Ringworm (microsporia) is a disease manifested as a fungal infection of the skin, nail plates and hair follicles. The pathogen is a mold fungus of the genus Microsporum. Its colonies form in keratinized substrates. Microsporia remains a relatively common disease - dermatologists identify 60-75 cases for every hundred thousand Moscow residents. The pathology has a pronounced seasonality. The peak incidence occurs at the end of summer and beginning of autumn - the period of breeding of offspring in cats and other animals.
Epidemiology of microsporia
Microsporia affects mainly children of primary and school age. The high incidence of ringworm in children is associated with an imbalance of cellular-humoral immunity, a reduced concentration of bactericidal components of the blood serum and a reduced level of enzymes in the hair follicles that destroy pathogens. Upon reaching puberty, the disease disappears.
Zoophilic microsporia
In our latitudes, among all species, zoophilic microsporia accounts for 90 - 97%. The cause of the disease is the fungus Microsporum canis, which is transmitted from sick kittens, cats, dogs (through contaminated wool), less often - from humans, as well as through objects containing pathogen spores (combs, toys, bedding and hats). Children often become infected when playing in the sandbox. The source of infection in most cases is stray animals.
The causative agents of ringworm are highly resistant in the external environment. From 7 to 10 years they remain viable on skin scales and hair. They can be stored in soil (sandboxes) for more than 1 month. The incubation period is 5 - 7 days.
Rice. 3. Ringworm in a dog.
Rice. 4. Ringworm in cats and kittens.
Anthropophilic microsporia
In our latitudes, among all types of microsporia, anthropophilic microsporia accounts for about 2% of cases. The cause of the disease is Microsporum ferrugineum (more often) and Microsporum audouinii (less often). The infection is transmitted only from a sick person and his personal belongings infected with fungi - hats, combs, clothes, towels, bed linen and hairdresser's tools.
Rusty microsporum (Microsporum ferrugineum) is the most infectious and virulent of all pathogenic fungi known today. The spread of the disease in children's groups is rapid and requires immediate implementation of intensive anti-epidemic measures.
Children aged 5 to 14 years old, mostly boys, are most often affected, which is associated with transmission of infection during haircuts. The disease disappears upon reaching puberty. The incubation period for Microsporum ferrugineum infection is 4 - 6 weeks.
Microsporum audouinii is most common on the African continent. The pathogen may be brought into the Russian Federation by tourists and migrants. Mostly children of preschool age are affected.
Rice. 5. A focus of microsporia on the skin of a person’s hand.
Geophilic microsporia
This type of disease develops when persons cultivating the soil become infected with the soil saprophyte fungus Microsporum gypseum.
Rice. 6. Microsporia in adults.
Development and transmission routes
The high degree of infectiousness is due to the presence of the fungus in the body of animals, in soil substrates, and in some plants. The pathogenic fungus Microsporum is a type of anaerobic microorganisms that require oxygen to maintain their vital functions. Fungi receive nutrition only on structures with a high content of proteins and microelements, so lesions are recorded only on the surface of the epidermis, as well as in hair follicles.
The vegetative body of the fungus is made up of mycelium - a multinucleated cell obtained as a result of the welded concentration of many fungal cells. The mycelium forms fungi, and when favorable conditions arise, spores. Spores are known to be a way for a fungal colony to reproduce.
Once on the surface of the epidermis, the fungus immediately begins its life activity in the vellus hairs of smooth skin, in the hair follicles. The main source of infection in the human body is contact with sick animals (guinea pigs, livestock, cats, dogs and their offspring).
Carriers can also be representatives of wild nature (monkeys, foxes, arctic foxes, lions, tigers). Infection can occur not only through direct contact, but also through the use of animal care equipment (bowls, food, toilet, wool). There are several main routes of transmission:
- contact (through direct or indirect contact with animal carriers or humans);
- through soil or plants (infection is possible through contact with soils and plants with which the hosts of the fungus have had any interaction).
Sometimes infection can occur from a sick person to a healthy one. Often, when in contact with sick animals, a person is not aware that they have a fungal disease. The disease in animals is often asymptomatic and occurs in a latent form. Epidemiologists note spikes in infection in the fall, as well as in the summer months, when cats give birth. Often it is kittens that become hidden carriers of a pathogenic fungus. To become infected, it is enough to pick up a kitten, stroke its fur, and put it to bed.
Causative agents of ringworm
Today, 12 species of fungi of the genus Microsporum have been studied and described. Pathogens of microsporia that are of interest to doctors are represented by 3 groups:
- The zoophilic group is represented by Microsporum canis and Microsporum distortum. Mostly animals - cats and dogs - are infected. The infection from them is transmitted to humans.
- The anthropophilic group is represented by Microsporum audouinii (more often) and Microsporum ferrugineum (less often). Mostly people get sick, rarely animals.
- The geophilic group is represented by Microsporum gypseum and Microsporum nanum. They live in the soil. The disease is rarely caused.
Rice. 7. Ringworm in dogs and children.
Microsporum canis (furry, feline)
Cat microsporum is the most common in the Russian Federation.
Type of colonies (macroscopic picture):
- When growing on nutrient media, fungal colonies are powerful, mealy in the center, loose and fluffy along the periphery.
- The reverse side of the colonies is red-brown in color, giving the overall appearance of the colonies a salmon tint.
Type of pathogens under a microscope:
- The mycelium is bamboo-shaped and consists of rocket-shaped cells. The hyphae are septate and produce numerous macroconidia.
- On the filaments of the mycelium there are large exospores (macroconidia) of a spindle-shaped form, they have a jagged-villous shell, spinous, multi-chambered, the shell is 2-contour.
- On the sides of the branches of the mycelium, microconidia are formed, which are single-celled formations of a round or pear shape, located singly or in groups.
- The organs of vegetative reproduction are represented by chlamydospores - round-shaped cells.
Rice. 8. Microscopic picture of microsporum fluffy. The mycelium (photo on the left) and numerous exospores (photo on the right) are clearly visible.
Rice. 9. The photo shows exospores of the pathogen. They are large, spindle-shaped, located on mycelial filaments.
Rice. 10. Colonies of microsporum fluffy fungi.
Microsporum ferrugineum (rusty microsporum)
Rusty microsporum rarely causes disease.
Type of colonies (macroscopic picture):
- Colonies of pathogens are wide, lumpy or flat, leathery, dome-shaped in the center, divided into convex sectors by grooves.
- They have a brownish, yellowish or reddish color.
- Some colonies are waxy, yellowish, line-like, folded, or whitish-powdery, finely lumpy.
Type of pathogens under a microscope:
- The mycelium of mushrooms is wide.
- Chlamydospores are 30 microns in diameter.
- Macroconidia are absent.
- Microconidia are rarely present.
Rice. 11. Microsporum ferrugineum colonies.
Rice. 12. Rusty microsporum under a microscope.
Microsporum gypseum
Microsporum gypseum is distributed throughout the world. They live in the soil. People cultivating the soil are getting sick. The disease affects hair and smooth skin. In addition to microsporia, they cause skin infections in the form of herpes zoster Corporis and Capitis. There is information about nail damage. The pathogen has been isolated by some researchers from dogs, horses, cats and rodents.
Type of colonies (macroscopic picture):
- Fungal colonies grow quickly.
- Flat and powdery in appearance, later a velvety-looking raised area forms in the center.
- They have a yellow-pink color and yellow on the reverse side.
Type of pathogens under a microscope:
- Macroconidia (exospores) are numerous, spindle-shaped, blunt-pointed, wide, smooth.
- Microconidia are numerous and oval or pear-shaped.
Rice. 13. Colonies of Micrsporum gypseum.
Rice. 14. View of pathogens under a microscope. Numerous spindle-shaped exospores are visible.
Folk remedies for treating microsporia
The following traditional medicines are used:
- apply napkins moistened with fresh onion juice to the affected areas;
- lubricate the affected areas with tincture of common lilac flowers: pour two tablespoons of dried flowers with 100 milliliters of 70% alcohol, leave and strain;
- wash the affected areas with a decoction of celandine herb: pour one tablespoon of dry herb with a glass of water and boil over low heat for 10-12 minutes, cool, strain; alternate with other means;
- lubricate affected areas with propolis oil: chop 15-20 grams of propolis with a knife, pour in 50 grams of vegetable oil and heat in a water bath or in the oven until the oil boils, stirring occasionally; let the oil boil two or three times; the wax will settle to the bottom of the dish, and the propolis will dissolve in the oil; when the prepared oil has cooled, carefully drain it from the sediment;
- lubricate the affected areas with an ointment prepared using the following mixture: burdock roots - two parts, hop cones - two parts, calendula officinalis flowers - one part; Preparation of the medicine: grind 10-15 grams of the dry mixture in a mortar into powder and mix with 40 grams of Vaseline.
Signs and symptoms of ringworm
Fungi of the genus Microsporum affect smooth skin, hair and, very rarely, nails. The clinical picture of the disease is different for different types of pathogens.
Signs of zooanthroponotic microsporia
Ringworm caused by Microsporum canis (fluffy, feline) is the most common in the Russian Federation. The incubation period for the disease is 5 to 7 days.
Scalp damage
At the end of the incubation period, 1 - 2 foci of hair thinning up to 3 - 5 cm in diameter appear on the head and many small ones (0.1 - 0.3 cm in diameter) along the periphery.
The lesions have a round shape, clear sharp boundaries, are covered with asbestos-like (grayish-white) thin scales (pityriasis peeling), the inflammatory component is weakly expressed. Infiltrative and suppurative forms of microsporia are registered.
Signs of hair damage
All hair in the lesions breaks off at a height of 5 - 8 mm above the skin level. Their fragments are surrounded by a muff (cover) of a grayish-white color, consisting of fungal spores. The hair is gray, dull, thickened, appears to be cut at the same level (the appearance of a mown meadow), is easily pulled out, and glows with a light green glow under a fluorescent lamp after 10 - 12 days.
Damage to smooth skin
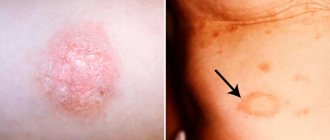
5 - 7 days after infection, foci of inflammation appear on the smooth skin of the face, arms, neck and even torso (children often pick up animals and often put them in bed). They are oval or round in shape, reddish in color, with clear boundaries; along the periphery there is a raised ridge covered with bubbles and thin crusts; peeling is visible in the center. The light-colored center and hyperemic edge in the shape of a roller make the lesion look like a ring. Areas of inflammation are single or multiple, 1 - 2 cm in diameter, sometimes merging, reminiscent of superficial trichophytosis. In 80 - 90% of patients, vellus hair is affected.
Exacerbation of ringworm begins from the central part, then a picture of circles inscribed into each other is formed.
Microscopy should be distinguished from superficial trichophytosis. The main clinical distinguishing features are:
- with microsporia, the evolution of rashes is faster;
- there is a tendency towards the appearance of multiple foci and their merging;
- formation of figures similar to double and triple rings.
A differential diagnosis is possible only taking into account the results of microscopy of the affected hair and examination of the scalp under a fluorescent lamp.
Sometimes an infiltrative-suppurative form of microsporia occurs (resembles suppurative trichophytosis). The disease is characterized by the appearance of fever and malaise, enlarged lymph nodes, and the appearance of mycids - rashes of an allergic nature. Dermatomycids can be superficial and deep, localized near the lesions or far from them. They resemble the rash of scarlet fever, measles, pityriasis rosea, parapsoriasis, etc. The appearance of dermatomycids is often accompanied by malaise, headache, weakness and increased body temperature.
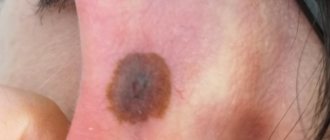
Rice. 15. Classic picture of damage to smooth skin with microsporia.
Rice. 16. Ringworm in children.
Rice. 17. Microsporia in a child.
Rice. 18. Ringworm on the face in adults.
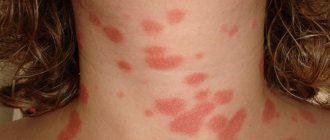
Rice. 19. Multiple lesions on the neck and face with microsporia.
Rice. 20. Ringworm in humans. The skin of the hands is affected.
Rice. 21. Multiple lesions on the body of a person with ringworm.
Signs of anthroponotic microsporia
In our latitudes, ringworm caused by Microsporum ferrugineum is very rare. The source of infection is sick people and their personal belongings, and very rarely animals. The incubation period for the disease is 4 to 6 weeks.
Scalp damage
The affected areas of the disease are multiple, usually small, irregularly shaped, with unclear boundaries and a roll-like edge. Their main localization is the marginal hair growth zone. When merging, foci up to 7 cm in diameter are formed. Sometimes the affected area covers 1/3 of the head area. Inflammation is mild. The skin is pale pink in color, often unchanged. Peeling is mild.
Signs of hair damage
Hair breaking under the influence of mushrooms occurs at different heights - usually 6 - 8 mm. Their fragments are surrounded by dense muffs consisting of pathogen spores. A lot of healthy hair remains in the lesions. Around the primary zone of inflammation, foci of elimination appear in the form of pink spots. When they merge, the affected area extends to the entire scalp and extends to smooth skin. Sometimes the affected areas are invisible and can only be identified using a fluorescent lamp. The glow in its rays takes on an emerald color.
Damage to smooth skin
At the site of the lesion, one or several foci appear, swollen, with clear boundaries, dark pink in color. The spot gradually increases in size; a continuous, raised ridge is formed along the periphery, with small bubbles, nodules and crusts located on it. Resolution of inflammation occurs from the center, where the skin turns pale and peels. As a result of evolution, the lesion takes the form of a ring. During an exacerbation, inflammation develops again in the center. The affected area becomes like a ring within a ring. Its diameter will be 0.5 - 3.0 cm. The disease occurs mainly without subjective sensations. Sometimes the patient is bothered by mild itching.
The disease is highly contagious, so early diagnosis can prevent epidemic outbreaks. Without treatment, lichen caused by Microsporum ferrugineum lasts a long time. Disappears by puberty.
Rice. 22. Microsporia caused by M. ferrugineum.
Classification of fungal infection
Microsporia in humans, initial stage photo
The classification of microsporia is important for clinicians to identify an infectious disease from skin lesions of another origin. Microsporia is classified according to the following main areas.
According to the location of the lesion:
- fungal infection of smooth skin;
- microsporia of the scalp;
- appearance on the nail plates.
Nail damage is a rare clinical situation and can only be caused by an advanced form of fungal infection of the human body. Fungal colonies can grow, affecting the nail plate. The rarity of the appearance of an infectious focus on the surface of the nails is explained by the lack of a nutrient medium for the fungus in this anatomical zone.
By pathogen type:
- Zoonotic microsporia. It is considered a type of zoophilic microorganisms carried by animals.
- Anthropotic form. The main carriers are people.
- Geophilic. This type of Microsporum fungus lives in soil substrates.
Classification according to the type of infectious agent does not have significant clinical significance in therapeutic practice, since the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment tactics are the same in all cases. This classification is used by epidemiologists to compile statistical values, as well as to determine the sources of infection in a certain area.
By type of clinical course:
- superficial;
- purulent (otherwise, infiltrative-suppurative).
The superficial form is characteristic of the anthropotic form of the fungus. The lesion covers the upper epidermal layers, causing peeling, redness of the skin, hair thinning, breakage, and loss in the affected areas. The infiltrative form of microsporia is one of the most severe clinical cases. Animals and much less often people are susceptible to infection, and only animals are the main carriers. In areas of skin lesions, large focal fragments with purulent exudate are recorded, and the patient’s general well-being suffers.
Diagnosis of microsporia
Diagnosis of microsporia is based on the clinical picture of the disease, epidemic history (contact with cats, dogs or sick people), microscopic and cultural data, and the presence of an emerald glow under a Wood's lamp.
Microscopic examination
Microscopic examination reveals the presence of fungal mycelium and spores. It is impossible to differentiate microsporia and trichophytosis by microscopy. Identification of pathogens is carried out using a culture method followed by microscopy.
The material for microscopy is the patient's scales and hair taken from the peripheral zone of the lesion. Hair breaks off 3 weeks after the onset of the disease.
With microsporia, under a microscope, the affected hair has a characteristic appearance:
- It is surrounded by numerous round spores, tightly adjacent to each other in chains in the form of a mosaic.
- The peripheral internal part is filled with septate mycelium.
- At the end of the hair shaft, a fringe consisting of mycelium threads is sometimes visible.
- In the scales taken for research, branching mycelium with clearly defined sparse partitions can be found.
- In the affected nails, fungal elements are similar to those in the scales.
Rice. 23. Microscopy of the affected hair with ringworm.
Rice. 24. In the photo on the left is a hair affected by Microsporum canis, on the right - Microsporum
Rice. 25. Microscopy of the affected hair with trichophytosis. Pathogen spores envelop the hair like a muff (photo on the left). The inside is filled with spores (photo on the right).
Diagnosis of ringworm using a Wood's fluorescent lamp
At the base of the hair, 10 - 12 days from the moment of infection, an emerald-colored glow appears in the rays of a Wood's lamp. The study should be repeated after 3 days.
Wood's lamp is a quartz lamp. Ultraviolet radiation passes through glass saturated with potassium salts. The examination is carried out in the dark. Hair should be washed with soap before the examination. This technique is widely used by medical professionals to identify sick people and animals.
Rice. 26. The emerald glow when using a Wood's lamp is characteristic only of microsporia.
Rice. 27. Wood's lamp is used to identify ringworm and monitor the effectiveness of treatment. An emerald-colored glow in a person (photo on the left) and an animal (photo on the right).
Differential diagnosis of ringworm
Differential diagnosis of ringworm is carried out with seborrheic dermatitis, a limited form of neurodermatitis, psoriasis, alopecia areata, discoid lupus erythematosus; in the suppurative form of microsporia - with trichophytosis, boil, carbuncle, favus.
Diagnostic measures
Some symptoms of the disease, especially if there is a history of other skin diseases, may be similar to each other. Diagnostic measures make it possible to accurately determine the development of the disease, exclude similar pathologies, and begin timely treatment. The main diagnostic methods include:
- laboratory tests (urinalysis, blood);
- biochemical blood test to determine liver function;
- scraping of fungi from the surface of the lesion to identify the type of pathogen;
- illumination with a fluorescent lamp.
The main task of differential diagnosis is to establish an accurate diagnosis in the shortest possible time, as well as to exclude the exacerbation of some chronic skin diseases.
Treatment of ringworm
When treating mycosis, it should be remembered that fungi in the stratum corneum of the skin are capable of maintaining not only vital activity for a long time, but also virulence (damaging ability). Therefore, in the treatment of microsporia, both local drugs with an antifungal effect, containing antiseptics and keratolytics, and drugs for oral administration are used. External treatment of ringworm lesions not only shortens the healing time, but also reduces the likelihood of transmitting the infection to others.
In the morning, the affected areas are treated with an antiseptic 2 - 5% alcohol solution of iodine and keratolytics are applied, in the evening antifungal drugs are used. If necessary, antimiotics are used 2 times a day.
Antifungal drugs for the treatment of ringworm
When treating single lesions on smooth skin, the use of antifungal drugs for external use in the form of ointments, creams, gels and suspensions is limited: Nizoral, Batrafen, Ketoconazole, Mikozolon, Travogen, Mikospor, Daktarin, Zalain, Terbizil, Lamisil, Mikospor, Exifin, Mikogel and etc.
An antibiotic with an antifungal effect, griseofulfin can be adsorbed in the horny substance of the epidermis, hair, nails and periungual beds. Contains the drug griseofulvin ointment and Fulcin suspension. Contains griseofulvin and salicylic acid cream, ointment and suspension Grimelan (Grimesad).
In case of a severe inflammatory reaction, it is recommended to use Travocot cream containing the glucocorticoid Diflucortolone and the antifungal drug Isoconazole.
If the scalp, smooth skin (more than 3 lesions) and vellus hair are affected, systemic antifungal therapy is prescribed. It is recommended to use the antimiotics Griseofulvin. If there is intolerance or contraindications, drugs containing terbinafine or intraconazole tablets are indicated.
Rice. 28. Ringworm in humans. With an exacerbation, the general appearance of the area of inflammation becomes similar to a ring within a ring.
Keratolytics for the treatment of microsporia
Keratolytic agents destroy the structure of keratin, soften and dissolve it, which facilitates the rejection of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Among keratolytic (exfoliating) agents, it is recommended to use preparations containing birch tar, salicylic and glycolic acids for ringworm. When treating the skin, 5% sulfur-salicylic and 10% sulfur-tar ointments, Wilkinson ointment, complex ointment with 3% lactic acid and 10% sulfur are used. Contains salicylic acid and the antifungal drug griseofulvin, the drug Grimelan (Grimexal).
Features of scalp treatment
The scalp is shaved before treatment and then 1-2 times a week until the end of treatment. It is recommended to wash your hair with shampoos containing antiseptics: povidone-iodine, selenium sulfide or resorcinol, antimyotic ketoconazole, exfoliating agents: birch tar, salicylic and glycoic acids, keluamide. Special medical dermatological shampoos are sold only in pharmacies.
Shampoos containing ketoconazole have a powerful antifungal effect. In case of illness, during the treatment period it is recommended to use shampoos with 2% ketoconazole (Ketoconazole, Nizoral, Mycozoral, Dermazol, Kenazol) and 1% ketoconazole (Sebozol, etc.). The Keto Plus anti-dandruff shampoo contains 2 antifungal components: 2% ketoconazole and 1% zinc pyrithione.
Features of treatment for smooth skin
Vellus hair removal techniques:
- Removal using epilin patch or griseofulvin patch.
- The affected area is lubricated with salicylic acid 2 times a day for 3 - 4 days. Next, a compress with 2% salicylic ointment is applied for a day. The peeled scales and vellus hairs are removed with tweezers.
- Removal using 10% milk-salicylic collodion (applied for 2 - 3 days) and then 2 - 5% salicylic ointment is applied on top under the compress for 2 days. After the procedure, the stratum corneum of the skin is easily scraped off. If necessary, the procedure can be repeated after 10 days. Next, the lesions are lubricated with antifungal and exfoliating ointments until the clinical manifestations of the disease disappear.
For ringworm, it is recommended to wash the body with medicated shampoos containing ketoconazole. You should not use a washcloth. It promotes the spread of infection. In case of severe inflammation, the lesions should be covered with cellophane or sealed with adhesive tape while taking a shower.
During the treatment period, you should wear a scarf covering your head and underwear made from natural fabrics. Change linen daily until the clinical symptoms of microsporia completely disappear.
During the treatment process, for the purpose of disinfection, underwear and bed linen are boiled in a soap-soda solution for 15 minutes. To prepare the solution, you need to take 10 grams of laundry soap and caustic soda per 1 liter of water. Outerwear, furniture covers and bedding are treated with iron steam.
Before using medications, you should carefully read the instructions.
Rice. 29. Ringworm in a child.
Treatment criteria and disinfection for microsporia
Ringworm treatment results are obtained using a Wood's lamp and microscopic examination of the scales and hair.
Cure criteria:
- Resolution of lesions.
- No glow under Wood's lamp.
- 3 negative tests performed using microscopy.
Rice. 30. The photo shows ringworm (microsporia) in a cat and a dog.
Treatment of ringworm is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor! Do not self-medicate. Carefully follow all recommendations for the use of medications.
Prevention and prognosis
Prevention of fungal skin infections comes down to maintaining hand and skin hygiene, and avoiding contact with other people's animals. Your own pets should be checked for various infections at least 2 times a year. This applies to families with small children. When a disease is detected, the patient must be isolated for adequate treatment and to prevent spread to other family members and surroundings. Household items and other personal belongings of the patient are subjected to antiseptic treatment and disinfection. With prompt consultation with a doctor and proper therapy, the prognosis for patients is favorable.
The disease does not pose any threat to the lives of patients. Proper treatment, organized on time, helps prevent irreversible damage to the structure of the skin (scars, scars). An untreated fungus on the scalp can cause baldness in the affected area and cause inferiority of the scalp. In addition to aesthetic defects, the disease can cause deep emotional distress, including depression and an inferiority complex. Timely therapeutic treatment can eliminate the risk of developing such negative complications.