In our last article, we talked about what candidiasis is and in more detail about candidiasis of the oral cavity and pharynx (candidal stomatitis, thrush, candidiasis of the tongue, etc.). In this text we will talk about skin candidiasis in children and adults.
Skin candidiasis can be divided into:
- candidiasis of skin folds;
- candidiasis of smooth skin (outside the folds);
— candidiasis of the corners of the mouth (jam);
Why do we start with the folds of the skin, because Candida fungi most often affect the folds of the skin.
The cause of damage to the skin folds is the moist environment of the skin folds, closed areas of the body in children when using diapers, plaster casts. In addition, candidiasis of the skin often occurs in large folds close to the entrance openings of the intestinal tube and vagina, thus, candida enters the folds from within the human body.
What is cutaneous candidiasis
This is an infectious disease caused by the Candida fungus . Candida fungus spores are always present in minimal quantities in the human dermis, but do not manifest themselves in any way.
Most often, the disease forms in the folds of the skin and on the mucous membranes, but it can also affect smooth skin. The most common areas where candidiasis occurs in women and men : armpits, groin areas, spaces between the fingers, under the breasts in women.
The development of the disease indicates the presence of problems in the body or a disorder of the immune system. It appears as a rash, often with pus and erosion.
Routes of infection
The amount of candida fungus can also increase upon contact with a previously infected person. For example, the causes of candidiasis in this case are as follows:
- during sexual contact (usually in this case the urogenital, vaginal or oral form develops);
- during pregnancy (in this case, the infection is transmitted from mother to child, and he/she develops symptoms of candidiasis at birth);
- during dental procedures (for example, prosthetics - in this case, an adult develops candidiasis in the mouth);
- injuries to the eyes, ears, skin (infection gets into the wounds).
Causes of candidiasis
Skin candidiasis begins to actively develop when it becomes pathogenic. This can be caused by several reasons:
- metabolic disease;
- avitaminosis;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- postoperative therapy;
- immunodeficiency;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
As a rule, it is internal factors that provoke the development of this disease. But occasionally it can be triggered by external factors, such as:
- microtraumas;
- wearing synthetic items or too warm clothes that increase sweating;
- poor hygiene;
- exposure to harmful substances on the skin.
People whose professions involve chemical production and have a lot of contact with water should especially carefully monitor the condition of their skin.
Complications
Medicines for candidiasis must be taken as early as possible, otherwise the disease may become advanced and become chronic. It is dangerous due to numerous complications.
For example, due to urogenital and vaginal candidiasis, diseases of the kidneys, urinary tract, and reproductive organs develop. There may even be infertility, cervical erosion in women, urethritis and prostatitis in men. If such a disease appears during pregnancy, a miscarriage is possible.
With ear candidiasis, sepsis may develop and hearing may deteriorate. With ocular vision, vision drops sharply. With candidiasis of the digestive organs, there is a possibility of developing anemia and peritonitis.
Classification of candidiasis and symptoms
The disease is classified according to the localization of the process and each type has specific symptoms:
- manifested by redness of the skin, rashes and swelling. It may also be accompanied by itching and burning in the genital area, and discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Urogenital candidiasis- Smooth skin candidiasis is the rarest form and affects the skin of the face. It manifests itself as papules, blisters and erosions, often accompanied by severe swelling.
- Candidiasis of large folds - manifests itself as red spots in the groin and thigh areas, as well as in the folds between the buttocks and under the breasts.
- Oral candidiasis is a disease that affects the mucous membranes. Plaque appears on the tongue and the inside of the cheeks, and redness of these areas, including the gums, also occurs.
- Childhood candidiasis - often manifests itself in infants, a rash appears on the buttocks, in the perineum and on the inner thigh.
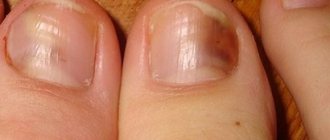
- Nail candidiasis - occurs directly on the surface of the nail plates, brown or yellow spots form, the nails begin to peel and peel, and then completely crumble.
There is a certain classification of candidiasis ; only a specialist can identify and determine the type of disease.
In recent years, there has been a steady increase in the incidence of diseases caused by opportunistic fungi, among which candidiasis is the most frequently recorded. The increase in the incidence of candidiasis is associated, first of all, with the use of modern therapeutic agents, as well as with environmental changes, in particular, with an increase in background radiation and other factors that weaken the immune system.
Etiology
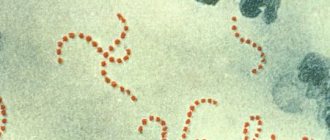
Candidiasis is caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida
, widespread in nature and classified as opportunistic microorganisms.
of Candida
are registered as causative agents of candidiasis , which are considered pathogenic for humans;
these include C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. krusei
, etc.
Epidemiology
The causative agents of candidiasis are isolated from the intestines, genitals and bronchial secretions on average in every third person. Primary colonization of the body occurs in the birth canal, and after birth - through contact and nutrition. Infection of a child can occur due to candidiasis of the mother's nipples, from service personnel, through household items, etc. There have been outbreaks of candidiasis in newborns in maternity hospitals. Sexual transmission of candidiasis cannot be ruled out.
Pathogenesis
The main factor in the development of candidiasis is considered to be a background condition or disease of the body, in which opportunistic pathogens acquire pathogenic properties. In recent years, many researchers have come to the conclusion that the main predisposing factor for the occurrence of superficial forms of candidiasis, incl. in HIV infection, is mainly a violation of cellular immunity. A certain role in the development of candidiasis is played by the frequent and not always justified prescription of broad-spectrum antibiotics, incl. for prophylactic purposes, as well as the widespread use of drugs that have an immunosuppressive effect - glucocorticoid hormones and cytostatics. According to Zh.V. Stepanova and L.L. Smolyakova, in children staying in somatic departments of hospitals and receiving antibacterial therapy, damage to the oral mucosa caused by yeast-like fungi is observed in 6.6% of cases, of the oral mucosa and skin - in 15%, of the intestines - in 2.5% , candidiasis in the intestines – in 9.2%.
Candidal paronychia and onychia on the fingers, as a rule, develops in women who have frequent contact with water, while separation of the nail skin (eponychion) from the nail plate is observed, creating favorable conditions for fungal infection in the matrix area. The disease can occur in people suffering from diabetes mellitus, HIV-infected people, who have been receiving antibacterial drugs, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, etc. for a long time. In recent years, women have begun to use false nails, and therefore another risk factor has emerged for the development of fungal and bacterial infections.
Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida
can cause damage to the mucous membranes, skin and its appendages, and internal organs. The most common forms of mycosis are superficial.
Clinical picture: Candidiasis of smooth skin
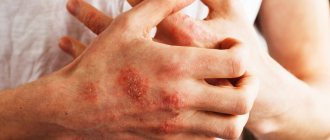
The main localization of the disease is large (inguinal-femoral, intergluteal, under the mammary glands, axillary cavities) and small (interdigital) folds, but rashes can occur on the smooth skin of the trunk and limbs, incl. palms and soles. Outside the folds, foci of candidiasis develop mainly in infants, as well as in adults suffering from diabetes mellitus or severe general illness. In large folds small bubbles, the size of millet grains, and sometimes pustules appear, which open to form erosions. Due to peripheral growth, erosions quickly increase in size and merge, forming large areas of damage. The lesions are dark red in color with a burgundy tint, shiny, with a moist surface, irregular in shape, with a strip of exfoliating epidermis along the periphery. Fresh small erosions (screenings) form around large foci. In children, especially weakened ones, from the folds the lesion spreads to the skin of the thighs, buttocks, abdomen, and sometimes to the entire skin. There may be painful cracks deep in the folds. Candidiasis of smooth skin outside the folds (chest, abdomen, shoulders, forearms, legs, etc.) in children has a clinical picture of seborrheic dermatitis; in adults, the disease can manifest itself in the form of erythematous spots with peeling in the center and small blisters along the periphery. Candidiasis of smooth skin of small folds (interdigital erosion) most often occurs between the 3rd and 4th, 4th and 5th fingers of the hands, less often of the feet, and is characterized by the formation of eroded foci of a rich red color with a smooth, shiny, as if varnished surface, clear boundaries, with flaking of the horny layer of the epidermis along the periphery. The disease can begin with the appearance of small blisters on the lateral touching hyperemic surfaces of the skin, then spreads to the area of the interdigital fold, swelling, maceration, and peeling appear. Interdigital candidal erosion is observed mainly in individuals who have prolonged contact with water, which contributes to the development of skin maceration; in addition, favorable conditions are created for the development of candidal infection. In addition to the third and fourth folds, others may be affected, not only on one, but also on both hands. Patients are concerned about itching, burning, and if there are cracks, pain. The course of the disease is chronic, with frequent relapses. Candidiasis of the smooth skin of the nipples in nursing women deserves attention. Its clinical manifestations can be different: slight hyperemia in the area of the isola; lesion near the nipple with maceration, clear boundaries; fissure with maceration along the periphery and small bubbles between the nipple and the isola.
Candidiasis of the palms and soles is rare. On the palms, the disease can occur as dry lamellar dyshidrosis (superficial lamellar, ring-shaped or garland-shaped peeling), vesicular-pustular form (vesicles and pustules against the background of hyperemic and edematous skin) and hyperkeratotic eczema (against the background of diffuse hyperkeratosis or individual areas of keratinized skin are observed sharply limited wide skin grooves with a dirty brown color). Candidiasis of the skin of the soles occurs mainly in children and is characterized by the presence of small blisters and pustules, hyperemic spots with peeling and exfoliating macerated epidermis along the periphery.
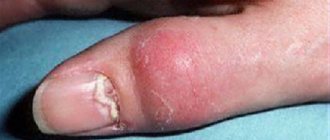
Candidiasis of the nail folds and nails (candidal paronychia and onychia)
The disease begins from the posterior ridge, most often in the area of its transition to the lateral ridge, with the appearance of hyperemia, swelling and swelling of the skin. Then the inflammatory phenomena spread to the entire roller, which becomes thicker and seems to hang over the nail, and peeling is observed along the edge of the roller. The skin of the roller becomes thin, shiny, and the nail skin (eponychion) disappears. When the roller is pressed, ichor, a lump of white crumbly mass, or a drop of pus may be released (due to the addition of a secondary infection). Later, the nail plate changes: it becomes dull, in the area of the lunula it is separated from the bed, destroyed as onycholysis, or transverse grooves and elevations appear on it. These changes are associated with impaired blood supply in the matrix area, i.e. they are trophic in nature and are caused by inflammation in the area of the cushion. When the fungus penetrates the nail plate, and this happens from the lateral edges, the nails become thinner, separate from the bed, acquire a yellow-brown color and look as if they are trimmed on the sides. In young children, inflammatory phenomena in the area of the cushion are more pronounced, and the nail plate changes from the distal edge. There is candidiasis of the nails without inflammation of the ridge. In this case, the change in the plate begins from the distal edge and develops according to the type of onycholysis; the plate becomes thinner, does not adhere to the bed, and there may be multiple lesions of the nails.
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis
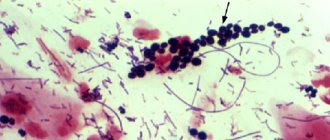
In superficial forms of candidiasis, the diagnosis is based on the presence of a characteristic clinical picture in the patient and identification of the fungus in pathological material (skin flakes, scrapings from nails) during microscopic examination. The diagnosis can be considered reliable if pseudomycelium or true mycelium and budding cells are detected. Sowing on a nutrient medium is carried out to identify the type of yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida
. Isolating only a culture of the fungus has no diagnostic value, since it can be obtained by culturing scrapings from the skin and nails of healthy people.
With candidiasis of smooth skin of large folds and outside the folds, the disease should be differentiated from seborrheic eczema, psoriasis, and other mycoses - inguinal athlete's foot, superficial trichophytosis, pseudomycosis erythrasma (complicated form); with interdigital candidal erosion on the hands - from dyshidrotic eczema, on the feet - from mycosis caused by Trichophyton interdigitale
and
Trichophyton rubrum
; when nails and ridges are affected - from onychia and paronychia of bacterial etiology, eczema and psoriasis.
Treatment
Considering that candidiasis is an opportunistic mycosis, first of all, it is necessary to identify and, if possible, eliminate the pathogenetic factors of the disease (study of the immune and endocrine status, gastrointestinal tract and corrective therapy). Limited and sometimes widespread forms of smooth skin lesions, especially those that developed during treatment with antibacterial drugs, as a rule, are easily treated with local antifungal agents and can resolve without treatment after discontinuation of antibiotics. Local and systemic antimycotics are prescribed as etiotropic therapy. In recent years, azole drugs with a broad spectrum of action, as well as polyene antibiotics, have been widely used in the treatment of candidiasis.
For candidiasis of large folds of smooth skin with acute inflammatory phenomena, treatment should begin with the use of an aqueous solution of brilliant green (1-2%) in combination with an indifferent powder and continue for 2-3 days, then antimycotic drugs should be prescribed until the clinical manifestations resolve.
For candidiasis of large, small folds and other areas of smooth skin, antifungal agents are used in the form of cream, ointment and solution: ketoconazole, clotrimazole, oxyconazole, bifonazole, natamycin. The cream or ointment is applied in a thin layer to the lesions and rubbed in 1-2 times a day, the duration of treatment is until the clinical manifestations resolve, then it is recommended to continue using the cream for another 7-10 days to prevent relapse. In case of widespread processes on the skin and the ineffectiveness of local therapy, systemic antimycotics are prescribed: fluconazole - for adults at a dose of 100-200 mg, for children at a dose of 5 mg/kg body weight; itraconazole - adults at a dose of 100-200 mg; nizoral - adults at a dose of 200 mg 1 time per day daily, as well as the polyene antibiotic natamycin (adults 100 mg 4 times a day, children 50 mg 2-4 times a day). The duration of therapy is 2-4 weeks.
For candidiasis of the nail folds and nails, anti-inflammatory treatment of the fold is first carried out using applications of pure ichthyol, which are done once a day until the inflammatory phenomena subside. Then apply antimycotic agents (ketoconazole, oxiconazole, isoconazole, clotrinazole, etc.) for topical use, rubbing them under and around the roller. The procedures are carried out 2 times a day, in the evening the drugs can be used under an occlusive dressing. It is possible to combine an ointment (cream) with a solution, alternating them. If the nail plate is involved in the process, you can not remove it or clean off the infected areas after softening with keratolytic agents (bifonazole in the nail treatment kit), and then treat the nail bed with antifungals for external use. Therapy is carried out until clinical manifestations resolve and a healthy nail plate grows. If it is ineffective, systemic antimycotics are prescribed: fluconazole according to an intermittent regimen (adults 150 mg once a week, children 5-7 mg/kg body weight); itraconazole (adults) using the pulse therapy method (200 mg 2 times a day for 7 days, then a 3-week break) for 2-3 months; nizoral (adults) 200 mg per day daily for 2-4 months.
Prevention
- To prevent the development of candida infection in children who are in somatic departments of hospitals and receiving antibacterial drugs, they need to be prescribed fluconazole at a rate of 3-5 mg/kg body weight once a day. The daily dose depends on the degree of risk, treatment is carried out during the main therapy.
- Patients with candidiasis in the intestines are prescribed nystatin 2-4 ml IU per day or natamycin 50 mg for children and 100 mg for adults 2 times a day for 15 days.
- Prevention of the development of candidiasis in patients with severe somatic and endocrine diseases, as well as with immunodeficiency (multiple mycological studies).
- Prevention of dysbiosis.
- Prevention of the development of candidiasis in newborns.
Diagnosis and treatment
It is not enough to see only the clinical manifestations and make a diagnosis; it is necessary to make a scraping with removal of separated particles from the affected area and undergo a series of other tests. Only after laboratory testing and a thorough examination can a doctor make an accurate diagnosis.
The disease requires a course of treatment, the basis of which is antifungal drugs. To achieve maximum therapeutic results, an integrated approach is required:
- carry out therapy to combat the pathogen;
- destroy the endogenous source of the pathogen;
- cure concomitant diseases that provoke skin candidiasis;
- carry out restorative therapy.
Advantages of taking tests at JSC "SZDCM"
- Own laboratory with the latest diagnostic equipment.
- Convenient location of terminals within transport accessibility from anywhere in the city.
- Qualified laboratory technicians and friendly staff.
- Fast analysis and several options for obtaining results. Choose the one that is most convenient for you.
Medical centers and laboratory terminals of the North-Western Center for Evidence-Based Medicine are located in St. Petersburg, Leningrad region, Veliky Novgorod, Okulovka, Kaliningrad and Pskov.
Analyzes
- Bacteriological study for opportunistic pathogenic flora (OPF)
- NC yeasts of the genus Candida: C.albicans, C.krusei, C.glabrata
- Study of the biocenosis of the urogenital tract in women (“Femoflor 13 - screening”)
- Candida albicans
- Mycoses: identification of clinically significant fungi with determination of sensitivity to antimycotic drugs (only for fungi of the genus Candida and Cryptococcus neoformans)
- Specific immunoglobulin E - Candida albicans
go to analyzes
Recommendations for effective treatment
In the process of undergoing medical therapy, it is necessary to give up bad habits and limit yourself to excessive consumption of foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates.
Treatment is prescribed only by a doctor; self-medication can lead to serious, irreversible consequences.
If you are faced with a problem such as skin candidiasis , immediately contact a dermatovenerologist. Only proper treatment will relieve you of the problem.
Risk factors for development
The likelihood of infection increases with casual sexual intercourse, uncontrolled use of antibiotics and drugs that disrupt the natural microflora. Foods with large amounts of sugar and carbohydrates create a favorable environment for fungal growth. Excessive sweating also leads to an exacerbation of candidiasis, so it is necessary to wear cotton underwear that allows the skin to breathe and moisture to evaporate.
At the same time, excessive cleanliness can also cause harm. We are talking about douching. It should not be used as a method of contraception, since it is not effective, and also as a means of hygiene, because it leads to the leaching of the protective flora. If you experience discomfort, you should first consult a doctor.
When to see a doctor
It is necessary to contact a specialist as soon as the first suspicion of candidiasis appears. This applies to symptoms such as mild malaise, discomfort, itching, peeling of the skin, splitting of the nails, redness of the skin and mucous membranes in the mouth, groin, cheesy discharge on the genitals, burning sensation when urinating, vomiting, chest and abdominal pain, diarrhea and etc.
In case of candidiasis, which doctor diagnoses and draws up a treatment regimen for candidiasis depends on the location of the pathological processes. This could be a dermatologist, urologist, gynecologist.
Treatment of candidiasis in women
Basically, to the general treatment described above, vaginal treatments are added on the gynecological chair with antiseptic, antifungal solutions, during which fungal layers are completely removed from the surface of the vaginal mucosa and a high concentration of drugs is created, which has a detrimental effect on the remaining Candida cultures.
After the first treatment, 95% of women feel significant relief and a decrease in the severity of symptoms.
The cost of the procedure is 800 rubles.
In case of a chronic process, a course of such treatments is recommended, which, in combination with probiotics, not only removes fungi, but also restores the normal microflora of the vagina and the state of local immunity.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is also carried out with a vaginal laser, electrophoresis, and baths with an ozonized sodium chloride solution, which helps to either completely get rid of relapses of chronic vulvovaginal candidiasis or reduce its exacerbations.
In case of a chronic process, two-stage treatment is always recommended for all patients, and especially women.
The first stage is the destruction of the fungus.
The second stage is the restoration of normal microflora of the intestines and vagina.
Treatment of candidiasis in men
Our clinic uses the following types of local treatment:
- Baths with antiseptics and antifungal drugs on the head of the penis.
- Wet-dry dressings for erosive and ulcerative lesions of the head and foreskin.
- Instillations into the urethra for candidal urethritis - 800 rubles.
- Total instillations for fungal infections of the posterior urethra and prostate. — 1000 rub.
- Ultraviolet irradiation of the skin of the scrotum and groin areas. — 800 rub.
- Electrophoresis of antifungal drugs into the lesion. -1200 rub.
- Laser irradiation of foci of chronic candidiasis. — 800 rub.
Transfer methods
There are several ways you can get this fungal infection. The most clinically important among them are:
- Infection of the fetus from a mother infected with candidiasis. In this case, the disease is contagious in 70% of cases from all births, regardless of whether the child passes through the birth canal (naturally or through a cesarean section);
- Contact and household path. Contact with a sick person or carrier (hugs, kisses, sexual intercourse, sharing the same dishes, bedding or clothing) is almost guaranteed to lead to transmission of infection;
- Sexual contact without using barrier methods of contraception (condom);
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. This is irregular use of water procedures, ignoring oral care (especially for carious teeth), prolonged wearing of underwear, etc.;
- Contact with surrounding objects on the surface of which fungi of the genus Candida are present. It is important to understand that these microorganisms can maintain their vital activity under optimal environmental conditions for two weeks.
- Through the gastrointestinal tract.
Prevention
In order not to think later about how to treat candidiasis, it is recommended to regularly prevent candidiasis. To do this, you need to switch to a healthy lifestyle, strengthen your resistance to any stress, infectious diseases, and avoid hypothermia. Hardening, consuming vitamin and mineral complexes, and a proper and balanced diet will also benefit. It is also important to promptly treat any diseases. Diet for candidiasis is also important: avoiding sweets, bread and confectionery, fatty foods, and fried foods. It is better to eat boiled and steamed food, as well as more fresh fruits and vegetables.