The most common dermatological diseases include lichen - an infectious lesion of skin areas caused by the action of microscopic fungi or viruses. The danger of lichen is that it is easily transmitted by contact from person to person or from sick animal to person and has several varieties that require a special approach to treatment.
What kind of lichen occurs, what type of therapy is more effective in each specific case, how to avoid complications - this will be discussed further.
Pathogens and carriers of lichen
The content of the article
Dermatologists distinguish several types of lichen, caused by different pathogens.
Most often, the appearance of lichen on human skin is initiated by fungi:
- zooanthropophilic - transmitted to humans from an infected animal, including from pets;
- anthropophilic - live only on human skin;
- geophilic - live in the soil and come into contact with human skin upon contact with the ground.
In addition to fungi, viruses are often the causative agent of lichen. Their cunning lies in the fact that they can live asymptomatically in the human body for a number of years and become more active when the immune system is weakened. This is exactly how, for example, those familiar to many with herpes or shingles behave.
Measures to prevent the disease
Since there can be many causes of lichen infection, it is impossible to completely exclude the possibility of the disease. However, compliance with preventive measures will reduce the risks. Prevention of lichen includes:
- timely treatment of acute respiratory diseases;
- compliance with hygiene procedures;
- taking a vitamin complex;
- increasing the level of immunity;
- use of shampoos with antifungal gels;
- hardening of the body;
- providing quality oral care, treatment of caries, gums and throat diseases;
- proper nutrition;
- avoiding contact with people infected with the fungus;
- vaccination of pets and periodic examinations at a veterinary clinic;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- preventing hypothermia of the body.
When diagnosing a chronic form of lichen, it is recommended to periodically visit a dermatologist’s office in order to identify possible foci of the disease.
Types of lichen
In order to cure lichen, it is not enough to make a general diagnosis. It is equally important to promptly determine the type of lichen, since each is characterized by its own symptoms and requires its own treatment.
Dermatologists distinguish the following types of lichen:
- shearer;
- encircling;
- pityriasis;
- pink;
- red flat;
- tubular;
- solar;
- scaly.
Only a competent dermatologist can draw a line between them and correctly prescribe a set of therapeutic measures. Therefore, under no circumstances should you self-medicate. The surest way is to go to the clinic at the first sign of deprivation.
Now about what changes in the skin should alert a person.
Diagnosis of pityriasis
If you find suspicious spots on the skin, you should promptly contact a dermatologist. During a visual examination, the doctor assesses the nature of the rashes, their shape, size, location on the body and is able to make the correct diagnosis. After dermatoscopy, the following studies are additionally carried out: biochemical tests of blood and urine, RMP (microprecipitation reactions with antigens), skin scrapings from injured areas.
A more complex diagnosis is carried out if the skin disease lasts more than six weeks. In these cases, discharge from the affected lesions is sent for bacterial culture. A biopsy and subsequent histological studies will help make the correct diagnosis. In order to distinguish Zhiber's disease from other types of lichen, toxicerma, psoriasis, complicated syphilis and other pathologies, fluorescent diagnostics are carried out, scrapings are checked for the presence of pathogenic fungi, RPR tests are done for syphilis, etc.
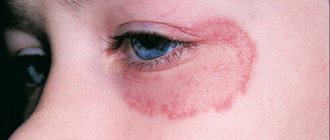
Ringworm
The source of trichophytosis - this is the second name for ringworm - can be any of the fungi that primarily affects the hairy parts of the body (head and beard), neck, shoulders, face. The symptoms of this type of lichen are usually as follows: first, swollen pink or red spots with clearly defined edges appear, then the edges of the spots become covered with bursting blisters and an itchy crust, and finally, the center of the spot begins to peel off, and the hair in the affected area breaks off and thins.
Ringworm is diagnosed using a Wood's lamp. If the disease is confirmed, the patient - children often suffer from ringworm - is protected from contact with others and is prescribed complex therapy, including taking special tablets (for example, Terbinafine) and the use of antifungal ointments. In particularly difficult cases, it is possible to take hormone-containing agents that help stop the inflammatory process on the skin.
Herpes zoster
It is caused by a virus that remains “dormant” in the human body for the time being. It appears in the form of fluid-filled blisters, usually located in the intercostal part of the body. Associated symptoms of herpes zoster: pain (caused by damage to the intercostal nerve endings) and itching of the skin in the affected area; sometimes fever with chills, headaches.
Treatment of herpes zoster is complex. Since the blisters of shingles burst, they are initially treated with brilliant green. And to lubricate the crust that forms in their place, use dermatol ointment. In parallel, the doctor may prescribe antipyretic, painkillers and antiviral drugs, quartz and laser therapy.
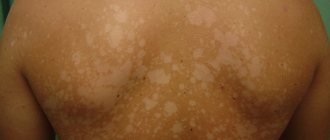
Pityriasis versicolor
It is also called multi-colored, because the small pink - and sometimes greenish - rash that appears on the back, stomach, shoulders, and chest changes color and turns brown as the disease develops. Moreover, on tanned skin (in summer) these spots appear discolored, but on white skin (in winter), on the contrary, they look quite dark.
Diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor can be carried out by a specialist who has resorted to microscopic examination of the dermis, Balzer iodine test, and Wood's lamp. He will also prescribe a special drug treatment (with the help of Orungal, Mycozolon, etc.) that can kill the fungus that causes the disease.
With proper therapy, pityriasis versicolor can be eliminated quite quickly (although without treatment, the disease drags on for many years). Additionally, the patient is recommended to adjust their lifestyle (a concomitant cause of this type of lichen may be increased humidity or air temperature), and carry out a complete treatment of clothing and linen.
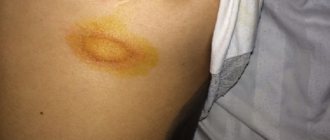
Lichen rosea (or Zhibera)
A little-studied type of disease that usually develops against the background of a weakened immune system in the autumn or spring season. The risk group in this case consists of girls who have a hormonal imbalance in their body.
The manifestation of lichen is the appearance of round or oval pink and light brown spots on the chest, shoulders, back, sides, and skin folds. Dermatological changes, accompanied by itching and flaking of the skin, may go away on their own within a few weeks, however, when the first signs of the disease appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor to rule out the presence of syphilis similar in symptoms.
Diet to eliminate the first symptoms of psoriasis
For patients with psoriasis, proper nutrition is very important. When the first symptoms of psoriasis appear or the process worsens, smoked foods, fatty meats, eggs, baked goods, coffee, carbonated and alcoholic drinks are prohibited. The consumption of sugar and confectionery products should be reduced to a minimum. Food should contain the necessary set of nutrients, vitamins and microelements, and not burden the gastrointestinal tract and liver. It is recommended to eat vegetables, fruits and berries, fresh herbs, lean meat, dairy products and cheeses, lean fish, bread made from wholemeal flour, whole grains or bran. In some cases, your doctor may recommend intermittent fasting.
An integrated approach to the treatment of psoriasis can significantly improve the quality of life of patients.
Lichen ruber planus
Flat multi-colored (from pale pink to purple) nodules of lichen red often appear on the mucous membranes, nails (they crumble), and delicate skin of the chest and abdomen. Their appearance is accompanied by severe itching, which, as a result of scratching, leads to the rapid growth of foci of skin damage.
Dermatologists find it difficult to determine the cause of the appearance of lichen red, but note that it is quite common in patients with diabetes, as well as those suffering from diseases of the stomach, liver, and biliary tract. Moreover, women over 40 years of age are primarily at risk.
Tinea tubularis
Malasezzia is the name of the fungus that causes tubular lichen. This fungus can live in the human sebaceous glands for a long time without revealing itself in any way. Under certain conditions: for example, a decrease in immunity or an imbalance in the acid balance of the skin, severe hypothermia or excessive sweating, endocrine disorders or the development of certain chronic diseases - it begins to multiply intensively.
As a result, small flaky spots appear on the skin, which gradually grow and merge into one large spot. And although the victim practically does not feel itching or pain, he should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
After diagnosing the disease (methods used - scraping test, iodine test, use of a Wood's lamp, etc.), the dermatologist prescribes local or complex antifungal drugs.
Ringworm solar
Under the influence of sunlight, excessive sweating, abuse of solariums and antibacterial agents, uneven, flaky dark spots may appear on the skin. Their occurrence is provoked by a fungus that multiplies on the dermis as a result of a violation of its acidity. Gradually, the spots grow to significant sizes, which causes aesthetic discomfort to a person: they clearly stand out against the tan. And although solar lichen is rarely accompanied by itching and pain, it requires mandatory therapy.
As a rule, solar lichen is diagnosed quickly: it is often enough to conduct an iodine test or use a Wood's lamp. At the initial stage of the disease, local antimicrobial drugs help well; in cases where the disease is advanced, the doctor prescribes complex therapy.
Factors influencing the intensity of itching
In any of its manifestations, lichen itches. Not all patients exhibit this characteristic in the same way. Sometimes the itching is mild, but more often it is a pronounced irritating symptom.
Several factors influence the intensity of itching:
- Type and form of lichen. Some varieties are accompanied by mild discomfort. Pink, red, pityriasis itches less often, the itching is less intense than that of ringworm and shingles.
- The size of the lesion and the depth of the skin lesion also influence the characteristics of itching. Superficial lichens cause less pronounced discomfort.
- Different people have different skin sensitivity thresholds. Feelings of the same intensity can be of different nature.
- The intensification of skin itching is influenced by liquid entering the affected areas of the skin. Sweat has especially high irritating properties; it makes the rash itch more intensely. People with excessive sweating experience more discomfort.
- Additional irritation of the affected areas of the skin with synthetic or woolen products increases the sensation and desire to itch.
Ringworm scaly
The causes and treatment of this lichen, better known as psoriasis, are not fully understood. However, it is noted that it appears more often in people suffering from diseases of the endocrine and nervous systems and prone to alcoholism.
Psoriasis is a chronic disease, often occurring latently, i.e. is hidden. First, small reddish spots appear on the skin - most often the bends of the legs and arms, lower back and buttocks, causing severe itching due to dryness. Gradually, the spots grow and turn into a lesion that affects a large area of the skin. The peculiarity of psoriasis is that when the plaque is removed, the lichen begins to bleed.
It is necessary to treat scaly lichen under the supervision of a doctor, who will select the necessary topical medications (when applying them, you must strictly follow the instructions), and, if necessary, prescribe antibiotics.
How to remove itching
Itching with lichen not only causes discomfort to the sick person, it can cause serious complications. Scratching the formations leads to the formation of ulcers, which, after completing the course of treatment, become scarred and have an unpleasant appearance. Bacteria penetrate into the wounds formed after scratching, which leads to the development of inflammatory processes. The resulting inflammation can lead to more severe skin diseases and blood poisoning.
When the lichen itches, it is recommended:
- Stick to a diet. It is necessary to exclude foods that are strong allergens from the diet.
- Refrain from scratching painful lesions.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to water; some forms of lichen are completely prohibited from getting wet.
- Use antihistamines.
- Take sedatives.
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- Follow your doctor's recommendations for treating the underlying disease.
Hygiene measures
To carry out hygiene procedures, sick people must have their own personal body care items. It is required to strictly ensure that none of the family members use the patient’s towel, washcloth or soap. Rubbing the skin vigorously with a washcloth is prohibited for almost any type of dermatosis.
Affected areas must be thoroughly treated and washed using detergents containing medications. This rule does not apply to forms of lichen, in which contact of the lesion with liquid is strictly prohibited. To choose the right cleanser, you need to consult a dermatologist.
Antipruritics
The most common way to get rid of unpleasant sensations and prevent rashes from scratching are antihistamines and sedatives. Medicines to relieve symptoms are available in several forms:
- Tablets and drops for oral administration (Suprastin, Tavegli, Fenkarol, Claritin, Ketotifen). Many of them have the side effect of drowsiness.
- Creams, gels and ointments. These drugs are applied to the affected areas of the skin (Triderm, Triakutan, Kremgen, Fenistil, D-Panthenol, Nezulin).
Antipruritic drugs are usually not used for more than 2 weeks. The dosage and duration of administration are prescribed by the doctor.
For severe, debilitating itching, herbal sedatives (valerian, motherwort, Persen) are sometimes prescribed.
Treatment of the underlying disease
Treatment of dermatosis is the main and most effective way to relieve symptoms. As the lesions heal, they stop itching. After testing and determining the form of the disease, the dermatologist prescribes medications to treat it. For the treatment of lichen, complexes of various drugs are used.
Patients are prescribed medications that have antiseptic and antiparasitic effects. For local treatment of spots, use brilliant green, Fukortsin, hydrogen peroxide, and ointment with the antibiotic Levomekol. To treat lichen caused by various fungi, Clotrimazole is prescribed, which has a strong antifungal effect.
Along with medications that fight pathogens, patients are prescribed immune stimulation agents. This is due to the fact that lichen often occurs against the background of a weakened immune system, and strengthening it allows dermatosis to be cured more quickly.
Are all types of lichen contagious?
Many people believe that absolutely all types of lichen are dangerous to others. Meanwhile, this is not entirely true. So, with pink, ringworm or shingles, the patient will really need to be isolated. But, for example, pityriasis or scaly ones are not dangerous for others.
And this is another reason why any change in the skin should be the reason for going to a specialist - only he will be able to correctly determine the type of lichen, assess the degree of its danger, give recommendations for treatment, and finally select a set of medications and therapeutic measures aimed at including general strengthening of the body.
Consequences
In the absence of therapeutic measures for a long time, the course of the disease may worsen. Depending on the type of lichen, a variety of complications can occur.
The greatest danger is the shingles form of the pathology. If left untreated, the likelihood of complications such as:
- impairment of auditory and visual function;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- viral pneumonia;
- postherpetic neuralgia;
- meningitis (inflammatory process of the spinal cord).
The weeping type of lichen is characterized by secondary infection. The scaly type of the disease is complicated by frequent relapses.