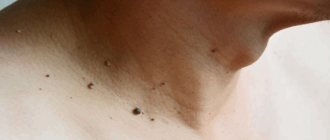
What is papilloma?
Often, papillomas look like small nodules that form in the vaginal area. They can acquire pigmentation from flesh to pink. There are both single specimens and several formations in one area. By merging with each other, they can form quite large clusters. If such a process develops, then we can talk about papillomatosis.
The emergence of such formations occurs under the influence of the human papillomavirus on the body. This pathogen is sexually transmitted and is quite common among the sexually active population.
In this article, we have already covered in detail the issue of human papillomavirus in women.
Is it possible to get pregnant if the vaginal walls are prolapsed?
Vaginal prolapse is not a death sentence for women who want to feel the joy of motherhood. There are many examples where both young and older women could still give birth to a child after such cases. However, it is necessary to focus on the stage of development of the disease. So, if the disease is in the first stage, you can get pregnant and give birth to children even without prior surgery. If the disease is at the second or more stages, an appropriate operation must be performed. Only under this condition can a woman become a mother. Otherwise, the risk of uterine prolapse cannot be avoided.
It is also important that after surgery to restore the vaginal muscles, a woman will not be able to give birth on her own: the child will be born exclusively by caesarean section.
Why do vaginal papillomas occur?
Of particular importance is the presence of disease-provoking factors:
- endometritis;
- inflammation of the ovaries;
- vulvovaginitis;
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea.
They lead to the rapid development of the virus inside the female body.
The development of papillomas in the vagina is also promoted by:
- early intimate life;
- avitaminosis;
- dysbiosis in the vagina;
- nervous shocks.
- decreased immune strength in the body;
- taking corticosteroids;
- performing surgical interventions on infected skin;
- pregnancy.
Papillomavirus has about a hundred different strains, of which only a few are capable of leading to the emergence and development of papillomas.
When the virus enters healthy tissue, a number of processes occur:
- The pathogen penetrates the basal layer of the dermis.
- Damages the cell membrane.
- Viral DNA is introduced into the center of the cell.
- The virus is waiting for favorable conditions.
There are many reasons for the development of pathology:
- Anomalies in the development of connective tissue may well be congenital,
- Intra-abdominal pressure was excessively increased (respiratory viral diseases, constipation),
- Birth complications (labor was too long, trauma to the vagina, the baby was quite large, obstetricians were forced to use forceps),
- Sudden loss of body weight,
- Too much physical activity
- Surgical intervention to remove the uterus without subsequent fixation of the vaginal dome,
- Age-related changes. After sixty years, prolapse of the vaginal walls affects quite a lot of women, because at this age the elasticity of the tissues gradually deteriorates.
- Several births. If a woman gives birth two or more times, then the risks of prolapse of the vaginal walls become much higher.
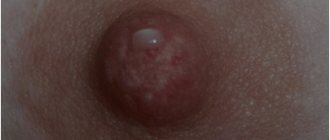
What do condylomas look like?
Quite often, the reason for visiting a gynecologist is the formation of condylomas on the intimate organs of women. Genital warts or condylomas are growths of the papillary epithelium, resulting in the formation of growths.
While condylomas are growing, the virus is not contagious. But as soon as the pathogen reaches the epidermis, there is a high risk of infecting its sexual partner.
There are two types of condylomas:
- Exophytic. The formations resemble genital warts in appearance. They are formed in the superficial layer and have a papillary surface. Such condylomas are provoked by HPV with low oncogenic activity. A photo of genital warts in women is presented here.
- Endophytic. They form flat condylomas. Very often they grow deep into the epithelium. Can provoke changes within healthy tissues. In the absence of timely treatment, they can cause oncological formations.
Condylomas can grow greatly, causing inconvenience:
- may bleed or be injured;
- interfere with intimate life;
- are in the nature of a cosmetic defect, while causing psychological discomfort;
- create problems during childbirth.
Photo
To understand the location and external signs of condylomas, use the photographic material provided below.
How our vagina changes at 20, 30, 40 and 50 years old
When asked to name the most obvious age-related changes, many people immediately think of crow's feet, skin that has lost its tone, and age spots (by the way, all this is completely normal and you have nothing to worry about).
But there is another part of the body that changes over the years along with the skin and muscles - the vagina. SPLETNIK.RU asked experts to talk about age-related changes in the vagina, which each of us should be prepared for, and what can be done to maintain sexual health. Like any other part of your body with skin, glands and hair follicles, the aging process affects the appearance of the vulva and vagina, no matter how well you take care of it, says Santa Monica, California-based gynecologist, MD ) and author of Sheology: The Complete Guide to Women's Intimate Health by Sherry Ross. And now we are not just talking about external changes that occur over decades, but about sensations during sex and comfort.
How your vagina changes at 20
The first major changes occur after reaching puberty. Due to hormones, the labia become enlarged, pubic hair actively grows, and daily discharge occurs.
Gynecologist at the LazerJazz clinic Svetlana Nosenko explains that at the age of 20, a woman’s body is fully formed and female sex hormones are at their peak. Estrogens help become a mother, and also maintain external and internal beauty: the vagina is more folded and comb-like, which affects the quality of sexual intercourse. Due to the amount of estrogen, a large number of lactobacilli are produced. They protect the vulva and vagina from inflammatory elements, says the expert.
How your vagina changes at 30
After the birth of the first child, the pelvic floor muscles and nerve fibers are stretched (some during childbirth resort to perineotomy - cutting the vaginal muscles), sometimes they can even tear. It must be taken into account that after this the muscles may not recover at all. The muscles heal, but scars appear. Scar tissue is less elastic, which reduces overall turgor and nerve endings become less sensitive. Stress urinary incontinence often occurs - this is one of the effects of hypermobility of the urethra (urethra).
To strengthen muscles, doctors recommend doing Kegel exercises. Radical methods include laser vaginal rejuvenation. What this gives: firstly, collagenosis improves - the surface of the vagina is quickly restored, secondly, the volume of tissue decreases, which leads to a narrowing of the vagina and, as a result, the quality of sexual life improves. This procedure is now painless and rehabilitation takes no more than a week, but the result is impressive.
At age 30, estrogen levels are high and many women enter their reproductive period. Some girls take contraceptives, which, unfortunately, does not always have a positive effect on the internal microflora of the vagina - dryness appears, libido decreases, and discharge appears, notes Svetlana Nosenko.
The outside of the vagina may sag a little, and it may feel as if something is sticking out. This is because there is excess tissue, says Cleveland OB/GYN Selena Zanotti.
During the postpartum period, it is important to check your hormones, especially testosterone, which has such an impact on sexual desire. Also, training such as wumbling and strengthening the pelvic floor muscles (in consultation with the gynecologist) is useful for maintaining sexual activity and sensitivity, advises sexologist Evgenia Lipchinskaya.
How the vagina changes at 40–50 years old
Given that the period of childbearing has shifted, menopause has also shifted. In fact, in the absence of other factors, the later the birth, the later the menopause. During this period, you need to be careful about your health.
After childbirth, the next important point is perimenopause (this is the 5-10 years preceding menopause). During perimenopause, the body begins to produce less estrogen (it preserves vaginal collagen and moisturizes the vagina, and also helps ensure good blood flow to the area), and not suddenly, but spasmodically - in the form of skipping the cycle, dryness occurs. Uterine prolapse is also possible. This may be related to weight loss. The female body is very sensitive to fluctuations, warns Svetlana Nosenko.
Many people experience this after age 40, but for some women it can happen much later, says Texas-based gynecologist John Toppil.
According to Dr. Zanotti, without stabilizing estrogen levels, the vagina becomes thinner and less elastic, and produces much less lubrication. After menopause (the average age of onset is 51 years), the vagina and clitoris may shrink, and the skin on the labia may become less elastic and change color.
The worst part is vaginal atrophy, which can make sex painful. Atrophy of the vulvar and vaginal mucosa is characterized by thinning of the epithelium, decreased vaginal folding, pallor, the presence of petechial hemorrhages, and signs of inflammation.
How to maintain sexual health
The good news is that these age-related changes don't have to make you feel overwhelmed or leave you unsatisfied with your sex life. Here's what experts recommend doing to slow changes or ease symptoms when they strike.
Procedures
Experts suggest doing biorevitalization and contouring with special density hyaluronic acid - this nourishes the mucous membrane and can, for example, enlarge the G-spot.
Lubrication
Lubricant is a great solution for women approaching menopause or moms experiencing vaginal dryness due to temporary fluctuations in estrogen. She can relieve pain and discomfort.
Additional dose of estrogen
An estrogen cream or ring can help relieve dryness and maintain the elasticity of vaginal tissue, Dr. Zanotti says. However, for some women (such as breast cancer survivors), estrogen is not recommended. You should definitely talk to your doctor before taking it.
Having sex
If you stop having sex, the vagina becomes stiffer and the vaginal tissue becomes less elastic, doctors explain.
Exactly the same age-related changes occur in the female genital organs as in the entire body - you need to understand and accept this, and do not be afraid to discuss this topic with a gynecologist. A true professional will always support and help.
Symptoms of vaginal papilloma
Often, with HPV in women, the formation of papillomas is asymptomatic at first.
In case of prolonged development and progression of the disease, symptoms may appear:
- There is a feeling of itching and burning in the vagina.
- Bleeding may occur.
- Detection of growths in the vagina upon palpation.
Depending on the speed of development of the disease, a diagnostic examination of the patient will be necessary, followed by removal or treatment of the growths.
Vaginal cancer treatment
The proximity of the vagina to the rectum, bladder, and urethra limits the dose of radiation that can be administered and also limits the margins of resection during surgical treatment. Moreover, for most patients, maintaining vaginal function is the most important factor when planning treatment tactics.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is based on achieving “clean” resection margins, that is, without tumor cells.
1. In stage I and damage to the posterior wall of the upper third of the vagina. A radical hysterectomy (removal of the uterus and surrounding parametric tissues), partial colpectomy (removal of part of the vagina with a tumor) and removal of the pelvic lymph nodes are performed.
2. If it is necessary to carry out radiation therapy in young patients, before it is carried out, it is recommended to perform an operation to transpose the ovaries in order to remove them from the radiation zone.
3. In patients in stage IVA, when there is a complication such as rectovaginal or vesicovaginal fistula, pelvic exenteration is the method of choice in treatment.
4. In patients with localized (solitary) recurrence of the disease, surgical resection is also the only treatment option.
Radiation therapy
- the method of choice in the vast majority of cases when treating patients with vaginal cancer. It is a combination of teleradiotherapy and intracavitary therapy.
Small tumors can be treated with brachytherapy, but in cases of more extensive disease, treatment usually begins with 5,000 cGy of external radiation to shrink the tumor and target the pelvic lymph nodes and continues with intracavitary radiation.
A combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy is also used.
Complications after a course of therapy are associated, as a rule, with dysfunction of adjacent organs: rectum, bladder, urethra, in 13-19% of cases - up to the complete loss of their functions, which certainly has serious consequences for the quality of life of patients. Less serious complications are cystitis and proctitis after radiation therapy, rectovaginal and vesicovaginal fistulas, and rectal strictures.
Forecast
The five-year survival rate for vaginal cancer is about 77%, 52%, 42%, 20%, 12% for stages I, II, III, IVA, IVB, respectively.
Diagnostics
To establish a diagnosis, a gynecologist needs a complete diagnosis:
- History of the disease. It includes knowledge of information:
- how long ago the growths appeared;
- whether there were unprotected intimate relationships;
- how long ago the last act of this kind took place.
- Examination by a gynecologist . In this case, the affected epithelial cells are collected for subsequent PCR analysis.
- PCR diagnostics. In this analysis, the number of pathogens and the type of papilloma viral infection are determined.
- Linked immunosorbent assay. It is necessary to confirm the presence of antibodies to the virus in a person. Based on which, one can judge the degree of development of HPV in the human body.
- Colposcopy. Inspection of the vaginal walls to determine damaged areas. It is carried out using a special colposcope device and staining the cervix with iodine solution.
- Anoscopy. Involves examining the anal area for the presence of papillomas.
- Cytological examination. Study of cells under a microscope, detection of damaged areas and their characteristics.
- Histological analysis. Studying the structure of damaged areas.
- Oncocytology. Study of cells in scrapings from the cervix and cervical canal under microscope magnification.
You might be interested! Treatment of papillomas in the intimate area in women and men
When papillomatosis is confirmed, timely treatment and correct selection of therapy are necessary.
Vaginal cancer diagnosis and staging
A biopsy is required to make a diagnosis. This can be done already at the examination stage, without anesthesia.
In case of changes in cytology and in the absence of clinical data in favor of the presence of a tumor or precancerosis, colposcopy is necessary. If the patient has previously undergone a hysterectomy and, according to colcoscopy, there are changes in the mucous membrane in the vaginal dome, complete resection of the vaginal dome is performed for a thorough histological examination.
The TNM system is used to stage vaginal cancer. In order to adequately determine the stage of the disease, it is recommended to carry out not only a basic range of examinations, including a gynecological examination, cystoscopy and colonoscopy, but also the use of radiation diagnostic methods (CT or MRI) to obtain a complete picture not only at the site of the primary tumor and in the pelvis, but also in the abdominal cavity, liver, retroperitoneal lymphatic nodes, as well as the urinary tract.
There are different stages of development of vaginal cancer
- Tx - Primary tumor cannot be assessed
- Then - There are no signs of a primary tumor
- Tis - Carcinoma in situ (pre-invasive carcinoma)
- T1 - Tumor limited to vagina
- T2 - Tumor grows into peri-vaginal tissue
- T3 - Tumor extends to the pelvic wall
- T4 - The tumor has invaded the lining of the bladder/rectum or has spread beyond the pelvis. The presence of bullous edema is not sufficient to classify a tumor as T4.
- M1 - There are distant metastases
Treatment of vaginal papilloma
Therapy for curing papillomas can be carried out in several approaches:
- Conservative treatment methods. Necessary to prevent the tumor from degenerating into a malignant formation. Includes purpose:
- Immunomodulators. They are used after testing the sensitivity of the papilloma virus to a specific medication. These include Viferon, Reaferon, Kipferon.
- Inducers of interferon production. Prescribed after determining the effect of such drugs on the affected areas. Representatives of drugs: Tamerit, Neovir, Larifan.
- Specific drugs that have an antiviral effect. Most often prescribed: alpirazine.
- Surgical techniques for the treatment of papillomas. Several types of formation removal are used:
- Chemical coagulation. Carry out under the influence of drugs: solkovagin, podophyllin.
- Cryodestruction. The procedure is effective for small affected areas.
- Electrocoagulation. It is carried out using a laser.
- Radio knife or excision with a scalpel. Prescribed only for extensive lesions.
Drug treatment
Very often, treatment of papilloma virus occurs under the influence of a whole range of medications.
They have the following properties:
- cauterizing;
- bactericidal;
- oppressive.
The main means of fighting infection include:
- lapis pencil;
- drops;
- pills;
- ointments.
If removal of papillomas is not practical, then you can get rid of the growths in 2-3 weeks with the help of medications.
The following have a detrimental effect:
- Feresol.
- Phenol in glycerin solution.
- Super clean.
- Salicylic acid.
- Cryopharma.
In addition to the direct effect of solutions on papilloma, general-effect drugs are also used that increase the immunological status of the body.
Removal
Sometimes it is impossible to cure papilloma without removing the affected area.
Then they resort to the following procedures:
- Excision of formations. It is carried out in cases of large lesions of the skin.
- Treatment with chemical drugs that have a detrimental effect.
- Freezing the damaged area. It is possible to carry out this procedure in the vagina. The advantage of this manipulation is to control the effects of cold without touching healthy tissue.
- Use of chemical removal techniques.
Diseases of the vulva and vagina
Causes
- HPV. The main cause of the risk of vulvar dysplasia is determined by the human papilloma virus. HPV is one of the most widespread viruses, and more than 30 types pose a threat to women's health. Medical research has established that the greatest danger is posed by anogenital carcinogenic HPV-16 and HPV-18, which are responsible for the growth and appearance of genital warts - one of the distinctive symptoms of vulvar dysplasia (atypical hyperplasia).
- Inflammatory processes. Advanced inflammation of the genitals and vagina, characterizing colpitis, vulvitis or bartholinitis, are possible harbingers of vulvar dysplasia.
- Age indicators and associated factors. The presence of pathology of the vulvar epithelium can also be provoked by neuroendocrine changes and an imbalance of metabolic processes due to age-related changes. Along with menopausal hormonal imbalances, some associated factors contribute to the occurrence of dysplasia. These include weakened immunity, smoking, premature sexual relations, chaotic sexual intercourse and sexually transmitted infections.
The presence of these items in the patient’s medical history means that she is potentially at risk for the occurrence of vulvar dysplasia and is the basis for urgent contact with specialists in order to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis.
Diagnostics
- Inspection. The patient's examination begins with a visit to the gynecological office for an examination, which can be supplemented by extended colposcopy and the use of the Schiller test. Due to the different reactions of healthy and damaged epithelium to iodine, the Schiller test allows us to identify pathological changes in the epithelium. Iodine-negative tissues require mandatory cytological examination and biopsy, based on the results of which a final diagnosis is made.
- HPV test. Papillomavirus is one of the main factors inducing atypical hyperplasia, which necessitates HPV analysis if this pathology is suspected. HPV testing is carried out using the PCR screening method, which allows not only to establish the presence of human papillomavirus in the patient’s biomaterial, but also to accurately determine its type due to the unique DNA of each infectious agent. PCR screening is an effective research method even for indolent infections.
- Cytological examination, biopsy, histology. If atypical vulvar hyperplasia is suspected, a cytological examination of epithelial cells is prescribed, the results of which make it possible to judge the specificity and severity of cellular atypia, as well as the signs of malignant neoplasms. If the diagnosis is confirmed, in order to exclude a cancer threat, a biopsy with the histology of the selected material is required, the results of which make it possible to differentiate atypical vulvar hyperplasia from benign lesions of the vulva and oncological diseases.
A comprehensive examination with the involvement of specialists from different fields of medicine (in addition to a gynecologist and oncologist, it is advisable to involve a venereologist and a dermatologist in the examination) makes it possible to carry out the most comprehensive diagnosis and select effective methods to combat the disease that are tailored to the patient’s needs.
Sign up
Treatment of vulvar dysplasia
Vulvar dysplasia should be combated within the walls of the appropriate institution with the involvement of specialists of the necessary profile. Professional intervention will help avoid cancer complications and save life. Thanks to the availability of the latest equipment and an established team of professionals, the medical center offers a whole range of services for diagnosing and effectively treating vulvar dysplasia. The presence of an operating room and a day hospital provide access to various treatment methods, including surgery.
The key to curing vulvar dysplasia will be an individually oriented course. Get comprehensive advice from leading medical experts on women's health issues. Timely consultation, comprehensive diagnosis and effective treatment are the key to your recovery and well-being in the future.
Taking into account the age category, severity of atypia, contraindications and concomitant infections, there are various options for combating the disease:
- Conservative treatment. It involves the use of sedatives, hormonal therapy, desensitizing drugs, restoratives, as well as adherence to a certain diet. Focused on controlling the psychological state, leveling out local manifestations and achieving possible remission. A positive test for HPV requires additional antiviral and immunocorrective prescriptions.
- Surgical intervention. Severe pathology predetermines surgical intervention. An alternative may be the use of liquid nitrogen, radio waves, or laser removal of small lesions, but these options are only possible in the initial stages of the disease and are aimed at patients who have not reached menopause. In case of severe atypia, relapse or large-scale lesions and a clear risk of cancer, it is recommended to perform a superficial vulvectomy - a surgical operation to excise the upper layer of skin followed by plastic surgery.
- Organ-sparing methods. In the treatment of vulvar dysplasia complicated by HPV infection, photodynamic therapy can be used. The PDT method involves the use of light-sensitive substances that accumulate in the cells of tissue affected by the pathological process. Exposure to light with certain characteristics causes a chemical reaction, resulting in the death of atypical cells.
After surgical treatment, patients are subject to observation at the dispensary. Cytological control is required. It is recommended to abstain from sexual activity, refuse to use sanitary tampons and douches, and limit exercise.
Prevention and prognosis of vulvar dysplasia
Prognosis of vulvar dysplasia is related to the severity of the disease and the period of development of the disease, the presence of concomitant factors, age indicators and individual characteristics of the patient. In the absence of proper treatment, atypical hyperplasia can progress to oncological pathology. And a mild degree of dysplasia, when detected in the early stages and following the recommendations for appropriate treatment, successfully regresses.
The sooner a visit to a gynecologist follows and the more comprehensive the diagnosis, the more likely a successful recovery. Due to the possibility of relapse, patients with a similar diagnosis are recommended to undergo mandatory monitoring by their attending physician, and in particularly severe cases, additional monitoring by an oncologist.
It is possible to reduce the risk of disease and relapse through a healthy lifestyle, which includes good nutrition and giving up bad habits. Special attention should be paid to barrier contraceptives and sexual activity. A prerequisite for recovery and monitoring a woman’s health condition is further regular visits to the gynecologist.