine, which does not go away within 10-15 minutes and usually occurs after prolonged rest (usually after sleep);
- back pain that can radiate to the arm, shoulder, lower limbs and buttocks (radiculopathy, radicular syndrome, lumbago, lumboischialgia);
- paresis, paralysis, tics, tremors and other neurological disorders in the lumbar region and limbs;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs (fecal and urinary incontinence).
Herniated disc
If the hernia has formed in the upper back (cervical and thoracic spine), specific symptoms associated with compression of the basilar and vertebral arteries also appear: dizziness, migraine, headaches, arterial instability. Hernias in the thoracic spine can cause pain in the chest area (thoracalgia) as well as difficulty breathing.
Note! You can visually notice a hernia in the form of a protruding subcutaneous lump on the back in cases where its size exceeds 10-20 mm. Of great importance in the ability to identify a formation as a result of a visual and physical examination is the constitution of the body and the localization of the hernia: in slender patients, as well as patients with hernias and protrusions in the cervical spine, a volumetric protrusion on the back is detected almost 4 times more often than in obese patients.
Microsurgical treatment of intervertebral hernia
Tumors on the back
Lumps and bumps on the back can be a symptom not only of inflammatory, degenerative and traumatic processes, but also of tumor diseases, including severe forms of cancer. If a tumor in the spinal area or in the surrounding soft tissues has a malignant etiology, timely diagnosis is of great importance to form a relatively favorable prognosis for future life and treatment, so any compactions and formations should be examined by specialists .
The most common types of tumors found on the back are:
Malignant neoplasms
Cancerous tumors are the most dangerous cause of lumps and growths on the spine. They can be primary, that is, they arise directly from the spine, or secondary - they are caused by metastasis of malignant processes localized in other organs. Spinal cancer is a rare disease, but it should not be ruled out either - it is an extremely dangerous disease that often leads to the death of the patient.
Metastases to the spine
The most common malignant neoplasms of the spinal column include:
- chondrosarcoma, which is formed from cartilage tissue;
- osteorital sarcoma grows directly in the vertebrae;
- myeloma affects nerve cells and destroys vertebral bodies, tumors can be single or multiple;
- chondroma is a malignant tumor growing from the notochord, characteristic of middle-aged and elderly patients;
- Ewing's sarcoma is diagnosed in childhood and affects the structures of the spinal cord.
Ewing's sarcoma
If we are talking about secondary tumors, then most often metastases to bone tissue are caused by malignant diseases of the mammary glands, prostate, kidneys, thyroid gland and respiratory organs. A tumor on the spinal column with cancer can only be palpated if it grows in the anterior direction; in other cases, it can only be detected during diagnosis or in the later stages, when the tumor has reached a fairly large size. The early stages of cancer are often asymptomatic, so they are detected quite late.