Last update: 02/21/2021
Allergic reactions often cause various skin manifestations - rash, redness, irritation or swelling. Allergic dermatitis can often be difficult to distinguish from other skin conditions, such as infections or hives. Allergies are especially often confused with prickly heat, which occurs due to poor hygiene or temperature conditions.
What is the difference between prickly heat and allergies and how to determine which disease a child or an adult is suffering from? In order to answer this question, it is necessary to know the causes and symptoms of each disease and the characteristics of their course. In addition, the photos of heat rash and allergies presented on this page will help you.
General information
Miliaria is a form of dermatitis.
This is a non-infectious skin lesion, which is associated with increased function of the sweat glands when the body overheats and profuse sweating. Miliaria is considered a childhood disease, which is associated with imperfection and instability of skin thermoregulation: heat transfer prevails over heat production, and the sweat glands do not function sufficiently. This makes it difficult to maintain body temperature at a constant level. The anatomical features of children's skin (thin stratum corneum of the epidermis, structural features of sweat glands with narrow excretory ducts) make children very susceptible to the appearance of heat rash , which can develop in the first months. Despite this, prickly heat also occurs in adults and occurs after exposure to heat, physical activity, or wearing clothes that are out of season. Miliaria is considered a physiological condition if it is not accompanied by complications. In adults, it has a slightly different localization (under the mammary glands, in the perineum and between the legs), can cause discomfort in everyday life, and given the possibility of a secondary infection, it requires timely treatment.
When and which doctor to contact
The patient copes with the first stage of prickly heat on his own. If severe swelling, crusts and pustules appear, the help of a dermatologist is required. After communicating with the patient, studying his medical record, and external examination, the doctor determines the cause of the condition and suggests measures to eliminate it. You may need to donate blood for a general analysis or to determine hormone levels.
The underlying disease is treated simultaneously with the elimination of signs of prickly heat. Medicines are prescribed by a doctor. Folk remedies are also used after its approval. If you are obese, you may need the help of a nutritionist. If the disease is associated with ovarian dysfunction during menopause, consultation with a gynecologist is advisable. Self-medication often causes serious complications, defects on the skin of the face and other parts of the body.
Pathogenesis
The sweating system is involved in the thermoregulation of the body, therefore, when the ambient temperature rises, the function of the sweat glands is significantly activated - intense sweat production helps cool the skin, and thus the body is protected from overheating. The same mechanism is activated when body temperature increases due to illness, physical activity, wrapping and thermal procedures. Intense sweating often leads to blockage of the sweat gland ducts and the development of prickly heat. Miliaria occurs especially often in newborns and children under one year old, since their sweat glands are not fully formed and have.
Classification
According to the clinical course, it happens:
- Miliaria crystalline (superficial).
- Miliaria rubra.
- White (papular)
- Yellow.
In the crystalline form, superficial blockage of the ducts occurs. Bubbles up to 1 mm with clear liquid appear on the skin, which easily open with the formation of peeling. The rash is localized in adults on the torso, and in children - on the body, face and neck.
Red is the most common type, appearing in hot weather in adults and with increased sweating in children. It is characterized by the appearance of red itchy spots with papules and papulo-vesicles. With this form, the level of blockage of the ducts is deeper. Localized in skin folds and infection is possible. When white, milky white blisters appear, which is associated with infection with coccal flora. With yellow, true blisters with yellow pus appear located inside the epithelium.
Rashes occur at any time of the year, but most often during hot periods, which is associated with increased sweating. With any type of rash, most often appear on closed areas of the skin, which sweat a lot under clothing and are additionally irritated by friction - the elbows on the arms, armpits, inguinal and intergluteal folds. In children and adults, irritation occurs in the mouth when in contact with synthetic “non-breathable” fabrics (bandages, clothing or low-quality diapers). With severe sweating, rashes appear on the face (mainly on the forehead), neck and head, which is accompanied by itching . If hygiene is not observed, complications can occur - vesiculopustulosis and sweat gland abscess .
Causes
Some of the reasons for this condition include:
- Increased sweating due to dysfunction of the apocrine glands.
- Infectious diseases with fever and increased sweating.
- Endocrine diseases: diabetes , hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism .
- Neurological diseases.
- Excess weight.
- Lack of hygiene.
- Hard physical work in a hot climate.
- Wearing clothes out of season (especially synthetic clothing).
- Skin injuries and abrasions.
- The use of oily foundation and nourishing creams in the summer, which creates artificial blockage of pores.
If we consider the causes of prickly heat in children, we can say that its appearance is caused by:
- Overheating of a child by wrapping.
- High temperature in the room.
- Rare diaper changes.
- Rare water and air procedures.
- Use of synthetic clothing.
- Use of low-quality skin care products.
- Frequent use of soap.
Why does it often occur in newborns?
If your baby has heat rash, don’t worry, because you can get rid of it quite quickly if you follow simple rules for caring for your child’s skin. Just try to start treatment as early as possible so that the process does not reach a serious stage.
Usually prickly heat in babies occurs in the summer heat. But, if you are used to wrapping your child in a blanket that is too warm in winter and spring, then it may appear in the cold season. When a baby's sensitive skin is severely irritated, a small red rash appears on it - the main sign of heat rash.
Why is the skin of newborns prone to prickly heat? It's all about unformed sweat glands, which will begin to work in normal thermoregulation mode only by the age of 5-6 years. In addition, children's skin is still very thin and sensitive, it has very powerful blood circulation, and it consists of 85% water (unlike adult skin, which retains only 65% moisture).
The processes of constriction and dilation of blood vessels, which occur quickly in an adult body, are still slowed down in a child’s body - so thermoregulation also occurs very slowly. This is why the newborn’s body overheats and becomes hypothermic instantly.
Symptoms of prickly heat
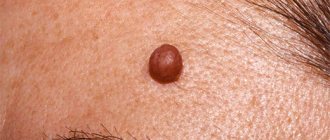
When considering the symptoms of prickly heat in adults, it should be noted that the rashes come in the form of papules (nodules) or blisters with contents. What does prickly heat look like in adults? Several types of rashes are possible. Miliaria crystalline appears as pearly blisters 1-2 mm in size, which can merge into larger formations.
Within a few hours, as a result of minor exposure, the vesicles open, dry out and form flaky areas. This type occurs in newborns on the face and neck. If we talk about adults, common locations are the chest, back, legs and arms on the flexor surface.
Miliaria rubra looks like red nodules of the same size. The nodules on the periphery are surrounded by an inflammatory halo, so the skin looks sharply hyperemic. This form involves large areas of skin. The rash may fill with clear fluid, forming vesicles that do not merge with each other. Purulent contents may appear.
Patients are concerned about itching, which intensifies with sweating and an increase in ambient temperature. This type appears in adults in hot weather or during physical labor. Areas subject to friction are affected: inguinal folds, under the breasts, axillary area, elbow and popliteal folds.
Papular (deep) is a severe form that lasts a long time and affects the ducts of the glands at the level of the dermis. It is considered as a consequence of red in the absence of treatment. The gland ducts become clogged with epithelium, and non-itchy papules resembling “goose bumps” appear on the skin.
The rashes are located on the torso, arms and legs. This type affects people who are poorly adapted to heat. It is found in tropical countries, which is why it is also called “tropical”. Papules increase when exposed to sweat, and when an infection occurs, microbial eczema .
Symptoms of pustular miliaria are characterized by the appearance of purulent contents in the blisters - small pustules (pustules) of varying degrees of severity appear on the skin.
This disease is called vesiculopustulosis . If the process is widespread, the temperature and malaise may increase (especially in children). After opening the pustules, purulent crusts appear, which, when rejected, do not leave scars or spots. In general, the process can take 10 days.
Prickly heat under the chest
Irritation and rashes appear when sweating and rubbing the skin with a bra. Considering that the skin here is delicate and sensitive, the process spreads quickly. Against the background of general redness, small papules appear above the skin.
The skin burns and itches, and the itching intensifies with sweating, which is accompanied by constant discomfort. The integrity of the skin is not compromised.
Miliaria in the groin in men
This problem is quite common in men and occurs more often than in women. This is due not so much to a sedentary lifestyle, but to wearing trousers in the hot season, which do not always meet the requirements for wearing cotton clothing. Wearing synthetic underwear also contributes to inguinal-perineal hyperhidrosis. For this reason, this disease may occur in men on the head of the penis or on the pubis. If its manifestations are ignored, the skin lesion spreads rapidly and invades new areas. This is how heat rash appears on the penis, around the anus. Scrotal hyperhidrosis is the most difficult to tolerate .
Miliaria rubra in the groin, scrotum and penis is manifested by inflammation of the upper layer of skin and the formation of a small rash. The affected area appears red, and discomfort occurs when moving or touching clothing. Occasionally itching may occur. In constantly moist and “unventilated” places, favorable conditions are created for infection by bacteria, so prickly heat is complicated by purulent inflammation, and scratch marks turn into weeping wounds.
Diaper rash
Most often, diaper rash (inflammation) forms in places where the skin constantly rubs, is damp and there is no access to air - for example, on the neck, in the armpits, under the breasts (in women), in the folds of the abdomen, in the groin folds, between the fingers. The main cause of diaper rash is poor hygiene. Sometimes taking certain chemotherapy drugs also contributes to diaper rash.
Diaper rash is characterized by itchy irritation, burning, and pain. The skin changes color, the boundaries of redness are blurred. There is an unpleasant smell.
Diaper rash differs from bedsores in the main symptoms of manifestations, the mechanism of development and the predominant localization.
There are 3 degrees of development of diaper rash:
1st degree. Initial
What it looks like: redness and itching without visible damage to the skin.
How to treat
Cleanse your skin regularly, allowing it to “breathe.” Replace bedding and underwear with seamless ones made from soft and natural fabrics. To make a person sweat less, review his diet and food temperature (food should be warm, not hot).
Organization of therapeutic nutrition for a seriously ill person Why appetite worsens, how to check swallowing function and what to feed a seriously ill person Olga Kotelnikova
Care
Wash the affected areas of the skin with an infusion of oak bark, chamomile, sage or string. After the procedure, let the skin dry thoroughly and powder with baby powder or potato starch. Or you can apply products with zinc or arginine - a thin layer until completely absorbed.
2nd degree. Moderate lesions
What it looks like:
skin is damaged. There are ulcers on it, there is itching and burning.
How to treat
Use mild, non-traumatic antiseptic solutions (chlorhexidine, rivanol, etc.) and agents for restoring the epidermis (dexpanthenol, bepanthen). To relieve itching, reduce inflammation and dry the skin, use antihistamines, as well as ointments or pastes (Lassara, Teymurova, Desitin).
3rd degree. Severe defeats.
What it looks like:
deep non-healing cracks, unpleasant odor. The affected area increases. There is a burning sensation and pain.
How to treat
The treatment approach is the same as in the 3rd stage of bedsore treatment.
All actions should be aimed at preventing the development of infection, relieving pain and reducing inflammation.
Miliaria in children
The skin of children differs in structure from the skin of adults, and the subcutaneous fatty tissue is loose. Despite the fact that sweat glands are formed in the 4-5th month of development, they begin to function in adolescence. In this regard, thermoregulation is impaired, which is especially evident in infancy. Excessive sweating when a child overheats causes dilation of the excretory ducts of the glands and the formation of cysts, which is manifested by prickly heat . Thus, immaturity of the skin and improper care are the main causes of this condition. In newborns, prickly heat can be considered a borderline skin condition.
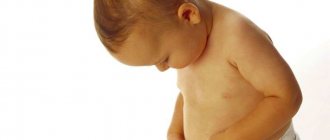
What does prickly heat look like in children? Miliaria appears as red dotted spots, nodules or transparent bubbles the size of millet grains, which are localized on the torso, neck, folds, lower abdomen and buttocks.
Photos of prickly heat in children
Symptoms of prickly heat in children, in addition to rashes, may include slight itching, but most often it does not cause discomfort to the child and the general condition of the baby is not affected.
What does prickly heat look like in newborns?
When overheated, obese infants often develop rashes that vary in nature. Crystalline prickly heat in infants looks like small transparent millet rashes localized on the face, neck and butt. Wearing a support collar can cause rashes on the neck. They are located scatteredly. In another form (miliaria rubra), abundant red nodules with a red rim around appear on the skin.
Characteristic localizations of rashes in children of different ages
Rashes on the butt and groin appear when using diapers that do not allow air to pass through, in the summer, with infrequent diaper changes and the absence of air baths. Heat rash on the face of a baby often causes discomfort - it can itch. Damage to the rash by active hand movements results in the formation of a flaky crust on the surface of the rash.
Miliaria in newborns with insufficient care quickly turns into white heat. These are bubbles filled with milky white contents that can be located on the face of newborns, skin folds, on the head and torso. Blisters of miliaria alba are located on reddened skin and are a manifestation of staphylococcal infection ( vesiculopustulosis ).
Treatment of prickly heat in children
Treatment begins with proper care. You can get rid of prickly heat in a newborn if you constantly follow the following rules:
- Ventilate the room several times a day.
- Maintain the air temperature in the nursery at 20-22 C and normal humidity (45-60%), since the baby does not tolerate dry air well (the loss of fluid from the body increases and overheating occurs).
- The side walls of the crib should allow air to pass through easily.
- The right choice of clothing - it should protect against heat loss, but not cause overheating, be natural, not restrict movement and be appropriate for the season.
- Daily morning toilet - treatment of folds with a tampon soaked in baby oil.
- Daily bathing with the addition of a decoction of herbs (chamomile, string, calendula). Use detergents no more than 2 times a week. The skin should be thoroughly dried, especially the folds, using blotting movements.
- Protection against irritating factors involves the use of powder or cream. Powdering prevents the skin from chafing, but it should be done in moderation, since using too much powder clogs the pores and inhibits sweating. Do not use baby oil in excess, as it makes it difficult for the skin to breathe.
- Use high-quality diapers that absorb waste well, keep it inside, and keep the baby’s skin dry.
How to treat prickly heat in children at home?
If to treat crystalline prickly heat it is enough to adjust your daily care, then for red prickly heat you need to use additional remedies. The main treatment for this condition is the use of baby powder. These can be powders based on talc and zinc, or they can be natural. You can use Babycoccole drying lotion (this is liquid talc), which eliminates heat rash, diaper rash , softens the skin and moisturizes due to chamomile bisabolol and vitamin F , linseed oil .
Some mothers try to choose organic powders that do not contain talc, since some studies have proven its adverse effects on the body. White clay (kaolin), flour from arrowroot root, and chamomile, lavender or calendula flowers ground into flour are indifferent in this regard. For prevention and at the first symptoms, you can use Flofeta Baby gel , which contains liquid extracts of chamomile , calendula , witch hazel , glycerin , polysorbate , and does not contain zinc oxide or talc .
Due to the increased absorption function of the skin on the face and head, it is important to carefully select drugs for external treatment. Treatment of prickly heat in newborns consists of using a solution of Furacilin and a weak solution of potassium permanganate to wash the affected areas. For treatment, preparations based on zinc oxide are used, which has an anti-inflammatory, astringent (drying) and antiseptic effect:
- Sanosan cream contains panthenol , zinc oxide , olive oil .
- "Weleda Calendula and Chamomile Extracts" . The cream contains zinc oxide, lanolin, glycerin, almond oil, sesame oil, calendula and chamomile extracts, beeswax, clay. The cream dries well, eliminates redness and irritation.
- Zinc paste , which is more acceptable for children because it is softer and more delicate in consistency than ointment.
- Emulsion Tsindol .
- Cream Belobaza Zinc . In addition to zinc oxide, this cream contains bisabolol, white petrolatum and cetearyl alcohol.
How else can you treat your baby? In pediatric practice, Bepanten is used in the form of ointment and cream. What is better to choose in such a situation - cream or ointment? The cream is recommended for prevention purposes against dry skin and a tendency to dermatitis. The ointment is used when problems arise, since it increases the protective function of the skin, but when used, the skin breathes. The main active ingredient of Bepanten is dexpanthenol , which has a regenerating effect and relieves redness and irritation. The composition of the ointment, compared to the cream, includes paraffin (liquid and soft), as well as almond oil. Lanolin has a protective effect, but does not interfere with gas exchange. If a child has itchy skin, this drug eliminates it. When using Bepanten, the symptoms disappear within 2-3 days, and following other care recommendations will allow you to finally cure heat rash in your baby. If there is a threat of infection, it is better to use Bepanten Plus (contains the antiseptic chlorhexidine, used in children from one year of age) or Drapolen (antiseptic). If the process is complicated by purulent infections, the doctor may prescribe ointments containing an antibiotic.
Parents should know that when caring for their baby, they should not squeeze out blisters, lubricate rashes with alcohol-containing solutions to avoid skin burns, or use topical antibiotics and corticosteroids without a doctor’s recommendation. When rashes appear for the first time, parents wonder: is it an allergy or heat rash in the baby? In these conditions, the nature of the rash and localization are different.
With heat rash, the rash first appears on the body, neck, and then on the face. Since there are no signs of inflammation, the rash does not affect the general condition. At the initial stages, the rashes do not contain fluid, and stretching the skin leads to their disappearance. With proper care and elimination of the provoking factor (overheating), the rashes disappear after 2-3 days.
The allergy manifests itself as a rash that first appears on the cheeks and then on the entire body. The skin with allergic rashes is swollen and inflamed. The rash may be small, like prickly heat, but the boundaries of the rash quickly expand. The child is bothered by severe itching, which increases, there may be lacrimation and sneezing, and in some cases the temperature rises. Even after eliminating the allergen, the rash does not go away quickly.
Bedsores
Bedsores are formed as a result of constant compression of soft tissues. Simply put, when a person lies in one position for a long time, some parts of the body are constantly compressed. Blood circulation and nutrition are disrupted, soft tissues begin to slowly die. This is called soft tissue necrosis.
Important The process of bedsore formation “starts” after just two hours of body immobility!
Bedsores are characterized by a change in skin color with clear boundaries, swelling, and weeping wounds. If they are not treated promptly, the volume and depth of the lesions rapidly increase. Most often, bedsores occur on the heels, knees, elbows, tailbone, and buttocks. It depends on what position the person predominantly lies in.
There are 4 stages of development of bedsores .
Stage 1. Fading redness
What does it look like:
A pale area of skin or, conversely, persistent redness. The skin is not damaged. If you press your finger into the center of the redness area, the skin will turn pale. This suggests that microcirculation is not impaired.
Stage 1 bedsore on the back. Photo: CPP
Stage 1 bedsore. Photo: ECDO Center
To be sick, but to smile is the norm. Alexey Vasikov, director of the Blacksmith Lobov House of Mercy, about what “norm” means for a seriously ill person and why it sometimes surprises us
Alexey Vasikov
About palliative care
How to treat
It is important to prevent the process of bedsore formation from developing further. Make sure that the person does not lie on the injured area, use protective film breathable bandages (like a “second skin”).
By the way, in this article we describe in detail what types of dressings there are and in what cases what to use.
You can lightly massage healthy skin around the redness area - stroke it clockwise. It is permissible to use activating agents for massage. They improve blood microcirculation in tissues, which leads to improved metabolic processes in tissues, and therefore to an improvement in their condition and increased resistance to negative factors.
These products include special creams and gels with camphor or guarana. But remember, under no circumstances should you use camphor alcohol.
and similar means.
This article will help you understand the variety of foams, dry shampoos, creams and lotions for hygiene, including in special cases - bedsores, stoma, urinary and fecal incontinence.
Stage 2. Non-fading redness
What it looks like: Skin color - bluish-red, spots with clear edges; skin with superficial damage - abrasions, blisters. Usually already accompanied by pain.
Stage 1 bedsore. Photo: Palliative Care Center, Moscow
Stage 2 bedsore. Photo: Palliative Care Center, Moscow
How to deal with unpleasant odors in the home of a seriously ill person Why do unpleasant odors form, is there a specific “smell of old age” and how to deal with this problem
Kristina Osotova
Care
How to treat
It is necessary to prevent the wound from becoming infected. It should be rinsed with sterile saline at room temperature, and then a transparent semi-permeable film, hydrocolloid or foam dressing should be applied. To prevent the formation of bedsores from developing further, follow all anti-bedsore procedures.
Stage 3. Damage to the skin up to the muscle layer or with penetration into the muscles
What it looks like: The edges of the wound are well demarcated, surrounded by swelling and redness; the inside of the wound may be yellow or red. This is necrosis (tissue death) or granulation (tissue growth around). There may be liquid discharge. Hurts a lot.
Stage 2 bedsore. Photo: Palliative Care Center, Moscow
Stage 3 bedsore. Photo: Palliative Care Center, Moscow
Video: Treatment of deep bedsoresWhat to do and how to care if a person has deep bedsores and you do not have the opportunity to see a doctor
Irina ProkopenkoCaring workshop
Care
How to treat
Stage 3 bedsores should only be treated by a doctor. It will cleanse the wound of exudate (liquid that is released from small blood vessels during inflammation) and pus. He will remove necrotic (dead) tissue surgically or dissolve necrosis using special gel dressings, and wash the wounds with saline solution. For secondary infection and purulent discharge, he will prescribe antibacterial agents (for example, metronidazole).
It is important to ensure the absorption of discharge and protect the wound from drying out and infection. For this, atraumatic bactericidal and absorbent dressings are used: based on beeswax with bactericidal properties, hydrogel, based on calcium alginate. They may also have a hemostatic effect.
After cleansing the wound, you need to stimulate its healing process. And, of course, continue all necessary anti-bedsore procedures.
Stage 4. Damage to all soft tissues, tendons and bones visible
What it looks like : Many holes are formed that can connect. The bottom of the wound often fills with black or black-brown masses of decaying tissue. Very strong, unbearable pain.
Stage 4 bedsore. Photo: Palliative Care Center, Moscow
Last stage bedsore, tissue necrosis. Photo: ECDO Center
How to treat
Such bedsores can also only be treated by a doctor. It does the same thing as stage 3 pressure ulcers, plus adds prophylaxis and bleeding control if necessary. For this purpose, atraumatic dressings are used and locally - a solution of ethamsylate and aminocaproic acid, calcium alginate.
Important Sometimes bedsores form in very unexpected places - for example, on the head. Read about this in the article “Bedsores on the head: prevention and treatment.”
Bedsores. Test for those caring for seriously ill people Do you know enough about caring for a sedentary person? Test your knowledge. Caring workshop
Symptomatic treatment
Prevention
Prevention of this condition in a child is to ensure:
- correct temperature conditions;
- air baths;
- daily bathing;
- regular drying of the skin;
- timely diaper change;
- using a “barrier” diaper cream.
If we consider the prevention of this disease in adults, then skin care and personal hygiene also come to the fore, especially in the hot season. If possible, you need to maintain the optimal temperature in the room (air conditioning). If this is not possible, then wear cotton clothes and shower daily. In case of severe sweating, showers should be taken 2 times a day, after which the skin should be thoroughly dried. It is also important to change clothes to dry ones during the day and give preference to clothes made from natural fabrics that allow air to pass through.
How to prevent heat rash in newborns
- Your baby will not develop heat rash even in the hot summer if you always dress your child according to the weather and monitor the temperature in the children's room;
- choose clothes for your baby not based on “beautiful”, but on the quality of “breathable” materials;
- dress your child in loose clothing;
- change your baby’s diapers regularly and often leave him naked to “ventilate”;
- bathe your baby daily;
- do not swaddle your baby too tightly;
- use powders and baby creams exclusively on a water basis;
wash children's clothes with special hypoallergenic products.
List of sources
- Dermatovenerology. National leadership. Ed. Yu. K. Skripkina, Yu. S. Butova, O. L. Ivanova. – M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2011. – 1024 p.
- Zanko N. I. Efficiency of new technologies for skin care for young children: abstract of thesis. dis. ...cand. honey. Sciences, M., 2000.
- F. A. Zverkova. Skin diseases of young children. Saint Petersburg. - Sothis. -1994 — 235 p.
- Yatsyk G.V., Akoev Yu.S. Clinical effectiveness of various newborn skin care products based on D-panthenol. Cons. Med. Pediatrics, 2004; 6 (2): 41-3.