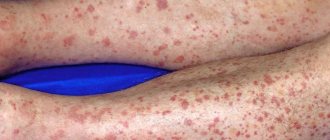
Vaginal blisters can appear on the vagina, labia, clitoris, and sometimes on the pubic area. These lesions are similar to regular blisters that appear due to friction or burns, except that they are caused by an infection or virus. Blisters in the vagina cannot be missed; this disease can be felt in the first stage, it is called prodrome.
Fluid blisters, sores, rashes and other irritation in the vaginal area can have many different causes. You need to visit a doctor so that he can make the correct diagnosis.
How does herpes infection occur in the vagina?
Herpes in the vagina appears as a result of a herpes infection.
It is transmitted through sexual intercourse.
70% of cases of pathology are caused by type 2 herpes, 30% of cases by the first (the one that usually causes blisters to appear on the lips).
A woman has a higher risk of becoming infected than a man.
If the spouse is a carrier of the virus, then the risk of infection of the woman within 1 year is 25%.
While men become infected from their spouse with only a 5% probability during the same period.
There is cross immunity to herpes viruses.
If a woman already suffers from labial herpes, then the risk of genital infection is reduced by 15%.
The incubation period of infection lasts on average 6 days.
The pathology has a high prevalence.
About 25% of all people are infected.
They are carriers of genital herpes, although they do not always suffer from its symptoms.
Among women of non-traditional sexual orientation, the carrier frequency is higher – 45%.
Among those who practice prostitution, herpes infection of the vagina and vulva is found in 75% of cases.
How is genital herpes transmitted?
Herpes in the intimate area in women is caused by the transmission of the HSV virus from an infected partner of a patient or a virus carrier during genital, oral-genital, or oral contact.
Fact Transmission of the genital herpes virus in women can occur in different ways, but the sexual route is the leading one.
Auto-infection is also possible (for example, with ophthalmic herpes, the virus is carried by hand from the conjunctiva of the eye to the genital area), infection through household items or personal hygiene, as well as transmission by blood transfusion (blood transfusion) and transplantation (organ transplantation).
In women infected with HSV-2, the virus is contained in saliva, nasal mucus, tears, blood, urine, vaginal secretions, menstrual blood, amniotic fluid, the contents of the herpetic vesicle, etc.
HSV enters the body through mucous membranes or damaged areas of the skin, where it multiplies. Further, regardless of the signs of the disease, the virus invades the sensory and autonomic nerve endings and then into the body of the neuron, into the ganglion, and continues replication there. Then it spreads to the skin along the peripheral sensory nerves, which explains the fact of the involvement of new surfaces located at a distance from the site of primary localization of the vesicles.
Herpes in the intimate area in women or genital herpes has some features compared to genital herpes in men:
- Women are more susceptible to the disease than men.
- Relapses of the disease occur more often in women than in men.
- In women, more often than in men, relapse is caused by hormonal changes.
- In women, subjective sensations (itching, burning, pain), as well as symptoms of general intoxication, are more common than in men.
- Women have a larger area of lesions than men, which is due to the structure of the genital organs.
- Despite the fact that the frequency of relapses of genital herpes in women and men is the same, the manifestations of relapses are different. In women, relapse is characterized by severe clinical symptoms, usually one lesion and a shorter duration than in men.
- In women, genital herpes more often occurs in a latent form than in men.
- In women, recurrent genital herpes more often than in men leads to psychoasthenia and neuropsychiatric disorders.
Chronic herpetic infection is an immunodeficiency disease with lifelong persistence of the virus in the cells of the nerve ganglia with dysfunction of both the autonomic and central nervous system, characterized by periodic exacerbations with the appearance of clinical signs (“herpetic vesicles”), localized in places that are constant for each patient - “Locus minoris” . Herpetic blisters affect the mucous membranes of the female genital area, the urethra, the anus, the skin, and when the process generalizes, the liver, brain and other organs. Rashes in the form of small, tense blisters on an edematous, hyperemic base after an incubation period of 2–4 days are accompanied by a period of increase in local clinical symptoms (tingling, burning) in some cases - general symptoms (malaise, weakness, fever). The lesion, without the addition of a secondary infection, disappears on days 7-9 without a trace.
What does herpes look like in the vagina?
Individual or grouped vesicles appear in the area of the vulva and vagina.
They are located on reddened areas of the skin and mucous membranes.
In the future, these inflammatory elements will disappear.
But in case of relapse, they may appear in the same place.
There is an increase in the size of the nearest lymph nodes.
Vesicles tend to become erosions.
They may be covered with plaque.
The contents of the vesicles (bubbles) are highly infectious.
When it comes into contact with nearby tissues, they also become inflamed.
Therefore, with herpes inside the vagina, inflammatory elements are often observed, located symmetrically on opposite walls.
The infection is transmitted to another person.
If the contents of the vesicles enter the recipient's genitals, the risk of infection is very high.
Herpes in the vagina is accompanied by an increase in body temperature in 60% of cases.
Bubbles appear in 90% of patients.
Exudation is typical for 67% of patients.
In 80% of women, herpes near the vagina recurs at least once during their lifetime.
Lymphadenopathy during herpetic infection is observed relatively rarely - in 20% of cases.
Symptoms depend on the type of herpes that caused the pathology.
This may be type 1 or 2 of herpes in the vagina.
In the second type, the pathology is often more severe.
More often, erosions appear and hyperemia is noted at the base of the vesicles.
Inflammatory lesions of the urethra are more likely to occur.
Frequent complaints from patients, in addition to rashes:
- insomnia
- nervousness
- malaise
- headache
Other causes of the symptom
Neoplasms on the labia can be signs of a number of other diseases and disorders in the body:
- Furunculosis occurs due to a bacterial infection. It is characterized by neuralgia, blisters in the form of subcutaneous pimples filled with pus.
- Hormonal imbalances during pregnancy and other periods with activation of the sebaceous glands and their clogging. Often found during puberty.
- Inflammation of the hair follicles. Painful formations that discharge pus after rupture. Not a dangerous phenomenon that does not require medical intervention.
- Bartholinitis - the causative agent of the inflammatory process is staphylococcus, E. coli, etc. Painful bloody pimples appear.
- Molluscum contagiosum. An infectious disease in which white pimples with a pearlescent tint appear on the labia. The infection is transmitted sexually.
- Fordyce granules. Non-hazardous formations of a benign nature that do not require therapy. This is a consequence of individual characteristics. Small pimples are light, beige or pinkish, not painful, rough.
- Papilloma virus. Pointed pimples can appear on any part of the body and are dangerous for the development of cancer.
Recurrence of herpes in the vagina
The listed symptoms usually develop during primary infection.
But relapses are possible in the future.
Once it enters the body, herpes remains here forever.
Another exacerbation can be provoked by:
- decreased immunity
- pregnancy
- hypothermia
- intoxication
- serious illness
Often, herpes worsens after the patient is infected with another sexually transmitted infection, for example, gonorrhea.
The symptoms are generally the same.
But they are less pronounced.
There are usually fewer vesicles and they disappear faster.
Lymph nodes do not enlarge.
There is no high body temperature, although low-grade fever is possible.
Vaginal herpes: clinical course of pathology and prognosis
Vaginal herpes cannot be completely cured.
But it often occurs without symptoms.
In the first year after infection, exacerbation occurs in 65% of those infected.
In the future, 25% of women will experience relapses once a year or less.
More than once a year, but not more than once a month, vaginal herpes worsens in 13% of patients.
In 2% of patients, relapses occur more than once a month.
Based on the severity of the symptoms that occur during primary infection, the further course of the disease can be predicted.
If the signs were mild, without fever, with a minimum number of blisters, relapses will be rare.
Perhaps vaginal herpes will not get worse at all.
If the pathology was initially severe, with a significant increase in body temperature, a large number of vesicles, and the formation of large erosions, this is a negative prognostic sign.
Exacerbations are highly likely to be frequent and severe.
Diagnostics
Which doctor should I contact: a dermatologist or venereologist.
To diagnose urticaria and allergies, skin allergy tests are performed, a general blood test and an immunoglobulin test are performed.
If the infectious nature of the rash is suspected, scrapings from the blisters and ulcers are taken to identify the pathogen for analysis using the PCR method. If the presence of the virus is confirmed, a blood test is done for antibodies. In case of furunculosis, the contents of the blister are examined for the presence of bacteria, their type and sensitivity to antibiotics are determined.
Candidiasis is initially diagnosed by light microscopy. Next, they take a urethral smear, prostate secretion, and ejaculate for bacterial culture.
Complications of herpes in the vagina
In women, herpes in the vagina can spread to other organs.
Sometimes herpes causes inflammation of the cervix, uterus and appendages.
The risk depends on:
- virulence of the virus strain
- immunity status
- duration of vaginal herpes
- severity of inflammation
When the appendages become inflamed, aching pain is observed in the lower abdomen.
The defeat can be either one or two-sided.
The number of organs affected by herpes affects the choice of treatment regimen.
There are three degrees of severity of herpes in women:
- – only the skin near the vagina is affected.
- – inflammation has reached the vagina.
The urethra and cervix may also be affected.
- – the pathology has spread to the bladder, uterus, and appendages.
Herpes has been found to increase the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Statistics show this.
In women infected with herpes infection, malignant neoplasms are detected more often.
Diagnosis of genital herpes in women
How to understand that it is herpes? What does genital herpes look like in women?
Diagnosis of genital herpes in women is made by collecting anamnesis, clinical examination, additional examination methods and is aimed at determining the severity of the condition and indications/contraindications for treatment.
Herpes in intimate places has a symptomatic typical course - there is no doubt in the doctor’s mind.
If there are characteristic elements of the rash and typical morphology, the diagnosis is established on the basis of clinical data, laboratory confirmation is not required.
If you have positive IgM, you absolutely cannot plan a pregnancy. Because genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection (STI), screening of all sexual partners is recommended
To detect the virus itself, highly accurate diagnostics using the PCR method is most often used, which is the “gold standard” for diagnosing HSV, because detects viral DNA. Electron microscopy can also be used. The material for isolating the virus most often is the contents of the vesicles, saliva, secretions of the nasopharyngeal mucosa, vaginal secretions, and blood. For serological diagnosis, reactions that detect antibodies, immunoglobulins, and Ig are used. Ig G is a class of antibodies that provide a person with long-term immunity to infections. Ig M is a class of antibodies that correspond to the severity of the process. If they are elevated, this is a relapse or primary infection. Their level increases by the 3-5th day of the disease.
If herpes occurs in the intimate area in women, what should you do?
Consult a doctor (infectious disease specialist, dermatologist-venereologist, gynecologist) for advice.
Self-medication is not acceptable!
Herpes in the vagina during pregnancy
Herpes is very dangerous for pregnant women.
Pathology increases the risk of spontaneous abortion.
Infection of the fetus in utero and premature birth are possible.
Sometimes fetal development is delayed.
Manifestations of herpes infection in newborns can be severe.
For 2-3 weeks of life, their skin, eyes, and oral cavity are affected.
In the most unfavorable cases, encephalitis occurs or internal organs become inflamed.
Prophylactic therapy is required to prevent fetal infection.
It is prescribed in the last 4 weeks before childbirth.
Indications:
- high frequency of relapses before pregnancy - from 6 per year
- infection during pregnancy
- at least one exacerbation during pregnancy
If primary infection or recurrence occurs after 34 weeks, this is an indication for cesarean section.
Because the risk of infection without drug prevention reaches 50%.
But it does not prevent infection 100%.
Therefore, newborns receive therapy with acyclovir, regardless of the manifestations of herpetic infection they have.
They are prescribed this drug at a dose of 30-60 mg per day.
The course lasts from 10 days to 3 weeks.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of blisters at the entrance to the vagina and in the organ itself, you must follow some recommendations.
Preventive measures:
- Make sure your sexual partner is healthy by getting tested for infections.
- Drink enough water.
- See your doctor if you have any discomfort.
- Participate in anger and stress management activities if necessary
- Quit smoking.
- Always keep your genitals clean and dry.
- Maintain proper nutrition always, not occasionally.
- Wear underwear only made from natural fabrics.
Only timely visits to the doctor and compliance with preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing blisters in the vagina.
Share:
Treatment of herpes in the vagina
There are specific antiviral drugs to suppress the herpes virus.
Medicines from the group of acyclic nucleosides are prescribed.
Acyclovir is used.
Viruses are susceptible to it in most cases.
Resistance is observed in only 3% of herpes simplex virus strains.
The earlier treatment is started, the better the results.
Symptoms go away faster.
The severity of the exacerbation is lower.
But at the same time, acyclovir does not affect the course of the disease in the long term.
There are no long-term results of therapy.
If you were treated with acyclovir today, this does not mean that in a few months the exacerbation will be less pronounced.
It may indeed become easier, but only if you take acyclovir again.
Other drugs in this group:
- famciclovir
- valacyclovir
They have the same effectiveness.
And they even have advantages: their bioavailability and duration of action are longer.
Causes of the defect
Often the problem arises under the influence of external factors. The reasons are hygienic aspects and allergic reactions.
- Hygiene. Insufficient hygiene leads to the accumulation of dirt and active reproduction of pathogenic microflora. As a result, unpleasant symptoms appear. Excessive enthusiasm for cleanliness is also not always useful. Under the influence of detergents and chlorinated water, delicate skin dries and cracks, and various new growths appear on it.
- Allergy. Red bumps in the genital area sometimes appear due to contact with allergens. Hygiene and detergents, vaginal suppositories, condoms, toilet paper, and pads with fragrances provoke a reaction. The process is accompanied by itching, the scratched areas become inflamed. In addition, local immunity decreases and pathogenic microorganisms become more active.
- Underwear. Synthetic fabrics prevent the skin from breathing and create excess moisture under the underwear. A similar effect is achieved by rarely changing sanitary pads. May cause a small rash on the labia.
Tight panties rub sensitive areas, resulting in something like calluses.
Suppressive therapy for vaginal herpes
Suppressive therapy is indicated for patients who suffer from frequent and severe exacerbations.
In this case, it is advisable to take the drugs constantly.
Valaciclovir is usually prescribed.
It is taken 0.5 g, 1 time per day.
Suppressive therapy usually lasts from 2 to 5 years.
It can be continued for a longer period.
For example, with vaginal herpes due to HIV infection.
If suppressive therapy is discontinued, delayed positive results of such treatment are observed.
With long-term use of the drug, the viral load decreases, exacerbations become more rare and less severe.
Suppressive therapy can also make a person non-infectious.
This is important in situations where a regular sexual partner is not yet infected.
With constant suppressive therapy during sexual intercourse, you can not use a condom outside the period of exacerbations.
But it is still impossible to have an intimate life while there are rashes in the vagina.
Suppressive therapy can be situational.
It is not prescribed constantly, but only during periods when there is a high risk of exacerbation of the disease.
For example, against the background of a serious illness, when infected with concomitant STDs, or after undergoing surgery.
After the end of the critical period, therapy is discontinued.
Preventive episodic treatment for irregular sexual activity is also possible.
If a woman does not have regular sexual intercourse, then to reduce the risk of infecting a partner, valacyclovir can be started 3 days before sexual intercourse.
In this case, there is a decrease in viral shedding by at least 100 times.
Therefore, the risk of infection is significantly reduced.
After sexual intercourse, you can stop therapy until the next time.
Immunomodulators are also used for maintenance treatment.
Symptoms
The symptoms of blisters are very clear, so even the woman herself will notice something is wrong. Bubbles appear as follows:
- Burning. This symptom is only a small part of the problems that a woman will experience with blisters in the vagina. It almost constantly accompanies the patient during urination, sex, and when walking in tight underwear.
- Tingling. During the formation of blisters, you may feel a tingling sensation in the area of the vaginal opening. Further, this feeling will gradually weaken. As a result, the tingling is replaced by severe pain.
- Itching is one of the main symptoms that appears long before blisters begin to form.
- Pus from the vagina. The presence of yellow-green discharge means that a serious inflammatory process is occurring inside, and the ulcers that formed at the site of the blisters began to ooze and fester.
The presence of blisters is one of the problems, but when they are accompanied by vaginal discharge, the problem inevitably becomes more complicated. The appearance of an uncharacteristic secretion may indicate the presence of an infection. Along with blisters in the vagina, ulcers on the pubis may appear.
Controlling the cure of herpes in the vagina
After specific treatment, clinical symptoms are assessed.
Laboratory control is not required.
Because herpes infection cannot be cured.
If suppressive therapy is prescribed, the results are also assessed clinically.
After discontinuation of maintenance treatment, its effectiveness is judged by two relapses.
Assess the time intervals at which they occurred and how severe the symptoms were.
Based on the results of monitoring, a decision may be made to resume suppressive therapy.
Why do you need a vaccine for herpes in the vagina?
Vaccination is prescribed not for prophylactic, but for therapeutic purposes.
It is indicated for patients with a high frequency of recurrent herpes infections.
Vaccination is used only during the period of remission.
The drug Vitagerpavak is used.
The first dose is prescribed 10 days after the symptoms have subsided.
It is injected intradermally into the forearm.
A total of 5 injections are required.
Injections are performed every 7 days.
The exception is women with very frequent recurrences of vaginal herpes.
If the disease worsens more often than once a month, the drug is administered at intervals of 10 days.
After completing the vaccination course, there should be a break of 6 months.
After this, the course is repeated.
The herpes vaccine is safe because it contains an inactivated (non-living) virus.
At the same time, its antigens are preserved, which provokes an immune response in the body.
There are usually no side effects.
If they exist, they pass quickly and do not cause significant discomfort.
There may be soreness and redness at the injection site.
There may be an increase in body temperature on the first day.
Contraindications to the administration of the vaccine:
- acute herpes
- any other acute infections
- severe somatic diseases
- cancer
- pregnancy
On the day of vaccination and for 2-3 days after it, you should not drink alcohol.
Treatment
If the blisters are a consequence of an infectious pathology or virus, then treatment can take place in a hospital setting. The patient will be prescribed medications that will quickly suppress pathogenic microorganisms.
Home remedies can help you get rid of vaginal blisters in no time. Traditional medicine also does not stand still.
Folk
Treatment methods:
- Carrot juice. Carrots contain beta-carotene, which helps in detoxifying the body. Take two small vegetables, grind in a meat grinder, squeeze out the juice. Drink it twice a day until symptoms disappear.
- Take a piece of aloe vera, apply the gel on the wounds and let it dry. It is cooling and helps in healing blisters. If they are not at the entrance of the vagina, but right in it, make a tampon and insert it for a while. As soon as you feel that the itching and pain have begun to subside, wait another half hour and remove the tampon.
- Take some baking soda, mix it with water and then apply the paste to the blisters near the vaginal opening. Let it dry. Wash yourself with warm water and wipe your genitals dry. This helps heal the blisters quickly.
- Cold compress. Take some ice cubes, wrap them in a cloth, and then place them on the affected area. This has a soothing effect on the blisters and helps in their healing.
- Add half a cup of vinegar to a bath of warm water. Take it within 5-7 minutes. Do this twice a day.
- Take a cold, wet tea bag and press it onto your vaginal opening. Keep it on for about 5-7 minutes and then remove. Tea helps relieve inflammation and redness.
- Take some garlic oil, mix with a little olive oil, and then apply directly to the blisters.
- Hydrogen peroxide is a disinfectant and can be used for blisters. Soak a tampon in this preparation and insert it into the vagina for 10 minutes.
- Lemon is very helpful in reducing inflammation. In addition, it has antibacterial and antiviral properties. You should drink at least 4 cups of black tea with lemon every day. You can just eat 1 citrus.
- Licorice root helps in strengthening the immune system and is essential for the body as it can fight the causes of blisters in the vaginal area. Mix 1 tsp. products with 0.5 tsp. water, it should turn out to be a paste. Apply the mixture to the bubbles. Repeat the procedure at least 4 times a day until the blisters begin to subside.
- Tea tree oil is a good pain reliever and anti-inflammatory. It is diluted with vegetable oil in a ratio of 10:1 and applied to the bubbles.
There are many more remedies that can be prepared at home. But the ones listed are the most effective.
Diet
In addition to the remedies discussed above, it is necessary to restore immunity. This can be done by increasing the amount of nutrients that can be consumed from food.
Dietary nutrition should include:
- Foods rich in L-lysine are especially helpful if vaginal blisters are caused by the herpes virus. They contain an amino acid that can prevent this virus from replicating. These include fish, turkey, vegetables, chicken and legumes.
- Red vegetables and oranges contain antioxidants such as carotenoids, vitamin C and bioflavonoids. They help in healing the skin and mucous membranes, and at the same time boost the immune system.
- Zinc is required for most reactions in the body, which help restore the skin and mucous membranes. This substance also protects the body from infections and viruses. It is necessary to eat liver, pumpkin seeds, spinach.
Proper nutrition is the basis of any treatment. It must be followed for a speedy recovery. If you have vaginal blisters, you should not drink alcohol or consume large amounts of sugar.