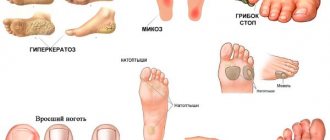
Mycosis of the feet - symptoms and treatment
Mycosis of the feet (dermatophytosis, Tinea pedis) is a disease of the skin of the feet, which is caused by pathogenic or opportunistic fungi. Skin changes on the feet are characterized by peeling, which is accompanied by itching. In case of severe lesions, against the background of red and swollen skin, erosions and deep cracks appear on the soles and in the spaces between the toes, which are accompanied by pain and make walking difficult.
The code according to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10) is B35.3.
The emergence of modern antifungal drugs has improved the epidemiological situation, but mycosis of the feet still remains one of the most significant problems in dermatovenerology. The use of some drugs is limited in the elderly and patients with chronic diseases [19].
Prevalence of mycosis of the feet. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 1/3 of the world’s population suffers from fungal diseases, the most common of which are mycoses of the feet; the incidence is growing annually [14].
According to Russian dermatologists [7], 10-20% of the adult population suffer from mycoses of the feet; in men the disease occurs 2 times more often than in women, and in older people more often than in young people. At the age of over 70 years, mycosis of the feet is registered in every second patient, which is associated with an increase in concomitant metabolic and vascular changes (diabetes mellitus, varicose veins, etc.). Increasingly, mycoses of the feet are being detected in children.
Millions of people are currently affected by this disease. Workers in a number of professions are at risk: miners, athletes and military personnel [12].
Causes of mycosis of the feet. The most common causes of mycosis of the feet are dermatomycete fungi: Trichophyton rubrum (90%), Trichophyton mentagrophytes, and less commonly Epidermophyton [20]. Sometimes mycosis of the feet can be caused by fungi of the genus Candida [3].
Risk factors for mycosis of the feet:
- Exogenous (external): microtrauma of the skin of the feet (calluses, corns), cracks, increased sweating, wearing tight shoes, shoes made of artificial materials, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, irregular foot washing and poor drying with a towel.
- Endogenous (internal): varicose veins and vegetative-vascular dystonia, which lead to insufficient blood supply to the skin of the feet; hypovitaminosis; taking glucocorticosteroids, cytostatic, antibacterial and estrogen-progestin drugs, which reduce the overall immunity of the body [16].
Infection with mycosis of the feet can occur directly from a sick person, and it can also be transmitted through contact and household contact (in a swimming pool, bathhouse, gym, through shoes, towels, rugs, etc.).
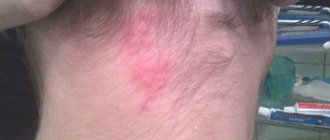
Redness of the feet
Acute or chronic inflammatory skin disease, occurring with periods of exacerbation (relapses) and relief (remissions) of the disease. The disease is characterized by rashes of various types (polymorphic), as well as itching. Among the main causes of the disease are hereditary predisposition, the negative effects of stress, hormonal imbalance in the body, as well as increased sensitivity to allergens. There are several forms of eczema: 1) true (idiopathic) - manifested by redness, swelling, against which blisters form, which quickly open. In their place, pinpoint wounds (erosions) form, from which liquid (plasma/exudate) is released, forming areas of weeping. The released liquid gradually dries out, forming grayish-yellow crusts. Skin lesions in true eczema usually begin in the area of the hands and/or feet. Eczema lesions vary in size with unclear boundaries. Characteristic is the alternation of affected skin areas with unaffected ones. The rashes are often symmetrical, with a tendency to spread to the skin of the arms, legs and other areas of the skin. Patients are bothered by itching of varying degrees of intensity, which contributes to the development of nervous system disorders and sleep disturbances 2) pruriginous - manifested by rashes of small, 1-2 mm in diameter, nodules and blisters on an inflammatory basis. Lesions are located on the skin of the face, elbows, popliteal cavities, and groin area. As a result of a long course, the presence of multiple scratches, the skin on the affected areas becomes dry, rough, thickened and darkened. Characterized by itching, neuroses, and sleep disturbances. The disease is chronic, with frequent exacerbations in winter 3) dyshidrotic - characterized by the formation of small, no more than 1 mm in diameter, dense blisters on the lateral surfaces of the fingers, sometimes on the skin of the palms and soles. Less common are large blisters, after opening which yellowish crusts form. Patients are often bothered by severe itching. Dyshidrotic eczema can occur against the background of emotional overload, the provoking factor can be humid and hot weather 4) microbial - develops against the background of bacterial or fungal diseases. The rash can occur on any part of the skin, but most often affects the skin of the legs. Microbial eczema is characterized by the formation of inflammatory lesions of various sizes, sharply demarcated from healthy skin, with the presence of redness, nodules, blisters with liquid, and wounds. In some cases, pustules, purulent or bloody crusts may appear. The rash is accompanied by itching 5) coin-shaped (nummular, plaque) - manifested by rounded lesions with a diameter of 1-2 cm with clear boundaries. Characterized by the presence of slight swelling, redness, weeping, and layers of serous-purulent crusts. The rashes are usually located on the hands; in some cases, the process can be general (widespread). This type of eczema is often associated with foci of chronic infection or parasitic diseases 6) paratraumatic - develops in the area of postoperative scars, with bone fractures, fusion of bone fragments (osteosynthesis), places of improper application of plaster casts; characterized by the appearance of redness, blisters with liquid or pustules, and the formation of crusts. Possible darkening of the skin and a decrease in the subcutaneous fat layer (atrophy) 7) seborrheic - develops on the scalp, face, behind the ear area, chest, area between the shoulder blades. It is characterized by the presence of round yellowish-pink lesions with slight inflammation, covered with fatty yellowish scales. Abundant layered yellowish crusts and scales form on the head. Patients complain of itching, sometimes very intense. In addition to the head, the process can be located in other areas of hair growth: in the area of the eyebrows, eyelashes, chin, etc. A long-term inflammatory process on the head can be accompanied by baldness
Effective prevention of foot hyperkeratosis
Most often, hyperkeratosis of the feet occurs as a result of the development of other disorders existing in the body. Therefore, the main preventive measure is their timely detection and treatment.
In order not to encounter hyperkeratosis of the feet in life or to prevent its relapse, it is necessary to exclude factors that provoke this disease:
- You need to choose the right shoes, especially those that are intended for daily wear. It should be the right size, not put pressure on the foot, and also be comfortable.
- If your work requires you to be on your feet all day (standing or moving), you can contact an orthopedic salon, where they will make insoles according to individual measurements.
- Avoid the formation of a hard keratinized layer, as well as its growth to critical sizes. Proper foot hygiene will help with this, which consists of regular washing and exfoliation of the feet.
- If you have diseases that cause metabolic disorders, it is necessary to choose certain care products that do not injure the skin, as well as specialized medications.
- It is also important to constantly visit your doctor and follow all the recommendations he gives.
If hyperkeratosis of the feet has gone too far, you need to consult a podiatrist, since it is unlikely that you will be able to cope with this problem on your own. Only he can prescribe effective treatment.
It must be remembered that hyperkeratosis of the feet is not always an exclusively cosmetic defect. In some cases, it can indicate the presence of disorders in the body related to the functioning of internal organs, and can also lead to quite serious complications. To treat this disease, various methods can be used, including the use of medications, folk remedies or hardware procedures.
Nowadays, you no longer have to spend a lot of time performing complex and unpleasant procedures at home. It is much easier to seek help from real professionals - the Veronika Herba beauty and health center, equipped with effective and modern equipment.
Why clients choose Veronika Herba Beauty and Health Center:
- This is a beauty center where you can undergo treatment for hyperkeratosis of the feet at a reasonable cost, and you will be treated by one of the best specialists in Moscow. This is a completely different, higher level of service!
- You can receive qualified help at any time convenient for you. The beauty center is open from 9:00 to 21:00, seven days a week. The main thing is to agree with your doctor in advance on the date and time of your appointment.
Sign up for a consultation with a specialist by phone +7 (495) 085-15-13
, and you will see for yourself!
Stages of SDS
In medicine, several stages of the disease are determined:
Zero or initial stage
:
· deformation of the bone structure of the foot
formation of calluses
· pale skin color
Itching may occur without visible damage to the skin
The most important task of this stage is to prevent damage, because any wound on the feet is a risk of developing an ulcer. It is necessary to ensure maximum skin care and, if possible, not to put any strain on the feet.
First stage
:
formation of ulcers and cracks on the skin of the feet
darkening of the nail plate, possible ingrown nails
The bones of the thumbs are deformed
wounds, abrasions and cuts do not heal for a long time
The lesions are superficial - bones, tendons, and muscles are not damaged.
At this stage, it is necessary to prevent the wound from becoming infected. It is important to keep the wound clean and speed up the healing process.
Second stage
:
· wounds become deeper
The ulcer begins to affect the subcutaneous tissues, muscles, tendons
When a wound becomes infected, swelling, redness, and pus appear
Damage to deep tissues and bones at the second stage is not yet diagnosed. The wound can be either infected or uninfected.
The main task at the second stage is to remove dying tissue, thereby avoiding suppuration.
Third stage
:
· damage becomes deeper, bones and joints are affected
Osteomyelitis develops (an inflammatory process that affects all bone elements)
an abscess develops (purulent inflammation)
Fourth stage
:
· the process of formation of gangrene (death of living tissue) begins
First, the area of the fingers turns black (starts from the tips), then the supporting part is affected. The limb can be saved with surgery.
Fifth stage
:
· the spread of gangrene continues along the entire foot, rising to the lower leg.
The areas with the affected tissue increase in size; the only way out at this stage is amputation of the limb.
The fifth stage of the disease is extremely dangerous and poses a threat to life.
According to statistics, the diagnosis of SDS is the most common reason for amputation. It is important for diabetics to remember that they must follow the rules for preventing diabetes, and at the first suspicion, immediately consult a doctor.
Treatment of spider veins
Spider veins tend to progress: an increasing number of neighboring capillaries are involved in the process, and entire “networks” are formed. The easier it is to get rid of “stars”, the smaller the area they occupy.
Removal of spider veins is carried out using various conservative and surgical methods: sclerotherapy, ozone therapy, radio wave and laser methods.
1
Sclerotherapy in MedicCity
2 Sclerotherapy in MedicCity
3 Sclerotherapy in MedicCity
The radio wave method (Surgitron) is the removal of an enlarged capillary using a thin electrode without damaging surrounding tissues and healthy vessels. An ideal method for removing single spider veins on the face, which does not leave scars.
1 Laser removal of spider veins in MedicCity
2 Laser removal of spider veins in MedicCity
3 Laser removal of spider veins in MedicCity
Removal of spider veins with a laser (laser coagulation) is used in the presence of widespread vascular network. The laser beam is selectively absorbed by the pathological vessel forming the spider vein and heats it. At high temperatures, the walls of the vessel stick together, and the vessel is irreversibly damaged.
Sclerotherapy (introduction of a sclerosant into the lumen of the vessel, which causes adhesion of the vessel walls) is effective against fairly large telangiectasias, located mainly on the legs.
You can learn how sclerotherapy is performed from the video. The procedure takes place on an outpatient basis, before our eyes: thanks to a simple injection, the patient gets rid of spider veins on her leg.
Spider veins may appear again. To prevent relapse, it is necessary to take medications to strengthen blood vessels and use compression stockings.
1 Before and after removal of spider veins using sclerotherapy in MedicCity
2 Before and after removal of spider veins using sclerotherapy in MedicCity
3 Before and after removal of spider veins using sclerotherapy in MedicCity
4 Before and after removal of spider veins using sclerotherapy in MedicCity
5 Before and after removal of spider veins using sclerotherapy in MedicCity
Complications of diabetic foot
DFS disease is characterized by impaired blood supply and metabolism of foot tissues, which is a serious threat to the rapid healing of wounds. Often the resulting microtraumas go unnoticed, because do not cause inconvenience or pain. Calluses, abrasions, wounds from foreign objects caught in shoes or caused by nail treatment do not heal for a long time. A long-term non-healing affected area is an excellent breeding ground for bacteria, infections and fungi. Complications of diabetic foot can be extremely sad - there is a possible risk of developing trophic ulcers, the formation of gangrene and further loss of limb. According to statistics, this happens in 20% of cases of SDS.
Main complications of DS
: skin and bone necrosis, deformation of bones and joints, ulcers, gangrene.
Infections
Any abrasions take a very long time to heal, and there is a high risk of infection.
It is unacceptable to ignore doctor's appointments! At an early stage, you need to contact a podiatrist.
Foot deformity
Damage to the nerves of the lower extremities leads to a decrease in motor activity of the muscles and their atrophy. Muscle tone becomes weak, which affects the musculoskeletal system of the limbs - the fulcrum points change, the correct distribution of weight is disrupted; Such disorders lead to the development of flat feet and changes in the ankle joint. The patient experiences changes in gait – lameness appears.
A serious complication associated with foot deformity is Charcot arthropathy.
Charcot's foot is a rare, rapidly developing, severe complication of diabetes, which is associated with the destruction of the soft tissues of the feet and joints; there is deformation of the shape of the foot and the formation of trophic ulcers in places of high pressure on the foot; full support on the leg is impossible.
Ulcers
In 20% of people suffering from diabetes, a complication such as trophic ulcers occurs, and ordinary wear and tear from shoes can cause its development. Often, it is long-term non-healing wounds that become the reason for visiting a doctor and further diagnosing diabetes mellitus.
Ulcers are mainly the result of self-medication!
It is very important to start treatment on time, because... the wound does not heal on its own, spreads deeper, and necrosis begins.
Independent and timely diagnosis of ulcers is difficult, because Symptoms do not appear until infection occurs - until swelling, unpleasant odor, irritation and itching appear.
Gangrene
Gangrene is necrosis of the tissues of a living organism. Tissue cells die and the skin turns black. To stop the spread of infection throughout the body and to save lives, a limb is amputated.
According to statistics, within five years after amputation, amputation of the second limb is performed in 50% of cases.
In rare cases and in the first stages of the disease, the only way to save a leg is to restore blood circulation in the extremities.
For people with diabetes, regardless of the stage and form of the disease, self-monitoring and strict care are extremely important! Constant monitoring of blood glucose levels, thorough daily examination and foot care will reduce the risk of dangerous complications by half!