It is worth talking about some indications for tissue coagulation in more detail, since the incidence rate is growing, and this method sometimes becomes a priority in the treatment of pathology. Cervical erosion is a structural change in the uterine mucosa. It can be present in a woman’s body under normal conditions, or it can reach enormous sizes after childbirth or surgery, which requires minimally invasive surgical intervention. If the patient refuses coagulation, then consequences such as cervicitis and cervical cancer appear. Papillomatosis is multiple formation of papillomas on the surface of the epithelium or mucous membrane of organs. In the initial stages it has a benign course. Without surgery, it tends to malignize, that is, it turns into a malignant tumor. Hemorrhoids are dilation of veins, the formation of hemorrhoids within the tissues of the rectum. Significantly reduces the quality of life, accompanied by itching, pain, bleeding and other symptoms. At the third or fourth stage, surgery in the form of laser coagulation is required, as the risk of thrombosis and necrosis increases.
Causes of coagulation
If we consider coagulation as the natural ability of blood to close wounds and prevent infection, then the mechanism of development here is as follows:
- disruption of tissue structure, the appearance of a wound becomes a trigger for subsequent chemical reactions;
- platelets, together with blood clotting factors, attach to the affected area, fibrin is produced;
- this fibrin is a thread intertwined with each other, which will ultimately become a framework for the resulting blood clot;
- an increasing number of platelets are attracted, the hemocoagulation process is suspended when the thrombotic mass completely prevents further bleeding.
Physical and chemical coagulation follows a completely different path. With the help of a laser and biochemically active substances, protein synthesis is disrupted at the cellular level, cells die in unusual conditions and cover the area of influence with a kind of crust consisting of dead tissue. If we are talking about capillaries, small vessels that undergo coagulation, then they simply curl up and stop functioning. Next, the human immune system is primarily involved, producing large numbers of macrophages, leukocytes, that is, cells with phagocytosis - the ability to break down and absorb foreign solid particles. All dead cells are broken down, and new healthy tissue is formed that is capable of performing its own functions.
Use in surgery
Coagulation began to be used in surgery relatively recently. It is used to “seal” bleeding vessels, remove malignant or benign tumors, and perform operations that require special precision and care.
- electrosurgical (contact and non-contact);
- thermal stapler;
- argon plasma;
- laser.
The electrosurgical method is performed using a charged scalpel in the shape of a ball, a loop needle. The instrument can be used to perform local dissection of the membranes in a small area. Moreover, all manipulations can be performed with minimal access to the organ, which avoids complications in the form of secondary infectious inflammation. Most often used for bleeding from erosions or ulcers located in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Using a thermal stapler, vessels are also sealed during surgery, and tissue incision is less traumatic. The advantage of this method is a clean surgical field, that is, the entire view is not obscured by leaked blood, a short tissue healing time, and a lower risk of complications. Used for laparoscopy, prostatectomy, hysterectomy.
Video of surgery to remove multiple papillomas
The duration of the recovery period after removal of papillomas on the eyelids depends on the location of the formation. The most problematic in terms of healing are papillomas located at the edge of the eyelids in the immediate vicinity of the eyeball; moreover, after their removal, scars often form that subsequently require laser resurfacing.
Complications
- Visual field defects - an incorrectly configured laser device can damage not only the target arteries, but also nerve fibers. A person begins to look as if through binoculars or a pipe.
- Allergic reaction. If there is a tendency to hypersensitivity, if there is an individual intolerance to electrical procedures, a person becomes covered with a rash, red spots, and dermatitis may develop.
- Suppuration of the affected area. If the skin or mucous membranes are not properly cared for after laser coagulation, active inflammation forms, first serous and then purulent exudate appears.
- Bleeding. If the rules of coagulation are violated, primary or recurrent bleeding may occur from a vessel at the bottom of the ulcer or the area where there was a neoplasm.
- Sanitation of the vagina using antifungal agents.
- Prevention of bleeding using special medications.
During the preparation process, it is important to take precautions that will increase the success of the procedure and reduce the risk of complications during the recovery period. Precautions include:
- Checking blood clotting function to prevent serious complications.
- X-ray examination of the lungs.
- Diagnosis of HIV infection, which leads to a significant decrease in immunity and will aggravate the postoperative process.
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections and their mandatory treatment.
- Identification of oncogenic tissues that require a separate treatment method (taking a smear for oncocytology).
Diagnostics
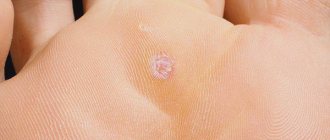
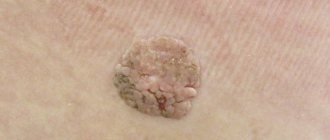
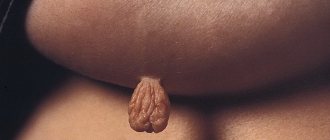
Diagnosing papillomavirus in the presence of nevi themselves does not present any difficulties. This can be done at a regular appointment with a dermatologist (as well as a urologist or gynecologist, if we are talking about genital neoplasms - genital warts). It is important to verify the viral nature of the nevus and recognize the type of virus (whether it is oncogenic). For this purpose, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis, histological examination, and Pap test are used.
According to the degree of malignancy, papillomaviruses are divided into 2 groups:
- HPV of high oncogenic risk. Of these, the most common types in Russia are 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59.
- HPV of low oncogenic risk. These include 6, 11, 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81 and other types.
Methodology for performing various types of procedures
Today, there are several types of cervical coagulation. They differ in the method of influencing the pathological focus. We will consider the most popular treatment methods below.
Diathermocoagulation with electric current
This type of influence is carried out using alternating current and a special loop (conductor). In this case, the pathological focus is cauterized and destroyed with the formation of a dense scab, which subsequently disappears. Electrocoagulation is carried out using two electrodes. Depending on the lesion, various loops are used that conduct electric current to the tissues.
Radio wave coagulation
The procedure involves exposing the altered area of the cervix to high-frequency radio waves. Unlike the previous option, the beam directed at the defect displaces it, acting in a targeted manner. This type of coagulation is based on exposure to high temperatures, which lead to the evaporation of the pathological focus without affecting healthy tissue.
Radio wave treatment of the cervix is carried out using a special device
Argon plasma method
Argon plasma coagulation is one of the modern and advanced methods of treating gynecological diseases. During the procedure, the affected tissue is exposed to a radio wave, which is amplified by ionized gas - argon. When exposed to a powerful radio wave, the affected area heats up and coagulates.
Laser beam vaporization and laser destruction
The first method is based on evaporation of the pathologically changed area using the targeted action of a laser beam. In this case, the wound heals quickly and there are no negative consequences. The second method is based on a deeper impact of a laser beam, which dehydrates the affected tissue. As a result, after the intervention, not even a trace remains on the cervix.
Chemical cauterization
Treatment involves influencing the pathological area using a special concentrated composition. It is applied to the cervix, causing a chemical burn to the affected area followed by the formation of a scab. Cauterization is the least effective coagulation method.
Cryocoagulation
Hypothermia of the cervical defect is performed using liquid nitrogen. If almost all previous methods were based on high temperature exposure, then this method, on the contrary, freezes the pathological focus to healthy tissue.
Causes
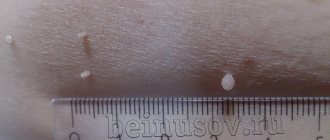
The cause of papillomas on the eyelids is infection with a virus from the papillomavirus family. The virus is transmitted from person to person through household or sexual contact; carriage of the virus is widespread. To become infected with the papilloma virus, microscopic damage to the skin is enough.
For a long period, the papilloma virus can remain in the body without manifesting itself. It is believed that the direct formation of papillomas is associated with a weakened immune system as a result of stress, lack of sleep, after illness, an unsuccessful visit to a solarium, etc. With age, the likelihood of papillomas increases, this is due to weakened immunity in older people.
Laser coagulation
This type of coagulation using electromagnetic radiation is used in the treatment of diseases such as:
- Varicose veins;
- cervical erosion;
- the presence of pigment spots;
- external hemorrhoids;
- rosacea;
- retinal dystrophy, tendency to detachment;
- formation of hemangiomas.
It has gained particular popularity due to its minimal point impact, which allows healthy nearby tissues to be preserved. Laser coagulation allows you to prevent complete loss of vision due to retinal detachment, and restore the beauty of the skin of the lower extremities and face, as clearly visible vessels are removed.
- Cataract is a clouding of the lens that cannot transmit laser beams to the deeper parts of the eye;
- Severe hemorrhages in the retinal area - it is not possible to direct the rays precisely to the required area;
- Thrombophilia is an increased tendency to form blood clots. After the procedure, there is a high risk of blockage of blood vessels with thrombotic masses, which will dramatically disrupt the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the tissues;
- Infectious diseases. Pathogenic microflora after laser correction can either contaminate the affected area or cause an inflammatory reaction in the periphery.
Prevention
To prevent infection with the papilloma virus, you should follow everyday hygiene recommendations: regularly wash your hands, use individual towels and bed linen, etc. Particular attention should be paid to eye hygiene, for example, do not touch your eyes with dirty hands, use swimming goggles when visiting the pool, etc. Since papillomas usually form in people with weakened immune systems, you need to pay attention to your diet, rest regularly, and adhere to a healthy lifestyle life, avoid overwork and hypothermia.
Mechanism of coagulation in surgery
At its core, argon plasma coagulation is an electrosurgical, monopolar, non-contact method of influencing biological tissues with high-frequency current using ionized and, as a consequence, electrically conductive argon - argon plasma. Argon gas, which is inert under normal conditions, is ionized under the influence of an electric field generated between the tip of the electrode located at the distal end of the applicator probe and the adjacent tissues. The resulting jet of argon plasma, regardless of the direction of the flow of argon itself, is automatically directed to those areas of the tissue surface that have the lowest electrical resistance and has a coagulating effect on them (Bagt O. et al., 1994). Rapid coagulation of a large surface occurs, creating a thin layer (up to 3 mm) of a reliable scab. When operating an argon plasma coagulator, the temperature on the tissue never exceeds 110° due to the cooling effect of argon. Once a scab has formed, no further penetration of energy into the tissue occurs. The depth of its penetration into the tissue is approximately 2 times less than with traditional coagulation, which significantly reduces the risk of perforation of thin-walled organs and allows the use of argon plasma coagulation in the duodenum and colon, as well as in the esophagus. Since argon does not support combustion, there is less charring of the fabric, and there is virtually no smoke.
Coagulation in medicine and cosmetology
Modern medicine uses coagulation to treat certain vascular diseases. With its help, you can get rid of spider veins on the face and body, as well as solve more serious problems. The darkening of some vessels, noticeable under the skin, is dead capillaries that have long lost their original functions. It is no longer possible to cure them, but it is very possible to get rid of them forever. Using a laser, the doctor exerts a targeted effect on the damaged vessel, causing a coagulation reaction in it. After some time, the vessel sticks together and resolves. The cosmetic defect disappears. In addition to spider veins and unsightly blue webs on the legs, coagulation can help you get rid of warts, moles and papillomas.