Intraductal papilloma (ductal papilloma).
Removal of papilloma on the nipple
Ductal papilloma (intraductal papilloma) occurs near the nipple; removal of papilloma on the nipple is possible using electrocoagulation under local anesthesia. Signs of intraductal papilloma (or nipple papilloma) are the appearance of blood-stained or transparent discharge from one nipple. Ductal papilloma is often a precancerous condition. Treatment of papillomas on the nipple and intraductal papilloma is carried out by a mammologist-oncologist.
On the picture:
papillomas on the face
The human papillomavirus (HPV) is widespread throughout the world. HPV causes warts, papillomas, and genital warts. Different types of human papillomavirus (there are more than 100 of them) cause different diseases.
Genital warts are small skin-colored formations, their size ranges from 1 mm to several centimeters. Genital warts can form on the genitals, near the anus, on the face, even in the mouth, on the body, abdomen, in the groin area, and in the armpits. This is a viral disease. The causative agent of genital warts is the human papillomavirus (HPV).
In men, the glans penis and frenulum of the foreskin are most often affected. In women, damage by the human papillomavirus appears on the labia, clitoris, vagina, and cervix.
Genital warts can be localized around the anus.
From single ones, genital warts can grow into rashes that can spread, taking on the appearance of cauliflower. “High-risk” HPV types (16, 18, 31, 33 and 35) cause cervical dysplasia and can become malignant.
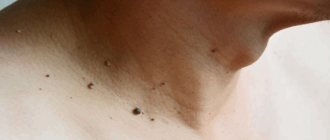
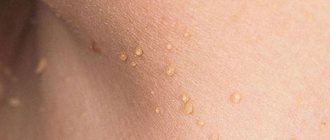
Skin papillomas
Acrochords, or filamentous papillomas, are warty growths on the skin of people over 40 years of age. Refers to viral skin infections.
Reason and locations
Filiform papillomas (warts) occur in people as a result of the human papillomavirus entering the human body. This virus (abbreviated as HPV) has many types. The types that cause the appearance of filamentous papillomas are 3,5,8 and 9.
Most often, the virus enters the skin through places where the skin is injured, where an abrasion or scratch appears. As for this particular disease, there is also a predisposition of human skin to this virus.
At first, a nodule appears on the skin, which begins to grow and stretch out, resembling a thread. Less commonly, the papilloma remains round on a thin stalk (as in this photo).
The main places where filiform warts appear are:
- Neck (see photo on the left)
- Face, mainly eyelids (pictured below)
- Armpits (photo below)
- Under the mammary glands
- In the folds in the groin
Considering this favorite arrangement of acrochords, we can conclude that the predisposing factors for their appearance are:
- Failure of a person to comply with the rules of personal hygiene in problem areas of the skin
- Excessive sweating in these areas
- Increased sebum production
- Frequent trauma to these areas
All of the above risk factors lead to a weakening of the protective properties of the skin in these areas, which then contributes to the appearance of filamentous warts in these areas. In addition, the fact of decreased immunity in older people is also important. That is why the frequency of this disease in people over 60 years of age exceeds 70%.
Treatment
Traditional medicine methods are used in the treatment of filamentous papillomas.
Warning: the acrochords themselves will never go away if left untreated.
Traditional treatment
- Removal of filamentous papillomas with laser. A laser is a high-energy light beam that, when exposed to a wart, literally burns it and evaporates it. As a result, a small crust appears on the surface of the skin instead. After 4-5 days, the crust disappears and healthy skin appears in its place. The procedure is performed under lidocaine anesthesia. Be sure to protect your eyes from laser radiation. The disadvantage is the high cost.
- Removal of acrochords by radio wave. The device for radio wave surgery resembles a laser in its effect on skin formations. Wart tissue also evaporates. The procedure is also performed under local anesthesia with lidocaine, and after it a small crust also appears.
- Removal of filamentous warts with liquid nitrogen. This technique has been used in medicine for 40 years. The procedure is performed without pain relief. The presence of a doctor is not necessary. The wart is burned with liquid nitrogen, after which it dies within a few days. After this, healthy skin appears in its place. The procedure is the cheapest of all removal methods.
- Removal using high-frequency electrocoagulation. This method is performed by a cosmetologist under lidocaine anesthesia or without anesthesia. The wart tissue evaporates, and after it a small crust also appears.
All of the above methods are safe for health.
The feasibility of removing papillomas and methods of their removal are chosen by the doctor during the consultation.
For more detailed information and treatment, you can contact a cosmetologist at the Ultrasonic Medical Clinical Hospital:
- Room 45 of the advisory clinic of the Medical Clinical Clinical Hospital;
- contact number.
Genital warts - routes of infection
The route of infection with HPV is contact. But household infection with the human papillomavirus is also possible. When a person comes into contact with infected skin or mucous membranes of a sick person, HPV infection occurs. Very often, this does not appear outwardly; the virus may not show itself for a long time. But under certain conditions (decreased immunity, concomitant diseases), HPV is released onto the surface of the skin and mucous membranes. In a latent (dormant) state, infection of other people with HPV is rare. From the moment of HPV infection to the appearance of genital warts, it can take from several weeks to several years.
Photo of condylomas on the genitals and in the perianal area
| In the photo: condylomas on the foreskin and on the frenulum of the penis | In the photo: genital warts in the perineum | In the photo: papillomas in the anus |
There are “low-risk” and “high-risk” types of HPV. Genital warts are caused by “low-risk” HPV types 6 and 11.
Treatment of papillomas, condylomas (HPV)
- performed on the body by a dermatologist-cosmetologist,
- on the male genitals - urologist,
- for women - a gynecologist,
- in the area of the anus and perineum - a proctologist.
There is now a treatment that is highly likely to eliminate HPV infection. Modern treatment for genital warts can not only remove or reduce the symptoms of the disease, it eliminates the HPV infection and prevents further transmission of the virus in many cases. However, after any treatment method, relapses are possible.
- Laser removal of genital warts is performed under local anesthesia.
- Electrocoagulation, removal of genital warts using high temperature, is carried out under local anesthesia.
- Interferon blockades (genital warts are injected with an interferon drug).
- Radio wave removal of condylomas. Today, the most effective method for removing genital warts. There is no trace left of condylomas.
Advantages of treating human papillomavirus at Deltaclinic
- Our clinic has all the necessary specialists (dermatologist, dermatologist-oncologist, proctologist, urologist, gynecologist) who remove condylomas and papillomas of any location.
- The most modern equipment (lasers, electrocoagulation, radio wave), which allows you to get rid of condylomas on the day of the visit.
- Condylomas are removed without leaving a trace. Excellent cosmetic effect - no trace remains on the skin and mucous membranes.
- Fast healing time.
- An accurate diagnosis of the type of papillomavirus is carried out. General immunostimulating and antiviral therapy is prescribed.
- Removal of candylomas is carried out on an outpatient basis; hospitalization is not required.
Photo:
Surgitron device for non-surgical (radio wave) removal of condylomas.
Do not delay your visit to the doctor, genital warts must be removed! If papillomas are not removed, they can spread throughout the body. The virus can be transmitted to other people with whom an HPV-infected person comes into contact. A woman can infect her fetus during childbirth. Cases of familial infection with the human papillomavirus are common.
Papilloma in children, causes, treatment and removal.
Papilloma in children. Basic principles of treatment.
Neoplasms on the skin or mucous membrane of the mouth, nose, pharynx, etc., which are viral in nature, are one of the most common skin diseases. They can appear in the form of moles, warts, papillomas. People of different ages suffer from this disease, among them, of course, children. With their appearance on the body, we can say that papillomavirus infection in children has been activated. The causative agents of the infection are human papillomaviruses, of which about 100 species are known today.
The main factors leading to the spread of the virus are decreased immunity and hormonal imbalances in the body. There are many ways of infection:
- Papilloma in children (especially the larynx) can occur after birth due to infection during childbirth if the mother had vaginal condylomas.
- Upon contact with a carrier of the virus, especially if there are microtraumas, cracks, or abrasions on the body.
- Autoinfection. If a child bites nails, hangnails, or tears off existing warts, more and more surfaces of the skin become infected.
In adults, infection also occurs through sexual contact.
So what does papilloma look like in children? How to treat them? Where are they most likely to be located? And, in general, how does papillomavirus infection occur in children?
Manifestation of papilloma in children.
Papilloma is a growth or tumor on the skin or mucous membrane, most often mushroom-shaped, on a thin stalk. Color varies from white to dark brown. The incubation period is on average 2-3 months, the virus is most active after 6 months of infection.
The forms of manifestation of papilloma are very diverse:
- warts (skin papillomas), most often observed on the hands;
- simple or vulgar papillomas. Most often they appear on the backs of the hands and knees in children. They look like hard bumps with a keratinized surface (from 1 to 10 mm);
- plantar papillomas. Quite painful formations that make walking difficult. Not to be confused with calluses, which have a smooth surface;
- flat papillomas. Smooth lumps of natural color can cause a lot of trouble for the child, in the form of redness, itching, inflammation and pain;
- A rare disease is epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Red-brown papillomas on the hands and feet, high risk of degeneration into malignant tumors (30%);
- juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis. Babies born from an infected mother are at risk. The growth of papillomas on the vocal cords can lead to speech impairment and even create breathing problems. It should be especially noted that the disease is quite rare.
Treatment of papillomas
Based on the fact that there is no single standard for the treatment of papillomas, parents must figure out for themselves what to do if papilloma is discovered in children. Of course, you need to watch her carefully. Is it growing, is there inflammation? How many tumors appeared? An appointment and consultation with a doctor will help dispel many doubts and fears.
Doctors, examining the tissue of papillomas, will be able to establish the correct diagnosis. Treatment of papillomas is complex. In the first place, of course, is the correction of immunity. As soon as the body’s natural defenses begin to work, it will become easier to fight the virus. There are many cases, especially in children, when papillomas disappeared spontaneously.
When fighting the human papillomavirus, a variety of antiviral drugs are used, and surgical removal of formations is also proposed.
Nowadays, there are a wide variety of surgical methods, where the removal of papillomas occurs quickly and painlessly. This can be cryodestruction (exposure to low temperatures), laser and/or diathermocoagulation (cauterization with electric