Causes of non-healing wounds
The immediate cause of non-healing wounds is insufficient activity of restoration processes in the body, slow tissue regeneration. Moreover, the conditions under which regeneration slows down can be varied.
Among the general factors (i.e., affecting the state of the body as a whole), the following can be identified:
• weakened immunity due to concomitant disease or chronic immunodeficiency state;
• chronic intoxication of the body;
• metabolic disease;
• diabetes; this condition can be considered a severe form of metabolic disorder, namely glucose metabolism. Disturbances in the normal absorption of glucose lead to increased tissue fragility and a slowdown in the regeneration process;
• circulatory disorders - both general and local. The cause may be atherosclerosis, deformation of vascular walls, and diseases of the cardiovascular system. Local circulatory disorders can be caused by prolonged compression of tissues and pinching of small blood vessels (an example of a chronic wound against the background of constant compression of tissues - bedsores);
• hypo- or avitaminosis of vitamins A, C, K and group B, which play an important role in the process of tissue regeneration;
• lack of calcium or zinc in the body;
• exhaustion – nutritional (due to insufficient or malnutrition) or senile;
• presence of cancer.
A specific factor in the appearance of chronic wounds is poor circulation in the legs, most often due to varicose veins. Against the background of impaired blood circulation, trophic ulcers develop on the legs (usually in the shins) - difficult-to-heal tissue defects.
Local factors affecting the wound itself and the area around it include:
• infection;
• the presence of necrotic tissue in the wound (they increase the risk of suppuration and, accordingly, the duration of healing);
• presence of foreign bodies in the wound;
• the presence of bleeding in the wound (also increases the risk of infection);
• repeated damage to an unhealed wound.
The risk of a wound becoming chronic increases if, in addition to the skin, other tissues are damaged - subcutaneous tissue, nerves, muscles, tendons, bones.
Diagnosis of skin cancer
Diagnosis of skin cancer, in addition to the standard examination of the skin and lesion, if necessary with dermatoscopy, consists of the following procedures:
- Cytological examination of impression smears or scrapings from the neoplasm.
- In the absence of convincing clinical and cytological data, a tumor biopsy is performed (removal of part of the tumor or complete removal for research).
- Palpation examination of the skin in the area of tumor localization, palpation of regional lymph nodes. Ultrasound examination of regional lymph nodes.
- In the presence of enlarged regional lymph nodes, a fine-needle puncture (aspiration) biopsy is performed.
- For large tumors, radiation diagnostic methods are used - (CT or MRI of the affected area with IV contrast to assess the extent of the process).
- In some cases, if a widespread tumor process is suspected, additional examination of the thoracic and abdominal organs using ultrasound, CT and MRI techniques may be necessary.
Symptoms of non-healing wounds
•constant pain;
•converging edges of the wound;
•constant bleeding;
• “stuck” wound at one of the stages of healing for more than three weeks;
•often – unpleasant odor;
•conventional treatments do not help or help little.
These signs indicate that the regeneration processes in tissues are disrupted for one reason or another. For the treatment of chronic wounds, local treatment is not enough; comprehensive measures are required.
To achieve progress in healing, it is necessary to provide conditions for restoring the normal rate of regeneration. They largely depend on the cause of the chronic wound, but there are recommendations that are common to all situations.
The body needs to provide:
•balanced nutrition - in particular, the diet should be enriched with vitamins A and B, which stimulate tissue regeneration, and vitamin C, which promotes the production of collagen - a substance involved in the formation of connective tissue that closes the wound in the first stages;
•normal sleep mode – during sleep the regeneration process occurs more actively;
•protecting the wound and the area around it from external influences, such as rubbing, squeezing, etc.;
•wound ventilation – without air circulation, the wound will quickly fester.
More specific recommendations depend on the origin and nature of the wound.
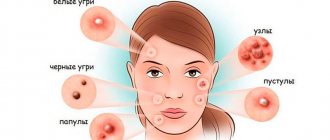
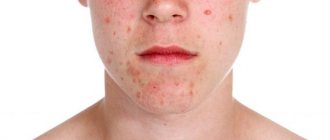
Acne wounds
Acne or pimples are inflammation of the sebaceous glands. The etiology of this phenomenon depends on many factors, ranging from improper hygiene to endocrine diseases. Single pimples go away on their own, leaving no traces, but if you injure the area of skin inflammation (start squeezing out pimples), there is a risk of encountering the formation of scars, which will be difficult to get rid of even with the help of modern cosmetology measures. Therefore, knowing how to quickly heal a wound on the face after a pimple is very important.
In order to get rid of a pimple, you need to disinfect the skin and relieve inflammation. Therefore, the first stage of treating the area around the pimple is identical to treating any scratch. You need to thoroughly clean the skin with water, and then degrease it with an alcohol solution.
After this, it is necessary to moisturize the skin area, otherwise the production of sebum will increase, causing inflammation.
But the product that will be used for moisturizing should not contain any oils that have a comedogenic effect. As a traditional medicine, you can use a decoction of chamomile flowers or fresh aloe juice, which should be used to moisten the pimple wound locally. It is extremely important not to rub your facial skin with a towel, so as not to irritate it and provoke further spread of inflammation. You need to wipe the skin with blotting movements.
Treatment of non-healing wounds taking into account their cause
When starting to treat injuries of this kind, it is necessary to understand the cause of their occurrence. Further actions will depend on this.
1. First of all, it is necessary to examine the wound for foreign bodies, necrotic tissue, and bleeding and, if necessary, clean it. Please note that it is strongly recommended not to remove foreign bodies yourself! Such attempts may cause additional tissue damage and increase the risk of infection. You need to seek help from a doctor.
2. If local blood circulation is impaired, it is necessary to eliminate the source of pressure on the tissue (change the position of the patient’s body with bedsores, wear looser clothes/shoes for “diabetic” wounds).
3. When treating trophic ulcers on the legs, it is necessary to use compression stockings or bandages - they will help “support” the blood vessels and normalize blood circulation, as well as “pull” the edges of the wound towards each other for faster healing.
4. In case of exhaustion and vitamin deficiencies, it is necessary to provide a normal balanced diet in order to provide the body with the necessary substances for tissue regeneration and the production of collagen - a substance that is actively involved in the early stages of the healing process and helps tighten the edges of the wound.
5.If you have diabetes (of any type), you need to monitor your blood glucose levels.
After creating optimal conditions for wound healing, you can begin to treat and treat it.
Ointments for acne
You can find an ointment that quickly heals wounds on the face at a pharmacy, for example, “Synthomycin”. Its advantage is its complex effect on the skin: anti-inflammatory and antibacterial.
You can also use the following drugs:
- "Banaderm";
— “Askosept”;
— “Manisoft”;
- "Kutasept."
In case of severe inflammation, when the pimple hurts and suppurates, it is best to contact a specialist who will open the pimple, carry out an antiseptic treatment and apply a regeneration agent. The dermatologist will also advise how to quickly heal a wound on the face from a pimple using modern drugs for external use.
Principles (stages) of treatment
Actions when treating a wound depend not only on the conditions and causes of its appearance, but also on the stage at which the wound process has stopped in it.
The first stage of the wound process is acute. During it, vascular changes occur caused by a reaction to damage, and the process of blood clotting is actively underway. If the wound is infected, pus is formed and toxic substances are simultaneously absorbed into the tissue.
At this stage, it is necessary, first of all, to clean the wound - remove dead tissue from it, remove foreign bodies (with the help of a doctor), drain it - remove pus and exudate from the wound. It is also necessary to prevent infection from entering the wound. It is best to wash the affected area with saline solution, as caustic disinfectant liquids can harm surrounding healthy tissue.
The second stage of the wound process is granulation. At this stage, a thin layer of connective tissue begins to form on top of the wound. The edges of the wound begin to tighten, and it closes itself. The thinnest capillaries are formed in the connective tissue layer, providing nutrition to regenerating tissues. Often chronic wounds stop at this phase, and the healing process does not proceed further; This is most often what happens with trophic ulcers.
At the granulation stage, it is important, firstly, to protect the newly formed tissue from mechanical damage, secondly, to stimulate further regeneration, and thirdly, to prevent the development of the inflammatory process - despite the fact that the wound is closed, the risk of infection and inflammation remains. To stimulate tissue regeneration, methyluracil ointment is used (you can use a ready-made Voskopran dressing with methyluracil ointment); to protect the surface of the wound, atraumatic dressings should be used that do not stick to the wound surface and do not injure it.
We should not forget about maintaining a maintenance diet and sleep schedule - this will help speed up the healing process.
Dressings for the treatment of non-healing wounds
When treating wounds of any nature, including chronic ones, the correct selection of dressing material plays an important role.
Dressing material for non-healing wounds should be:
•hygroscopic;
•"breathable";
•elastic and flexible – the bandage will have to be worn for a long time, so it should not interfere with movements.
Biotekfarm company offers a wide selection of dressings for the management of wounds of any complexity and at any stage. So, for wounds in which there are fragments of necrotic tissue or hemorrhage, a Parapran dressing with chymotrypsin is suitable - the drug included in the dressing helps to break down necrotic tissue, helping to cleanse the wound.
To moisturize “dry” chronic wounds (bedsores, trophic ulcers) and accelerate their healing, it is recommended to use the “GelePran” dressing with miramistin or colloidal silver. This soft transparent dressing, consisting of 70% water, moisturizes the surface of the wound, and the medicine it contains (miramistin or silver) disinfects and promotes regeneration.
For the treatment of infected wounds, bactericidal dressings Voskopran with Povidone-iodine ointment, antimicrobial dressings Voskopran with Dioxidin ointment, and anti-inflammatory dressings Voskopran with Levomekol ointment are suitable. Polipran dressings with Dioxidin are excellent for preventing infection of wounds at the granulation stage.
The Chitopran dressing based on chitosan nanofibers will help stimulate regeneration. It provides optimal conditions for healing - sufficient humidity, breathability and protection from damage, and promotes the rapid growth of its own cells. It is worth paying attention to the fact that this bandage does not need to be removed - it resorbs on its own as the wound heals.
Wound healing time and consequences
Healing a chronic wound is a long and complex process that can take from 1 to 3 months, depending on the depth and size of the wound. It should be borne in mind that epithelization of chronic wounds is very slow - no more than 1 cm per month. After complete epithelialization, the “new” skin increases its strength for another 6 months.
Recommendations for caring for the problem area are quite simple:
•protect the wound from compression and mechanical damage;
•change the bandage regularly (depending on the stage of healing and type of bandage);
•at the granulation stage - use dressings that accelerate healing.