When children get sick often, this is a sure sign that the immune system is not working at a sufficient level. To cope not only with the manifestation of the disease itself, but also to take a comprehensive approach to solving the problem that has arisen, you first need to make an appointment with a pediatrician and then an otolaryngologist. His consultation is indispensable when frequent diagnoses of a child at different ages sound like:
- ARVI, acute respiratory infections;
- exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis and adenoiditis;
- otitis;
- laryngitis;
- pharyngitis;
- angina.
Specialists from the first children's medical center in Saratov will help you select a comprehensive and effective treatment, who will conduct diagnostics, prescribe active treatment measures, and in addition select effective methods of prevention.
What to do if growths are visible in a child’s throat?
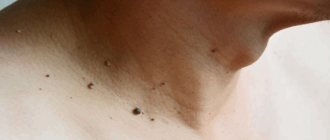
It is not uncommon for tumors to appear on the tonsils. This is a consequence of the papilloma virus, which manifests itself on the skin and mucous membranes. It would seem, where can a child catch this dangerous virus, which infects more than 70% of all inhabitants of the planet? First of all, in the womb, during birth, and also through contact and everyday life.
In the pharynx, neoplasms are most often found on the tonsils, but can be on the small tongue, palatine arches, and buccal mucosa. Only a pediatrician or otolaryngologist can make a diagnosis after examination.
Neoplasms on the larynx in children can form from birth; clinical manifestations often manifest in early childhood from 2 to 5 years. In children, this form of the disease indicates that treatment is necessary quickly and as competently as possible. Only an ENT doctor can diagnose such a localization of the process.
The active papilloma virus most often affects boys, but after 30 years, more women are affected. As a rule, the growths begin to manifest as impaired vocal function in the form of hoarseness, decreased timbre and rapid fatigue.
Risk factors
In children, risk factors are frequent infections of the ENT organs:
- chronic tonsillitis (angina);
- laryngitis, tracheitis, pharyngitis;
- acute and purulent otitis media.
The disease papillomatosis is common in people aged 20 to 40 years, who lead an inappropriate lifestyle, are subject to stress, and have bad habits.
There are indirect factors that can affect the activity of the virus:
- taking hormonal contraceptives by women;
- passive smoking;
- air pollution from exhaust gases and industrial emissions;
- improper oral care;
- heredity;
- age and associated hormonal imbalances (children under two years of age, adolescents during puberty, women during menopause, pregnant women are most at risk);
- stress.
chronic tonsillitis (angina); laryngitis, tracheitis, pharyngitis; acute and purulent otitis media.
taking hormonal contraceptives by women; passive smoking; air pollution from exhaust gases and industrial emissions; improper oral care; heredity; age and associated hormonal imbalances (children under two years of age, adolescents during puberty, women during menopause, pregnant women are most at risk); stress.
How dangerous is this?
Often papillomas on the tonsils are benign in nature, but at any age it is not worth the risk, and it is better to initially seek professional advice to eliminate all risks. Medical specialists identify the following among the main factors provoking the appearance of education:
- heredity;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- frequent colds and their complex course.
What color are the formations?
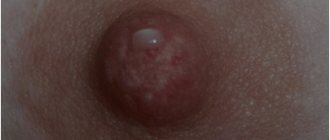
Papillomas blend in with the color of the mucous membrane of the throat, but sometimes they can change their pigmentation, becoming light pink or dark brown. Initially, one formation may appear, which is similar in size to a pea or the head of a pin. Over time, the number of formations can increase significantly and the lesion will look like a cauliflower with multiple papillomas. Sometimes the appearance process can be accompanied by inflammation.
Therapy after the removal procedure
After excision of tonsil papilloma, the patient must complete full treatment to the end to prevent the risk of reappearance of growths. To do this, you should take a course of anti-HPV medications.
Until the surgical wound is completely healed, a person needs to limit his intake of spicy and hot foods. If necessary, rinse the mouth with chamomile decoctions or other disinfectants.
The International Body of Disease Classification classifies papilloma on the uvula and throat as benign formations. However, the risk of developing cancer is still present. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of illness, you must seek help. The sooner this happens, the more effective the treatment will be.
How does the tumor feel?
Sometimes the patient does not feel any changes at all due to its small size, since there are no nerve endings in the papilloma, but as the formation grows, symptoms such as awkwardness when swallowing, a feeling of a foreign body in the throat, and cough appear. Similar sensations occur during pharyngitis or laryngitis, and in order to exclude the appearance of formations, it is necessary to urgently make an appointment with a doctor. With a child, the situation is complicated by the fact that he cannot accurately describe his sensations, and it is also difficult for him to carefully examine the oral cavity and pharynx on his own.
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of recurrence of papillomas is carried out only by a medical specialist under the careful supervision of all stages and the obligatory condition of checking the oncogenic nature.
Possible methods of treating laryngeal papillomas.
Careful removal of papillomatous growths under a microscope and using a CO2 laser is fundamental. However, removal must be carried out exclusively within the mucous membrane, where the formations are located. Moreover, the normal mucosa must be preserved. The surgeon must be experienced and thoroughly understand the mechanism of papillomas formation. Otherwise, gross surgical intervention leads to loss of voice, severe scarring, and stenosis.
Studies have shown that intraepithelial administration of antiviral drugs can reduce the number of operations to remove papillomas, leading to partial regression of the growth of formations. Also, local administration of an antiviral drug avoids systemic toxicity.
The mechanism of action of interferons in laryngeal papillomatosis is unknown, however, they are often used as an additional treatment. Interferons are naturally produced by white blood cells in response to various stimuli, including viral infection. They bind to specific cell membrane receptors and change metabolism, providing antiviral, antiproliferative and immunomodulatory effects. The clinical effectiveness of interferons in the treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis is ambiguous and controversial. The main limitation for their use are side effects when administered intravenously: increased levels of transaminases in the blood, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. Patients may experience weakness, nausea, fever, arthralgia, and headache.
Indol-3-carbinol can be extracted from cruciferous plants (broccoli, cabbage). In vitro studies have shown promising results on the growth of papillomas by influencing estrogen metabolism. When administered orally to a small number of pediatric patients, no adverse effects were observed. However, the clinical effectiveness of this drug remains in doubt.
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine . A prospective randomized controlled trial showed that intraepithelial administration of MMR vaccine could prolong the period of remission after surgical treatment.
HspE7. A new vaccine targeting oncogenic HPV types has also been used to successfully control relapses of laryngeal papillomatosis.
The presence of GERD was associated with an increased likelihood of complications. The irritating effect on the mucous membrane can act as a trigger for the proliferation and spread of papillomatous growths. Studies have shown that the use of drugs to treat GERD promotes better control of laryngeal papillomatosis and prolongs remission.
According to a Cochrane review, photodynamic therapy has not been shown to be effective in the treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis.
Watch the video BEFORE/AFTER surgery to remove laryngeal papillomatosis
Relapse-free postoperative follow-up for a year. Endoscopy in NBI mode. Credit: Professor Roberto Pujedo.
Look at the photos BEFORE/AFTER the operation by Prof. Roberto Pugedu
Photos “before” and “after” surgery to remove laryngeal papillomatosis. Credit: Professor Roberto Pujedo.
Move the slider to see the difference.
How to protect the body?
Since more than 600 strains of human papillomavirus are known in the world today, it is difficult to combat such microparticles comprehensively and constantly. First of all, it is necessary not only to see a doctor once, but also to undergo a regular course of treatment. Using folk remedies without supervision from medical personnel, formations on the larynx can develop into a malignant tumor, so self-medication, especially if the patient is a child, is strictly prohibited.
During the transitional climatic period, as well as in winter, there is a frequent exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis. This is due to the fact that the child does not always inhale frosty cold air through the nose, but breathes through the mouth. As a result, it is observed:
- elevated temperature;
- inflammatory processes in the throat;
- dry or wet cough;
- weak appetite;
- bad mood, high level of moodiness.
At an appointment with an otolaryngologist, a red throat is also diagnosed, and as a result, complications can spread to the nose, causing a chronic runny nose, and to the ears, causing otitis media, which is difficult and painful.
Sometimes, due to the fact that there is an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, it is difficult to visually determine the presence of a growth on your own. A swollen throat does not allow you to independently diagnose the formation, and if you do not consult a doctor for primary indications, you can lose valuable time for treatment.
There are times when, when it is necessary to treat otitis, all attention is switched to inflammatory processes in the ear, and parents do not even look into the child’s oral cavity. As a rule, concomitant diseases of the ear-nose-throat-system occur together, and competent comprehensive treatment is important so that getting rid of one ailment does not switch the development of the disease and complications in the other direction.
In the most advanced cases, complete removal of the affected “tonsil” is required (as patients often call the palatine tonsils). That is why it is important to consult a doctor in time to minimize this risk. If a child has frequent manifestations of colds, laryngitis or pharyngitis is diagnosed, then in addition to consultations with specialists at the center during the active stage and recovery from the disease, it is worth regularly showing the baby to doctors in order to exclude possible complications in the development of diseases.
The tumor on the tonsil itself does not go away, it may simply decrease in size, but this is not a reason to put off visiting a specialist. You shouldn’t risk your health, much less the health of your baby. Particular attention to the throat cavity should be paid in the following cases:
- when visiting a kindergarten and mass illness of children in it;
- when starting visits to sports sections, in particular the swimming pool.
A gathering of people who may also be carriers of the papilloma virus in one place can negatively affect the child’s health. The reason for a more thorough analysis of the throat cavity may be the use of antibiotics before this, non-compliance with the hygiene regime, as well as the active manifestation of oral diseases. If before this the child had a sore throat, and is now in the recovery period, then it is worth paying special attention to the condition of the throat in order to protect the child from formations on the tonsils. In case of mild laryngitis or pharyngitis, experts recommend carefully observing the child’s throat for a couple of days. To do this, in the morning and evening, ask the child to open his mouth to visually inspect for any formations on it, watch how the child eats, drinks and breathes.
Early stages of infection
Juvenile formations on the tonsils have different causes, but if there is a conclusion that the child has been diagnosed with the papilloma virus, this requires parents to constantly monitor and pay attention to their health status. Specialists from the first children's medical center in Saratov will help you decide on the most effective preventive and therapeutic measures. If your child often coughs for no apparent reason, or says that he has an uncomfortable sensation of the presence of a foreign object in his throat, immediately sign up for a consultation and visit a specialist who will select the most appropriate and effective treatment.
How is tonsil mass treated?
Traditionally, in the fight against otitis media or exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, antibiotics and concomitant therapy are prescribed to minimize the negative impact on the gastrointestinal tract. If formations on the tonsils are confirmed and their nature is clarified, treatment is prescribed by a specialist. It is forbidden to rip off or burn papillomas yourself.
An experienced otolaryngologist, as well as with the necessary consultation of a professional surgeon, prescribe the most effective treatment methods, including:
- removal of tumors with laser;
- radio wave excision;
- freezing and removing formations using cold;
- electrocoagulation, when the papilloma is removed using current.
The method is selected taking into account:
- degree of damage;
- age;
- general condition of the body;
- individual reactions.
The papilloma virus cannot be cured, but everything can be done to block its manifestation.
Make an appointment with a surgeon
Choose a doctor