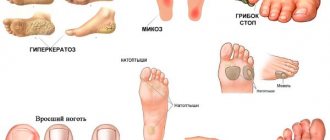
A callus is a formation on the skin of the toes, which is a growth of keratinized epithelium. This type of callus has a rounded outline and is characterized by the formation of a core that grows into the deep layers of the skin. A deep callus causes pain and causes a lot of inconvenience: it interferes with wearing the desired shoes, is subject to friction and is simply in the way.
Medical diagnosis of callus
Core-type calluses are fairly easy to diagnose.
After an in-person consultation, a dermatologist can provide a conclusion and diagnosis about the type of skin growth.
The only difficulty may be differentiating an ingrown callus from Verruca plantaris (plantar wart).
Because they have the same location and appearance.
You can distinguish a callus from a wart by the following features:
- An ingrown callus is not accompanied by bleeding even with strong pressure on it.
- A wart, unlike a callus, is not a single formation. Typically, upon examination, several warts that resemble cauliflower can be identified.
- The callus in its central zone has a small depression, which can be seen upon detailed examination. In the case of a wart, the HPV formation consists of thin fibers; petechiae (black dots) are observed on top, which bleed when injured.
- If a wart is present, pain occurs when the lesion itself is palpated; there is no pain when walking. In the case of calluses, pain is observed with any mechanical movement.
To confirm the diagnosis and determine the cause of the disease, the dermatologist prescribes a blood test for diabetes mellitus.
Also an analysis to determine the human papillomavirus, to exclude HPV.
Additionally, the doctor can redirect the patient to other specialized specialists.
See a podiatrist (a doctor who treats foot pathologies), a rheumatologist or an orthopedist.
An important point is to exclude Morton's neuroma.
Morton's neuroma is a benign or non-cancerous growth of fibrous tissue.
Develops in the area of the tibial nerve, most often between the third and fourth fingers.
The pathology is accompanied by thickening of the plantar nerve, pain when walking, and a feeling of numbness in the fingers.
The disease is also known as Morton's metatarsalgia, plantar neuroma, and intermetatasal neuroma.
Calluses: Common Risk Factors
The immediate cause of calluses is mechanical friction to which the skin is exposed.
However, some people develop hyperkeratosis and others do not.
The reason for this is external and internal factors that affect the risk of calluses.
Common factors include:
- age
- floor
- body mass
With age, the risk of hyperkeratosis increases.
In men, the peak incidence is 50-60 years, and in women – 60-70 years.
This is due to age-related skin changes.
They are as follows:
- dehydration of the epidermis
- reduction in the thickness of subcutaneous fat
- epithelial cells become flatter
- other dermatological diseases are added that make the skin more vulnerable to mechanical stress
As you age, your skin becomes tougher.
It is less elastic and not as resistant to stretching.
The most statistically significant correlation between the risk of callus formation and age is observed in diabetics.
It is also known that with age, the feet become flattened.
The height of the longitudinal arch decreases.
This changes the pressure that the body weight puts on different parts of the feet.
Gender influences the risk of developing calluses.
Statistics show that women with foot hyperkeratosis seek medical help higher than men.
The reasons for this phenomenon are not known.
Women have higher skin elasticity.
It would seem that the frequency of callus formation in them should be lower.
Some researchers have linked the higher incidence of hyperkeratosis in females to shoe preferences.
Men primarily choose convenience over design.
While women often wear uncomfortable shoes that rub their skin, just to look more attractive.
Diabetes mellitus affects the appearance of calluses in both men and women.
The risk of their formation increases.
In addition, diabetics are characterized by peculiarities in the localization of calluses.
They usually appear on the dorsum of the little toe or the plantar surface of the first (“big”) toe.
Another common risk factor for calluses is a person's body weight.
It has been reliably determined that the higher it is, the more often hyperkeratosis is formed.
Moreover, its main localization is the heel region.
It is the back of the foot that experiences increased stress in obesity.
To a lesser extent, it increases in the midfoot.
The fingers don't suffer at all.
Therefore, the frequency of callus formation here is the same as in people with normal weight.
Methods for treating and removing ingrown calluses
The only and effective method of eliminating this problem on the legs is to remove the stratum corneum of the callus and its root.
In this case, it is important to completely remove not only the surface of the callus, but also the root.
Otherwise, the risk of relapse reaches 100%.
There are various methods for removing calluses; the optimal treatment option is selected individually.
Depending on the clinical signs, the neglect of the case and how deep the root has penetrated into the layers of the dermis.
External risk factors for callus formation
Some external factors influence the likelihood of calluses.
These primarily include:
- physical activity
- shoes
- foot support
The influence of the level of physical activity on the risk of hyperkeratosis formation is beyond doubt.
Athletes develop calluses much more often than the average population.
Including more often than in older people with low levels of physical activity.
The reasons for this are obvious: when playing sports, a person often puts stress on his legs.
The result of friction on the skin of the feet is calluses.
In older patients, research shows there is a direct correlation between the risk of developing dry calluses on the feet and the amount of time they spend on their feet.
Certain types of physical activity lead to the appearance of calluses on certain parts of the body.
In runners, they often form in the area of the metatarsal head.
These areas of hyperkeratosis can be quite painful.
They are difficult to treat.
Calluses always recur with continued physical training.
Shoes are another factor that contributes to the appearance of calluses on the feet.
The discrepancy between the shape of the shoe and the foot leads to increased mechanical pressure on the skin.
To avoid the formation of hyperkeratosis, shoes should have a wide toe box.
Typically, tight shoes cause calluses on your toes.
But shoes that are too wide can also harm your feet.
In this case, calluses may be found in the heel area, as well as along the edge of the foot.
Wearing high-heeled shoes is also considered harmful.
This is one of the reasons for the formation of calluses in women.
The risk of their occurrence increases with a heel size of 2.5 cm or more.
In this case, calluses appear mainly in old age.
In youth, the risk of their formation is much lower.
Removing callus using drilling
This procedure can be carried out in a pedicure salon.
During the manipulation, a special device resembling a drill is used.
The procedure does not require the use of anesthesia.
Since it is not accompanied by pain.
Drilling/excision of callus areas is carried out using special attachments.
An antibacterial ointment is first placed in the deepening of the callus to prevent the development of the inflammatory process.
For the first few days, the patient may feel minor discomfort, which goes away on its own and does not require treatment.
Dry callus is removed using a similar method, but provided that it is not neglected.
The drilling procedure has certain disadvantages:
- If the rod is located deep enough, this manipulation may be ineffective. Often several manipulations are required to completely remove the callus.
- In the process of drilling out the keratinized area of the dermis, damage to healthy skin is possible. The procedure requires a highly qualified specialist.
- This type of callus removal is a contact type of procedure, which means it is accompanied by an increased risk of infection.
How to use the “Salipod” medicinal patch
To carry out the procedure for treating calluses with Salipod, you need to wash and dry your feet well, stick a special patch , and attach a regular patch on top of it. The patches should be removed only after the third day of treatment. After three days have elapsed, “Salipod” needs to be removed, the feet should be steamed, and the core of the callus should be removed.
If the disease is advanced, the treatment will have to be repeated. In most cases, after removing the rod, a small hole will remain in the skin; it must be disinfected with iodine and covered with a regular plaster. During the treatment of a growth in which there is a rod, it is recommended to use orthopedic shoe insoles to reduce pain and relieve pressure on the sole of the foot.
Removal of callus with liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction)
Cryodestruction is an innovative, highly effective method of removing calluses on the foot, heel or toes using liquid nitrogen.
During the procedure, the keratinized area of the skin is frozen, after which the destruction of the callus is observed.
It has been noted that the procedure is associated with an extremely low rate of callus re-development.
Many dermatologists note that no other method for removing core calluses gives results as favorable as cryodestruction.
Removing callus with liquid nitrogen takes about 10-20 minutes.
It is performed under local anesthesia, so the procedure is completely painless and safe.
Side effects are extremely rare (no more than 3% of cases).
Include callus recurrence, pain, discomfort, bleeding, infection, scarring.
The first few days after the procedure, the formation of a cold bubble is observed, which under no circumstances should be pierced.
Within 10-14 days, the healing process occurs; a crust forms in place of the bubble, which falls off on its own.
The process is not accompanied by the formation of scars.
The procedure is usually well tolerated, with minor discomfort possible.
Some disadvantages of cryotherapy:
- If the rod is extremely deep, cryodestruction is not always able to completely rid the patient of the callus.
- If you do not properly care for the skin after the procedure, there is a risk of an infectious process.
- Freezing the callus with liquid nitrogen is not used when large areas of the epidermis are affected. Cryodestruction used on large calluses can lead to a number of complications. For this reason, in advanced cases, they resort to other therapeutic methods.
Application of callus plasters
Heel calluses, both dry and wet, respond well to treatment using special callus plasters.
Such products are developed on the basis of advanced hydrocolloid technology. These patches are sometimes compared to a second skin, as they fit tightly to the heels, relieve pain, protect against infection and speed up the healing process. That is, they do not just cover corns, blisters and burst calluses on the feet, but treat them.
You can also buy callus patches with salicylic acid in pharmacies. Such products are considered quite effective, although they are more aimed at disinfecting the problem area and softening it, rather than healing the skin.
Callus patches with salicylic acid
Application of the patch:
- The feet are steamed in a soap and soda bath, then wiped dry.
- Apply the patch for a day, then remove it and replace it with a new one.
The course of treatment is 3-4 days until the desired effect is achieved.
Laser excision of callus
Laser callus removal remains a priority treatment method.
Allows you to effectively eliminate the problem with minimal risk of recurrence.
The laser penetrates into the deep layers of the dermis, which makes it possible to remove the root completely, rather than partially.
The operation of the device is based on the reproduction of a laser beam with special light properties:
- Monochromatic: Has only one specific wavelength or color.
- Coherence: Vibrates in the same phase or synchronously.
- Divergence: the beam works in a given direction.
During the manipulation, the epidermal layer is “burned out”, one after another.
The manipulation requires the use of an anesthetic.
The average session duration is no more than 10-15 minutes.
Before using the laser, the callus is treated with antiseptic drugs.
After laser irradiation, a dense crust forms, which will disappear after 10-14 days.
Laser treatment to remove calluses leads to cell regeneration.
It has an anti-inflammatory effect and stimulates the local immune system.
Thus, it promotes rapid healing of wounds.
However, the main advantage of the laser is the complete removal of callus even with a deep root location.
Often, one visit to a dermatologist is enough to effectively eliminate the problem.
Radio wave removal of callus
Callus removal by radio wave is carried out using a special device “Surgitron”.
The Surgitron device uses advanced radio wave technology.
Ensures accuracy, versatility and safety of medical procedures.
The surgical electrode, which is a tungsten wire, emits 3.8 MHz radio waves and slides through the tissue without putting pressure on it.
The pathologically changed area is evaporated, which leads to the destruction of the callus.
An important advantage is that the electrode is self-sterilizing during use, which reduces the likelihood of infection after the procedure.
Other benefits of radio wave treatment:
- Excellent cosmetic results; the manipulation is not accompanied by the formation of scar tissue.
- Fast recovery for the patient, since the treatment process does not affect the healthy tissue surrounding the callus.
- Reduced postoperative pain; in addition, the manipulation itself is not accompanied by pain.
After radio wave removal, the callus becomes covered with a crust, which falls off on its own after 7-10 days.
After which a new, healthy layer of new skin appears, which over time blends with the natural color of the epidermis.
Treatment of callus with medications
It is immediately worth noting that drug treatment of calluses has the least therapeutic effectiveness.
This phenomenon is associated with the inability of drugs to penetrate deep into tissues, eliminating the root of the formation.
The products used for core calluses often contain keratolytic components and can be effective at the beginning of callus development.
As a rule, products based on salicylic acid are used.
Salicylic acid is a keratoplastic and keratolytic agent.
In addition, it has an antibacterial and antifungal effect.
Salicylic acid works by softening keratin, a natural protein that is part of the skin's structure and produced by the body.
The drug has a softening effect on the stratum corneum of the dermis, which facilitates its removal.
Salicylic acid is often used in combination with other substances.
Allows for a higher therapeutic effect.
When using salicylic acid preparations, the simultaneous use of the following drugs is not recommended:
- Alcohol-containing medications.
- Any other local medications that contain dibenzoyl peroxide or retinoid.
- Soapy substances that have a drying effect.
- Cosmetics that have an exfoliating effect.
Remedies for foot calluses
There are medicinal ways to combat calluses.
Keratolytics are used for this purpose.
This is a group of drugs that dissolve the protein keratin.
It forms the basis of the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
At home, you can use urea preparations (for example, Uroderm) for this purpose.
They are produced in the form of ointments with a concentration of active substance of 25-30%.
In general, the drug is safe.
There are only some restrictions to its use.
Do not apply urea to large areas of skin if you have kidney or liver failure.
Avoid contact of the drug with mucous membranes.
Urea does not remove calluses on the ball of the foot, but only softens it.
After this, you need to remove the stratum corneum of the epidermis using pumice or a brush.
If sufficient softening does not occur after applying the ointment, it is necessary to apply it for a longer time under the patch.
The drug usually has no side effects.
Although some patients may experience itching and redness at the application site.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of calluses
Folk remedies cannot affect the development of callus and are not an effective treatment method.
The treatment and removal of callus must be carried out by a qualified specialist.
This will minimize negative consequences and complications.
It is necessary to begin treatment of callus in the early stages of its development.
When there is still a chance to get rid of the problem without resorting to surgical methods.
As it progresses, the root of the callus will penetrate into the deeper layers of the epidermis.
Then it may be necessary to use more radical and expensive methods of therapy.
Callus on a child's foot
If your child has a callus on his foot, the first thing you need to do is find out why it happened.
The pathological factor must be eliminated.
For example, if a child wears uncomfortable shoes, they need to be changed to something else.
After this, a small area of hyperkeratosis may disappear on its own.
If this does not happen, you need to remove the callus on your foot by consulting a doctor.
You should not “poison” a child with folk remedies.
In most cases they are ineffective.
But they can bring suffering to the baby or cause allergies.
You cannot cut the callus yourself.
You may injure the child.
In turn, trauma often becomes the cause of infectious complications.