Diseases that begin with the letter “L”: Lactostasis, Laryngitis, Laryngotracheitis, Cor pulmonale, Pulmonary fibrosis, Leukemia, Leukemia in children, Leukoplakia, Leucinosis, Leprosy, Dental treatment, Lymphadenitis, Lymphangitis, Lymphogranulomatosis, Lymphoma, Lymphostasis, Lipoma, Listeriosis , Lichen, Pediculosis pubis.
Ringworm belongs to the group of dermatological diseases of the fungal and viral type. It is characterized by the appearance of dry or weeping areas of skin that periodically itch severely. Ringworm is a fairly common disease and it is customary to distinguish several varieties depending on:
- causes of occurrence (causative agent);
- type of change in the structure of the skin;
- location;
- degree of infectiousness to others.
The disease has a long development period and a high risk of relapse.
What is ringworm?
Ringworm is an infectious skin disease caused by the parasitic fungi Microsporum canis and Trichophyton tonsurans, it is part of the group of ringworms that primarily affect the skin, hair and nails. This is an infectious dermatological pathology caused by dermatophyte fungi. It is also called dermatomycosis, scab, micro- and dermatophytosis.
Doctors distinguish several types of ringworm, depending on the location, nature of the course and the causative agent.
The main types of the disease are:
- chronic or ringworm of smooth skin;
- surface;
- ringworm of the nail plate;
- infiltrative-suppurative.
Since ringworm is caused by two types of fungi, in medicine it is diagnosed as microsporia and trichophytosis. These fungi have persistent pathogenicity, pronounced virulence and often cause acute diseases with varied clinical manifestations.
A disease caused by fungi of the genus Microsporum canis is microsporia. Depending on the location, there is microsporia of smooth skin and microsporia of the scalp.
Trichophytosis is caused by the activity of the dermatophyte Trichophyton tonsurans, which, through the anthroponotic route of infection, causes inflammation of the scalp and smooth skin, and through the zootroponotic route, inflammation in the deep layers of the dermis, accompanied by suppuration.
The presence of fungal spores does not always provoke damage to the skin and its appendages. The transition of the fungus from an inactive state to a pathogenic state is facilitated by metabolic and endocrine disorders, immune diseases, hypovitaminosis or vegetative-vascular dystonia. This increase in the pathogenicity of dermatophytes provokes an exacerbation of inflammatory processes, the spread of the fungus through the blood and lymph flow.
The disease is weakly expressed during the development of a latent infection and when localized in previously affected areas, and the high virulence of the fungus is formed during a relapse, gradually decreasing during the course of the infection.
Symptoms of ringworm: At the end of the incubation period, itchy ring-shaped spots of red-pink color appear on the skin, on the surface of which bubbles appear, after which a crust and peeling remain. The hair at the site of the lesion breaks and falls out.
Normally, the immune system is able to cope with the pathogen and prevent its activity, but there are a number of factors that increase the risk of ringworm, namely:
- skin microtraumas;
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- prolonged contact with the source of infection;
- high humidity and air temperature;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases, etc.
In a situation where there is an adult or child with lichen at home, it is necessary to take preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of its spread, namely:
- use separate towels and bed linen;
- wash your hands thoroughly with soap, especially if you touched the patient’s things;
- use gloves when touching areas of disease;
- undergo examination and take tests to identify pathogens, etc.
The main method for diagnosing ringworm is the use of a Wood's lamp, under the light of which the affected areas acquire a characteristic greenish glow. Microscopic examination and culture of skin and hair scales are effective to confirm the diagnosis.
Timely diagnosis and a properly selected treatment regimen can effectively eliminate ringworm in children and adults, preventing its spread. The pathology is prone to relapse, since the presence of spores of viable fungi can cause repeated damage. It is extremely important to complete the course of treatment and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
Reasons for development
The natural chemical composition of the secretion of the sebaceous glands of the skin contains linolenic acid. It prevents the proliferation of fungi. When the function of the sebaceous glands is impaired (hypo- or hyperfunction), pathogenic microorganisms, including fungi, begin to develop on the skin. They are present on the surface of the skin and are normal, but in small quantities. When the pH of the skin changes, fungi begin to multiply and negatively affect the skin epithelium.
The reasons for the development of seborrheic dermatitis include the following factors:
- proliferation of the yeast-like fungus Malassezia, which changes the composition of the skin microflora;
- prolonged exposure to stress;
- hormonal disorders, which often occur in adolescence, with malfunctions of the thyroid gland;
- adverse environmental influences (for example, water quality, dry indoor air during the heating season, sudden changes in climatic conditions);
- taking certain medications, using cosmetics that cause skin irritation;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract
- hereditary predisposition.
In addition, the development of seborrheic dermatitis is facilitated by factors such as poor personal hygiene, obesity, and frequent consumption of spicy, salty, and sweet foods.
How is ringworm transmitted?
Ringworm is transmitted in two ways:
- from a sick animal – zoonotic with an incubation period of one week;
- from an infected person – anthroponotic with an incubation period of up to 6 weeks.
Children are at risk because they most often come into contact with the carriers of the pathogens of this disease - cats and dogs. Children's skin is characterized by low density of the stratum corneum and weak protective properties of the water-lipid mantle. The stratum corneum prevents the penetration of the fungus into the layers of the skin, since its spores are located between the horny scales, and the water-lipid mantle forms a barrier to the penetration of pathogens.
The infection is also transmitted by non-compliance with personal hygiene standards and the use of other people's personal belongings containing fungal spores (hats, combs, bed linen, etc.).
How does ringworm begin?
Favorable conditions contribute to the introduction and reproduction of a pathogenic fungus in the skin, triggering the infectious process. In the initial stages, this period is asymptomatic. After which the development of the pathology acquires clinical manifestations, the signs of which depend on the stage of the pathology.
The stages of the infectious process during the development of ringworm are:
- incubation period;
- period of mushroom growth;
- refractory stage (period of insensitivity, rest);
- regression.
In the skin, the fungus forms branched mycelium, which gradually invades new areas of the skin, while old lesions become the location of its spores. This period of fungal growth is determined by the rapid increase in the colony of the pathogen, active division of skin cells and the high rate of exfoliation of the affected epidermis.
Since most often the growth of the colony outstrips the rate of change of the stratum corneum, the infectious process spreads. An intense immune reaction (inflammation) in the lesion is displayed in the form of a red ring, which, in the chronic course of mycosis, becomes the permanent residence of the pathogen.
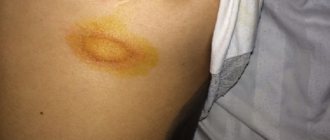
What does ringworm look like?
Clinical manifestations of ringworm depend on the type of pathogen, course and stage of the disease. Dermatophytes secrete enzymes and toxins that destroy keratin protein (they feed on it), so the severity of symptoms directly depends on the ability of fungi to produce these substances.
Common symptoms of ringworm on the scalp are:
- hair thinning;
- the appearance of localized peeling of the skin;
- redness of the epidermis;
- hair breaking off at the root;
- the appearance of small bubbles with cloudy contents along the edges of bald patches, after opening which yellow crusts form.
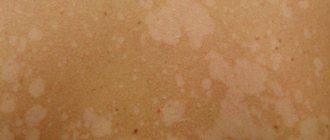
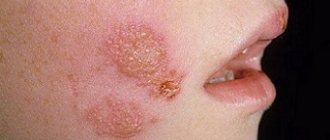
Ringworm of smooth skin includes the following symptoms:
- pronounced itching;
- the appearance of round red spots;
- light epidermis at the site of damage, surrounded by gray scales;
- the edges of the damaged area consist of pink-red bubbles;
- growth of the lesion in diameter.
The chronic form of the disease is accompanied by the presence of microscopic blisters on the affected areas, the formation of scars after their opening and severe itching. In a situation where the site of the lesion is the nail plate, its separation, discoloration and thickening are observed.
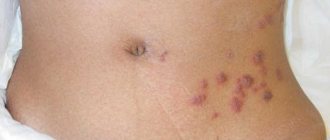
Ringworm of the infiltrative-suppurative form is characterized by the appearance of large bright red spots up to 10 cm in diameter, the outer surface of which is lumpy and uneven, and purulent follicles form along the edges. Pain, swelling and hyperemia of the affected areas are also observed.
The appearance of the first signs of the disease requires a mandatory visit to a dermatologist. The lack of qualified treatment can lead to the rapid spread of infection throughout the body and cause a number of complications: tissue scarring, death of hair follicles, allergic reactions and the addition of a secondary infection.
Treatment of rosea lichen Zhibera - outdated and modern methods
The pathogenesis of pink dandruff remains in the realm of more or less probable speculation. Therefore, treatment of patients should be aimed at relieving symptoms and preventing possible complications.
Misunderstanding of the cause of the disease has led to various attempts at treatment in the past.
In 1922, Burchardt wrote in his textbook Diseases of the Skin: “Pityriasis rosea does not require intensive treatment... the use of strong drugs can sometimes make the situation worse, since they aggravate the inflammatory symptoms, unnecessarily irritate the skin and cause itching. In most cases, it is sufficient to recommend starch baths at 28 degrees 2 times a week and lubrication once a day with 10% zinc ointment with the addition of salicylic acid or 1-2% resorcinol, sulfur (1-3%), thiol or ichthyol (up to 5% )".
Uch. Roxburgh recommended 2% salicylic ointment at night to exfoliate the lesions in most cases, followed by exposure to ultraviolet light. Instead of ultraviolet light, it was recommended to use a 20-minute bath with the addition of potassium permanganate or sodium thiosulfate, and then apply salicylic ointment. Other authors write about the effectiveness of using 2% salicylic ointment twice a day.
2% salicylic ointment
Sutton recommended bathing in a 1% mercuric chloride solution. Opponents of treatment with sulfur and mercury preparations recommended lubricating the lesions with a paste that reduces itching. They emphasized the importance of frequent bathing. Marshall wrote that when itching predominates, it is useful to use a mixture of zinc oxide and lime water with the addition of 2% phenol.
They tried to dissolve the scales with an aqueous saline solution. A 2% eosin solution, a 6% alcoholic solution of bergamot oil, tar, olive oil and lime water in 0.25% menthol were used.
It is currently believed that active treatment of pityriasis rosea that is not accompanied by itching is not necessary. And in case of itching, it is recommended to rub it with weak corticosteroid drugs in the form of creams and lotions, selected by a dermatologist. The patient should be instructed not to use harsh soaps or wear tight clothing due to the potential for irritation.
Other external methods that have been used in extensive cases include radiation therapy. Some scientists recommended irradiating each side of the body in turn, suggesting that the most effective therapy was started at the beginning of the inflammation, and that after a week there should be some improvement. Others have written about superficial radiation therapy, which involves taking a single dose or a small portion of it.
There are scientists who recommended using a quartz lamp in difficult cases so as not to cause an erythematous reaction. Others have emphasized the role of ultraviolet light in clearing lesions more quickly, while pointing out the potential for discoloration of spots that persist for months. It is recommended to use erythematous-exfoliating doses - sometimes one such dose is enough.
More recent studies have included UVB radiation used daily for 5 days at doses that cause erythema. The treatment reduced itching and suppressed the development of lesions. The remaining authors started with 80% min. dose causing erythema, and increased it by 20% with each subsequent irradiation. Itching with this treatment may disappear even within 24 hours.
UV-B radiation
In general treatment of PR, attempts have been made to administer streptococcal vaccines, staphylococcal toxoid, fungal and yeast extracts, milk injections, salicylates, calcium bromate, calciferol, and potassium iodide. There are reports of very beneficial effects of a single injection of typhoid vaccine.
In 1940, academician Willes and Klumpp used convalescent plasma (5 cm intramuscular) and human gamma globulin to treat pityriasis rosea. The latter, administered in the first week of treatment, changed the course of the disease, while its administration later, like convalescent plasma, did not affect the outcome.
In 1948, student. Grzybowski argued that the correct treatment of pink dandruff is the administration of antistreptin in the amount of 4.0-5.0 g or cibazol in the amount of 6.0-8.0 g per day for 4-5 days, sodium bromide and autohemotherapy.
In the same year, Hallstrom reported the beneficial effects of bismuth and salvarsan, and 2 years later the Polish Medical Weekly reported rapid regression of lesions after intramuscular injection of 4-6 injections of 10% bismuth oil suspension every 2 days, 1 ml. every. The good effect of the therapy was so rapid that it was postulated that bismuth would become a specific treatment.
A successful attempt was made to administer streptomycin. Injections of penicillin in various doses: 300,000 units, 450,000 and 500,000 units did not bring the expected results. Supportive measures were taken including vitamin C (0.5 g/day) and vitamin B (20).
Another drug that has been used to treat PR is Encortone. Even without external treatment in small doses (5 mg), this turned out to be a fast and effective method. More recent studies have shown that steroids may need to be prescribed in general from time to time to control very generalized lesions. Prednisolone was used intramuscularly at a daily dose of 15-40 mg. For blisters that do not respond to general steroids, dapsone 100 mg twice daily is recommended for short-term treatment.
Recently there has been interest in erythromycin. Adults were prescribed 250 mg/day 4 times a day, children - 20-40 mg/kg/body weight, in 4 divided doses. Some experts claim that the effect of this method is comparable to placebo, while others argue that since it is impossible to specify the exact cause and the exact treatment, trials of erythromycin treatment that produce results are recommended and safe.
Oral antihistamines are now recommended in cases of itching. Rare oral symptoms can be relieved with toothpaste containing diphenhydramine hydrochloride or tetracycline hydrochloride.
How is ringworm treated?
In each case, treatment for ringworm should be selected individually, since its composition and duration have their own specifics and are determined by the type, location and stage of the pathology.
Only prescriptions from a dermatologist are effective; they take into account the current clinical picture, the characteristics of the patient’s physical health and his age.
Therapy is aimed not only at relieving the symptoms of the pathology, but also at inactivating the pathogen. The chronic form of the disease also provides support for the immune system, normalization of metabolism and hormonal levels.
The following groups of drugs are used to treat ringworm:
- systemic and local antimycotics;
- antiseptic solutions;
- multivitamin complexes.
Correct treatment of pink dandruff in Gibert's disease
Treatment of pityriasis rosea is primarily based on the diagnostic results and recommendations of the dermatologist based on his knowledge and experience. Independent attempts to cure pathology usually lead to the appearance of accompanying symptoms, sometimes very dangerous.
Considering the symptoms, the dermatologist prescribes:
- ointments with corticosteroids acting in several directions - relieve skin tightness and accelerate the healing of the rash;
- antiallergic - antihistamines - relieve itching;
- immunomodulators – stimulate natural immunity;
- antiseptic solutions – prevent secondary infection;
- dandruff softening ointments.
During treatment, the dermatologist recommends:
- Avoid hot water procedures and swimming. Showering with a soft sponge is allowed;
- Wear loose, natural underwear. Synthetics do not allow the skin to breathe, exacerbating symptoms;
- Eliminate allergens: eggs, chocolate, red fruits.
- Reduce fried, flour, smoked foods;
- Do not use cosmetics.
How long does it take to treat ringworm?
The treatment process for ringworm is lengthy, usually taking at least six weeks, with systemic therapy lasting mainly 15-25 days.
The effectiveness of therapy is assessed using laboratory tests. In a situation where tests indicate a significant decrease in the number of fungal spores after 2 weeks of a medication course, it is necessary to continue the chosen treatment. In some cases, fungal shedding can last for several months.
After the signs of pathology disappear, you need to scrape the epidermis three times in previously damaged areas:
- immediately after completion of therapy;
- 7 days after therapy;
- after 2-3 months.
The result of therapy is considered successful if all three tests show negative results.
Diagnostics
Sometimes, to determine the type of lichen, an external examination and collection of anamnesis is enough - a history of the development of symptoms of the disease and possible connections with risk factors (hypothermia, contact with pets). But in some cases, the diagnostic search turns out to be more difficult.
To correctly determine the type of lichen, the dermatologist carries out:
- visual inspection;
- examination using a Wood's lamp (“black lamp”);
- examination of scraping damaged skin under a microscope.
Also, to assess the general state of health, doctors often prescribe blood and urine tests, and a study of the immunological status.
How to treat ringworm in children?
Treatment of ringworm in a child is the responsibility of a pediatric dermatologist, since the characteristics of the child’s body require special doses and composition of medications.
Hygiene and child care are also important elements of pathology therapy:
- boiling and ironing clothes in contact with affected areas of the skin;
- treating household surfaces with disinfectants to prevent the spread of spores;
- frequent change of bed linen;
- washing in the shower rather than the bath, etc.
Self-medication: consequences and dangers
Scratching the rash can cause scars to form on the skin.
Photo: LaCameraChiara / Depositphotos Treatment of lichen without the help of doctors most often turns out to be ineffective - it is almost impossible to independently determine the exact cause of the disease. Self-medication can also be dangerous - for example, erroneous use of antibiotics for herpes zoster not only affects the manifestation of a viral disease, but also causes a toxic effect on the body and the development of antibiotic resistance in the future. A common complication of herpes zoster is postherpetic neuralgia. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, any of the variants of the disease can progress, become more difficult to treat, become a chronic pathology and cause the formation of irreversible changes on the skin - scars.
Can I go to work or school with ringworm?
The presence of this diagnosis requires isolation of the patient from the team for at least two weeks. In schools and other children's institutions, it is mandatory to notify parents for timely detection of the disease in other children.
The disappearance of ringworm symptoms and 3 negative tests for the presence of fungus are a reason to return to school or work.
If a dermatomycosis infection has been detected in a team, then to prevent pathology, you can use antifungal shampoos for some time, carry out wet cleaning with the addition of antiseptic solutions, and strictly observe personal hygiene.
- Treatment of lichen in Kharkov;
- treatment of lichen in Uzhgorod;
- treatment of deprivation in Sumy;
- treatment of lichen in Poltava;
- treatment of lichen in Odessa;
- treatment of deprivation in Nikolaev;
- treatment of lichen in Mariupol;
- treatment of deprivation in the Dnieper.
3
1
1
Article rating:
3.8 out of 5 based on 5 ratings
Author: Mangusheva Victoria Yurievna
Dermatovenerologist, trichologist. Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category. Work experience more than 10 years.