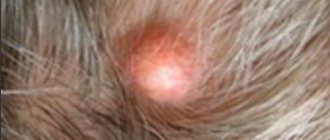
A food allergy is an adverse reaction of the immune system to proteins in food.
In general, around the world, about 2.5% of the world's population suffers from food allergies; this figure varies in different countries, ranging from 1 to 10%. According to the World Allergy Organization (WAO), as well as the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology (EAACI), there is a current increase in the incidence of food allergies and a steady increase in this disease is predicted in the coming years.
The EAACI white paper (2018) states that by 2050, more than 4 billion people will suffer from allergic diseases worldwide.
Price
Allergology-immunology
| Name of service | Price |
| Consultation with an allergist-immunologist, primary | 3 500 ₽ |
Advantages
- The latest, constantly updated equipment
- Interest-free installments for all services
- Online consultations with an ENT doctor
- Visit of an ENT doctor to your home
- Friendly and qualified staff
- 24/7 ENT assistance
A food allergy is an abnormal reaction of the immune system that occurs shortly after eating a certain food. Even small amounts of an allergic food can cause signs of a food allergy, such as digestive problems, swelling and skin marks. In some people, food allergies can cause serious symptoms or even a life-threatening reaction called angioedema (swelling of the airways) - also known as Quincke's edema.
You should not tolerate a condition that can significantly reduce your quality of life. Contact a professional allergist who will determine the source of your food allergy and give competent clinical recommendations.
Prevention of disease in children and adults
For many years, it has been recommended to avoid introducing highly allergenic foods into complementary foods. However, recent studies show that early complementary feeding and a varied diet in infancy reduces the risk of developing food allergies.
If a food allergy causes an anaphylactic reaction, to prevent fatal consequences you should:
- give up foods that cause allergies;
- avoid cross-allergens;
- carry an epinephrine pen with you (consult your doctor);
- Carry a bracelet or note with information about allergies.
Life with food allergies can be colorful. Compliance with recommendations for the prevention of exacerbations and basic therapy help achieve tolerability of the products.
Symptoms of food allergies
Manifestations of food allergies usually develop within a few minutes to two hours after consuming the trigger food. In more rare cases – up to several days.
The most common symptoms of food allergies include:
- discomfort in the oral cavity;
- skin form of food allergy: redness, rashes in the form of small blisters, itching;
- swelling of the lips, face, tongue and throat (mostly) or other parts of the body (less often);
- difficulty swallowing;
- wheezing or shortness of breath;
- nasal congestion or difficulty breathing;
- abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting;
- dizziness, feeling unwell;
- sneezing or itchy eyes (allergic conjunctivitis).
A few words about our smaller brothers
It turns out that animals also suffer from food allergens. For example, food allergies in cats occur regardless of gender, breed and age. The main signs are itchy skin, hair loss, scratching on the skin.
Most often, food allergies in cats occur to soy, gluten, seafood, beef, dairy products, and lamb.
In its manifestations, food allergies in purebred dogs are no different from food allergies in dogs – “ mongrels”:
- itching, pimples on the scalp, abdomen, paws;
- discharge from the eyes, nose, ears.
But let's go back to the representatives of the species Homo Sapiens, or, more simply, to people.
Angioedema - or how food allergies manifest themselves in the worst way?
Acute food allergies can cause a serious allergic reaction called angioedema. Prompt treatment is critical for this condition. Without treatment, angioedema can cause asphyxia, coma, or even death.
Life-threatening signs of a food allergy:
- tongue swelling;
- a feeling of a lump in the throat that makes it difficult to breathe;
- problems swallowing or speaking;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure;
- rapid pulse;
- dizziness, lightheadedness, or loss of consciousness
With such symptoms, you should urgently call an ambulance.
Treatment of pathology
There is no cure for food allergies. Modern methods of immunotherapy help reduce the aggressive reaction of the immune system to the allergen. To do this, there are three main ways to introduce minimal doses of the allergen into the body:
1. Oral – “the allergen is eaten”;
2. Sublingual – “allergen under the tongue”;
3. Epicutaneous - a patch with an allergen is applied to the skin.
The dose of the allergen is gradually increased until the reaction to the food product disappears completely.
Food allergies in children
Childhood food allergies affect 6 to 8% of children under 3 years of age. Often, food allergies in children go away without treatment as they grow older, but you should not wait for this to happen and neglect medical help. Food allergies in a child can affect his growth and development, so in any case you should consult a doctor.
A food allergy in a newborn may manifest itself not as rashes on the body, but as excessive and inconsolable crying, even if the child is fed and does not need to change diapers. This occurs due to colic in the abdomen.
The following foods most often cause an allergic reaction in children:
- eggs;
- milk (if a baby has a food allergy to any type of milk, as well as to baby food and formulas that include milk, it is imperative to include other foods containing calcium in his diet);
- soy;
- wheat;
- peanut.
Complications
The most severe complication from strong food allergens is anaphylactic shock. It develops due to hypersensitivity to certain foods or ignoring the first signs for a long time. The entry of an allergen into the human body leads to increased symptoms and further development of shock. The authors Pampura and Khavkin come to the conclusion that “in some patients, anaphylaxis appears only if physical activity is preceded by the consumption of a certain product” (Pampura A.N., Khavkin A.I., 2003, p. 1126).
If the allergy is manifested by vomiting and diarrhea, then prolonged contact with the allergen leads to electrolyte disturbances. They, in turn, often require correction in a hospital setting and also threaten human life and health.
Other complications include the addition of a bacterial infection when scratching the skin, the formation of cross-allergy to pollen or household dust.
Types and causes of food allergies
Food allergies occur because the immune system perceives harmless substances in certain foods as harmful.
In the most common type of food allergy, an antibody known as immunoglobulin E (IgE) mistakenly targets a specific protein found in food as a threat. Immunoglobulin is involved in the release of a number of chemicals that form an allergic reaction, the most serious of which is histamine. It causes most of the typical symptoms of an allergic reaction. For example, histamine:
- causes small blood vessels to dilate, causing food allergies in the skin (the skin becomes red and swollen);
- increases the amount of mucus produced by the nasal mucosa, which causes sneezing, itching and burning.
There is another type of food allergy known as non-IgE-mediated food allergy. It is more difficult to diagnose because there is no test that can accurately confirm it. This type of food allergy also manifests itself on the body and causes problems with the digestive system (heartburn, diarrhea, nausea). In infants, non-IgE-mediated food allergies can also cause diarrhea and reflux, when stomach acid leaks into the throat.
Food allergies in adults are most often caused by the following foods:
- nuts – walnuts, almonds, peanuts, pistachios;
- fish;
- seafood - shellfish, crabs, lobsters and shrimp;
- celery;
- Gluten is an allergy to food protein found in grains;
- mustard;
- fruits and vegetables - usually food allergies in adults to them occur only on the skin around the mouth;
- meat – some people are allergic to only one type of meat, others are allergic to different types; the main manifestation is food allergy on the face;
- alcohol;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - aspirin or ibuprofen.
"Sugar is not an allergen." Pediatrician - about food allergies, hay fever and atopic dermatitis
Is diathesis from sweets really a myth? Are there allergies to the weather? Is it even possible to outgrow this condition? These and other questions from parents are answered by pediatrician, allergist-immunologist, professor of the Department of Pediatrics and Children's Infectious Diseases at Sechenov University Daniil Munblit.
An allergy is a non-standard reaction to something very standard and common. To put it in a very exaggerated way, an allergy is always a reaction to protein. Our body does not react to an apple as an “apple” - it reacts to the specific protein that makes up this or that product.
Everything we eat and breathe consists of various proteins, that is, proteins. When we eat eggs, we get proteins that are part of the egg. These are the conditional “bricks” from which the egg is built. The same thing, for example, with pollen - an allergic reaction appears to its proteins.
We don't know why people with allergies develop allergic reactions to foods that others eat without any consequences. An allergy can occur to any product or substance that contains proteins, and during the life of any person.
How is an allergy different from a food intolerance?
It's a question of mechanism. The most traditional and classic type of food intolerance is lactase deficiency, when a person is unable to break down lactose, that is, milk sugar. Lactase, in turn, is an enzyme that allows lactose to be broken down. If there is not enough lactase in the body, manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract appear.
An allergic reaction is a response from our immune system. A person eats, for example, an egg, which contains protein, to which he has a classic allergic reaction of the immediate type. The human immune system, his “Ministry of Defense,” sees that the enemy has arrived. We have antigen presenting cells - they act as butlers. The system encounters an allergen, butler cells report: “The allergen has arrived!” And the body reacts immediately, because it is interested in instantly getting rid of the allergen protein. This immediate type reaction develops within seconds and minutes, less often - a couple of hours.
The most common symptoms of an allergic reaction:
- Edema
- Hives
- Itching
- Bronchoobstruction (narrowing of the airways)
- Cough
- Vomit
- Acute reactions from the gastrointestinal tract
Can allergies be outgrown?
Yes, children do often “outgrow” allergies to certain foods. This primarily applies to eggs and milk. In most cases, the allergy ends by the beginning of puberty, maximum by the time you enter university. Unfortunately, there are also foods to which people “outgrow” allergies much less often - these are, for example, nuts and peanuts. In 80-85% of cases, this allergy remains for the rest of life.
One of the signals that a child will “outgrow” an allergy is a different reaction to heat-labile and heat-stable proteins of the same product. The first ones are destroyed during heat treatment, the others are preserved. If a person reacts to a heat-labile protein, then he will neutrally tolerate the product after heat treatment.
Let’s say a child tolerates baked goods that contain an egg, and if he simply eats it, he gets an allergic reaction. This is a very good sign, which indicates that in the future this allergic person will be able to tolerate eggs in a less thermally processed form.
Can allergies arise from frequent consumption of the same foods? For example, if you eat eggs all week?
I can't really imagine such a situation. It happens that a person calmly eats a certain product all his life, and then one day he discovers an allergic reaction to it. But such an allergy will not go away instantly - once it appears, it will be with the person for a long time, and if we are talking about the occurrence of food allergies in an adult, then most likely until the end of life.
In adulthood, allergies to eggs or milk are extremely rare. Most often, adults are allergic to seafood, shrimp, nuts, and peanuts. But a situation where a person has allergies for a week and not for a week is impossible.
Are there allergies to the weather?
A reaction to the weather itself cannot be an allergic reaction. But there are natural phenomena that can contribute to the development of an allergic reaction, for example, thunderstorm asthma. People suffering from respiratory allergic diseases may experience its consequences when walking in a park or forest after a thunderstorm.
Natural conditions cause pollen clumps to absorb moisture and shrink, or when bombarded by heavy raindrops, they explode and become finely dispersed. This makes them easier to penetrate into the respiratory tract.
Also, after rain, mold actively grows, so people who are allergic to mold fungi (that is, the proteins that make up their composition) react and are forced to cope with the consequences of a weather phenomenon that is harmless to others.
What can be a food allergen?
Anything can be an allergen. Among the “children’s” allergens, the most common are: milk, egg, wheat, soy, peanuts, nuts, fish, seafood and, in recent years, kiwi and seeds. The prevalence of allergies to certain foods also varies somewhat depending on sociocultural characteristics and diet in different regions.
In Asia there is an exotic dish - bird's nest soup. They take birds' nests, boil them and eat them. In those Asian countries where this dish is common, there are people allergic to this soup.
What influences the development of allergies?
If the child's parents, mother or father, have allergic diseases, the risk of developing allergic diseases in the child increases sharply.
There is also the so-called “hygienic” hypothesis. She says that previously people encountered bacteria and viruses much more often, lived in direct contact with domestic animals, in very different conditions with an insufficient level of hygiene. Now in developed countries, on the contrary, it is popular to fight various infections - people treat everything around with antibacterial wipes and teach children to do this. Because of this, contact with bacteria and viruses is minimized, the load on the immune system is reduced - and allergic diseases appear more often.
Is it possible to be allergic to sugar?
There is no such thing as a sugar allergy because sugar is a carbohydrate, not a protein. Additionally, sugar has no effect on how the body responds to proteins.
The impossibility of an allergy to sugar does not mean that sweets cannot cause allergies at all. The reaction may appear to proteins of other products that are part of the dessert.
In addition, the child may develop what in Russia is usually called a pseudo-allergic reaction to dyes and preservatives that are included in the products. It can manifest itself in the form of itching and skin rashes.
Let's take jelly bears, which children love - they contain many dyes, which can cause a pseudo-allergic reaction. Of course, it is uncomfortable for the child, but it has nothing to do with allergies and does not lead to severe anaphylactic reactions that are life-threatening.
How to distinguish atopic dermatitis from food allergies?
The manifestations of various non-allergic reactions are often associated with allergies, but in fact they are only sometimes associated with it. For example, atopic dermatitis and food allergies are often equated. But in reality these are different diseases. I often hear the phrase from mothers: “It pours on everything.” If your child is rashing on everything, the rash is most likely not related to a food allergy.
Exacerbations of atopic dermatitis can occur from stress, temperature changes, hard water, and contact with certain types of synthetics or wool. There can be many reasons, so it is important to consult with a specialist rather than take tests yourself. Otherwise, you can simply waste money or, even worse, find diseases that the child does not have.
Atopic dermatitis remains - you need to look at the dynamics of each individual patient. However, if atopic dermatitis sharply worsens after eating specific foods, you should think about the possibility of a food allergy and consult a doctor. Often a child needs to be tested for food allergies when it comes to severe, intractable atopic dermatitis in young children. Other signs of a food allergy may include delays in physical development, especially if the child regularly experiences severe gastrointestinal symptoms.
How to deal with food allergies?
The most effective way is to eliminate the allergen from the diet. If you do not come into contact with the product, then there will be no reaction. You need to understand that you don’t need to exclude everything. If we are talking about an allergy to egg whites, you need to exclude eggs. But there is no need for a global diet.
And, of course, there is no need to remove red or orange foods, which parents very often do.
It must be remembered that the reaction does not occur to the product or its color, but to a specific protein that is part of the product
Sometimes a person can independently understand whether he has an allergic reaction by detecting hives and difficulty breathing after taking a certain product. But people tend to exaggerate: many find they have allergies that they actually don’t have. Allergic diseases should always be diagnosed by a doctor.
In addition, simply removing the product from your diet will not be enough. If we are talking about a milk allergy, a person will need to eliminate milk, fermented milk products, and the milk of other animals - in 90% of cases, a person with an allergy to cow's milk will be allergic to the milk of many other animals (for example, goat). The diet is also prescribed by an allergist. And if several foods are excluded at once, it is worth consulting with a nutritionist on how to properly build a diet taking into account the exclusion of several foods.
Call to all parents: |
| You should not make allergy treatment decisions on your own. Don't hesitate to contact specialists. This is not a question of conformity to the norm, but a question of help and support. Do not self-medicate - it leads to even greater problems, as we often see. In my practice, there was a child with bronchial asthma who received treatment with “inhalers” and everything was fine. But since the active ingredient in the inhaler was a hormonal drug, my mother, like many parents, was very frightened. At some point, she decided to treat her son with homeopathy. A week and a half later, he found himself in serious condition in the hospital in a state of suffocation, where they tried to pull him out of this state. Since then, my mother no longer went to homeopaths. So why start and put the child’s life at risk? |
How does allergies affect your life?
In the spring, allergic rhinitis worsens in children with allergies as a result of a reaction to flowering. They constantly sniffle and sniffle, sometimes becoming the target of bullying because of this. This affects the general physical and psychological condition of the child.
Allergic rhinitis - hay fever during the dusty season - makes it difficult for children to concentrate on anything other than allergy symptoms, which are poorly controlled by medications.
In the worst case scenario, the presence of an allergy can lead to the development of anaphylaxis, which can also develop in children with food allergies. It can be fatal, but fortunately this is extremely rare.
Just during the period of exacerbation of allergies, teenagers take exams for admission to university, not only in Russia, but also, for example, in the UK. There was a study that showed that children with symptoms of allergic rhinitis or children taking first-generation antihistamines, which cause drowsiness, performed worse on exams. As a result, the proposal to allocate a separate exam window for children with this disease was seriously discussed.
What determines the severity of an allergic reaction?
Predicting the severity of an allergic reaction is extremely difficult. The human immune system reacts not only to a specific protein, but also to a combination of different factors when consuming this protein.
The level of protein load that is part of the product also depends on the amount of allergen consumed. The difference between 2ml of milk and 200ml is huge - and the amount can affect the likelihood and severity of a reaction.
You also need to take into account the context of the situation. For example, an allergy sufferer drank milk before exercising. Active physical activity can cause a severe allergic reaction, including the development of anaphylaxis.
An example from the practice of a London professor I know: a teenage girl with a peanut allergy who was well aware of her reaction. She did everything right - she checked the ingredients, watched what she bought and consumed. One day, in a familiar candy bar, where there shouldn't be peanuts, there were peanuts. The girl spat out the piece, but already felt swelling developing. She forgot the syringe pen with adrenaline, which could have helped her in this situation, at home. She got scared and decided to run home to get a pen. The distance was about a 10 minute walk. As a result, she fell and died before reaching a few meters.
It is likely that if she had simply walked calmly or stayed where she was and called an ambulance, she would not have developed the anaphylactic reaction that ultimately killed her. Unfortunately, the combination of allergen consumption and physical activity resulted in death. This happens extremely rarely, but it happens nonetheless.
In reality, an anaphylactic reaction is rarely fatal. We cannot always say exactly why in some cases the attack ends in death and in others not. And, although this is due to the mentioned factors in the course of the reaction, it is not possible to predict its course, and therefore we simply advise you to avoid foods to which the patient is food allergic.
How to help an allergy sufferer
Of course, the provision of assistance depends on the age of the child. If we are talking about a small child, then parents should help him first of all. They should also be sure to notify school teachers and parents of friends in whose home the child may spend time about the risk of developing an anaphylactic reaction. To relieve symptoms from the respiratory system, bronchodilators are usually used, which is quite logical: during an attack, the lumen of the bronchi decreases, and it becomes difficult for the child to breathe. The same thing can happen with anaphylaxis.
In the West, many children suffering from allergic diseases always have a pen with adrenaline with them. Parents and medical staff of the educational institution where the child studies have the same ones. In Russia, syringe pens, unfortunately, are not registered, so you cannot buy them in a pharmacy. But you can order it on the Internet - at customs, most likely, a parcel with injectors will not be turned around, it is not a narcotic drug.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to find an adequate analogue of a syringe pen. The whole point of such a device is that a person can quickly inject adrenaline into his muscle. Someone carries an ampoule with adrenaline and a syringe separately, but the fact is that the person himself will not be able to quickly inject himself with this substance.
A study was conducted in which nurses, intensive care unit nurses, doctors and patients were asked to inject themselves with a certain dose of adrenaline under normal, non-stressful conditions. The only ones who coped more or less well were the intensive care nurses. And we were talking about normal, not stressful conditions.
When we talk about the fact that a person will administer adrenaline to himself without preparation and in a stressful situation, there is always a risk of administering the wrong dose of the drug. Especially if it's a child. However, people sometimes carry ampoules and syringes with them - this is better than nothing.
A home first aid kit for a child with allergies should include:
- Second generation antihistamines (eg, loratadine or cetirizine). They, unlike the first drugs, do not cause drowsiness.
- Bronchodilators (eg, Ventolin or salbutamol). If the child has asthma or has had cases of bronchial obstruction due to the consumption of certain foods. Such drugs expand the lumen of the bronchi, which narrows during an allergic reaction.
- Syringe pens with adrenaline. If a child is at high risk of anaphylaxis or has had a history of anaphylaxis, it is important to have a pen syringe not only in your home medicine cabinet, but also for both the child and the parent at all times.
If we send a child with friends and relatives for a walk or on a trip, we need to take medications from the home medicine cabinet with us. By the way, it’s more difficult with relatives here. Many mothers and fathers complain to me that grandparents do not believe in the child’s allergies: “Oh, you made it up!” But this goes away after they witness an acute allergic reaction.
The most interesting thing is that often other children, friends of a child with allergies, take his illness more seriously than adults
Although strangers may even offend the child because of his allergies, close friends understand what is at stake, worry, and learn to use a pen.
At the same time, their parents may be more frivolous. Therefore, it is important, when sending a child on a trip with other adults, to explain to them the principle of action of medications and the need for their use, and to explain what needs to be done in case of an unexpected reaction.
How to distinguish ARVI from allergies and prescribe treatment?
The symptoms of acute respiratory viral infections and allergies sometimes actually coincide, but they can be distinguished by the presence of temperature and the duration of the disease. Speaking very roughly, ARVI is an acute condition that is accompanied by a rise in temperature, but goes away after a week. Allergic diseases have been a concern for a long time. But to know for sure that the child does not have ARVI, but an allergic reaction, you need to go to the doctor. And it is the doctor who must tell whether we are talking about an allergic disease and prescribe the correct treatment.
A child is not allowed to go to school with an inhaler. What to do?
Unfortunately, if a child is not allowed to go to school with an inhaler, it is easier to change schools. In the West, many countries have “nut-free” schools: you are not allowed to bring nuts, they are not used anywhere, and they are not in the kitchen. There are also schools that do not allow you to bring latex products, for example there are no balloons there.
We have practically no such analogues, but the situation is gradually changing. Previously, parents of allergy sufferers reacted negatively: “What kind of nonsense are you talking about? Your child is just like everyone else.” This is now a rare response to warnings of possible allergic reactions, especially in private schools.
If we are talking about a secondary school where you are not allowed to carry an inhaler and from which you don’t want to leave, you need to get a doctor’s report about bronchial asthma and contact the school nurse with a request to store the inhaler. But this is generally an unlikely situation. The school, on the contrary, is interested in the child having an inhaler and being able to help himself.
What to do if a child begins to choke?
If the child begins to choke, you need to urgently call an ambulance. Speaking of emergency measures, it is worth immediately using a bronchodilator drug if we are talking about a child with bronchial asthma, or we know that he has a food allergy and accidentally ate an allergen.
It is difficult not to see that it is becoming difficult for a person to breathe. Shortness of breath occurs, wheezing can be heard, and the person often takes a forced position. In young children the reaction may be more noticeable. Their body turns on additional mechanisms to inhale as much air as possible, and additional muscles are used. You can see the retraction of the intercostal spaces, or supraclavicular fossae. This is called “recession of the pectoral compliance.”
Can allergy sufferers really benefit from a special conditioner?
Air conditioners with HEPA filters, which have a good degree of filtration of small particles, can make the life of an allergy sufferer easier to a certain extent. This is more relevant for children with allergies to house dust mites and pollen. In such situations, various devices with a HEPA filter - humidifiers, air conditioners - are relevant. However, they are often not enough to achieve control over the allergic disease.
Will moving help overcome allergies?
A person with allergies may benefit from traveling to another country during the flowering season. It helps people with allergic rhinitis. But for people with food allergies, moving will not help, since it always stays with them.
Can food allergies be cured? (Maybe)
Today, children suffering from food allergies can try to get rid of the disease not only by eliminating the product from the diet (in fact, in this case, the allergy remains but does not manifest itself), but also by special therapy.
Oral immunotherapy (also called desensitization and allergen-specific immunotherapy) is initiated only in a clinical setting and consists of giving a person a certain dose of the allergen daily. Gradually, his immune system learns to perceive it normally. The effectiveness of this therapy in patients with food allergies is still the subject of debate, but it is already being actively implemented in university clinics in the USA, Spain, Great Britain, Germany and other countries. In Russia, oral immunotherapy is currently unavailable.
There may be many explanations as to why this method is not so well developed in Russia. One possible reason, in my opinion, may be poor regulation of the judicial system in relation to doctors. Although Russian patients, like those in the West, sign a document stating that they are aware of the potential consequences, the doctor can still face criminal prosecution if the patient ends up in intensive care or dies.
As a result, doctors are afraid to even give a drug that is indicated for the patient, but is not prescribed in the recommendation documents, let alone a treatment method that could potentially lead to anaphylaxis. Perhaps this is why new treatment methods are introduced with great difficulty and fear.
A child wants to have a pet, but he is allergic. Is there a way out?
A pet allergy is truly an allergic reaction of the immune system that classically manifests itself as swelling, hives, itching, congestion, or nasal discharge. The reaction occurs to proteins found in animal hair, dander, urine or saliva.
One treatment option is allergen-specific immunotherapy, for example, for a cat or dog allergen.
In world practice, such immunotherapy is done either subcutaneously or sublingually. If carried out for 3-5 years, allergies to pet hair will significantly decrease.
In Russia, cat or dog allergens are not registered, so such treatment cannot be carried out in the country, and some parents take their children abroad to initiate it there, and then continue to take sublingual therapy upon returning to their homeland.
Another option currently being explored is vaccinating cats to reduce levels of a protein that people are most allergic to. There is also work to vaccinate people. Now such a remedy for relieving allergies to cats is being developed at Sechenov University.
Finally, there are cat foods that reduce the production of one of the proteins that many people are allergic to. But people react to different proteins and to different levels, so to prove the effectiveness of feeds, we need to collect an evidence base and do more high-quality research so that specific recommendations can be made.
Photo: Shutterstock/MiMaLeFi
Link to publication: mel.fm
Diagnosis of food allergies
The main method of identifying the cause of food allergies is keeping a food diary for several weeks, which allows you to identify the causative factor and significantly narrow the range of suspicious foods. Food allergy tests are always just an additional tool and are not a basis for excluding a product from the diet.
Testing for food allergies can vary depending on the type:
- if symptoms develop quickly (IgE-mediated food allergy), a skin test and blood test will be performed;
- if symptoms develop more slowly (non-IgE-mediated food allergy), a diet that excludes certain foods will be prescribed to identify the allergen.
During a food allergy skin test, drops of standardized food extracts are applied to the skin. The skin is then pierced with a small lancet, which allows the allergen to come into contact with immune system cells. Itching, redness and swelling indicate a positive reaction.
A food allergy blood test measures the amount of allergic antibodies in the blood.
The food allergy diet eliminates foods that are believed to cause the allergic reaction. Typically restrictions are imposed for 2-6 weeks. These products are then reintroduced. If symptoms disappear without trigger foods but return when they are reintroduced, this indicates a food allergy or intolerance to those foods.
Do not attempt a food elimination diet on your own without discussing it with a qualified allergist.
What about the children?
Food allergies in a child are a serious problem. Therefore, the main task of parents is to quickly identify the product that causes the allergy and exclude it from the baby’s diet. Food allergies in infants, like food allergies in children 2 years of age and older, are manifested by various rashes: nodules, blisters, pink or red spots. The allergy is located on the face, neck, skin of the extensor surfaces of the joints, torso, buttocks, and itchy skin. The baby eats poorly, sleeps poorly, becomes capricious and restless.
By the way, the statement that a child may be allergic to mother’s milk is nothing more than a myth! Most likely, the baby’s body reacts to allergens that enter the mother’s milk along with food: perhaps the mother ate an egg, fish, chocolate or peanuts the day before...
Various congenital diseases associated with metabolic disorders, for example, phenylketonuria, can also disguise themselves as symptoms of food allergies in children. With such diseases, the body is not able to absorb certain substances - proteins, carbohydrates, etc. The diagnosis can be made through a series of biochemical and genetic studies.
Treatment of food allergies
Therapy for food allergies consists of two components: elimination therapy (excluding causative foods from the diet) and drug therapy for manifestations of the disease.
There are 2 main types of medications that are prescribed to relieve the symptoms of an allergic reaction:
- Antihistamines – used to treat mild to moderate allergies. They work by blocking the production of histamine, which is responsible for initiating an allergic reaction. Avoid drinking alcohol after taking antihistamines as it may cause drowsiness.
- Corticosteroids are stronger drugs. They inhibit the production of substances that promote inflammation, reduce capillary permeability, which eliminates swelling.
When asked how to treat severe food allergies (anaphylaxis), the answer is adrenaline. Adrenaline constricts blood vessels and opens the airways to ease breathing difficulties. This procedure should only be performed by qualified healthcare professionals.
Food allergies: recommendations to avoid
The most effective prevention of food allergies is to eliminate foods that act as allergens from the diet.
It is important to always check the ingredient list on all pre-packaged foods and drinks. Pay attention to “may contain” labels, such as “may contain traces of peanuts.”
Be careful with products labeled as vegan. There is no official definition of veganism, which means that products under such brands are not always completely free of animal substances. If you have food allergies to milk, eggs, fish, crustaceans or shellfish, carefully read the ingredient lists of vegan products. Pay attention to "may contain" warning labels.
The Ear, Nose and Throat Clinic in Moscow treats food allergies in adults and children. You can also get tested for food allergies with us.
Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help maintain your health.
Don't delay treatment, call right now. We work around the clock. tel. (24 hours a day)
The most common allergens
Products that most often cause food allergies:
- eggs;
- nuts (hazelnuts, almonds, peanuts, etc.);
- fish;
- citrus fruits (oranges, tangerines, etc.);
- berries (strawberries, wild strawberries, etc.);
- chocolate;
- milk;
- legumes (soybeans, beans, peas, etc.).
- nutritional supplements.
Allergens found in some foods may be similar to pollen allergens. This is called cross allergy. For example, wormwood pollen is a cross-allergen for peppers, carrots, mustard, bananas, and citrus fruits. This means that a patient with hay fever may also have food allergies.