Botox: contraindications to the procedure
Botox injections are a popular cosmetic procedure designed to cleanse facial skin of facial wrinkles. The Botox injection procedure can only be performed in medical institutions that have the appropriate license. Before administering botulinum toxin, it is necessary to ensure that the patient has no relative (temporary) or absolute contraindications.
Relative contraindications
At the first visit to a cosmetologist, the patient should tell the doctor in detail about previous diseases and operations, about individual reactions to cosmetic procedures, as well as about all medications, sports nutrition and nutritional supplements that she takes. Taking certain medications is a relative contraindication for Botox injections. These include:
- Tetracycline antibiotics, sulfonamides, macrolides, other antibacterial drugs.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that affect the blood coagulation system (ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid).
- Direct (heparin) and indirect (warfarin) anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents.
If you are taking any of the medications listed above, Botox injections are possible only after you have completely stopped it. Moreover, at least two weeks should pass between the course of antibacterial therapy and “beauty injections”. If you are taking substances that affect blood clotting, botulinum therapy is carried out after normalization of hemostasis indicators, which are assessed by laboratory tests (prothrombin index, coagulogram).
Some components of dietary supplements may affect the effectiveness of the anti-aging procedure. Women who take any dietary supplements should inform their cosmetologist about this.
A relative contraindication to the procedure is the presence of signs of an inflammatory process on the facial skin: redness, rashes, swelling. Exacerbation of herpes labialis is another common temporary limitation to the administration of botulinum toxin. Injection rejuvenation is possible only after complete restoration of the skin. Patients with a history of herpetic infection, but without manifestations of viral activity, are prescribed preventive antiviral therapy before the session.
A cold, flu or acute infectious disease is also a temporary limitation to Botox therapy. It is not advisable to do Botox injections during a seasonal exacerbation of allergic rhinitis. It is also not recommended to get Botox injections at the beginning of your menstrual cycle.
Absolute contraindications
Any injection and hardware cosmetology procedures are contraindicated for patients with cancer, regardless of the location of the tumor process. Severe somatic diseases in the acute stage, that is, diseases of the hepatobiliary, respiratory, urinary or digestive systems, are also a contraindication to cosmetic procedures. During the period of remission, anti-aging injections are possible after consultation with a specialist and laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
Bleeding disorders are another absolute contraindication to Botox therapy. The cause of disruption of the hemostatic system can be either a hereditary pathology (for example, hemophilia) or an iatrogenic disorder caused by taking medications. Such drugs are often prescribed to patients with cardiovascular diseases and chronic venous insufficiency of the lower extremities (varicose veins). If the disorder is acquired, rejuvenation with botulinum neurotoxin injections is possible after restoration of normal blood clotting parameters.
In a small percentage of patients, Botox administration leads to the development of an allergic-type response. If there is a history of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, it is necessary to choose a different method of dealing with cosmetic defects.
Botulinum therapy is not carried out during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Facial rejuvenation is possible only after the end of the lactation period. Feeding a baby with breast milk is a contraindication to all cosmetic procedures.
Since botulinum toxin acts on nerve endings and blocks the transmission of impulses from the central nervous system to muscle fibers, Botox therapy is contraindicated in patients with myasthenia gravis. Another absolute contraindication is severe myopia.
Contraindications are also decompensation of endocrine system disease, chronic liver or kidney failure, chronic heart failure.
What is contraindicated after injections
Botulinum toxin acts locally, that is, only in the area where Botox is directly administered. It does not have a systemic effect on the body, but migration of the active component (the toxin itself) into nearby tissues is possible. Migration over short distances does not lead to side effects, but allows for a more uniform smoothing of wrinkles. Excessive migration can lead to the development of complications:
- Dry eyes or watery eyes (when correcting glabellar lines or wrinkles in the corners of the eyes).
- Impaired binocular vision.
- Lowering of the eyebrows (when smoothing out forehead and eyebrow wrinkles).
- Ptosis of the upper eyelid.
- Facial asymmetry.
- Dysphagia (impaired swallowing when Botox is injected into the skin of the lower third of the face).
The cause of side effects after Botox injections is most often the low level of qualifications of the specialist. If you entrust facial rejuvenation to a cosmetologist with extensive (at least two years) injection experience, you don’t have to worry about complications. To completely eliminate the risk of undesirable consequences and increase the aesthetic effect of anti-aging injections, follow the following recommendations during the recovery period (7-10 days):
- Take a break from sports.
- Avoid thermal procedures, including hot baths and saunas.
- You can't massage your face. It is advisable to limit the use of decorative cosmetics.
- Do not expose your skin to ultraviolet light. After Botox injections, both solarium and sunbathing are contraindicated.
- Alcoholic drinks are strictly prohibited.
The first days after Botox injections, facial muscles need to be provided with facial rest. You cannot “make faces” or express emotions through facial expressions. For the first two to three days after rejuvenating the frontal area (forehead) and eyebrow area, you should not blow-dry your head, since warm air increases blood circulation, which increases the degree of migration of botulism toxin. It is advisable not to bend over, as increased blood flow to the skin of the face is fraught with the same consequences.
The next group of prohibitions and restrictions is related to medicines and dietary supplements. After Botox injections, you should not take medications that affect the hemostatic system. These include anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents and almost all substances with anti-inflammatory activity from the non-steroidal group: ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid, diclofenac and others.
Antibiotics should not be taken either before or after anti-wrinkle injections. Be sure to review your nutritional supplements: take a break from taking fish oil, omega-3, omega-3-6-9, multivitamin complexes containing B vitamins and vitamin E for 1-2 weeks.
Following the recommendations for the recovery period after injections will help to obtain optimal results. You will receive detailed information about the botulinum therapy method during a consultation with a medical cosmetologist (Moscow).
The influence of antibiotics on the effect of Botox use
Antibiotics do not act directly on botulinum toxin. They do not destroy it and do not affect its pharmacokinetics in tissues, even if the concentration of a particular antibacterial agent in the injected muscle is quite high.
On a note
In principle, no antibiotic can act on the botulinum toxin molecule. The fact is that the mechanism of action of antibiotics is to suppress the vital activity of bacteria that cause infections. Botulinum toxin is not a bacterium.
The problem of compatibility between antibiotics and Botox, as well as other botulinum toxin preparations, is due to the fact that some antibacterial drugs have an effect similar to that of botulinum drugs. In particular, they reduce neuromuscular conduction and lead to muscle relaxation. Already under their influence, some facial muscles, as well as the muscles of the neck, can relax, which leads to partial or complete smoothing of wrinkles.
If Botox is also injected into the target muscles at this time, the effect may be excessive: a complete blockade of the innervation of the muscle fiber will occur, which will lead to the occurrence of undesirable phenomena - disturbances in facial expressions, facial symmetry, disturbances in articulation and diction.
Another undesirable phenomenon associated with taking such antibiotics is the difficulty in adequately assessing the strength of muscle contractions when planning Botox injections. A situation is possible when the muscles are somewhat relaxed under the influence of antibiotics, as a result of which, when assessing wrinkles, the doctor decides to inject small doses, and after botulinum therapy, when the effect of the antibiotics ends, the muscles will restore full tone, wrinkles will appear and it turns out that the dose was clearly insufficient.
Under the influence of some antibiotics, the effect of Botox injections can increase uncontrollably, which in some cases leads to undesirable consequences.
The important thing here is that not all antibiotics affect the effects of Botox in the same or similar way. The weakening of neuromuscular transmission itself is a kind of side effect, which does not manifest itself in every one of these drugs. Therefore, it would be a mistake to believe that taking any antibiotics is a contraindication for botulinum therapy. Below we will find out which specific of these medications change (or can change) the effect of “beauty injections”.
Now we emphasize that a similar effect that enhances the effect of botulinum toxin can be exerted by other agents that also disrupt neuromuscular communication or otherwise affect muscle tone.
There are also drugs that, on the contrary, weaken the effect of botulinum toxin. They either potentiate muscle tone in response to receiving a nerve impulse, or themselves stimulate muscle fiber contraction. Consequently, taking them during botulinum therapy may result in the effect of the injections being either less pronounced than expected or not at all.
How Botox works
A drug based on botulinum toxin type A has been used to correct wrinkles for more than 20 years. Regular administration of Botox does not affect the state of health, nor does it affect the rejuvenation process. When injections are administered, muscle paralysis occurs in the target area. The toxin does not migrate, which makes it possible to avoid unnatural frozen facial expressions.
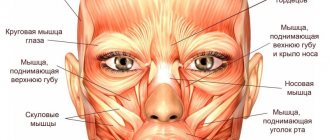
The main areas of correction are the upper part of the face - forehead, bridge of the nose, crow's feet of the eyes. Less commonly, cosmetologists use Botox to eliminate wrinkles in the mouth and nasolabial folds.
The effect of the toxin is reversible, the effect lasts from several months to a year. Injections do not improve lymph outflow or collagen synthesis; they only affect the tone of muscle fibers. The rejuvenating effect, which is noted by many patients after the end of the period of action, is associated with a change in the habit of expressing strong emotions through facial expressions.
The rate of elimination of the drug depends on the brand of botulinum toxin, the number of injections, and individual characteristics. The neuromuscular channels destroyed under the influence of the toxin during the procedure are gradually restored.
Note! To prolong the result of smooth skin, the patient’s lifestyle and compliance with all rules and recommendations are of great importance.
Drugs that reduce the effectiveness of Botox
On the other hand, there are drugs that increase spasticity of muscles, including facial muscles, even when taken orally. Due to this antagonistic effect, they can reduce the effectiveness of Botox injections until the effect of the latter is completely eliminated.
For example, botulinum toxin therapy is not advisable during concurrent or recently completed treatment of malaria with chloroquine or other 4-aminoquinoline derivatives. Side effects of these drugs include seizures and spasms of various muscles, including skeletal and facial muscles. Depending on the strength of such spastic phenomena, they can affect the adequacy of assessing the condition of the muscles before injections and provoke the doctor to inject more product than necessary.
Botulinum toxin injections into the forehead and between the eyebrows.
Likewise, taking many other types of medications can lead to muscle spasms and seizures. In particular, such phenomena have been described for some hormonal drugs, certain antiviral drugs, antidepressants and antibiotics, which are generally not contraindicated in botulinum therapy, but in individual cases can become a reason for canceling or postponing procedures.
For example, the antiherpetic drugs Acyclovir, Valtrex and Famciclovir should not be taken either immediately before or immediately after injections of Botox or its analogues. Side effects of these drugs also include muscle cramps.
Other prohibited drugs
Negative consequences may be caused by the influence of other drugs that are not antibacterial. The effect can be enhanced by medications in which the main active ingredient is derivatives of neurotoxins. These include curare-like muscle relaxants:
- Ditylin;
- Condelfin;
- Mellictin;
- Dioxonium;
- Paramion;
- Cyclobutonium;
- Anatruxonium;
- Kvalidil;
- Diplacin;
- Tubocurarine chloride.
Buyanov Sergey Yurievich (Expert Doctor):
Centrally acting muscle relaxants are used in anesthesiology and resuscitation. There are no similar products on sale. But, it is important to know that such drugs can be used when administering general anesthesia. Therefore, it is necessary to tell your doctor about Botox injections before surgery.
When planning injection rejuvenation, you should not take muscle relaxants of central and peripheral action. They relax the musculoskeletal system, relieve spasms and pain. This group includes:
- Sirdalud;
- Baklosan;
- Mydocalm;
- Pancuronium;
- Bendazole;
- Tizanidine;
- Tolperisone.
Shortly before Botox injections, you should postpone taking anxiolytics and tranquilizers. These psychotropic drugs eliminate emotional stress, suppress anxiety and fear. When combined with Botox, the body's response can be unpredictable. List of similar medicines:
- Diazepam;
- Phenazepam;
- Buspirone;
- Benactizine;
- Tetrazepam;
- Atarax.
Also avoid:
- combined sedative drugs - Corvalol, Dormiplant, Menovalen, Sedasen, Novo-passit, Sedariston.
- blood anticoagulants - Vikasol, Vitamin K1, K2.
- drugs that increase calcium levels - Calcium-D3 Nycomed, Natekal D3, Natemille, Tevabon, Calcium Magnesium Chelate.
When can you inject Botox after taking antibiotics?
For each type of antibiotic, a period is regulated after which botulinum toxin injections can be given after its use. For most drugs from the aminoglycoside, macrolide and tetracycline groups, this period is approximately 14-21 days (2-3 weeks). During this time, the substance is completely eliminated from the body, and its effect is completed, therefore, it will no longer affect the results of Botox injections.
At the same time, some antibiotics are eliminated from the body faster (within 2-3 days), others can be contained in tissues in high concentrations for several months. Therefore, it is extremely important for a cosmetologist to know what specific drug his patient took in order to set a date for the procedures.
It is also useful to read: Which is better: Botox or Dysport?
Also, when assessing the timing of possible use of botulinum toxin, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body - gender and age, body weight, sensitivity to a specific antibiotic and botulinum toxin preparation. All of them can either shorten or increase the period after which botulinum therapy can be carried out.
On a note
The instructions for botulinum toxin preparations do not clearly indicate how many days after taking antibiotics injections can be performed. The decision on the admissibility of performing procedures is made by a cosmetologist.
In any case, the patient must understand that the priority of Botox injections is always lower than the priority of antibiotic treatment. Health, and sometimes even life, depends on adequate antibiotic therapy, but practically nothing depends on whether a patient develops a wrinkle in a week or two or not.
Therefore, it is completely unjustified to rush to Botox injections without having yet completed the course of taking an antibiotic or any other drug - an antidepressant, blood anticoagulant or any other, that is, in fact, without having yet completed the treatment of a serious illness. It would be more correct to first fully recover and allow the body to regain its strength, and then plan cosmetic procedures.
Side effects
Before injecting Botox, you need to stop taking incompatible medications. If this is not done, complications of varying severity are possible:
- severe swelling, hematomas;
- bleeding;
- worsening mental disorders;
- violation of facial expressions;
- difficulty swallowing;
- problems with articulation, diction;
- lack of result;
- allergic reaction;
- anaphylactic shock;
- headache;
- muscle weakness;
- decreased performance;
- increased drowsiness;
- drooping upper eyelid;
- double vision;
- facial asymmetry;
- limitation of lip mobility.
Buyanov Sergey Yurievich (Expert Doctor):
The most common undesirable effect is a decrease or complete absence of the effect of Botox. In such cases, a second injection is not carried out until the cause that prevents the creation of artificial muscle paralysis is identified and eliminated.
Opinion of cosmetologists
Experts assure that accurate information about medications taken will help avoid complications:
What other types of medications are incompatible with botulinum toxin?
If we consider standard recommendations, simple medications are advised to be taken 14 days before/after the procedure. But, for example, paracetamol can be taken immediately after the procedure - it has an exclusively local effect. Any antipsychotics should not be taken 1 month before and 1 month after botulinum therapy. Mental disorders, depression and other unpleasant consequences may await you after taking this combination of drugs.
It is also not recommended to take any medications that contain aspirin. This can cause severe swelling and bruising. Doctors recommend abstaining from such medications and using them only as a last resort.
In addition, you should definitely ignore any alcohol tinctures, as well as alcohol in its pure form, they are also incompatible with botulinum toxin. Taking alcohol will lead to severe swelling of the face, the effect of the procedure will be invisible, but the harm to the body will be significant.
Why can’t you use this medicine before the procedure and after a while?
Antibiotics have no effect on Botox . The chemical composition inhibits the activity of bacteria. Botulinum toxin is not a bacterium, it is a toxic substance. It is injected into the muscle and inhibits the contraction of muscle fibers, which leads to their temporary paralysis. The skin and muscles stop moving, relax, and wrinkles disappear. You will find a detailed description of the effects of Botox in this article.
To achieve the desired result and not cause harm to health, it is important to correctly calculate the dosage of the drug.
The doctor can do this under an important condition: there must be no medications incompatible with the injection in the patient’s blood. Especially antibiotics.