Papilloma viruses are the only group of viruses today for which scientists have proven the induction of cancer tumors. Moreover, HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection; more than half of adults are infected with it. Find out how the papilloma virus manifests itself and how to treat it.
Appointment with a gynecologist - 1000 rubles. Appointment with a urologist - 1000 rubles. Removal of tumors - from 500 rubles. Consultation with a doctor based on the results of ultrasound and tests - only 500 rubles. (at the request of the patient).
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
What is papillomavirus, papillomas, condylomas
The content of the article
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV) belongs to the genus A of the Papovaviridae family and is transmitted primarily through sexual contact, infecting epithelial (cover) cells - the skin, mucous membrane and urogenital area. Infection of the skin and genital organs occurs through microtraumas. The papilloma virus is contained in the urethra, Bartholin's glands and seminal fluid. The development of malignant tumors of the penis, vagina, and cervix is associated with human papillomavirus.
HPV strains, of which science knows more than 100, behave differently in the cell. Some exist separately from chromosomes, others are able to integrate into the cell genome (they most often cause complications). When the viral DNA is inserted into the nucleus of the host cell, it controls the cell's genetic material, leading the cell to malignant transformation. During the replication cycle, the human papillomavirus genome expresses 8–10 protein products. Oncogenicity is determined by proteins E6 and E7. It is difficult to kill the infection - the virus remains viable at a temperature of 50 degrees. From 30 minutes.
The virus infects stem cells located in the basal layer, and they transmit the infection to the surface epithelial cells. Superficial dividing immature cells are especially susceptible to HPV, which explains the high risk of oncogenes affecting the vulva, lower part of the vagina and cervix.
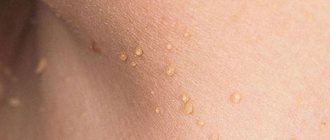
The most common visual manifestation of papillomavirus is papillomas. The formation got its name from the Latin papilla - nipple + Greek oma - tumor. Papillomas can develop into cancer. The development of oncology can be prevented by monitoring the development of papillomas and removing them in a timely manner.
A type of papillomavirus in women and men is genital and flat condylomas that develop on the genitals. They must also be removed.
A complication of the virus is a precancerous condition - cervical dysplasia and its logical conclusion - cervical cancer. You can avoid cancer by treating dysplasia. Treatment also involves removing the affected layer of cells.
How does the disease manifest in women?
The main sign of infection is the formation of excess tissue. This occurs as a result of the division of cells containing viral DNA. This process is not accompanied by visible symptoms until papillomas begin to appear on the mucous membranes of the vagina, cervix or skin. At this stage, other unpleasant sensations may occur, but they are caused by injury to neoplasms, for example, upon contact with underwear, clothing, or during sexual intercourse.
If the growth is exposed to external factors, intercellular processes accelerate, as a result, excess tissue increases in size and spreads, covering healthy areas of the body. Damaged skin may develop an inflammatory process caused by the addition of other infections.
The signs are as follows:
- redness of the outer skin;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- burning when urinating;
- unpleasant odor from the vagina;
- the presence of uncharacteristic discharge.
In addition, with the gradual development of HPV type 66, the structure of the upper layers of the epithelium changes, so during an external examination by a gynecologist, papillomas, condylomas, and flattened formations may be noticed, which gradually increase in size. The growths differ in shape. Genital warts most often appear on the genitals. As the virus develops, those excess tissues that are localized close to each other combine into a large growth. In appearance, it often resembles cauliflower.
How papillomavirus is transmitted, risks
Papillomavirus enters the human body in different ways, the probability of infection is 60%. You can get an infection in the following ways:
- Sexually, regardless of the type of sexual relations - oral, genital and anal. The presence of genital warts in a partner guarantees infection by 98-100%.
- Contact household - in the case of using a shared towel, washcloths, etc. The virus can also be transmitted through saliva during a kiss.
- Through wounds - a violation of the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes - an open gateway to the body.
- Infection of a child during the passage of the birth canal - children suffer from rare forms, papillomas grow in the nasopharynx and sinuses. Recent studies have shown that children born by cesarean section also become infected - this may indicate that the virus is able to penetrate the placenta.
Infection does not always guarantee the development of the disease. HPV causes disease in the body in 50% of cases, the rest are limited to carriage of the infection: a strong immune system can keep the virus in numbers that are not dangerous to the body. The incubation period ranges from a year to 20 years, with an average of 3-5 years.
The development of the disease is provoked by hormonal imbalances, immunodeficiency states, and sexually transmitted infections (STDs, STIs). Any condition that reduces immunity increases the risk - pregnancy, bad habits, chronic diseases, stress, etc.
It should be understood that infection of epithelial cells is a necessary but not sufficient factor for the development of oncology. According to Professor V.A. Molochkov, a well-known and respected scientist in the world of medicine, a number of other factors are necessary for the development of irreversible neoplasia:
- active expression of genes E6, E7 of highly oncogenic types hpv16 and hpv18;
- induction of estradiol metabolism to 16-OH;
- multiple damage to chromosomal DNA in an infected cell.
The first stage of CIN I neoplasia is expressed by active copying of the virus and its asymptomatic course. Tumor development is stimulated by the interaction of papillomavirus with cytomegaloviruses, trachomatis, mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, and herpes simplex virus type 2.
Reasons for virus activation
A jump in the development of infection is observed under certain conditions:
- hormonal changes in a woman’s body, for example, during pregnancy, lactation, and menopause;
- excessive physical activity;
- chronic fatigue;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- frequent illnesses;
- chronic diseases;
- STD;
- regular stress;
- lack of vitamins and nutrients;
- taking antibiotics;
- abortions.
With frequent changes of sexual partners or unprotected sexual intercourse, the infection enters the body, but begins to develop if at this stage the person’s immunity is reduced. For this reason, HPV may not manifest itself for a long period.
As soon as immunity is significantly reduced, the virus begins to actively multiply, which provokes the appearance of excess tissue in the genital area.
The above factors contribute to a decrease in immunity. By themselves, they are not the cause of the development of HPV genotype 66.
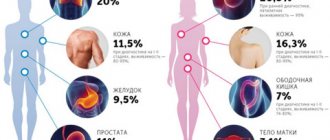
Important numbers: the statistics are scary
- In the last 10 years, the number of people infected with hpv
has increased 12-fold. - HPV ranks second after genital herpes among all female infections and is found in 70% of adult women.
- Papillomavirus is the cause of all cases of cervical cancer.
- HPV is associated with 50% of anogenital cancers.
- The greatest risk of infection is between the ages of 18 and 25. The peak age for development of cervical dysplasia is 30 years, and cervical cancer is 45 years.
Types of HPV
Scientists know more than 100 types of papillomaviruses. A third of them infect the human urogenital tract, affecting the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs. A fifth of the viruses in this group have not yet been studied and may well present new unpleasant surprises.
The papilloma virus is classified according to its oncogenicity and area of damage:
- Non-genital - nasopharynx, mouth, sinuses, vocal cords, lungs;
- Affects the organs of the urinary system - ureters and bladder, urethra, renal pelvis;
- Genital in women - affects the mucous membranes of the external genitalia, the vestibule of the vagina and the vagina itself, the perianal area, the cervix, the perineum;
- Genital in men - affects the glans penis, foreskin, frenulum, coronary sulcus, shaft of the penis, scrotum, groin skin, pubis, perineum, perianal area. The external opening of the urethra in men is affected in 20-24% of cases.
Based on oncogenicity, HPV can be divided into:
- HPV low risk - type 6,11,42,43,44;
- HPV average risk 31,33,35,51,52,58;
- HPV high risk 16,18, 45, 56.
The most dangerous types of HPV papillomavirus (hpv) - those belonging to the high cancer risk group - are 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52. They cause genital cancer.
How dangerous the papillomavirus is for men and women can be understood by looking at the table of diseases associated with HPV activity.
Diseases caused by HPV (table)
| Disease, clinical manifestation | Type hpv |
| Skin diseases | |
| Plantar warts | 1,2,4 |
| Common (simple) warts | 2, 4, 26, 27, 29, 57 |
| Butcher's warts | 7 |
| Flat warts | 3, 10, 28, 49 |
| Verruciform epidermodysplasia (hereditary disease - verrucous dysplasia) | 2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19, 20, 36, 37, 46, 47, 50 |
| Diseases of the genital mucosa | |
| Flat condylomas, cervical dysplasia | 6, 11, 16, 18, 30, 31, 33, 39, 40, 42, 43, 51, 52, 55, 57, 61, 62, 64, 67 |
| Condylomas acuminata | 6, 11, 42, 54 |
| Cervical cancer, genital cancer, vaginal cancer, anal cancer | 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 54, 56, 66, 68 |
| Diseases of the mucous membranes | |
| Epithelial hyperplasia of the oral mucosa | 13, 32 |
| Neck, lung and head cancer | 2, 6, 11, 16, 18, 30 |
| Respiratory tract papillomatosis | 6, 11, 30 |
One patient can be infected with several types of papillomavirus at the same time, which is usually the case.
Symptoms of papillomavirus
HPV infection can be asymptomatic or give the following symptoms:
Genital warts (genital warts)
Fibroepithelial (skin) neoplasms with a thin stalk or a broad base. They can be single or merge, forming a growth that looks like a cauliflower head. Condylomas can become inflamed and bleed when injured, as they contain blood vessels that feed them.
Condylomas can be found on the clitoris, labia minora, urethra, vagina, cervix, around the anus and in the anus. Exophytic forms of OC are a consequence of the activity of benign types of the HPV virus - 6, 11. Endophytic condylomas (flat and inverted) grow on the cervix and initially do not give symptoms. Detected during extended colposcopy. Genital warts affecting the lips, tongue and palate are visible during routine examination.
People with HIV and during pregnancy develop very large genital warts. Giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma is not uncommon.
- Anal warts.
Anal warts can be found up to the dentate line of the rectum. At first they do not cause discomfort, but over time they itch, hurt, and smell unpleasant. - Urethral warts.
In women, the external urethral opening is affected in no more than 8%. Such warts are easily identified by a gynecologist. Deep damage to the urethra (urethra) cannot be determined visually, but the disease gives symptoms of sluggish urethritis. Urethral warts in men cause a split urine stream associated with a narrowing of the urethral opening.
Flat condylomas
Flat condylomas do not protrude above the surface of the mucous membranes, which is why they got their name. These formations have a high oncogenic potential. Most often, flat condylomas are located on the cervix and vaginal mucosa. Flat condylomas can only be detected by colposcopy.
Dysplasia, cervical cancer
Dysplasia is a tissue pathology associated with the modification and degeneration of cells. This is a precancerous condition. There are 3 degrees of the disease, all of which are detected by colposcopy. Stages 2 and 3 require surgical treatment. Cervical dysplasia is preceded by cervical erosion.
Cervical cancer is a consequence of dysplasia. It is the most common tumor of the female reproductive organs. It may be asymptomatic or cause pain, bleeding and other symptoms characteristic of problems with the female reproductive system.
Collection of biomaterial and preparation
The material that is taken for HPV analysis is epithelial cells, which are taken from the cervical canal in women, and from the urethra in men. For this purpose, a small diagnostic brush is used, which is inserted into the endocervix or into the urethra. After removing the brush, epithelial cells settle on its villi. The instrument with the resulting biopsy is lowered into a sterile container and sent to the laboratory. For the patient, the collection of material does not cause any particular discomfort, but if HPV is detected in the analysis, then the benefits of it significantly outweigh the discomfort.
You need to prepare specifically for an HPV test. Before the examination, you are not allowed to use antibacterial and antiseptic products for intimate hygiene, douche, use vaginal suppositories, or have intimate relations for two days. If the patient is undergoing antibacterial therapy or taking anticoagulants, you need to notify the doctor about this, the drugs may distort the result. Before collecting biomaterial, you need to urinate.
Papilloma virus - diagnosis
Human papillomavirus can be detected in its early stages only by laboratory methods. The infection can be detected visually only when condylomas or papillomas appear. If HPV is suspected, the following are prescribed:
- Gynecological examination
or examination by a urologist with taking smears for an HPV test. If condylomas are detected, urethroscopy is performed. In case of cervical erosion, the gynecologist must take a smear for oncocytology. - If HPV is detected, a colposcopy is required - examination of the vagina and cervix with a gynecological microscope - colposcope. The doctor uses special tests to exclude hidden pathologies.
- Colposcopy with biopsy.
Indicated for all women with neoplasia. At the same time, coloring and exposure to suspicious areas is carried out. A sign of APC may be whitish areas formed after treatment with vinegar, uneven accumulation of iodine when exposed to Lugol's solution, a mosaic pattern, and protrusions of the epithelium. - Histological and cytological examination
- assessment of the cellular composition, and the cells themselves, for atypicality (cancer). - PCR – search for traces of papillomavirus DNA. This is the most accurate and diagnostically informative analysis that detects the papilloma virus in men and women and specifies its type.
To assess the viral load, a quantitative HPV test is recommended, which determines the critical concentration of the virus associated with the risk of malignancy of tumors. The analysis is also carried out to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
Treatment of papillomavirus
Unfortunately, medicine is not yet able to completely rid the body of the virus. Therefore, the task of the doctor and the patient is to deal with the consequences in a timely manner. It is recommended to remove all warts and treat precancer and cancer stages. According to recent studies in the USA, the human immune system is able to cope with HPV on its own within 2 years after infection in 90% of cases. If this does not happen, treatment is strictly necessary. Papillomas are removed using the following methods:
- Surgical removal
is an outdated but effective method. Recommended in exceptional cases. - Electrocoagulation
– cauterization of affected areas with electric current. Not everyone likes the method, as it can also affect healthy tissue. - Laser coagulation
- laser cauterization - is the most modern and effective method that gives a minimum of complications. - Cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen
differs from other methods in that the pathological growth is affected by cold. Requires a lot of experience from the doctor. - Chemical cauterization
- the doctor acts on the diseased area with concentrated acids or alkalis. The method can also affect healthy skin - the chemical will leave a scar. - The radio wave method
is the most expensive, but the best. Does not cause pain, complications, bleeding. Does not leave scars.
You can read more about methods for removing tumors in the “Low-traumatic operations” section.
After removal, antiviral treatment and means to restore and strengthen the immune system are prescribed.
Prevention of papilloma virus
You can prevent the appearance of warts by maintaining personal hygiene. You should not touch other people's papillomas, condylomas, etc. You can protect yourself from genital warts by barrier contraception (using a condom), but if the formations are on external tissues, this will not help. The most effective method of protecting against HPV is strengthening the immune system.
Girls and boys are recommended to get vaccinated against HPV. The vaccine prevents the occurrence of cervical cancer, vulvar cancer, vaginal cancer, genital warts and other diseases associated with papillomavirus. There are three types of vaccines against papillomavirus. In Russia, the drug Gardasil is recommended, directed against 4 types of hpv (16, 18, 6, 11).
The vaccine is given three times, starting at age 9 and before the start of sexual activity. Women can get vaccinated up to 26 years of age, but the drug will not work against viruses that are already in the body.
How to prevent disease
Considering that HPV does not manifest itself at the incubation stage, it will be difficult to detect the virus without additional examination. To avoid infection and the development of the disease, you should follow simple rules:
- casual sex should be avoided;
- It is recommended to use barrier contraception during sex;
- Frequent changes of sexual partners are undesirable.
Intimate hygiene and maintaining a high level of immunity - these factors also help prevent the development of the disease.
Where is papillomavirus treated in St. Petersburg, prices
You can contact the Diana private clinic in St. Petersburg for diagnosis and treatment of papillomavirus. We use modern methods approved in the best European clinics, and the prices for specialist services are quite affordable.
Here you can get tested for the human papillomavirus and remove any tumors. Removal of formations associated with HPV is carried out using the latest Fotek radioknife with a coagulator that prevents bleeding. Price for removal of condylomas, papillomas, etc. — from 500 rub. We also offer the HPV vaccine with Gardasil.
Routes of transmission of HPV 66
Methods of penetration of the human papillomavirus into the body:
- sexual;
- contact and household;
- vertical.
In the first case, HPV type 66 is transmitted during sexual intercourse. The likelihood of this is present not only during classical, but also during oral and anal sex. The main condition for the penetration of harmful particles into the human body is the presence of microtraumas. If the integrity of the outer covering is not broken, infection will not occur. Barrier contraception does not guarantee complete protection. Using a condom only significantly reduces the risk of infection.
The sexual route of infection is the most common. Virus genotype 66 can also enter the body through hygiene items, linen, towels, and razors, but this happens much less frequently.
It must be remembered that harmful particles are capable of maintaining viability outside the human body for a short period. For this reason, infection can also occur through household contact. In this case, there is a risk of infection not only when using other people’s hygiene items, but also when visiting a bathhouse, sauna, or swimming pool.
Much less often, the virus penetrates the body of another host vertically. In this case, HPV is transmitted from mother to child during labor. To find out whether a woman is infected, she undergoes an examination during pregnancy.