Lactofiltrum: instructions for use
INSTRUCTIONS
on the medical use of the drug
Lactofiltrum®
Registration number: LSR-008904/08
Trade name of the drug:
Lactofiltrum®
International nonproprietary name or chemical (group) name of the medicinal product:
lactulose + hydrolytic lignin
Dosage form:
pills
Composition per tablet
Hydrolyzed lignin (in terms of dry matter) 355 mg, Lactulose (in terms of 100% matter) 120 mg
Excipients:
croscarmellose sodium 20 mg, magnesium stearate 5 mg, microcrystalline cellulose to obtain a tablet weighing 550 mg
Description:
Capsule-shaped biconvex tablets of dark brown color with white-gray inclusions with a score.
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
enterosorbent
ATX Code:
A07BC
Pharmacological properties:
The pharmacological effect of the drug is due to the properties of the active components - lignin and lactulose.
Hydrolytic lignin is a natural enterosorbent consisting of hydrolysis products of wood components, has high sorbing activity and a nonspecific detoxification effect. Binds in the intestines and removes from the body pathogenic bacteria and bacterial toxins, medications, salts of heavy metals, alcohol, allergens, as well as excess of certain metabolic products, including bilirubin, cholesterol, histamine, serotonin, urea, and other metabolites responsible for the development of endogenous toxicosis.
Non-toxic, not absorbed, completely eliminated from the intestines within 24 hours.
Lactulose is a synthetic disaccharide, the molecule of which consists of galactose and fructose residues. Lactulose is not present in the stomach and upper intestines; absorbed and not hydrolyzed. Lactulose released from the tablets in the large intestine as a substrate is fermented by normal intestinal microflora, stimulating the growth of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. As a result of the hydrolysis of lactulose in the large intestine, organic acids are formed - lactic, acetic and formic, which suppress the growth of pathogenic microorganisms and consequently reduce the production of nitrogen-containing toxic substances. The described process leads to an increase in osmotic pressure in the lumen of the large intestine and stimulation of the peristaltic.
The complex effect of the drug is aimed at normalizing the microbiocenosis of the large intestine and reducing the intensity of endogenous toxic conditions.
The use of the drug in complex therapy of bacterial vaginosis (vaginal dysbiosis) leads to an increase in the effectiveness of therapy, including an increase in the number of lactobacilli in the vagina, as well as effective suppression of the growth of opportunistic flora.
Indications for use:
Disorders of the intestinal microflora (intestinal dysbiosis), including as a result of antibiotic therapy; in complex therapy of irritable bowel syndrome, hepatitis and liver cirrhosis; allergic diseases (atopic dermatitis, urticaria), bacterial vaginosis (vaginal dysbiosis).
Contraindications
Individual intolerance to the drug, intestinal obstruction, gastrointestinal bleeding, galactosemia. It is undesirable to use the drug during exacerbation of gastric and duodenal ulcers, or intestinal atony.
Directions for use and dosage:
Orally, if necessary, after preliminary crushing, with water, an hour before meals and taking other medications. For intestinal dysbiosis:
– adults and children over 12 years old – 2-3 tablets 3 times a day,
– children from 8 to 12 years old – 1-2 tablets, 3 times a day,
– children from 3 to 7 years old – 1 tablet, 3 times a day,
– children from 1 year to 3 years – ½ tablet, 3 times a day.
For bacterial vaginosis (vaginal dysbiosis):
2 tablets 3 times a day.
The average duration of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
Long-term use of the drug and repeated courses of treatment should be carried out only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Side effect
Allergic reactions to the components of the drug are possible, rarely - flatulence, diarrhea.
Overdose:
Symptoms:
constipation, abdominal pain.
Treatment:
stop taking the drug.
Interaction with other drugs:
It is possible that the therapeutic effect of some drugs taken orally may be reduced.
special instructions
The drug can be used in complex therapy together with other drugs, subject to the rules of separate administration.
Release form
Pills.
10 or 15 tablets in a blister pack made of polyvinyl chloride film and printed varnished aluminum foil. 30 or 60 tablets in a plastic bottle with a screw cap or in a polymer jar with a screw cap.
1, 2, 3 or 6 blister packs of 10 tablets each, 2 or 4 blister packs of 15 tablets each, or 1 bottle or 1 jar, together with instructions for use, are placed in a cardboard pack.
Storage conditions
In a place protected from moisture and light at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies:
Over the counter.
Name and address of the legal entity in whose name the registration certificate was issued/organization receiving claims:
JSC "AVVA RUS", Russia, 121614, Moscow, st. Krylatskie Hills, 30, building 9. Tel/fax avva.com.ru
, Russia, 610044, Kirov region, Kirov, st. Luganskaya, 53a. Tel.,
General Director of JSC "AVVA RUS" Egorov A.G.
Advice from a nutritionist for lactose and milk intolerance
“Why do I have such a reaction to milk?” — it is with this question that patients very often come to visit a gastroenterologist. Let's find out!
Milk is an emulsion, and therefore, due to its physical properties, it is a very favorable product for the digestive tract. It has viscosity and enveloping properties, which often has a good effect on the digestive system and the body as a whole.
Milk is a multicomponent product: proteins, fats, carbohydrates. There are as many sides to a product as there are so many possible problems. Complaints about fat content are usually rare, but the carbohydrate composition most often causes complaints, mainly due to the main sugar of milk - lactose!
Lactose intolerance (lactase deficiency) in adults is a fairly common phenomenon and depends both on hereditary predisposition and on the place of residence and tradition of drinking milk. For example, in the northern regions of Europe, lactose intolerance in adults occurs in 25% of the population, and among the indigenous peoples of Africa, Southeast Asia, North and South America, living closer to the equator, its frequency reaches 95%.
Lactase deficiency in adults is divided into secondary and primary. Primary lactase deficiency can manifest itself in childhood and can develop with age. Secondary occurs under the influence of intestinal infections and other causes that cause damage to cells of the small intestine of various origins.
According to the degree of severity, it is divided into hypolactasia - partial enzyme deficiency, and alactasia - complete enzyme deficiency.
What is the difference between lactose and lactase?
Lactose (milk sugar) is a carbohydrate of organic origin, which consists of two molecules of glucose and galactose and is one of the main components of mammalian and human milk. In its undigested form, lactose cannot be absorbed by intestinal cells. Therefore, to assimilate it, a reaction is carried out in the small intestine that separates lactose into its components - glucose and galactose, which, penetrating the cells of the small intestine, enter the general bloodstream and then the liver. In the liver, they are used to synthesize and store glycogen, which is fuel for the processes occurring in our body.
Beneficial properties of lactose
- plays the role of a prebiotic, improving the composition of microflora;
- participates in the synthesis of B vitamins;
- affects the absorption of calcium, magnesium and other microelements and its own enzymatic activity;
- is a source of energy.
Lactase is a special enzyme that is produced by the cells of the small intestine and controls the reaction of lactose breakdown. When the production of this enzyme decreases or stops, undigested lactose enters the large intestine, where a fermentation reaction occurs with the participation of bacteria, which produces an abundance of gases. In addition, if the consumption of dairy products regularly causes loose stools or pain, cramps, then an inflammatory reaction is triggered, which in the future can lead to prolonged duodenitis or functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, changes in the intestinal microflora.
Symptoms of lactose intolerance
The main clinical symptoms are loose stools (diarrhea), bloating, as well as disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract that occur immediately or within 24 hours after drinking milk or dairy products.
In addition, in the presence of intestinal dysbiosis, substances formed during the microbial breakdown of lactose in the large intestine have a toxic effect and can cause general malaise, headaches and, according to some reports, even mental disorders.
People with lactose intolerance are concerned
- diarrhea and loose stools;
- rumbling in the intestines;
- flatulence;
- cramps and pain in the abdomen;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased fatigue;
- weakness.
The intensity of symptoms depends on the quantity and amount of lactose obtained from food and lactase produced by the cells of the small intestine.
What foods contain lactose?
Milk and animal milk products naturally contain lactose, and many industrially manufactured products may contain added lactose. Any product containing milk, lactose, whey, cottage cheese, or milk powder contains lactose, so before purchasing products, you must familiarize yourself with the ingredients listed on its packaging.
Prepared foods that typically contain lactose include:
- cakes, cookies and pastries;
- cheese sauce;
- puree soups;
- custard;
- milk chocolate;
- pancakes;
- omelette;
- some types of mashed potatoes.
Some products may contain “hidden lactose” and its content may not be declared on the packaging. Examples of products with hidden lactose:
- granola bars;
- bread;
- breakfast cereals;
- margarine;
- some instant soups;
- lollipops, chocolates and chocolates;
- ham or sausage;
- sauce or salad dressing and mayonnaise.
About 20% of prescription drugs, such as birth control pills, and about 6% of over-the-counter drugs, such as those for heartburn, contain lactose. Therefore, people with lactose intolerance (especially alactasia) should tell their doctor about it when prescribing new medications.
How to replace milk if you are lactose intolerant?
Dairy products are a good and affordable source of calcium, proteins and vitamins. Therefore, people with lactose intolerance need to use alternative sources.
Some people with reduced lactase production retain some lactase activity and can include varying amounts of lactose in their diet without experiencing symptoms. For example, they have difficulty digesting fresh milk but eat certain dairy products, such as cheese or yogurt, without discomfort. These products are made using fermentation processes that break down most of the lactose in milk. In this case, yoghurts with live cultures, cheeses in which lactose has already been fermented by bacteria, or low-lactose dairy products are recommended.
If it is necessary to completely eliminate milk, you can use lactose-free milk, in which lactose has already been broken down into glucose and galactose, as well as its plant alternatives - nuts (almond, cashew, etc.), flaxseed, cereals (oatmeal, rice, buckwheat, etc.), coconut or soy milk. Grocery stores often offer a wide selection of lactose-free alternatives to various foods.
Instead of milk, you can add calcium sources of plant and animal origin to your diet:
- sesame;
- nuts and seeds;
- soy milk and cottage cheese;
- legumes;
- greens - dill, parsley;
- fatty fish such as salmon, tuna and mackerel;
- eggs.
Alternative sources of vitamin A include:
- carrots, broccoli, sweet potatoes, pumpkin,
- melon, apricot, papaya, mango;
- legumes;
- liver, eggs.
Vitamin D levels can be increased through exposure to natural sunlight, fatty fish, eggs, fish oil and some fortified foods.
Basic principles of a lactose-free diet
For both primary and secondary lactose intolerance, a lactose-free diet is the mainstay of treatment. Successful adherence to it ensures recovery and cessation of disturbing symptoms.
The diet is selected individually depending on the severity of symptoms and involves limiting or excluding foods containing lactose from the diet. The duration of the diet also depends on the cause of the disorder and the severity of the symptoms. The amount of lactose that can be consumed without harm to health depends on the nature of the disorder. Many people have residual lactase enzyme activity, so everyone needs to determine their individual lactose tolerance threshold after consultation with their doctor.
When using a product with lactose, two factors are taken into account - the amount of milk sugar in it and its volume. To create a diet, it is convenient to use tables with lactose content per 100 g of product.
The basis of the diet for a lactose-free diet is products that do not contain lactose. Lactose-free dairy products are a good replacement for conventional products.
low-lactose dairy products :
- fatty foods - butter, cream;
- fermented foods - cheeses, yoghurts, fatty cottage cheese.
The higher the fat content, the lower the milk sugar content.
When preparing dishes, almond, soy, oat milk and any other plant-based drinks will help replace regular milk. Using alternative milk, you can make not only drinks, such as smoothies or cocktails, but also pancakes, omelettes, waffles and baked goods.
The diet of a person with lactose intolerance should be balanced and replenish the protein, vitamins and calcium that he is deprived of, excluding dairy products.
If you are concerned about symptoms of lactose intolerance, do not switch to a lactose-free diet without consulting your doctor. It is possible that these symptoms may be caused by other causes, and in particular inflammatory bowel disease. Food additives (enzymes containing lactase) can be an addition to the diet; they are taken in capsules or added to milk, or used in the home production of lactose-free fermented milk products.
Cow's milk protein food intolerance in adults
It remains to discuss the last facet of milk - protein . We will mainly discuss cow's milk protein as the most common protein consumed in our country.
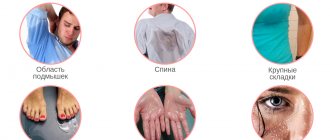
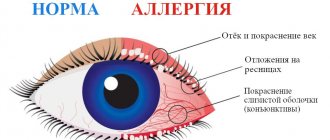
Most often, it, as a “foreign” protein for our body, can trigger allergic reactions that are detected in childhood due to the brightness of the manifestations - rashes, skin itching, vomiting or Quincke's edema after consuming cow's milk or products made from it.
In adulthood, food intolerance to cow's milk protein is more common - this is a slow reaction of the immune system with sluggish, but no less inconvenient symptoms: bloating, unstable stool, cramps, pain, belching, mild periodic incomprehensible skin itching, general weakness, aching pain in the joints. In the case of this reaction, the main thing is that against the background of the symptom, local inflammation does not start - the gastrointestinal tract or systemic.
For these purposes, elimination diets or restriction in the consumption of certain food groups are used. The timing should be determined by a doctor; it is also important to prevent a lack of protein, vitamins D, calcium in the diet and to select the best available replacement for all components of cow's milk and fermented milk products made from it.
You can get advice from a nutritionist-gastroenterologist specializing in the management of patients with milk intolerance (lactase deficiency and milk protein food intolerance) at the Expert Gastroenterological Center. For express diagnostics of the above conditions, we suggest using the comprehensive LactoCheck program developed by the center’s specialists.
How it works
It is a mistake to think that rashes, dryness or other skin problems will go away on their own. Makeup is just a mask that hides the visible part of the problem. Truly beautiful and healthy skin depends on gut health.
Intestinal dysfunction and dysbacteriosis can provoke acne, allergic skin rashes, pigmentation, peeling, redness and other problems.
If you have such problems, take the test and find a solution
A special case is allergic rashes caused by atopic dermatitis. Read about the use of Lactofiltrum® for allergies here.
A modern innovative dual-action drug Lactofiltrum® has a complex effect on the body, restoring the balance of intestinal and skin microflora, reducing the toxic load, the drug helps to improve skin health and restore natural beauty.
- sorbent, which cleanses and removes toxins from the body;
Lactofiltrum® contains a natural sorbent - lignin.Lignin is a unique natural sorbent produced according to international quality standards. The efficiency of lignin is much higher than that of the popular activated carbon - for example, 2500 times for the sorption of E. coli! At the same time, lignin is safe and can be used by very young children, pregnant and lactating women. An important property is that lignin does not damage the mucous membrane of either the stomach or intestines. It is known that activated carbon cannot be used for more than 10-14 days, precisely because there may be ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane. Lignin is recommended for long-term detoxification courses. Lignin is not just a sorbent; scientific research shows the presence of immunotropic (immune-strengthening), anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects.
- prebiotic , restoring intestinal microflora.
The function of a prebiotic in the composition of Lactofiltrum® is performed by lactulose , which helps restore the own beneficial microflora of the intestines and skin and also has immunotropic properties.
How does Lactofiltrum work?
Lactofiltrum® Healthy intestines - beautiful skin!
10 reasons to choose Laktofiltrum
- Lactofiltrum is the effect of two drugs at once: enterosorbent + prebiotic. Lignin cleanses and removes toxins, lactulose restores the balance of microflora.
- Lactofiltrum is 2500 times more effective than activated carbon in sorption of harmful bacteria and toxins.
- Laktofiltrum does not damage the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, and can be recommended for long-term use , unlike activated carbon and other sorbents.
- Lactofiltrum does not cause constipation even with a long course of use.
- Lactofiltrum helps to successfully cope with intestinal dysbiosis. The result is improved overall health and strong immunity.
- Lactofiltrum helps solve skin problems associated with skin and intestinal dysbiosis. Visible skin improvement after 4 weeks (confirmed by 80% of women).
- Lactofiltrum can be taken by pregnant and lactating women; it is safe .
- Lactofiltrum can be taken even by small children! Which is especially important for children suffering from allergies and dermatitis.
- Lactofiltrum is perfect for course detox programs .
- Lactofiltrum, thanks to its complex action, helps fight allergic skin rashes, quickly removes allergens from the body , and relieves itching.
How to take the drug
- Take 1-1.5 hours before or after meals and medications.
Dosage:
- 2-3 tablets 3 times a day, with plenty of water. The tablet can be crushed.
Admission course
- 21 days - to restore healthy and beautiful skin.
- from 14 days or on the recommendation of a doctor - for other indications.
The drug can be used in complex therapy with other drugs, subject to the rules of administration.
Can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Contraindications: individual intolerance to the components of the product.
Lactofiltrum, tablets 500 mg, 30 pcs.
Manufacturer
ABVA RUS, Russia
Compound
Composition per tablet:
Hydrolytic lignin (in terms of dry matter) - 355 mg
Lactulose (calculated as 100% substance) - 120 mg
Excipients:
Croscarmellose sodium - 20 mg
Magnesium stearate – 5 mg
Microcrystalline cellulose - to obtain a tablet weighing 550 mg
pharmachologic effect
The pharmacological effect of the drug is due to the properties of the active components included in the composition - lignin and lactulose.
Hydrolytic lignin is a natural enterosorbent consisting of hydrolysis products of wood components, has high sorbing activity and a nonspecific detoxification effect.
Binds in the intestines and removes from the body pathogenic bacteria and bacterial toxins, medications, salts of heavy metals, alcohol, allergens, as well as an excess of certain metabolic products, including bilirubin, cholesterol, histamine, serotonin, urea, and other metabolites responsible for development of endogenous toxicosis. Non-toxic, not absorbed, completely eliminated from the intestines within 24 hours.
Lactulose is a synthetic disaccharide, the molecule of which consists of galactose and fructose residues. Lactulose is not absorbed or hydrolyzed in the stomach and upper intestines. Lactulose released from the tablets in the large intestine as a substrate is fermented by normal intestinal microflora, stimulating the growth of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
As a result of the hydrolysis of lactulose in the large intestine, organic acids are formed - lactic, acetic and formic, which suppress the growth of pathogenic microorganisms and consequently reduce the production of nitrogen-containing toxic substances.
The described process leads to an increase in osmotic pressure in the lumen of the large intestine and stimulation of peristalsis. The complex effect of the drug is aimed at normalizing the microbiocenosis of the large intestine and reducing the intensity of endogenous toxic conditions.
The use of the drug in complex therapy of bacterial vaginosis (vaginal dysbiosis) leads to an increase in the effectiveness of therapy, including an increase in the number of lactobacilli in the vagina, as well as effective suppression of the growth of opportunistic flora.
Indications
Disorders of the intestinal microflora (intestinal dysbiosis), including as a result of antibiotic therapy; in complex therapy of irritable bowel syndrome, hepatitis and liver cirrhosis; allergic diseases (atopic dermatitis, urticaria), bacterial vaginosis (vaginal dysbiosis).
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
There are no data on the safety of using the drug Laktofiltrum during pregnancy, lactation and in children.
Contraindications
Individual intolerance to the drug, intestinal obstruction, gastrointestinal bleeding, galactosemia. It is undesirable to use the drug during exacerbation of gastric and duodenal ulcers, intestinal atony.
Side effects
Allergic reactions to the components of the drug are possible, rarely - flatulence, diarrhea.
Interaction
The therapeutic effect of some drugs taken orally may be reduced.
How to take, course of administration and dosage
Orally, if necessary, after preliminary crushing, with water, an hour before meals and taking other medications.
For intestinal dysbiosis:
- adults and children over 12 years old - 2-3 tablets 3 times a day; - children from 8 to 12 years old - 1-2 tablets 3 times a day;
- children from 3 to 7 years old - 1 tablet 3 times a day;
- children from 1 year to 3 years - 1/2 tablet 3 times a day.
For bacterial vaginosis (vaginal dysbiosis):
2 tablets 3 times a day.
The average duration of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
Long-term use of the drug and repeated courses of treatment should be carried out only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Overdose
Symptoms: constipation, abdominal pain.
Treatment: stop taking the drug.
Special instructions
Precautions when taking the drug
The drug can be used in complex therapy together with other drugs, subject to the rules of separate administration.
Interaction with alcohol
There is no data on interaction with alcohol.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
The drug is approved for use as a means of OTC.
Release form
Pills
Storage conditions
In a place protected from moisture and light at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Best before date
3 years
Active substance
Lactulose, hydrolytic lignin
Dosage form
pills
Barcode and weight
Barcode: 4607003669010, 4680020231668 Weight: 0.025 kg