As is known, the human papillomavirus has many serotypes, more than 200 of them have been described. Among them, there are types with a high oncogenic risk, they cause cancer at the site of their localization, with a low oncogenic risk and non-oncogenic. Human papillomavirus types 6 and 11 belong to the low oncogenic risk group. However, it causes 90% of all cases of genital warts and perineal condylomas, and is also a cause of respiratory papillomatosis.
Rice. 1. Papillomavirus types 6 and 11 are among the most dangerous
Detailed description of the study
Human papillomavirus (HPV), also called papillomavirus, is a member of the papillomavirus family. Its peculiarity is the presence of a circular DNA molecule, which is capable of existing as a separate particle with genetic material in the nucleus of the host cell. The introduction of HPV into cells causes their changes (mutations), which increases the risk of oncological processes in the organs where the pathogen is located.
HPV causes damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Infection occurs during unprotected sexual intercourse, as well as through contact and household contact and from mother to fetus during childbirth. An early age at sexual debut and a large number of sexual partners increase the risk of infection with this virus.
There are many types of HPV. They are usually designated by numbers. HPVs are classified according to their oncogenic potential, that is, the ability of the pathogen to provoke cell mutations leading to the development of cancer of a particular organ. The following risk factors for the negative consequences of HPV infection are noted:
- Immunity impairment;
- Development of sexually transmitted diseases;
- Smoking;
- Taking oral contraceptives;
- Exposure to radiation and UV radiation.
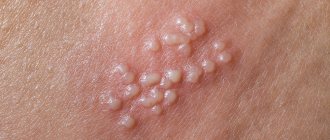
HPV types 6 and 11 are classified as viruses of low oncogenic potential. This type of virus causes the appearance of warts, or genital warts, on the affected tissue. Usually this is the area of the genital organs and rectum, the perianal region, but condylomas are also detected in the larynx and esophagus.
Condylomas are single or multiple formations of pale pink color with a sharp tip, protruding on the surface of the skin or mucous membrane, having folds. The size of warts can vary from 1 to 20 cm. Their transformation into malignant formations is rare. In men, these formations are often found on the penis, while in women in the area of the external genitalia, as well as on the cervix.
The appearance of pointed papillomas in the rectum may be accompanied by discomfort in this area during bowel movements. These formations in the larynx and esophagus are also associated with a feeling of discomfort, a foreign body, and difficulty swallowing. Their appearance on the skin usually does not cause any symptoms and serves as an external defect.
For the purpose of early detection and treatment of human papillomavirus types 6 and 11, and confirmation of its presence in the body, a scraping of the urogenital tract is performed, followed by an analysis of the number of copies of the genetic material of the pathogen.
A study to identify the causative agent of papillomavirus infection types 6 and 11 (Human Papillomavirus 6/11), during which the genetic material (DNA) of the papillomavirus is determined using the real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method in a biomaterial sample.
Synonyms Russian
Human papillomaviruses types 6 and 11, human papillomaviruses types 6 and 11, HPV 6, 11.
English synonyms
Papillomavirus hominis 16.11, DNA.
Research method
Real-time polymerase chain reaction.
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Rectal scraping, urogenital scraping.
General information about the study
Human papillomaviruses (HPV) infect the epithelium of the skin and mucous membranes and can lead to cancer. They are spread mainly through sexual contact and household contact. It is possible to transmit HPV from an infected mother to her fetus. Factors that provoke the development of HPV infection include: early onset of sexual activity, a large number of sexual partners, reduced immunity, the use of oral contraceptives, sexually transmitted infections, vitamin deficiencies, smoking, living in large cities.
The incubation period lasts from 2 months to 2-10 years. In 30% of cases, spontaneous recovery from the virus occurs within 6-12 months.
Different types of HPV can have different effects on the epithelium: low-oncogenic risk HPV types 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 11, 30, 40, 42, 43, 44, 53 and 61 contribute to the occurrence of benign formations (papillomas, warts, condylomas), high-oncogenic risk HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 and 68 can cause severe dysplasia and cancer.
Low-oncogenic risk HPV types 6 and 11 are the most common cause of the development of genital warts (about 90%), or genital warts - softish formations on a thin base with a lobed structure, reminiscent of cauliflower. In men, they usually occur on the foreskin and coronary groove of the glans penis, in women - in the vestibule of the vagina, on the labia minora and majora, and in the anus. With a decrease in cellular immunity (including during pregnancy), giant Buschke-Levenshtein condylomas can be observed. Along with genital condylomas, there are often cervical papillomas: exophytic papillomas (condylomas), similar in structure to anogenital condylomas, or endophytic papillomas (flat condylomas), localized in the thickness of the epithelium (detected during colposcopy) and prone to metastases (within 3-5 years in 4-10% of women).
To detect HPV types 6 and 11, the polymerase chain reaction method is used, which makes it possible to detect HPV type 6 or 11 DNA in the biomaterial being studied. The principle of the method is based on the amplification (multiple increase in the copy number) of a DNA section specific for a given pathogen.
What is the research used for?
- To detect papillomavirus infection type 6 or 11.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of HPV vaccination.
When is the study scheduled?
- For genital warts.
- When determining indications for vaccination against HPV.
- When screening for cervical cancer (along with cytological examination) in women over 30 years of age.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: negative.
Reasons for a positive result
- Infection with papillomavirus types 6 and/or 11.
Reasons for a negative result
- Absence of papillomavirus infection caused by HPV types 6 and/or 11.
- Low levels of HPV type 6/11 in the blood.
What else is prescribed with this study?
HPV type 16/18, DNA (HPV, PCR, genotype determination) scraping, quality.
19.92.1. Scraping 1 day
290 ₽ Add to cart
HPV type 16/18, DNA (HPV, PCR, genotype determination) scraping, count.
19.93.1. Scraping 1 day
320 ₽ Add to cart
HPV 16/18/31/33/35/39/45/51/52/56/58/59 type, DNA (HPV, PCR, genotyping) scraping, quality.
19.46. Scraping 1 day
830 ₽ Add to cart
HPV 16/18/31/33/35/39/45/51/52/56/58/59 type, DNA (HPV, PCR, genotyping) scraping, count.
19.57. Scraping 1 day
900 ₽ Add to cart
References
- Baranov, A.A., Namazova-Baranova, L.S., Tatochenko, V.K. and others. Vaccinal prevention of diseases caused by the human papillomavirus. Issues of modern pediatrics, 2022. - V. 16(2). — P. 107-117.
- Rakhmatulina, M.R., Sokolovsky, E.V., Perlamutrov, Yu.N. and others. Federal clinical recommendations for the management of patients with anogenital (venereal) warts. Russian Society of Dermatovenereologists and Cosmetologists, 2015. - 27 p.
- Luria, L., Cardoza-Favarato, G. Human Papillomavirus. StatPearls, 2022.
Human papillomavirus type 6/11, HPV DNA 6/11
Human papillomavirus type 6/11, HPV 6/11
— qualitative detection of human papillomavirus of low oncogenic risk in scrapings of the urogenital tract using the polymerase chain reaction method with real-time detection. The PCR method with real-time detection of results allows you to determine the amount of DNA of clinically significant HPV types in a sample.
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
is a widespread infectious disease of the genitourinary organs, which can cause cervical cancer in women and squamous cell carcinoma in men.
Different types of HPV cause the development of:
- cervical, vulval, vaginal dysplasia of the cervix;
- pre-invasive and invasive cancer of the cervix, cancer of the vagina and perianal area;
- genital warts, urinary tract;
- genital warts.
Routes of spread of infection
The main route of transmission of HPV is sexual, but cases of household transmission of infection have been described. Women and men are infected at the same rate. In approximately 70% of those examined, HPV is detected in both sexual partners. Intrauterine infection is possible.
According to some researchers, the frequency of infection with the virus is directly proportional to the number of sexual partners: with one partner, HPV is detected in 17-20% of women, with 5 or more partners - in 70-80%.
Incubation period
The incubation period can last from 2 months to 2–10 years. HPV is characterized by a latent course of the disease, in which there are no clinical manifestations and no changes are detected during colposcopic, cytological and histological examination. In 30% of cases, the virus can be cleared within 6–12 months. Diagnosis of latent HPV infection is carried out only by PCR.
Clinical manifestations
HPV can affect the epithelium in different ways: contribute to the emergence of benign formations (papillomas, condylomas) or the combination of papillomavirus DNA with the cell gene, which leads to dysplasia and neoplasia, and subsequently to cancer. The most common area of cancer localization is the transition zone of the cervix to the cervical canal.
Clinical forms of human papillomavirus infection are found in 40–60% of men who are sexual partners of infected women. Their lesions are caused by the same types of HPV as women. In 2/3 of cases, characteristic rashes appear on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs.
HPV types 6 and 11 are considered to be of low oncogenic risk and are associated with the development of genital warts (multiple growths of connective tissue covered with stratified squamous epithelium) and mild cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). For HPV type 11, an association with laryngeal condylomas has also been proven. Despite the fact that HPV 6, 11 are relatively safe, it is advisable to remove the caused condylomas and papillomas.
Indications for the study:
- for genital warts;
- when determining indications for vaccination against HPV;
- when screening for cervical cancer (along with cytological examination) in women over 30 years of age.
Preparation Men
Before taking a urogenital scraping, it is recommended to refrain from urinating for 1.5–2 hours.
Women
Submitting scrapings is not allowed on menstrual days. Avoid taking antibiotics for two weeks, and vaginal suppositories, tampons, spermicides three days before collection. One day before the test, you should not have sexual intercourse. You should not douche on the eve of the examination. After an ultrasound using a transvaginal probe, at least 48 hours must pass.
Interpretation of results
The format for issuing the result of HPV type 6/11 is detected/not detected.
Reasons for the positive result:
- infection with papillomavirus types 6 and/or 11.
Reasons for negative results:
- absence of papillomavirus infection caused by HPV types 6 and/or 11.
What can influence the result?
- A false negative result is possible if the material is collected and stored incorrectly, as well as if the virus content in the material is below a detectable level.
- A false positive result may be due to contamination of the material.
Important Notes
- HPV infection does not always lead to cervical cancer.
- Simultaneous infection with several HPV genotypes is possible.
- The result of the analysis must be interpreted taking into account the conclusions of cytological and histological studies.