Nail fungus or onychomycosis is an infectious contagious disease caused by microscopic pathogenic fungi. It occurs 5 times less often in children than in adults. However, if changes appear on the child’s nail plate, this diagnosis cannot be excluded. It accounts for 15% of cases of all nail pathologies in children. Over the past few years, there has been a tendency in pediatrics to increase the incidence of onychomycosis.
Symptoms
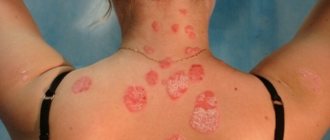
With microsporia, clearly defined spots, oval or round in shape, appear on the skin.
Foci of lesions appear on the scalp, in which the hair is broken off at a height of 5-6 mm, and nearby skin tissues are covered with grayish-white scales. With keratomycazos, yellowish-brown or pink spots appear on the back, chest, sides of the body or abdomen. Over time, they can change their color (pityriasis versicolor) or cause peeling and itching of the surrounding skin (pityriasis versicolor).
A common type of fungus in young children is trichophytosis, which has the following symptoms:
- brittleness, dullness and loss of elasticity of hair;
- the formation of round bald spots covered with flaky particles;
- pale color of the central part of the lesion.
Characteristic symptoms of candidiasis include a white coating on the face and mouth, a vesicular rash and the appearance of ulcers localized in natural folds of the skin.
If you identify the symptoms described above, you must make an appointment with a pediatric dermatologist. Parents should be aware that after an illness, the child’s body does not develop lasting immunity, which can lead to re-infection.
Fungal infections in children
The traditional increase in the incidence of fungal infections in children, colloquially called “ringworm”, and in medical language dermatophytosis, occurs in the autumn months - September, October and November. Another peak in incidence may occur in the spring.
These diseases are caused by fungi of the genera Microsporum and Trichophyton, which are classified as dermatophytes. At the same time, ring-shaped lesions appear on the skin (interestingly, in English they are called ringworm, literally a ring-shaped worm). If the fungus gets on the scalp covered with hair, areas of hair breakage and hair loss occur.
Dermatophyte fungi require keratin for their growth, and their distribution in the human body is limited to structures containing this protein - hair, nails and skin. Some dermatophytes spread directly from one person to another (anthropophilic organisms). Others live and are transmitted to humans from the soil (geophilic organisms), and still others spread to humans from animals (zoophilic organisms). In animals, an asymptomatic course of infection is possible, which can lead to human infection from an apparently healthy animal. Ringworm most often occurs in kittens, cats and dogs; small domestic rodents such as guinea pigs or hamsters and farm animals can also become ill. Transmission of infection can also occur indirectly through contact with household items contaminated with fungi (such as upholstery, combs, hats). Due to the protective properties of the skin, children and young women are usually affected. The incubation period from the moment the fungus gets on the skin to the appearance of visible skin changes or hair breakage and loss when infected with different types of fungi can range from several days to 1.5 - 2 months.
To confirm the diagnosis of dermatophytosis, the doctor may conduct an examination under ultraviolet rays (Wood's lamp). A greenish glow will only appear during infection with certain types of fungi of the genus Microsporum, so the absence of a glow does not exclude the diagnosis of dermatophytosis. To identify the disease, it is necessary to examine skin flakes or hair from the lesions under a microscope. To exclude infection, the study must be carried out until several (up to five) negative results are obtained. Receiving even one positive result allows you to diagnose a fungal infection and begin treatment.
How to protect yourself from infection:
- do not use other people’s clothing or personal hygiene items;
- Make sure your skin is clean and dry;
- wash your hands with soap and running water after playing or contacting animals;
- thoroughly vacuum and clean animal habitats in the house;
- if there is a sick animal in the house, wear gloves when caring for it, vacuum and treat its habitats in the house with a disinfectant solution;
- If you suspect that an animal has ringworm, you need to contact a veterinarian and examine all the animals living in the house.
Author:
Vera Removna Voronina , dermatologist
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, a consultation with a mycologist is necessary.
After clarifying the patient’s complaints and reviewing the provided medical documentation, the specialist prescribes a list of laboratory tests, which include:
- visual examination of the patient under a Wood's lamp, revealing uncharacteristic glow of the scales;
- collection of clinical material to determine the type and tissue form of mycoses;
- Sowing the scrapings separated for microflora helps to determine the susceptibility of a particular fungal disease to chemotherapy drugs.
Diagnostic methods
To effectively treat nail fungus in children, the doctor accurately determines the causative agent of the infection. For this purpose, not only a visual inspection is carried out, but also laboratory diagnostics:
- microscopic examination of scrapings from affected areas of the skin and nail plate;
- bacteriological cultures with a high probability of bacterial infection;
- PCR to determine the causative agent of the disease.
If necessary, a small patient can be referred to other specialists.
Treatment
Therapy for this pathological process is carried out on an outpatient basis, but if this does not bring the required results or the course of the disease is complicated, the patient is admitted to a specialized hospital.
The affected areas of the outer skin are treated daily with medication, serous crusts are removed at the source of infection and the hair is shaved off.
The use of antifungal ointments, antifungal pastes, creams and emulsions is also indicated. If complications occur, laser therapy of damaged areas or surgical removal of the nail plate is possible.
To achieve a greater effect, decimeter (UHF) therapy, darsonvalization and medicinal electrophoresis are used.
Symptoms and manifestations
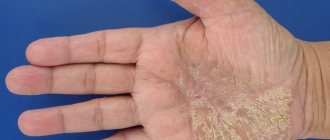
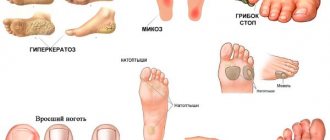
Nail fungus in a child can be suspected by characteristic signs, such as yellowness or gray color of the nail plate, changes in its structure. Furrows and stripes may appear on the nails, redness and dryness of the surrounding skin. The child notes itching and burning of the skin of the feet.
The skin between the toes may also be affected. If left untreated, the nail may thicken, crumble, and the skin becomes covered with cracks, which is accompanied by pain, bleeding, and makes walking very difficult. If the integrity of the skin is compromised, the likelihood of a secondary bacterial infection increases.
gormed.su
Despite the wide variety of mycotic skin lesions in children, they all have much in common, for example, they are accompanied by redness, itching, a grayish coating, dry skin and other symptoms. Of course, each type also has its own individual symptoms, such as hair loss, specific discharge, etc. What are the general principles of treatment for dermatomycosis in children?
What determines the choice of treatment regimen?
It is much easier to cope with a fungal disease in the early stages, therefore, if you discover signs of it in your son or daughter, you should immediately make an appointment with a dermatologist. Under no circumstances should you begin self-treatment by turning to traditional medicine for help: there are a huge variety of fungi, which means there is a high probability of not only not helping, but also harming your child.
After the examination, the doctor will conduct special tests - scraping or culture, the results of which will help determine which fungus caused the rash. Only based on this information, as well as after analyzing the general clinical picture and health status of the young patient, can a course of treatment be prescribed.
How is the treatment process organized?
Mycoses are treated both on an outpatient basis and in a hospital if the disease has reached an acute stage or has a complex form. In general, recovery occurs after 2-4 months. Patients are prescribed:
- ointments and creams for topical use;
- plasters, varnishes, if we are talking about nail fungus;
- drugs for oral administration, for example Diflucan, which has repeatedly proven its effectiveness and safety in the case of young patients.
Most modern antifungal drugs are designed for several types of fungi at once, but this does not mean that you can independently “prescribe” the one that the pharmacy recommends to you as the best. It is equally important to choose not only the drug, but also the dosage, which depends on the type of fungus and the age of the patient. Only a doctor can cope with this task. If you exceed the dosage, the experiments will, at best, end in the treatment of food allergies, and at worst, poisoning the child’s body.
What is the prevention of microsporia in children?
A child can become infected with a fungal disease from a stray animal, in which it is often asymptomatic. Therefore, for preventive purposes, it is better to protect the baby from such contacts. If there is a danger of becoming infected from a person, for example a close relative, total disinfection of the room and things will be required. Even the walls and floors are treated, especially in the bathroom. The underwear and clothes of the infected person are washed at high temperatures and ironed on both sides.
Even if everything is clear to you, you still shouldn’t experiment with a fungal disease on your own child. The child's body does not tolerate all medications. In addition, the doctor will recommend safe products to improve the condition of the skin and give other useful tips that will help your son or daughter get rid of this annoying disease faster.
How to avoid thrush in a child:
- the most important thing is strict adherence to child and personal hygiene;
- you also need to make sure that you yourself do not suffer from thrush;
- timely hygiene of the child after defecation;
- do not lick baby pacifiers (as the risk of fungal infection increases), you should always have several sterile pacifiers in stock;
- do not bathe your baby in a shared bathroom (this can even lead to the development of other diseases);
- You should avoid keeping your child in a diaper or nappy for a long time (this will prevent the growth of fungi);
- regularly check the condition of the child’s genitals: there is no redness or discharge;
- For preventative purposes, it is necessary to regularly sterilize baby bottles and nipples.
If a pathology caused by fungi is suspected, in particular if there is damage to the skin, hair, or nail plates, skin and nail scales are taken for examination in our medical center (the procedure is painless and safe).
To clarify the diagnosis, other types of studies (blood, feces, urine) may be required. Treatment of any disease should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor. It is very important to control the treatment process, since fungi grow slowly in the human body and therefore the positive effect is not immediately visible. And the disappearance of the manifestations of the disease does not mean complete recovery, because the remaining elements of the fungus can give rise to a new growth of the disease.
Patients and methods
In the Department of ENT Pathology of Children, State Budgetary Healthcare Institution “NIKIO named after. L.I. Sverzhevsky" DZM on the basis of the State Budgetary Institution "DGKB No. 9 named after. G.N. Speransky" DZM examined and treated 306 children with chronic tonsillitis and 402 children with chronic adenoiditis aged 2 to 16 years.
The diagnostic algorithm for examining children with fungal infections of the pharynx included: collection of complaints and medical history, otorhinolaryngological examination, endoscopic examination of the nose, nasopharynx and oropharynx, microbiological diagnostics (bacteriological and mycological).
When collecting an anamnesis of the disease, attention was paid to the child’s complaints, previous viral infections, and the presence of chronic diseases, in particular diabetes mellitus; features of the course and frequency of recurrence of the inflammatory process of the pharyngeal and palatine tonsils. The collection of medical history included anamnesis of antibacterial, corticosteroid and immunosuppressive therapy, since with long-term use of these drugs immunosuppression occurs, leading to the activation of a fungal infection.
During an objective examination, attention was paid to the condition of the nasal mucosa; for the presence and nature of pathological discharge in the common nasal passage; for the presence or absence of changes in the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, palatine tonsils, regional lymph nodes (submandibular, anterior cervical, posterior cervical).
When conducting an endoscopic examination of the nasopharynx, we assessed not only the shape, size and location of the pharyngeal tonsil in relation to the paranasal structures, but also the absence or presence of signs of inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsil (swelling, hyperemia, smoothness of the grooves, the presence of secretions, the nature and extent of pathological overlays).
When collecting pathological material from the surface of the pharyngeal tonsil in children, we used a method developed by us, which allows us to take material directly from the pharyngeal tonsil, excluding contamination from adjacent paranasal structures (priority certificate for the issuance of a RF patent for an invention No. 2011107242). The use of endoscopic control during the selection of pathological material made it possible to visualize and select the exact localization of the pharyngeal tonsil site. When carrying out this method, a rigid endoscope with 0° optics was used.
To determine the prevalence of fungal inflammation, samples were taken from different loci (from the palatine tonsils, from the nasopharynx and from the surface of the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall).
Laboratory microbiological diagnostics were carried out in two directions: microscopy of pathological discharge from various loci of the pharynx and nasopharynx, as well as cultural research methods - inoculation of pathological discharge on liquid and solid nutrient media, followed by counting fungal colonies and determining the growth rate. The preparations were stained using the Gram method, and the calcofluor white staining method was also used. When conducting a cultural study, Sabouraud's medium was used to identify the fungus. Species identification was carried out using standard API 20 test systems (bioMerieux, France).
The sensitivity of fungi to antifungal drugs was determined using the disk diffusion method to modern antifungal drugs: fluconazole, ketoconazole, clotrimazole, itraconazole, voriconazole and amphotericin.
To identify the bacterial flora, 5% blood agar, 10% yolk-salt agar, and Endo medium were used as nutrient media. After isolating a pure culture, the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics was determined using the disk diffusion method.
To exclude side effects of systemic antifungal drugs, on the 5th day of taking antifungal therapy, a biochemical blood test was performed (monitoring liver enzymes: ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase).
Causes of fungus
Not everyone gets sick with deep mycoses. The body of healthy people successfully resists these infections. People with reduced immunity and those suffering from chronic diseases are most susceptible to deep mycoses, for example, bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis, diabetes mellitus, and inflammatory diseases of the genital organs. Sometimes people who have undergone major operations become infected, because their body’s resistance is sharply reduced. Mycoses can also develop during long-term use of antibiotics.