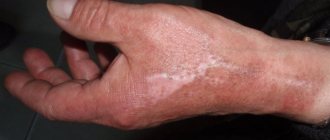
Mechanical or scientifically dermographic urticaria characterizes the pathological condition of the skin when raised scars form on it. From the Greek word "dermatographism" means "inscriptions on the skin." Indeed, marks on the skin resemble white or red scars and can be in the form of drawings and words. The disease is common and occurs in 17% of people.
Types of urticaria
Mechanical urticaria can be different and have different causes. Main types:
- Red. The cause is seborrheic dermatitis. After touching, red stripes remain on the skin.
- Cholinergic. Stains remain after exposure to cold.
- White. After mechanical action, not red, but white stripes remain.
- Family. Passed on by inheritance.
Another classification divides urticaria depending on the cause of the disease:
- Dermatographic. Appears after mechanical impact, for example, pressure from household items or clothing. Accompanied by redness and burning. Lasts from 30 minutes to several days.
- Solar. Changes occur after exposure to infrared and ultraviolet study.
- Aquagenic. Rarely seen. The cause is water getting on the skin, regardless of its temperature.
- Heat/cold. Swelling and redness appear under the influence of a certain temperature, even after drinking hot or cold drinks.
- Papular. Appears after an insect bite. It is dangerous if allergies and swelling appear in the throat area, there is a risk of suffocation.
- Cholinergic. Appears due to increased sweating during stress.
What are the symptoms of peripheral edema?
Peripheral edema is divided into two types depending on what happens when you press on the swollen area:
- ulcerative swelling, in which marks persist when you stop pressing;
- swelling without pitting, in which the mark immediately disappears after pressing;
Sock marks are more pronounced if you have acute swelling.
Other symptoms of peripheral edema include:
- tight, shiny skin;
- redness;
- fluid oozing from the skin (if severe);
Causes
Mechanical urticaria appears unexpectedly; it won’t even be immediately clear what the cause was. There is a group of factors that activate pathological processes.
- metabolic and thyroid function disorders;
- allergy;
- infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- genetic predisposition;
- mechanical influences;
- physical stress;
- emotional stress;
- release of histamine by mast cells onto the skin, causing swelling.
The cause can be any malfunction in the human body: decreased immunity, long-term chronic diseases, wearing tight clothes.
Doctors are most inclined to believe that the main cause is stress. Diseases of internal organs have a lesser impact.
A pathological skin reaction can be provoked by taking medications: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, codeine, morphine, X-rays, iodine-containing ones. Failure may occur after a blood transfusion.
Dermatographic urticaria is not always a separate disease. It may be a symptom of a more serious problem.
How is peripheral edema treated?
There are several methods you can use to reduce mild peripheral edema. You can also use them in conjunction with treatment for the condition that is causing your swelling.
WAYS TO REDUCE SWELLING
- Reduce salt intake.
- Start losing weight.
- Raise your feet above heart level while sitting or lying down so that gravity pushes fluid out of your legs rather than into them.
- Take frequent breaks and elevate your legs if possible when standing or sitting for long periods of time.
- Wear compression stockings.
- Train your calf muscles. The contractions help push blood through your veins so it can't pool in your leg and leak into the soft tissue.
Diuretics
Diuretics (diuretics) remove excess fluid from the body. They are used only when peripheral edema is caused by a medical condition.
Treatment for specific causes
Treatment may depend on what is causing the peripheral edema. Here are some possible treatment options for specific causes of peripheral edema:
- venous insufficiency: compression stockings, vein stripping (vein removal), or surgical repair;
- congestive heart failure: diuretics or medications that help your heart work more efficiently;
- kidney disease: medications that increase urine production, dialysis or kidney transplant;
- liver disease: antiviral medicine for hepatitis, limiting alcohol, or having a liver transplant;
- poor nutrition: a nutritious diet that contains sufficient protein;
- lymphedema: compression stockings or lymphatic drainage massage;
- DVT: blood thinner;
- cellulite: antibiotics;
Symptoms
The main manifestation is red or white marks, swelling after mechanical or temperature exposure. Inflammation appears on any part of the skin except the scalp and genitals. The latter rarely happens, and large areas of skin are also rarely affected.
If you run a sharp object over the skin of a healthy person, a white stripe appears, which disappears after a while. A person with mechanical urticaria will develop a red, inflamed welt that is white in the middle.
Redness appears a few minutes after mechanical impact and disappears after a few minutes. In severe forms of dermography, marks can last for several days, months and even years. With proper treatment, discomfort and redness disappear within a few days.
- burning and itching;
- scarring;
- pain;
- increased symptoms at elevated ambient temperatures;
- general weakness.
Symptoms may appear slowly or immediately. In the first case, the scars remain for several days and appear a few hours after prolonged exposure, in the second - after light pressure on the skin, the symptoms disappear after a couple of hours.
Body temperature rarely rises; usually a person feels general malaise, headache, chills, and aches.
Diagnostics
If the above symptoms appear, you should consult a therapist, dermatologist, allergist, or immunologist.
A visual examination and skin test are sufficient to make a diagnosis. The doctor acts on the surface of the skin with a blunt object and waits for a reaction. With mechanical urticaria, a white mark resembling a scar immediately appears. To identify cholinergic dermographism, apply a piece of ice to the skin. Solar urticaria is detected by irradiation with waves of different lengths.
The doctor’s actions are determined based on the patient’s complaints. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe a test for immunity, thyroid hormones, a general blood test and culture for intestinal flora.
How is peripheral edema diagnosed?
Your medical history and physical examination will give your doctor clues about the cause of leg swelling, but tests are often needed for diagnosis.
The test is selected based on the organ being assessed.
- blood tests that evaluate the function of most organs, including your heart, liver and kidneys, as well as albumin levels;
- a urine test that evaluates kidney function;
- chest x-ray, an imaging test that evaluates your lungs and heart;
- electrocardiogram, another test to evaluate your heart function;
- Ultrasound, an imaging test to help diagnose DVT and abdominal mass (ascites);
- CT scan of the abdomen, an imaging test that helps your doctor check the abdominal mass;
Treatment
A mild form of mechanical urticaria does not require treatment. Symptoms leave a person within a few hours . Medication is needed only for serious symptoms that affect the quality of life.
Treatment of mechanical urticaria usually gives poor results. The main goal of therapy is to eliminate the manifestations of urticaria and discomfort. It is much more effective to identify the cause and get rid of it.
Obsessive manifestations will help eliminate:
- antihistamines;
- antiallergic drugs;
- histamine receptors;
- leukotriene receptor antagonists.
When taking a bath, you need to avoid hard washcloths and aggressive detergents.
How to provide first aid? First, you need to eliminate the causes - the direct mechanical impact. Next, it is recommended to take an antihistamine or glucocorticosteroid and, if you are not allergic to cold, apply an ice cube of water or chamomile decoction. You can make a compress from a warm chamomile decoction.
If the form of the disease is severe and the patient begins to weaken, you should immediately call an ambulance. There is a risk of getting anaphylactic shock or Quincke's edema.
Bottom line
Sock marks on feet are caused by the pressure of the elastic band in them. Peripheral edema will make the marks more visible.
Most often, peripheral edema develops when excess fluid in your body is pulled toward your legs by gravity. The swelling is usually mild, temporary and harmless.
However, peripheral edema may be a symptom of a serious medical condition. If this is the case, the swelling becomes more pronounced and persistent, and is usually accompanied by other symptoms.
If your sock marks are more noticeable, take a closer look at your feet. If you notice new, enlarged swelling or ulcers, consult your doctor immediately. You may have a medical condition that requires immediate treatment.
ADDITION
Sock marks are a sign of leg swelling, which can be caused by high blood pressure.
Treatment with folk remedies
Using decoctions of some herbs, you can weaken the form of the disease or get rid of it completely.
- Instead of tea in the morning and evening, you can drink an infusion of the series.
- A decoction of herbs: black currant, yarrow, raspberry and mint will help get rid of skin problems.
- It is beneficial to take celery root juice twice a day. Single dose – 1 teaspoon.
- A lotion of nettle and lemon juice will help get rid of symptoms faster. The mixture relieves itching and redness.
Don't forget about eliminating risk factors. Clothing should be looser, not tight or chafing, and made from natural materials. It is recommended to use sunscreen in summer and frost protection in winter.
The diet also changes. The menu should not contain seafood, potatoes, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, chocolate, cheese, dairy products, eggs, processed foods. You should add foods rich in vitamin E, C. B5, fresh fruits and vegetables, flax seeds, pumpkins, nuts, durum wheat pasta.
By self-medicating, you can trigger a disease that will be impossible to get rid of in the future. Simple preventive rules at the initial stage will help you get rid of unpleasant symptoms forever.
Dermographic urticaria, which has other names - autographism, urticarial dermographism, dermatographic urticaria, is considered as a special type of mechanical urticaria, which manifests itself with long-term or short-term exposure to a mechanical irritant on the skin. In this article we will look at photos, symptoms and treatment of demographic (dermographic) urticaria, the causes of its appearance and features of the disease.
Features of the disease
Factors that provoke autographism can be belt pressure, clothing friction, vibration, or the movement of a blunt object along the skin with pressure. In this case, the skin does not always itch, but reacts to provocation by forming swellings, redness, blisters that repeat the shape of the irritant object or its trajectory. For example, if a patient scratches an itchy area, whitish-pink stripes will appear above the skin as they scratch.
The dermographic form also includes urticaria due to pressure, when skin reactions occur in the form of swelling and irritation after 2–6 hours. For example, under a wristwatch, after prolonged pressure, a bracelet-shaped blister will swell around the wrist. Tight compression stockings and tight shoes can have the same effect.
Autographism is observed in 8–13% of all types of urticaria. More often (65 - 95%) the disease affects people predisposed to allergies, often occurring in parallel with other types of allergies - heat urticaria, cold urticaria, cholinergic urticaria, dermatitis, Quincke's edema. But with dermographic urticaria, itching appears less frequently.
Urticarial dermographism (photo)
Sock marks may indicate high blood pressure
Standing or sitting for too long can cause swelling of the lower leg, the first symptoms of which are tight shoes and marks from socks.
These symptoms are not always an indicator of a serious problem if they are mild and infrequent. Repeated or worsening swelling of the lower leg may be a sign of a chronic health problem.
“Swelling in the ankles is not normal,” said Dr. Michael McGill, a cardiologist at the Marshfield Clinic. “You need to take this seriously, especially if symptoms occur too often. Even if this happens from time to time, you should consult a doctor.”
High blood pressure is the most common cause
Swelling occurs when excess fluid accumulates in the lower legs. Swelling is usually not painful in itself, but if your legs and feet are swollen, shoes and socks may be uncomfortable to wear.
“Sodium retention causes high blood pressure and fluid retention, which is the most common cause of leg swelling,” McGill said.
High blood pressure can be accompanied by diastolic dysfunction, a type of heart failure that makes it difficult for the heart to pump blood throughout the body. The body responds to insufficient blood flow by retaining fluid, which settles in the lowest parts of the body, usually the legs and feet.
Venous insufficiency is another cardiovascular problem that can cause swelling. Venous insufficiency occurs when the veins in the legs do not allow blood to flow back to the heart. When the valves in the veins don't work well, blood can pool in the legs and cause painful swelling. This condition is also known to cause varicose veins.
Kidney and liver problems and certain medications can cause swelling in the lower leg. The doctor must conduct tests to find out what is causing the problem.
Classifications of demographic urticaria
By shape
- primary form , which develops directly under the influence of a provoking factor;
- secondary , when the disease is provoked by an existing internal pathology (mastocytosis, neurological diseases, systemic lupus, serum sickness).
This video will tell you what autographism is:
By reaction speed
Based on the speed of reaction, there are three types of autographism:
- immediate type (more frequent), in which the skin reaction is visible 2 to 5 minutes after pressure, lasting about half an hour;
- medium , when swelling and irritation develops in the interval from half an hour to 2 hours and lasts up to 3 – 9 hours;
- late (rare type), giving a skin reaction after 4–6 hours, which lasts up to 2–3 days.
With a medium and late reaction, itching, soreness, swelling and hyperemia appear in places where prolonged and strong pressure was applied to the body:
- on the shoulders after the straps of a backpack or shoulder bag;
- on the ankles after squeezing them with a tight elastic band of socks;
- on the wrists after the belt of a bag or bracelet;
- in any places squeezed by tight underwear or belts;
- on the feet after prolonged walking;
- on the buttocks when sitting for a long time, on the skin from the inside of the thighs after horseback riding and cycling.
With all types, a clear sequence of skin changes is observed: the action of a physical irritant causes redness of the skin, then the reddened area swells, swelling forms, which increases, becoming wider.
By type of reaction
They differentiate according to the type of reaction:
- Local dermographism , in which skin reactions are limited to the area of irritation.
- Reflex , when changes in the skin after pressing and running a hard, sharp object over the body appear after 5–20 seconds in the form of a bright red stripe up to 6–7 mm wide. This phenomenon is explained by the expansion of small arterioles and is a typical vasomotor reflex.
By manifestation
There are several types of dermographism:
- Red , in which red or bright pink streaks appear on the skin, caused by strong pressure from a blunt, hard object. Better expressed on the upper body.
- White dermographism. With slight short pressure, it is characterized by the appearance of white stripes, which is caused by a spasm of the capillaries. It is more pronounced on the legs and lasts longer than “red” dermographism. Unlike “red,” this vascular reaction is explained not by expansion, but by narrowing of the capillaries.
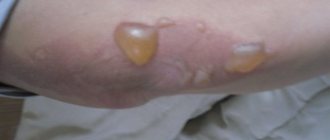
- Dermographism sublime , in which red stripes up to 60 mm wide with uneven contours are initially formed, which after 2 - 3 minutes are replaced by white blisters that swell above the skin and persist for a long time. Such skin changes are due to the high permeability of the vascular wall.
The following are the causes of urticarial dermographism.
What causes peripheral edema?
Most often, peripheral edema is the result of fluid retention in tissues and is not a disease. This swelling is usually mild and goes away over time.
Dependent edema
When you stand or sit for long periods of time during the day, gravity pulls blood toward your legs. The increased pressure forces fluid from the blood vessel into the soft tissue, causing mild swelling.
Swelling associated with gravity is called dependent edema. This is more pronounced later in the day, which is why sock marks on your feet are more pronounced in the evening. By morning they usually disappear.
Salt
Consuming a lot of salt causes your body to retain water. This results in peripheral edema, which can cause more noticeable sock marks in the evening of the next day.
Hormonal changes
Hormone levels change during a woman's menstrual cycle. This can cause water retention and swelling of the legs in the week before your period.
Pregnancy
As a pregnant woman's uterus expands, it can put pressure on the blood vessels leading to her legs. This slows the movement of blood from her legs to her heart, which can lead to peripheral edema.
Most pregnant women experience peripheral edema, but it can also be a sign of a serious condition called preeclampsia. Other symptoms include the sudden onset of high blood pressure and protein in the urine (proteinuria). In this case, urgent medical attention is required.
Thermal edema
Peripheral edema often occurs in hot weather. Heat causes your blood vessels to open wider, so there is more blood in your legs. If fluid gets into the tissue, swelling develops.
Overweight
Obesity can cause excess fat in the abdomen and pelvis, which can put pressure on blood vessels, slowing blood flow from your legs. It accumulates in the veins, and the increased pressure pushes fluid into the soft tissue.
In such cases, peripheral edema is usually more severe and does not go away without treatment.
Venous insufficiency
One-way valves in your veins prevent blood from flowing into your legs.
These valves can weaken and begin to fail as you age. Blood enters the veins of the legs and leads to peripheral edema. This disease is called venous insufficiency. It can also cause cramps and pain in the legs.
Chronic heart failure
Congestive heart failure occurs because your heart is weak or damaged and cannot pump blood effectively. Blood and fluid return to your legs and sometimes to your lungs (pulmonary edema).
Other symptoms include rapid weight gain and shortness of breath.
Kidney disease
With kidney failure, your body can't remove enough fluid from the body, so it accumulates in your tissues—especially in your legs. Swelling around the eyes (periorbital edema) is not uncommon in such cases.
Liver disease
Diseases such as hepatitis and alcoholism can damage your liver (cirrhosis), making it difficult for blood to pass through the organ.
As a result, blood flows into the lower body and fluid accumulates in the abdomen (ascites) and legs. Yellow eyes and skin (jaundice) may also appear.
Poor nutrition
May lead to low levels of a protein in the blood called albumin.
Albumin helps retain fluid in your blood vessels. Without it, fluid begins to seep into the soft tissue.
Some medications
Medicines that can cause peripheral edema:
- contraception: estrogen-containing birth control pills;
- diabetes mellitus: rosiglitazone (Avandia), pioglitazone (Actos);
- high blood pressure: calcium channel blockers such as amlodipine (Norvasc) and nifedipine (Adalat CC, Afeditab CR and Procardia XL);
- inflammation: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen (Advil);
- Parkinson's disease: pramipexole (Mirapex);
- seizures: gabapentin (Neurontin);
Causes
Medical analysis of the mechanism of occurrence and development of dermographic urticaria and its variations has not been completed. It has been established that painful changes in the skin with pressure, vibration, or pressure are caused by stimulation of mast cells. In response to provocation, they actively release large portions of histamine into the blood - a regulator of allergic reactions - which activates processes that increase the permeability of the microvascular wall, which further determines the nature and severity of symptoms.
Skin coloration under line pressure is associated with:
- extension (red autographism) or
- narrowing (white form) of small vessels providing blood supply to the skin.
But it is not clear why exactly the skin of different patients reacts in one way or another.
It has been established that urticarial dermographism affects people:
- with a hereditary predisposition to the disease;
- after a viral infection;
- with special emotional instability;
- after severe stress, prolonged nervous strain;
- after poisoning with ethanol, heavy metals, and other toxins.
Symptoms
The symptoms of autographism depend on the type of disease, but in any case, with mechanical irritation of the skin, the basic signs remain as follows:
- the appearance of red, pink, whitish stripes directed in the direction of the stimulus or repeating its shape;
- itching, swelling, burning and feeling of skin tension;
- swelling of the skin in the form of blisters.
A feature of dermographism, unlike many other allergic skin reactions, is the frequent absence of itching or its very weak intensity.
Types of dermographism and symptoms Table No. 1
Reaction Type of dermographism Basic symptoms May occur Onset and duration
| immediate | white (weak fast pressure); red (strong, longer pressure) | red or white streaks, blisters, erythema (redness) | Itching, burning, soreness, general weakness, chills, headache, nausea | appear in the range from 3 seconds to 10 minutes after pressure on the skin; |
lasts 0.5 – 2 hours
Stage 2: Linear whitish blisters rising above the skin (similar to burn blisters) surrounded by a pinkish-red area
Stage 2 lasts from half an hour to 36 hours.
Diagnostics
Immediate-type dermographic urticaria is fairly easy to identify. The allergist irritates the skin with a blunt spatula, moving it over the patient's body with medium pressure. The appearance of red or white stripes or blisters in the area of irritation within 3 to 20 minutes confirms the diagnosis.
The delayed type of dermographism is more difficult to identify, since all signs develop several hours after prolonged pressure on the body.
We will find out further whether urticarial dermographism can be treated.
Treatment
In a therapeutic way
Local remedies that relieve skin manifestations - itching, erythema, swelling: Radevit, Elidel, Psilo-balm, Protopic, Eplan, La-Cri, Skin Cap. Glucocorticoid external agents help in severe cases.
They are divided according to their effects:
- Weak glucocorticoid ointments: Sinaflan, Flucinar, Laticort, Hydrocortisone.
- Medium: Afloderm, Fluorocort, Triamcinolone;
- Strong: Advantan, Celestoderm B, Lokoid, Elokom, Cloveit, Dermovate
By medication
Dermographic urticaria is treated with the same groups of medications as other types of urticaria. First of all, antiallergic drugs of different generations are used, which are selected depending on the patient’s individual reaction to a particular drug.
- Some doctors recommend vasoconstrictors for the red form of dermographism and vasodilators for the white form.
- Others have a negative attitude towards this treatment option, since the effect of such drugs on the body is general, which means their influence extends to the vessels of all organs, including the brain and heart. Therefore, the use of vasodilators (vasodilators) or drugs with opposite effects can lead to problems in the blood supply to the cerebral and coronary vessels or their sudden expansion, which threatens hemorrhagic stroke and thromboembolism.
The treatment regimen for urticarial dermographism is discussed below point by point.
Antihistamines II – III generation
Typically, therapy begins with the use of standard doses of antihistamines of the 2nd - 3rd generation. Daily dosage for adults:
- Claritin, Lomilan (loratadine) – 10 mg;
- Telfast, Fexadine (fexofenadine) – 150 mg. Strictly prohibited for pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children under 6 years of age;
- Xizal, Suprastinex, Zodak, Glencet, Cesera (levocetirizine) – 5 mg, contraindications are the same as for drugs with fexofenadine;
- Ebastine (piperedine) – 10 mg;
- Erius, Allergostop (desloratadine) – 5 mg;
- Zyrtec, Zodac (cetirizine) – 10 mg.
A new drug that helps well with dermographic urticaria, but does not cause sedation (drowsiness) is Trexyl with the active component terfenadine. Used in tablets and suspensions. The recommended dose for adult patients, starting from 12 years of age, is 60 mg (or 10 ml of suspension) 2 times. Children's doses: 3 - 7 years old - 15 mg, 7 - 12 years old - 30 mg, morning and evening.
If the latest generations of antistamins do not help, the dosage, as a rule, is not increased, but a second medicine with a different active substance is added to the treatment regimen.
Or they use 1st generation remedies, which are often more effective for urticaria: Diphenhydramine, Suprastin, Tavegil, Pipolfen. For severe skin manifestations with severe itching, Tavegil and Suprastin are administered intramuscularly.
For frequent exacerbations of long-term dermographism, use:
- Ketotifen. Adult dose 0.001 - 0.002 g twice a day. Children are given syrup: up to six months - in a daily dose of 0.05 mg per kilogram of the baby's weight, from six months to 3 years - 0.5 mg twice a day, from 3 years - 1 mg.
- Cyproheptadine: 4 – 8 mg (3 or 4 times); The pediatric dose, based on the norm of 0.25 - 0.5 mg/kg, is also divided into 3 - 4 doses.
Histamine H2 receptor suppressors
If the patient does not respond to therapy with antiallergic medications, they try the introduction of drugs that suppress histamine H2 receptors:
- Cimetidine: 0.3 grams up to 4 times a day. Children's daily doses from one year of age are calculated: 25 - 30 mg per 1 kilogram of weight, for infants up to one year - at the rate of 20 mg / kg of weight;
- Ranitidine for patients over 12 years of age: 0.150 - 0.300 g (2 or 1 time per day);
- Famotidine (from 12 years old) - twice 0.020 g.
Hormonal agents
In those rare cases when the severity of symptoms does not decrease, it is necessary to use hormonal agents in short courses (2–4 days) that quickly relieve swelling and itching.
Prednisolone is usually prescribed in a daily adult dose of 0.04 - 0.06 grams, Dexamethasone - 0.004 - 0.020 g (or 1 injection per day) in the acute period.
Elimination of common symptoms
General symptoms are eliminated by taking:
- Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Ketonal for painful blisters, headaches, fever;
- Cerucal - for nausea;
- Decitel, No-Shpu - for abdominal cramps.
Since experts associate the development of dermographic urticaria with instability of the nervous system, they prescribe courses of:
- B vitamins, including Neuromultivit, Milgamma, vitamins B1, B6, B12 in injections;
- sedatives: decoctions, tinctures, tablets with valerian root, motherwort, Novopassit;
- during exacerbations - Bellantaminal, Belloid (tablet 3 times a day).
Since skin manifestations of dermographic urticaria are associated with abnormally high permeability of the vascular wall, the following is used:
- ascorbic acid;
- flavonoids (Rutin, Ascorutin, Quercetin, Vitamin P) under the control of blood clotting to avoid increased viscosity;
- vitamers (semi-synthetic derivatives) – Venoruton, Phlebodia, Detrolex, Troxevasin in various forms (capsules, gel, solutions).
For severely tolerated symptoms - particularly severe itching, insomnia, neurological disorders, it is advisable to prescribe tranquilizers from the group of benzodiazepines (Phenazepam, Xanax, Diazepam) and antidepressants - Paxil, Doxepin.
Disease prevention
In order for exacerbations of dermographism to occur less frequently, it is necessary:
- Avoid situations involving pressure on the skin, especially long-term pressure accompanied by friction.
- Do not wear clothes made of synthetic or woolen fabrics.
- Do not use hard washcloths or rub your body with a towel.
- Avoid power massage (only the stroking type).
- Avoid overwork, stress, overheating and cooling, which can provoke illness.
- Conduct consultations and examinations with a gastroenterologist to exclude infection of the gastric mucosa with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, an endocrinologist (diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease), a parasitologist (to identify possible giardiasis, helminthiases), and an immunologist.
Complications
With the development of urticarial dermographism, the consequences may be as follows:
- Frequent exacerbations of urticaria deplete the nervous system of patients, leading to depression.
- Prolonged pressure, often repeated in the same places, contributes to thinning and damage to the dermis. At the same time, pyogenic bacteria easily penetrate deeper, leading to pustular skin infections, furunculosis, local suppuration with the development of an abscess.
- General symptoms of malaise that often accompany skin reactions - fever, nausea, headaches - contribute to a decline in the body's immune defense.
- Since any allergic diseases are “reinforced” by other types of allergies, dermographic urticaria in rare cases is complicated by Quincke’s edema, dangerous laryngeal edema, and anaphylactic shock.
Forecast
A timely diagnosis and treatment undertaken slow down and alleviate the disease. Strengthening the immune system, the vascular wall, and the nervous system contribute to the mild course of the pathology.
This video provides useful information about dermographic and other types of urticaria:
Dermographism is a greatly increased sensitivity of the skin to external irritants. From the slightest touch or too much pressure on the skin, pronounced traces of impact remain on its surface, which can appear in the form of red or white stripes. The type of dermatological disease is determined by their color, and the patient is subsequently diagnosed with red or white dermographism. The exact cause of the disease is still not known. It is believed that this is a type of urticaria, the appearance of which may be associated with external or internal irritants of the body.
General characteristics of the disease
Translated from Greek, dermographism is referred to as “writing on the skin” or “skin writing.” People suffering from this pathology of epidermal tissues daily observe many different patterns on their bodies, which sometimes resemble inscriptions and drawings. The nature of their occurrence is that sensitive skin turns red and appears in stripes after interacting with hard environmental objects. Tight clothing, pressed folds from a blanket, and normal stroking of the skin can lead to swelling, redness, or the appearance of multiple white edema of irregular shape.
Based on the type of skin reaction, acute and chronic dermographism are distinguished. The first type of disease is characterized by an increased degree of sensitivity of the epidermis. In case of mechanical impact on the skin, not only its upper layer becomes inflamed, but also deeper tissues. Swelling from touching a hard object may not go away for several days, and the inflammatory process begins to develop so extensively that it affects other areas of the skin that were not injured. Chronic dermographism of red or white etiology does not occur so aggressively and is limited to local irritation of the epidermis directly at the site of contact between the skin and an object from the environment.
Causes of bruises on the body
21.01.2022
The appearance of bruises or subcutaneous hematomas is almost inevitable. The main reason for their appearance is a bruise or gift. However, if it appears for no reason, it may indicate a serious problem. They often appear suddenly and are accompanied by bruising. In this case, you should not delay to the doctor the blood vessels are in normal condition , hemorrhage does not occur in the upper layers of the skin. On the other hand, if injured, they can remain on their feet . And this is a normal phenomenon that does not require outside intervention.
Age
With age-related changes, part of the subcutaneous fat, which serves as a cushion, softening blows and bruises, wears out. Capillaries become fragile and lose their elasticity. Therefore, to form a bruise, much less force is required than for the skin at a young age.
Diabetes
blood glucose levels . Metabolic disorders during illness affect the entire body. The blood vessels narrow, and the blood clots worse. Dark spots appear where the skin touches. They can be easily confused with bruises. These spots are actually caused by insulin resistance.
Taking medications
Blood thinners are one of the most common causes of persistent hematomas. These include: aspirin and its analogues, antipyretics, medications containing vitamins C, D, A, E, omega 3. Naturally, it is difficult to do without these drugs during the winter season and the period of illness. However, individual calculation of an adequate level of drugs will not harm the body.
Varicose veins
A disease that affects most of humanity. Blood vessels are significantly weakened. Minor contact with a hard object leads to injury. Blood enters the tissues. This is how bruises are formed, surrounded by a capillary network.
Lack of vitamins
A frequent case of bruises on the body is an insufficient amount of vitamins K and P. They promote the production of protein - collagen, which protects capillaries from cracks and ruptures. A lack of collagen in the skin leads to vasoconstriction , which leads to frequent bruising.
Hemorrhagic vasculitis
The cause of the disease is a malfunction in the immune system , when cells of the circulatory system are perceived as foreign. As a result, thousands of small bruises appear, most often in the lower leg . From the outside it looks as if the body was sprinkled with red pepper. In this case, bruises are the cause of blood from microscopic capillaries.
Blood diseases
The main pathologies that provoke the formation of hematomas are leukemia and thrombocytopenia. In addition, additional symptoms of bleeding gums , swelling of the lower extremities, and nosebleeds appear .
Preventing bruises
As a rule, bruises disappear after 2-3 days. The larger the area, the longer the recovery will be. To speed up the process, special gels and ointments are used. A compress made from raw potatoes is considered a good budget folk remedy.
- Stick to proper nutrition. Receive a complex of vitamins and minerals in a timely manner.
- Follow safety rules to prevent injury.
- After consultation with a specialist, reduce the use of thinning medications. Be sure to use additional creams and ointments to strengthen blood vessels .
The most important wealth in a person’s life is his health. Therefore, if the body gives signals in the form of bruises, you should not ignore or hesitate. It is important to learn to hear and see warnings about possible problems from your body.
Published in Articles without category Premium Clinic
Species classification of dermographism
This dermatological disease is divided into types based on the observed clinical picture of its course at all stages of manifestation. Dermographism is classified as follows:
- White. The appearance of white stripes and patterns after mechanical impact on the skin is considered a normal reaction in people with a hypersensitive surface of the epidermal tissue. Swelling of the skin with a pronounced white tint forms after even slight pressure and rubbing with a finger or any hard, sharp object.
- Red. This type of dermographism is formed after a stronger mechanical effect on the patient’s skin. This reaction of the body indicates disturbances in the vasomotor response of the peripheral nervous system. Red marks appear on the skin 15 seconds after contact. In the chronic form of the disease, they persist for about 1-2 hours. In the acute type, the course of dermographism, red stripes on the body may not go away for 1 to 3 days.
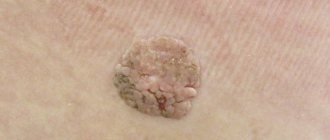
- Urticarial. The most common type of dermographism. It accounts for about 15% of all dermatological diseases. In addition to the characteristic red spots and stripes, a small urticarial rash forms on the irritated skin, which itches and causes physical discomfort.
- Hydropic. This type of disease is the least common in medical practice and represents a unique individual reaction of the skin. When it appears, the epidermal tissues do not acquire any characteristic color, and oblong swelling in the form of a roller forms at the points of contact. The height of the swelling is from 1 to 3 mm, and the width is 2-3 cm. They appear with a slow reaction - 10-15 minutes after touching the skin, and disappear after a few hours. In this case, the patient does not experience any tactile discomfort.
When to see a doctor
When socks leave marks on your feet, this may not always be a sign of any serious illness. Sometimes this can occur during prolonged standing, pregnancy, or flying on an airplane. However, persistent or frequent swelling may be a sign of a medical condition. You should talk to your doctor if swelling in your legs, arms, or other parts of your body occurs regularly. It's also important to see a doctor if other symptoms accompany swelling, such as high blood pressure or blurred vision. Your doctor can determine the cause of the swelling and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnostic value of the disease
Dermographism may not always act as an independent skin disease. Quite often, this is just an additional symptom to the main pathology, which lies in the unhealthy state of one or another internal organ of a person. When a patient with signs of red or white dermographism seeks medical help, doctors refer him for examinations to exclude the presence of diseases such as:
- depletion or intoxication of the nervous system;
- meningitis;
- psoriasis;
- autonomic neurosis;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- sympathetic innervation;
- parasympathetic nervous system disorder.
An inadequate reaction of the skin to normal contact with environmental objects is always associated with the activity of nerve endings, which are concentrated in multiple quantities and located in the layer of the skin. Therefore, if after a comprehensive examination of the body no concomitant diseases of the internal organs are revealed, no parasitic life forms are found in the skin and organs of the gastrointestinal tract, then in 90% of cases the cause of red, white, edematous and urticarial dermographism lies precisely in the unstable functioning of the nervous system at all its functional levels.
What to do if only one foot has sock marks?
Peripheral swelling in only one leg is never normal and requires urgent medical attention. Reasons include:
DVT
A blood clot in your leg vein is called deep vein thrombosis, or DVT. It causes sudden pain and swelling, usually in the lower leg area.
Without prompt treatment, the clot can rupture and travel to the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism and can be life-threatening.
Cellulite
Infected skin or soft tissue (cellulitis) is usually swollen. Surgery is necessary to prevent the infection from spreading into the bloodstream or bone.
Lymphedema
Lymph is a fluid containing white blood cells. It flows through lymph nodes and special channels throughout the body.
Lymphedema develops when a tumor or other mass pushes through and blocks lymph channels, or when lymph nodes are removed by surgery or damaged by radiation therapy.