More than 50% of men and women are infected with papillomavirus.
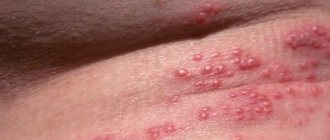
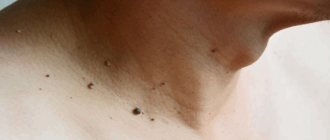
Often, signs of HPV appear on the abdomen. Such papillomas are benign in nature and have a drop-shaped shape.
Often, papillomas located in the abdominal area do not cause any particular inconvenience to their owner. But damage to formations can lead to adverse consequences.
Doctors strongly recommend removing papillomas on the abdomen. However, it is first necessary to diagnose the type of growth and assess the possible risks that arise after radical treatment.
Causes
Papillomas are soft skin formations. Warts can be flat or raised on the body on a thin stalk.
The leading factor that causes papillomatosis is infection of the body with HPV infections. In a healthy person, the virus may not manifest itself for years.
But why then do papillomas form on the abdomen?
The causes and methods of treatment of neoplasms depend on their type and the presence of provoking factors.
Papilloma on the abdomen is the leading cause of appearance:
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- weak immunity;
- stress;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- promiscuity;
- infections;
- long-term use of medications, including antibiotics;
- smoking;
- depressive states;
- visiting beaches, saunas, swimming pools.
Routes of transmission of the virus
The leading way of occurrence of HPV is considered to be frequent change of sexual partners. Also, umbilical papilloma, located in the navel and abdomen, is formed after infection of the fetus as it passes through the infected birth canal. That is, the virus is transmitted directly from a sick mother to a child.
An equally common way to get papillomavirus is visiting public places:
- sauna;
- gym;
- pool;
- bath;
- toilet.
In addition, HPV can get on the skin of the abdomen after it is injured during hair removal, shaving, wearing piercings, etc.
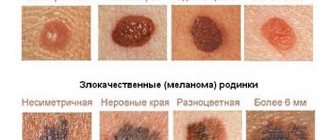
Classification of papillomas
Papillomas come in a variety of types. And in the abdomen and navel area they diagnose:
- Regular or vulgar growths. Outwardly they resemble a flat, rounded nodule, the diameter of which does not exceed five millimeters with a keratinized scaly surface;
- Flat neoplasms. They are compactions slightly raised above the skin. Often lead to inflammatory processes of the epithelium, which causes additional discomfort to its “owner”;
- Acrochords or filamentous papillomas. Round defects that grow in length. Externally, the edge of the growth resembles a torn thread. Not accompanied by pain or itching. Often damaged.
It is not difficult to determine what kind of papilloma has appeared on the skin using photographs from the Internet. However, don't rush to conclusions. The final diagnosis will be made by a dermatologist.
Types of growths and their danger
The pathogens that provoke the appearance of growths on the abdomen are low-oncogenic species that degenerate into malignant neoplasms. There are more than 100 types of warts that form on the body.
What papillomas on the abdomen are called and look like is indicated in the table:
| Kinds | Color | Form | Manifestations | Peculiarities |
| Simple Up to 1 mm | Light brown, gray-brown | Round Cornified | They do not cause discomfort. | Most often occur in adolescents or children. |
| Flat 8-10 mm | Bodily | Angular Smooth | Skin inflammation, redness, itching. | Flat papilloma on the abdomen is very noticeable, which causes significant aesthetic discomfort. |
| Filiform (acrochords) Up to 6 mm | Grey, black, brown | Elongated, knob-shaped Crust-shaped | The friction of the abdomen against clothing injures the affected area, leading to inflammation and bleeding. | Formed in adulthood and old age. |
| Pointed | Brown, nude | Grain-shaped, may resemble cauliflower. Wet, fluffy | Burning, discomfort, itching, bleeding. | There is a high risk of malignant degeneration of condylomas. |
The danger of papillomas is that they are a cosmetic defect. Therefore, the owner of growths may experience stress when exposing his stomach on the beach, in the pool or sauna.
Also, the growths are easily injured and inflamed by friction with clothing, which can lead to subsequent infection of the wound and the spread of the virus.
But the greatest risk of the formation of papillomas on the abdomen is the likelihood of their degeneration into an oncogenic strain.
Possible treatment
Neoplasms
If a formation is detected in the navel area, you should contact a surgeon. The examination can also be carried out by a local physician, who will refer you for further examination. If the abscess is suspicious and there is a possibility of its malignancy, only an oncologist should carry out treatment. To determine the type of formation, it is necessary to do an ultrasound and x-ray. Sometimes they are sent for gastroscopy. Once an accurate diagnosis is made, surgical excision is performed in most cases.
Fungus in a child
Most often, fungus treatment in infants is carried out at home. The main thing that needs to be monitored is careful care of the wound and cauterization of formations. To achieve the desired effect, the procedures must be repeated every day. Also, for speedy healing, it is important to ensure that the growths do not come into contact with the diaper.
To eliminate fungus in a child, you will need to treat the area with special preparations and carry out hygiene procedures more carefully.
| Methods of treating fungus in children | |
| Umbilical toilet | The umbilical wound must be thoroughly washed with water every day. |
| Antibiotics | If necessary, use antibacterial agents in the form of ointments, creams, solutions or sprays. |
| Hydrogen peroxide | A peroxide solution is instilled into the washed wound. |
| Zelenka, potassium permanganate or iodine | Treat the growth with disinfectant solutions. |
| "Chlorophyllipt" | The advantage of treating with an alcohol solution of Chlorophyllipt or another colorless antiseptic is that they do not stain the skin. Thanks to this, it is possible to notice inflammation in time. |
| Regular salt | Twice a day, salt is poured into the wound, sealing it with a band-aid. After 30 minutes, the navel is washed with water. |
If home treatment with conservative methods does not produce results, it is necessary to resort to surgery.
Course of the disease
After entering the body, HPV infects the basal epithelium. In an infected cell, the pathogen lives in two types. The episomal form (the virus does not infect the cell chromosome) is benign. With the introsomal type, the pathogen invades DNA cells, which increases the risk of oncogenicity.
Often, papillomas on the abdomen bother people with weakened immune systems. The incubation period of HPV can last from 30 days to 2-3 years. The disease has a latent course.
When infected, several strains of HPV can enter the body at once. Provoking factors contribute to the activation and multiplication of the virus, against which clinical signs appear.
With chronic recurrent HPV, the growths can be single or merge with each other due to the spread of infection. As the disease progresses, the formation may change in size, type or color of papillomas.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the type of papilloma in the navel and abdominal area, you need to consult a dermatologist. First, the doctor examines the growths and, if necessary, prescribes instrumental diagnostic methods.
There are 2 main methods for determining the HPV type:
- Digene HPV test - allows you to determine the type of virus and its concentration.
- PCR – determines the presence of infection and its type.
- Cytological examination is effective in 80% of cases.
If, after studying the results, the doctor suspects that the formation may be oncogenic, then further diagnostics are carried out aimed at determining the malignancy of the growth. For this purpose, colposcopy is prescribed, which determines the parameters, location of the wart and the degree of risk of cancer. A biopsy is also done, which involves examining a small part of the papilloma under a microscope.
To identify the nature of the virus and prescribe optimal treatment, in addition to the diagnostic methods described above, scrapings, smears and blood are taken from the infected person for analysis.
Tumor in the intestine: signs and early diagnosis of neoplasms
An intestinal tumor is a pathological formation formed as a result of the proliferation of cells in which the processes of reproduction and/or growth rates have significantly changed (benign neoplasms) or the maturation processes have been disrupted (intestinal cancer).
Benign intestinal tumors are neoplasms that develop in different layers of the wall of the small or large intestine and are characterized by slow growth and a relatively favorable prognosis.
A separate type of intestinal neoplasms are heterotopias from other organs (proliferation of cells from other organs) - endometriosis and carcinoid (a hormonally active tumor in structure resembling cancer, but characterized by slow growth and a benign course).
Malignant tumors of the intestine include intestinal cancer. A malignant tumor arises as a result of the rapid division of immature cells or as a result of malignancy of benign tumors.
Signs of an intestinal tumor
The first signs of an intestinal tumor in a person depend on:
- on its location (small or large intestine);
- histological structure and type of growth;
- development period (latent, prodromal and severe symptoms);
- patient's gender;
- the age of the patient and the presence of concomitant pathology;
- forms and stages of the disease.
In the latent or latent period, both with benign neoplasms and the development of malignant intestinal tumors, there are no symptoms of the disease, and the pathological process can be determined during instrumental examinations of the patient (contrast radiography, FGDS) or accidentally during planned or emergency surgical interventions.
The first signs of a tumor in the intestine appear in the prodromal period in the form of nonspecific symptoms:
- persistent dyspepsia (belching, heartburn, bitterness in the mouth, heaviness in the stomach, nausea, and less often vomiting);
- bloating, difficulty passing gas, intestinal colic;
- periodic aching or cramping pain in the abdomen, turning into a constant pain syndrome;
- prolonged diarrhea or constipation, their alternation;
- loss of appetite, weight loss (with malignant neoplasms, there is an aversion to meat or other products);
- pale skin, fatigue, weakness, anemia, difficult to treat with iron-containing drugs (especially in benign vascular tumors - cavernous or capillary hemangiomas, as well as intestinal cancer);
- darkening of stool, which is associated with latent (hidden bleeding);
- prolonged low-grade fever (body temperature does not fall below 37 C);
- mucus, streaks of blood in the stool.
During the period of severe symptoms, there are clear signs of the presence of a neoplasm in the intestinal cavity or germination into neighboring organs:
- progressive deterioration of health and increase in all nonspecific symptoms;
- significant reduction in body weight;
- persistent pain in the area where the tumor is located;
- palpable tumor in the abdomen;
- signs of intestinal obstruction (prolonged retention of stool, gases, increased peristalsis);
- mucus, blood in the stool, sometimes the presence of pus;
- intestinal bleeding;
- pain when urinating, urinary retention (when a tumor grows into the prostate gland and bladder in men);
- the release of gases and feces from the vagina when an intestinal tumor grows into the uterus and vagina and the formation of retrovaginal fistulas are symptoms of an intestinal tumor in women.
Early detection of intestinal tumors
Timely diagnosis of an intestinal tumor and removal of a benign tumor significantly increases the patient’s chances of a complete recovery.
Today, there are various methods for diagnosing the presence of a neoplasm in the intestine:
- “routine” (simple) methods: collection of complaints and medical history, palpation, digital examination of the rectum, radiography using contrast agents (irrigoscopy), FGDS, colonoscopy, transrectal ultrasound;
- new universal methods: determination of tumor markers in blood serum, CT and MRI, positron emission tomography.
Therefore, it is important to know what symptoms exist for an intestinal tumor, and if they appear, contact a medical facility as soon as possible to exclude or confirm the diagnosis.
To diagnose intestinal tumors, specialists at our clinic use Expera endoscopic equipment, which allows for examination with high quality and image resolution. Also, this new generation device has the ability to perform narrow-spectrum gastro- and colonoscopy in NBI mode.
This method allows you to:
- identify a tumor at the earliest stages of its development immediately after the first symptoms appear;
- carry out a simultaneous biopsy to determine the cellular composition of the tumor or with minimal likelihood of suspicion of malignant growth;
- stopping intestinal bleeding;
- removal of a foreign body from the intestine.
Today, endoscopic examination with intravenous sedation (introducing the patient into short-term sleep) is justified, which contributes to the early diagnosis of intestinal tumors and elimination of symptoms (the prognosis of the disease improves).
Is it necessary to remove papillomas?
When the body is infected with papillomatosis, many believe that papillomas in the navel are an aesthetic defect. However, HPV can change the DNA of cells, causing them to reproduce abnormally. This suggests that skin formations are dangerous and can cause the development of cancer.
Removal of papillomas on the abdomen is necessary if:
- warts quickly spread throughout the body;
- the formation is constantly exposed to injury or friction;
- the growth changed color, increased in size, and began to bleed or hurt.
It is noteworthy that eliminating warts does not guarantee that they will not form again in the future. After all, HPV is often present in the body, without manifesting itself at all until a favorable period appears when immunity decreases.
Treatment methods
Often, papillomas located on the abdomen do not threaten human health and life, because such formations rarely transform into cancer. But there is a minimal probability, in particular, when the wart is systematically injured.
If papillomas are present on the abdomen, then treatment is selected based on the strain of the virus. Complex therapy is often carried out, including removal of the growth, either medicinally or radically, as well as the use of antiviral, immunostimulating agents, and vitamin complexes.
Mechanical removal
The appearance of papilloma in the navel indicates that the infection is actively spreading throughout the body, allowing the disease to progress. Therefore, doctors advise using drastic methods to eliminate the growth.
How to remove papillomas on the stomach?
To get rid of warts, mechanical types of elimination are used:
- cryosurgery - formations are frozen with liquid nitrogen, which leads to the destruction of pathogenic cells. Wound healing takes 2-4 weeks.
- Radio waves - the method of cutting off papilloma involves using a special electrode that emits radio wave energy. The method requires the additional use of analgesics.
- Laser coagulation - the growth is excised with a light beam. The advantages of the procedure are rapid regeneration of treated tissues, minimal risk of scar formation.
Also, papillomas located on the abdomen are removed using electrocoagulation. The essence of the procedure is burning out the growth with high-frequency current.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment of papilloma on the abdomen consists of the use of drugs that burn out the tumor. The use of antiviral, immunomodulating agents, and vitamin complexes is also indicated.
To burn off warts at home, chemical solutions are often used, which lead to necrosis and subsequent rejection of the warts.
Popular drugs for removing papillomas:
- Cryopharma;
- Feresol;
- Salicylic acid;
- Verrucacid;
- Podophyllin;
- Super clean.
To suppress viral activity, the dermatologist prescribes antiviral medications for external, rectal and oral use. These drugs include Groprinosin, Acyclovir, Panavir, Viferon, Isoprinosine, Allokin alfa.
To activate the body's defenses, with frequent relapses and severe cases of HPV, immunomodulators are used.
The basic component of such drugs is interferon, obtained artificially from human immune cells. Popular immunostimulants are Interferon, Reaferon, Thymosin.
To stimulate the body's protective function, therapy for papillomavirus includes the use of vitamin complexes. It is preferable that such products contain vitamins A, D, C, B, PP, F, E.
Folk remedies
In the acute course of HPV infection, when papilloma appears on the abdomen, drug therapy can be supplemented with traditional methods of treatment. Garlic is often used to remove growths at home. The peeled cloves are crushed, combined with cream and applied to the infected area.
Cover everything on top with adhesive tape and leave for 3 hours. Treatment is carried out every day for up to one month.
Celandine is also often used for papillomavirus. Juice is obtained from the plant, which is used to treat the affected skin. Gauze is placed on top and a bandage is applied. The procedure is carried out until the growths completely disappear.
Other folk methods for removing tumors in the abdominal area:
- wipe condylomas or acrochords with apple and dandelion juice.
- Apply beaten egg white to the wart, which should be used for up to 3 months.
- Rub a mixture of boric acid, aspirin, ethanol, and iodine into the formation.
To suppress viral activity, herbal decoctions are taken orally. Medicinal drinks are prepared from horsetail, lemon balm, nettle, dandelion, and plantain.
Navel: anatomy, physiology, causes of fistula formation
The navel or belly button is a scar that remains on the anterior abdominal wall after the remnants of the umbilical cord, which previously connected the baby through the placenta with the mother’s body, fall off. In the embryonic period, the following pass through it:
- two umbilical arteries (aa. umbilicales)
- umbilical vein (v. umbilica)
- vitelline duct (ductus vitellinus)
- urinary duct (urachus)
With the baby’s first breath, the vessels stop functioning, and the vitelline and urinary ducts become overgrown normally at 3-5 months of embryogenesis, with the first turning into a Meckel’s diverticulum, and the second into a median ligament running along the inner surface of the abdominal cavity from the bladder upward.
What are umbilical fistulas?
- coming from the vitelline duct
With a complete fistula, the ileum communicates with the external environment through the navel; symptoms include the release of intestinal contents from the navel, an enlarged umbilical ring. The condition is dangerous due to intestinal strangulation in the umbilical ring and its necrosis with the development of intestinal obstruction. An incomplete fistula (1-2 cm deep from the umbilical fossa) is manifested by sanguineous or purulent discharge - a symptom of a “wet navel”. These fistulas appear in the first months after birth.
- emanating from the urachus
Complete fistulas are manifested by urine discharge from the navel and recurrent cystitis; incomplete fistulas are similar to a vitelline duct fistula (non-closure of the distal part) or a diverticulum in the bottom of the bladder (non-closure of the peri-vesical part). Incomplete fistulas can also occur in adults.
- coming from the vessels
Vascular fistulas lead to bleeding and umbilical sepsis and are diagnosed in the first weeks after birth.