12/01/2017 There are many factors that can cause infectious dermatitis on the legs. In most cases, it is a sign of a serious malfunction in the body. Skin rash worsens the aesthetic appearance and general well-being of a person. Therefore, this problem can and should be dealt with.
Our medical center provides services for the treatment of nail and skin diseases, including infectious dermatitis on the legs. The treatment regimen for the disease is selected by doctors individually and carried out after a high-quality diagnosis.
Causes of dermatitis
The disease develops due to three main reasons:
- exposure to an irritating factor;
- decreased general immunity;
- deterioration of the protective properties of the skin.
Factors that cause dermatitis can be divided into two large groups: external (exogenous) and internal (endogenous).
External factors:
- mechanical impact - prolonged compression, friction;
- physical impact - high and low temperatures, sun rays, radioactive radiation;
- contact with chemicals - cosmetics, household chemicals, alkalis, acids, salts of heavy metals;
- contact with poisonous, burning plants, pollen, biological fluids;
- bacteria, viruses, fungi.
Internal factors:
- errors in nutrition, metabolic disorders, hypo- and avitaminosis;
- internal diseases – endocrine disorders, gastrointestinal pathologies;
- neuropsychiatric disorders;
- taking medications (antibiotics, hormones, drugs with novocaine).
Knowing the causes of dermatitis, you can understand that in most cases it is not a contagious disease. Only dermatitis of an infectious nature is contagious - those caused by various microorganisms (herpetic, scabies).
Material and methods
The material was selected at a consultation with patients at the Department of Skin and Venereal Diseases with a course in cosmetology at the Medical Institute for Advanced Medical Studies (MIUV). For examination, patients were sent to the Allergy Center named after. prof. HELL. Ado. The severity of AD was assessed using the international SCORAD (Scoring atopic dermatitis) scale. The diagnosis of superficial candidiasis was made in accordance with the classification of A.M. Arievich, Z.G. Stepanishcheva (1965), and SO - A.Yu. Sergeeva, Yu.V. Sergeeva (2001). The effectiveness of AD therapy was assessed using the following clinical criteria: recovery, significant improvement, improvement, no effect. Recovery was defined as complete resolution of AD lesions. A significant improvement was considered to be persistent positive dynamics of the process, which was characterized by a 4-fold decrease in SCORAD. Improvement was understood as a slow positive dynamics of the process with a 2-fold decrease in SCORAD. In the chronic course of AD, the transformation of the continuous course of the disease into a recurrent one, as well as the lengthening of the inter-relapse period, were taken into account.
Determination of specific IgM and IgG to C. albicans
carried out by solid-phase indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) on a Multiskan Ascent spectrophotometer (Thermo Electron);
Enzyme immunoassay test systems produced by Vector-Best CJSC (Novosibirsk) were used. Determination of total IgE in blood serum was carried out by ELISA using Dia-plus test systems of NPO Biotechnology on a UniCap-100 analyzer (Phadia, Sweden), the result was expressed in IU/ml. Determination of specific IgE to lipophilic yeasts of the genus Malassezia
spp
.
carried out on a UniCap-100 device (Phadia, Sweden) using the supplied standard reagents.
Determination of the cell wall antigen-mannan of yeast-like fungi Candida
spp. carried out by ELISA using standard Candida-Ag kits (Bio-Rad, France).
The bacteriological method was used to isolate and identify opportunistic mycotic microflora. For sowing material on Malassezia
spp
.
scales of the stratum corneum of the epidermis were scraped off from an area of 1 cm2.
The material was collected with a cotton swab moistened with sterile olive oil. The material was subcultured three times on Notman-agar (LNA) selective medium. The inoculated dishes were incubated in a thermostat at 32°C for 2 weeks. Species identification of representatives of the genus Malassezia
spp.
were carried out according to morphological (colony morphology, cell size and shape), physiological (growth at 37 and 40 °C) and chemotaxonomic (catalase reaction, utilization of Tween 20, Tween 40, Tween 60, Tween 80) characteristics. The results were assessed in the number of CFU/cm2. Definition of Candida
spp
.
from skin and CO was carried out by inoculating the material on sugar broth.
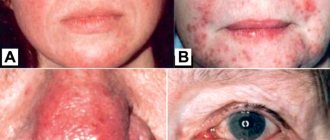
General symptoms
Characteristic signs for all dermatitis are hyperemia (redness) of the skin, swelling, local increase in temperature, feeling of heat and itching at the site of the lesion. After prolonged contact with the provoking factor or as the disease develops, a vesicular rash, blisters of various types, skin cracks, scabs, and areas of necrosis appear.
conclusions
The prognosis for the initial stages of contact dermatitis is good, but self-medication is quite long (about a month). The body's reactivity remains for life. The patient must take into account the characteristics of his body and, if possible, avoid contact and be sure to carry out timely treatment.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Classification of types of dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis
Develops as a result of contact with an allergen in people with a family history and a history of allergic diseases (hay fever, bronchial asthma). The risk group also includes people who are forced to constantly come into contact with sensitizing factors due to their professional activities.
This type of disease can develop acutely, immediately after interaction with the allergen, or after some time. With constant contact with an irritating substance, the disease becomes chronic.
Allergic dermatitis is characterized by redness, itching, and swelling of the affected areas. Symptoms are more severe in younger patients.
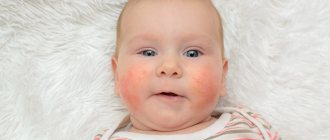
Atopic dermatitis
Most often it develops in childhood and is caused by a hereditary predisposition to allergies and dietary errors. In adults, atopic dermatitis mainly appears due to inspiratory allergens, most often house dust, or medications. The disease is chronic and difficult to cure.
Distinctive features are the localization of lesions on the face, neck, in the elbow and popliteal fossae, armpits, in the groin area, on the scalp, under the earlobes. There is no sharp hyperemia, the lesions peel off, and ichthyosis and keratosis may develop. One of the features of this species is the high probability of secondary infection with bacteria, viruses or fungi.
Seborrheic dermatitis
This is a chronic inflammatory process in areas of the skin with a large number of sebaceous glands. The glands produce excess secretion, which becomes a favorable environment for the pathological reproduction of microorganisms that live on the skin under normal conditions - the fungi Pityrosporumovale and Malassezia. Provoking factors for uncontrolled proliferation of fungi can be hormonal disorders, stress, and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. This type is characterized by seasonal spring and autumn exacerbations.
The lesions are mainly located on the scalp, chest, back, and certain areas of the face. The disease is divided into oily, dry and mixed types. A characteristic symptom is symmetrical areas of inflammation in the form of pink-red plaques covered with whitish scales. With the oily type, the affected areas become wet and yellowish crusts appear on them. Damage to the scalp leads to hair loss.
Toxic-allergic (food) dermatitis
It develops in response to the introduction of an allergen into the body through food, drinks, air, and medications. Additional factors that provoke its occurrence are some chronic diseases.
In the toxic-allergic form, local symptoms (itching, hyperemia, burning) are accompanied by general symptoms of intoxication - weakness, chills, lack of appetite, nausea.
If you are allergic to medications, a severe course of toxic-allergic dermatitis - toxicdermia, the extreme degree of which requires emergency medical care, cannot be ruled out.
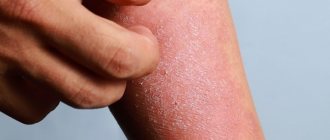
Traumatic dermatitis
Inflammatory reaction of the skin in response to mechanical stress. It is local in nature (damage at the site of impact), as a rule, goes away when the traumatic factor is eliminated.
The clinical picture of this type of dermatitis depends on the degree and time of exposure to the damaging factor and the initial condition of the skin. More often it occurs in people with sensitive, dry skin, or, on the contrary, prone to hyperhidrosis, in patients with chronic diseases that are characterized by impaired microcirculation (diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis).
Manifests itself in the form of abrasions, calluses, including water calluses, calluses, and diaper rash. These manifestations may be accompanied by a secondary infection.
Thermal (cold) dermatitis
Skin reaction to cooling. It manifests itself as inflammatory changes that look like red itchy spots with a surface prone to peeling and cracking. Most often, lesions are located on open parts of the body - face, ears, neck, or closed, but sensitive to cold, hips and knees. External manifestations are often accompanied by a runny nose and conjunctivitis.
Increased sensitivity of the skin to low temperatures is observed in people with diseases of the ENT organs, gastrointestinal tract, and genitourinary tract.
Infectious dermatitis
Caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. The entrance gates for the entry of microorganisms are microdamage to the skin, abrasions, scratching. It manifests itself in the form of pyoderma - pustular rashes.
In another case, infectious dermatitis is one of the symptoms of various infectious diseases - herpes, rubella, measles, chickenpox. In these situations, the clinical picture will be different, depending on the underlying pathology.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis
A feature of the treatment of atopic dermatitis is a stepwise approach from simpler methods of external therapy and skin care to complex innovative techniques.
Remedies and methods for treating atopic dermatitis
When treating atopic dermatitis, the following are used:
- Softening and moisturizing creams and ointments are the basis for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. These products help keep your skin hydrated and soft.
- Steroid creams and ointments are applied to the skin and help relieve redness and itching. In severe cases, steroid tablets or injections may be required, but your doctor will keep the course of treatment as short as possible, since the high effectiveness of injections comes with a high risk of side effects.
- Medicines that affect the immune system are highly effective, but have side effects and may be prescribed when safer treatments do not produce the desired results.
- Antihistamines may be used in patients who report decreased itching.
- To increase the effectiveness of therapy, it is possible to perform wet wraps (Wet Dressing, Wet Wrap Therapy).
Wet wraps (Wet Dressing, Wet Wrap Therapy)
Treatment with Wet Wrap Therapy helps to quickly clear skin of rashes and can be used both in a medical facility or hospital, as well as at home. The effect is associated with improved penetration of the drug used, deeper and longer-lasting hydration, and reduced water loss by the skin. The dressings provide protection from scratching, which leads to the formation of an itch-scratch cycle, preventing scratches from occurring, which further intensify the itching, which makes the skin heal better. Cooling the surface of inflamed skin by evaporating water from the dressings helps reduce inflammation, itching and soreness.
For severe eczema, wet wraps are prescribed in a medical facility. They can also be used at home to maintain good health or at the first sign of deterioration and can reduce the need to seek medical help and the likelihood of hospitalization.
There are various modifications of Wet Wrap Therapy; the essence of the method is to use external medications (emollients or steroids) under two layers of bandages. The bottom layer is warm and moist, on top of which a second, dry layer is made. For the bandage, you can use a regular bandage, special tubular bandages, or special clothing. The bottom layer must be periodically moistened with ordinary warm water, preventing it from drying out. The use of topical steroids under a wet dressing can increase the effectiveness of treatment. The procedure can be performed 1-2 times a day, every day, during an exacerbation. As the exacerbation decreases, the procedure can be done less frequently, performed 1-2 times a week during the period of remission. If well tolerated, the bandage with the medicine can be left overnight, remembering to periodically moisten the bottom layer of tissue.
The procedure takes quite a long time, and in the first stages (especially in patients with severe skin damage) may require the participation of medical personnel. After training and improvement, the procedures can be continued at home.
Diagnosis and treatment principles
The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture, the patient’s medical history, and laboratory tests. If characteristic signs appear - redness of the skin, itching, rashes, you should immediately consult a doctor for timely diagnosis and successful treatment. Depending on the cause of its occurrence, dermatitis should be treated by a dermatologist or allergist. You should not self-medicate, as this can lead to the disease becoming chronic, which will be much more difficult to get rid of.
Basic principles of dermatitis treatment:
- elimination of the irritating factor;
- hypoallergenic diet;
- correct daily routine;
- exclusion of hot baths;
- detoxification of the body;
- antihistamines;
- local treatment - treatment with antiseptics, ointments;
- mild sedatives;
- physical therapy;
- therapy of chronic diseases.
The danger of self-medication
You can get rid of skin infections on your legs forever only with the help of professional and modern treatment. There are the following reasons for this:
- It is impossible to independently determine the type of dermatitis and its root cause.
- Traditional recipes can aggravate the situation. They should be used only after consultation with a specialist and in combination with drug therapy.
- It is important not to confuse infectious dermatitis with psoriasis or lichen. Therapeutic regimens for these diseases are different.
- In most cases, consultation with several specialists is required: a dermatologist, gynecologist, infectious disease specialist, and therapist.
- Poor quality therapy often leads to relapses of the disease, scars and spots on the skin.
It is important to follow the rules of hygiene, lead a healthy lifestyle, and at the first symptoms of infectious dermatitis on the legs, contact the specialists of our center.
Diet
Diet is very important for the prevention of dermatitis and their treatment in both adults and children. Foods that provoke allergies should be excluded from the menu: citrus fruits, nuts, red fish, eggs, chocolate, honey. It is recommended to limit irritating foods as much as possible - spices, vinegar, salty, spicy and smoked foods. Patients are advised to take light soups, low-fat foods, and fermented milk products. It is necessary to drink enough water.
For infants suffering from atopic dermatitis, it is advisable to continue breastfeeding. At the same time, the mother should exclude allergens from her food as much as possible. If breastfeeding is not possible, the child is prescribed special formulas with a minimum content of cow's milk protein. Complementary feeding is introduced to such children as late as possible, with extreme caution. Each new product and the reaction to it should be recorded in a food diary.
Article sources:
- Characteristics of seborrheic dermatitis. Shukurov I.B., Yakhshieva M.F., Rustamov M.K. Scientific journal, 2018
- Atopic dermatitis of adults. Dvoryankova E., Denisova E., Piruzyan A., Korsunskaya I. Doctor No. 3, 2022. p. 9-13
- Maintenance pharmacotherapy for atopic dermatitis. Petrova I.V., Omarov N.N., Sargsyan M.S., Khamroeva S.A., Osmanova Z.S., Proshin S.N. Reviews on clinical pharmacology and drug therapy, 2022. p. 60-63
Advantages of the Mama Papa Ya clinic
The network of family clinics “Mama Papa Ya” offers a range of medical services for the diagnosis and treatment of dermatitis. Our advantages:
- consultations with a highly qualified dermatologist and allergist;
- diagnostic studies to detect allergen;
- the possibility of simultaneous treatment in the clinic of several family members, both adults and children;
- affordable prices for diagnostic and treatment procedures.
Make an appointment with a doctor at a time convenient for you by phone or through the form on our website.
Reviews
Good clinic, good doctor!
Raisa Vasilievna can clearly and clearly explain what the problem is. If something is wrong, she speaks about everything directly, not in a veiled way, as other doctors sometimes do. I don’t regret that I ended up with her. Anna
I would like to express my gratitude to the staff of the clinic: Mom, Dad, and me. The clinic has a very friendly atmosphere, a very friendly and cheerful team and highly qualified specialists. Thank you very much! I wish your clinic prosperity.
Anonymous user
Today I had a mole removed on my face from dermatologist I.A. Kodareva. The doctor is very neat! Correct! Thanks a lot! Administrator Yulia Borshchevskaya is friendly and accurately fulfills her duties.
Belova E.M.
Today I was treated at the clinic, I was satisfied with the staff, as well as the gynecologist. Everyone treats patients with respect and attention. Many thanks to them and continued prosperity.
Anonymous user
The Mama Papa Ya clinic in Lyubertsy is very good. The team is friendly and responsive. I recommend this clinic to all my friends. Thanks to all doctors and administrators. I wish the clinic prosperity and many adequate clients.
Iratyev V.V.
We visited the “Mama Papa Ya” Clinic with our child. A consultation with a pediatric cardiologist was needed. I liked the clinic. Good service, doctors. There was no queue, everything was the same price.
Evgeniya
I liked the first visit. They examined me carefully, prescribed additional examinations, and gave me good recommendations. I will continue treatment further; I liked the conditions at the clinic.
Christina
The doctor carefully examined my husband, prescribed an ECG and made a preliminary diagnosis. She gave recommendations on our situation and ordered additional examination. No comments so far. Financial agreements have been met.
Marina Petrovna
I really liked the clinic. Helpful staff. I had an appointment with gynecologist E.A. Mikhailova. I was satisfied, there are more such doctors. Thank you!!!
Olga