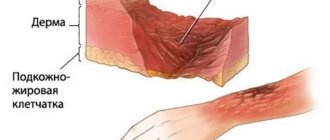
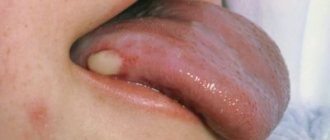
A tongue burn is an injury that damages the mucous membrane, and in some cases even muscle tissue. This problem brings a lot of discomfort - from pain and the inability to eat or drink liquids to death. It is very important to urgently contact a specialist who, after studying the cause of the burn, will prescribe treatment. If you neglect the help of a qualified dentist, serious complications can occur, including necrotic decomposition of soft tissues and infection of the entire body.
Types of tongue burns
Depending on the cause of origin, the following types of injury are distinguished:
- Chemical burn of the tongue or oral cavity - when tissues are damaged as a result of exposure to aggressive chemical compounds;
- Thermal - when the surface was exposed to a high temperature object.
- Electrical - occurs as a result of tissue contact with electricity. For example, when performing dental procedures. Electric current affects not only the tissues of the tongue, but the entire body as a whole.
Causes of burns and methods of preventing them
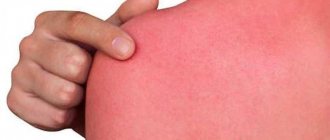
The most common cause of burns is contact of oral tissues with liquids or high-temperature steam. The oral mucosa turns red, swelling appears, and then the upper layer peels off. Electrical burns occur due to incorrect electrophoresis. The size of the lesion will correspond to the size of the electrode.
Chemical burns most often occur in children when trying to test household chemicals, but burns sometimes occur in the dental chair. This can occur upon contact with silver nitrate, solutions for cleaning the dental canal, etc. In case of a chemical burn, the severity of the condition depends on the chemical composition of the substance that has entered the mouth and the strength of its concentration. Ionizing radiation is used in radiation therapy and can also cause burns to the mouth and larynx.
It must be said that the method of preventing burns is basic caution. Drinks or food that are too hot should not reach the table. Steam inhalations for children under 14 years of age are extremely dangerous and do not have any therapeutic effect. As for chemical burns in children, household chemicals must be carefully isolated and have warning labels. Do not pour chemical solutions into other containers, especially drinking bottles.
Symptoms of a tongue burn
Symptoms depend on the extent of soft tissue damage:
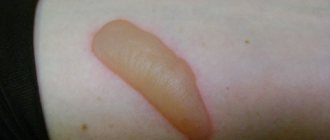
First degree - a burn occurs due to short-term exposure to high temperature tissue. The patient experiences slight redness and swelling of the mucous membrane. Often, a burn condition is provoked by consuming too hot food or liquid.
Second degree – swelling of the mucous membrane, redness, and multiple blisters on the surface are observed.
Third degree - accompanied by tissue death, large blisters, redness of the surface, the organ itself seems to “change its consistency.” As a rule, it occurs due to exposure to gases, liquids at elevated temperatures, or chemical compounds.
The fourth degree is a severe lesion when the tissues are charred. This burn condition is rarely compatible with life.
Clinic
The clinical picture is dominated by the following symptoms: pain (retrosternal or epigastric), difficulty breathing, drooling, dysphagia, refusal to take fluids, vomiting. The clinical picture does not always predict the degree of damage to the esophagus. One study examining the correlation between the severity of esophagitis and the presence of three symptoms: nausea, drooling and difficulty breathing found that in the absence of all three symptoms, as well as in the presence of only one of them, there was no significant damage to the esophagus, whereas a combination of two symptoms has always been associated with severe damage.
How to properly treat a tongue burn?
Treatment methods depend on the type of thermal injury.
What to do in case of a thermal burn of the tongue?
- rinse your mouth with cool water;
- apply ice or a cold object to the damaged area;
- treat the burn site with a disinfectant solution;
- rinse with a disinfectant to prevent bacteria from entering the oral cavity;
- use local anesthetic compounds;
- while the tongue is recovering, eat liquids, fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins C and B. Avoid spicy, pickled foods, foods that can have a mechanical effect on tissue (nuts, crackers, seeds, etc.).
- rinse the mouth thoroughly;
- neutralize aggressive chemicals. Depending on the source of the burn, a specific neutralizer is used;
- After neutralization, the burning sensation should go away. For pain relief, it is worth using anesthetics and antihistamines;
- if the mucous membrane is severely burned, with damage to the structure of the tongue and muscle tissue, it is necessary to urgently go for an examination to a doctor.
If there are bubbles on the surface of the tongue, you should urgently seek help from a dentist! Under no circumstances should you open blisters yourself! You may need hospital treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
How to treat a chemical burn of the tongue?
Note! If the oral cavity is burned with an alkaline solution, it cannot be rinsed with water, since moisture promotes more active penetration into the soft tissues of the tongue.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component oral skewers ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component skewers - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Consumer Reviews
Natasha (vseotzyvy.ru)
“Mouth rinse Vertex JSC Asepta mouth rinse is sold in pharmacies, that’s why I bought it, it has more medicinal properties than just a cosmetic product, and indeed this rinse perfectly removes bad breath, disinfects gums, menthol gives freshness for almost a day perfectly helps smokers."
Dilya09 (otzovik.com)
“Hello to all readers of my review! I wanted to tell you my story about how I started using the Asepta oral brush.
It all started with the fact that I had an implant installed instead of an extracted tooth and was given strict instructions to rinse my mouth with chlogrexidine and, preferably, an oral scavenger. At the pharmacy, my choice fell on the Asepta drug, despite the price, because after the implantation procedure I had the feeling that now I would brush my teeth after every meal and rinse my mouth (it was just creepy). The price of this skimmer in pharmacies is above 160 rubles.
It doesn’t taste very nasty like some skimmers; after rinsing, it freshens your breath due to the “Lime” and “Mint” flavors. By the way, I don’t use it regularly anymore, I often forget to rinse my mouth, but, nevertheless, it is always present in the bathroom.
Of course, over the years, the memories of implantation have become dull, much has been forgotten, but Asepta and I are now friends. I take not only the skimmer, but also toothpaste. In general, not only is the skipper good, but the whole series is good. I recommend it to everyone who uses oral skewers.”
How exactly to neutralize a chemical burn in the mouth?
Carbolic acid is well neutralized by glycerol.
Baking soda and water neutralize acidic compounds.
If alkali gets into your mouth, rinse the cavity with citric acid diluted in water.
If exposed to aggressive household chemicals, the mouth should be rinsed with cool running water.
It is important! Tongue burns take a long time to heal. Unfortunately, these tissues cannot be made motionless for a certain time; the tongue is constantly in motion. On average, it can take several weeks for the tongue to recover from injury.
Alkalis
Unfortunately, alkalis are tasteless and practically odorless, which makes their accidental use more likely. Burns of the oral cavity are typical for the use of alkali, but their absence in no way indicates the absence of damage to the esophagus; in 25% of cases, in children with no pathology in the oral cavity, severe damage to the esophagus was observed after consuming alkalis. The stomach is affected in 20-25% of cases. When exposed to alkali on the esophageal mucosa, liquefaction necrosis occurs, quickly spreading to the underlying layers until the alkali is neutralized by tissue fluid. Accordingly, the higher the alkali concentration, the deeper the damage it causes, even to the point of perforation. There are three stages of the effect of alkali on the esophagus: the stage of liquefaction necrosis, the stage of repair and the stage of scarring. Reparation begins on day 5-6 and can last up to 2-3 or more weeks. During this phase, the scab is rejected, granulation tissue appears, and re-epithelialization occurs. Massive deposition of collagen in the third phase leads to the formation of scar strictures.
Treatment of a burn to the oral cavity in a child
According to statistics, a large percentage of patients who turn to a doctor for help as a result of a burn to the mouth or tongue are children. Young patients up to a year and older can unknowingly “taste” household chemicals or alcoholic drinks accidentally left on the table by their parents. Also common causes of burns are eating too hot food.
The mucous membrane of a child’s tongue is more delicate and thin, and therefore requires more delicate handling in case of a burn. For treatment, you must urgently contact a pediatric dentist.
Classification
We use the following classification of caustic injuries of the esophagus:
- 0 - no damage
- 1 - erythema and swelling
- 2 - ulceration is not circular
- 3 - circular ulceration
- 4 - perforation
There are also more detailed classifications:
- 1st degree - erythema and edema (damage is limited to the superficial layers of the mucosa, their rejection with subsequent epithelization without scar formation is possible).
- 2a degree - vulnerability, hemorrhages, erosions, exudate, blistering (mucosal, submucosal and muscular layers are involved).
- 2b degree - the same as 2a plus deep or circular ulcers.
- Grade 3a - deep ulcers, “gray or black esophagus” (transmural lesion).
- Grade 3 - extensive necrosis.
Related articles:
- Articles: ENDODIAGNOSTICS FOR ESOPHAGUS BURNS WITH ALKALI
- Articles: FEDERAL CLINICAL GUIDELINES “Toxic effect of corrosive substances”, “Toxic effect of soaps and detergents” 2014
- Articles: Zargar classification - assessment of damage to the esophagus when swallowing caustic (caustic) substances
CLASSIFICATIONS section
When to perform endoscopic examination?
Initial endoscopic examination should be performed within the first 2-3 days after injury. Contraindications to it are: shock, respiratory disorders, perforation, mediastinitis.
In the period from 5 days to 3 weeks, during the repair stage, the wall of the esophagus is thinnest and the risk of perforation during endoscopy is very high, therefore, it is highly undesirable to perform it at this time. After three weeks, dense fibrous tissue usually forms and endoscopy becomes safer. In addition to endoscopic examination, radiography of the chest and abdominal cavity, clinical blood test, urea, and liver tests are indicated.
Treatment and prognosis
The prognosis is largely determined by the amount of damage. Thus, two independent studies carried out in the 70s of the last century showed that with 0-1 degrees of damage, the probability of stricture formation is 0, with 2 degrees it reaches 17-23%, and with 3 degrees - 100%. More recent data also suggest that acute mortality and the rate of stricture formation in stages 1-2a are minimal, burns 2b-3a lead to strictures in 70-100% of cases, and grade 3b is associated with a mortality rate of 65%. The pH of the product also plays an important role; if it is more than 12.5 or less than 2.0, the likelihood of severe damage is very high.
Treatment of caustic lesions of the esophagus is difficult; they are easier to prevent than to treat. First of all, it is necessary to establish the type of caustic agent. At the pre-hospital stage, treatment should be aimed at maintaining vital functions. Previously recommended attempts to neutralize the caustic agent with weak acids (in the case of alkalis) and weak alkalis (in the case of acids) are now considered harmful because increased heat generation from the chemical reaction can further damage the tissue. In addition, the experiment proved that a 3.8% alkali solution affects the mucous and submucosal layer within 10 seconds after administration (a higher concentration of alkali over approximately the same period of time damages the muscle layer), which makes neutralization attempts pointless. The only exception is the use of 200-250 ml of water or milk within 30 minutes of consuming alkali granules, but even then the risk of vomiting must be taken into account. Attempts to “dilute” the acid with water are contraindicated because lead to increased heat generation as a result of a chemical reaction. Emetics are also contraindicated because lead to repeated exposure of the agent to the esophageal mucosa. You can allow the patient to rinse his mouth with water (spitting it out).
It is extremely important to start eating as quickly as possible. Patients with grade 1-2a lesions begin to be fed within the first 24 hours (of course, the food should not be coarse, hot or cold). In patients with more severe damage, observation for 48 hours is necessary to rule out perforation, then feeding can be started cautiously. If the esophagus is damaged at grade 2b-3 during endoscopy, it is reasonable to leave a nasogastric tube for enteral nutrition (but no more than 2 weeks). The same probe can be useful for passing a string to bougienage the resulting strictures of the esophagus. To reduce chest pain (in patients who can take liquids), you can use liquid agents containing anesthetics, for example Almagel A. Despite the fact that there are studies showing a decrease in the formation of post-burn strictures of the esophagus with the use of hormones, they are currently not widely used due to with the risk of developing infectious complications. If hormones are used, their doses vary from 1 to 2 mg/kg per day, and treatment should begin no later than 48 (and preferably 24 hours) after the burn, with gradual withdrawal of the drug over 2 months. Antibiotic therapy with broad-spectrum drugs when using hormones is mandatory. After dilatation of strictures, the use of steroids is justified, as it leads to a decrease in the number of their relapses. Sometimes recommended antisecretory therapy with proton pump blockers and H2 blockers is of questionable effectiveness. We will not dwell on the surgical treatment of this pathology.