General information
Papular rashes are one of the common reasons for visiting dermatologists.
A papule (nodule) is an element of skin rashes, morphologically representing a cavityless, dense/soft on palpation formation, rising above the skin level, having a smooth/rough surface. A papule occurs as a result of the proliferation of skin tissue or due to the accumulation of cellular infiltrate/deposition of metabolic products (mainly cholesterol). The nodule refers to the primary elements of the rash, which occurs on unchanged skin and can in some cases transform into vesicles, pustules, and also increase in size and merge into plaques, combined with other elements of the skin rash. As a rule, the size of the papule can vary from 1 mm to 3 cm (Fig. below), and the color can range from white and yellow to gray and red (with inflammation).
Papules can be single or multiple, localized on any surface of the body. Papular rash can be a manifestation of a variety of processes. For example, papules on the face/neck, eyelids, and décolleté that appear after biorevitalization are a side effect of “rejuvenation” procedures based on the subcutaneous injection of hyaluronic acid . They are formed due to the administration and accumulation of the drug in the skin and, as a rule, last no more than 2-3 days (Fig. below). The rate of their resorption is determined by factors such as the thickness of the skin, the state of the lymphatic system, and the sensitivity/moisture of the skin.
Another example of a papule is the tuberculin diagnostic process (Mantoux reaction). What is a mantoux papule? Mantoux is a diagnostic test for tuberculosis , in which tuberculin is injected intradermally and after 72 hours the result is assessed: the absence of a papule/or its size does not exceed 1 mm indicates a negative reaction: the presence of a papule (up to 4 mm in diameter is a questionable reaction; a papule size 5 -16 mm – positive reaction).
The same principle is used to evaluate the result of Diaskintest , which is a new, much more specific/effective method for diagnosing tuberculosis . Unlike the Mantoux test, which is based on the introduction of tuberculin, the solution for Diaskintest contains synthetic proteins ESAT6/CFP10 characteristic of tuberculosis pathogens.
Also, a variant of the norm in men are pearly papules on the penis (pearly papules), which, according to various sources, occur in 10-40% of males, regardless of race. The papules are smooth, transparent, pink or white, 1-2 mm in diameter, and can completely/partially surround the glans penis (see photo of pearly papules on the glans penis below).
Pearly papules are benign angiofibromatous formations that are not prone to malignancy. Papules in men persist throughout life after their appearance and become less noticeable with age. Pearlescent papules do not require treatment and are not sexually transmitted. Currently, their appearance is considered as a cosmetic defect that can be removed if desired. Removal is carried out using electrodissection, CO2 laser, cryodestruction.
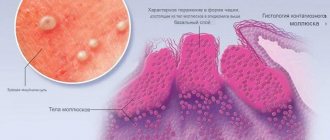
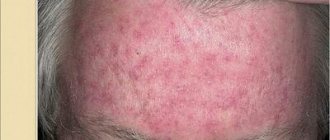
Much more often, a papular rash is one of the signs of both infectious diseases and dermatoses of viral, bacterial or parasitic etiology, and can also be a consequence of immunological reactions - allergies to medications, food, pollen, household chemicals, animal hair, house dust and etc. Rash elements in the form of papules occur in diseases such as measles , chicken pox , rubella , enterovirus infection , molluscum contagiosum and are accompanied by decreased appetite, chills, fever, pain in the abdomen/throat, indigestion, and headaches . Below we will consider diseases such as lymphomatoid and bowenoid papulosis .
Bowenoid papulosis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by HPV (human papillomavirus), manifesting as erythematous spots, papules or plaques in the anogenital area (genitals, perineum or thighs). The average age of patients is 31 years, and the high-risk group includes persons 17-40 years old, which is due to the high sexual activity of males and females during this period and promiscuity. No ethnic or gender differences were identified. The course is benign, often with spontaneous regression: Bowenoid papulosis can persist for a long period of time, however, in conditions of immunosuppression in elderly people, especially men, there is a risk of transformation into Bowen's disease / squamous cell carcinoma of the penis . Histologically, skin formations are sharply limited, exophytic tumors of the epidermis and irregular acanthotic cords are present. Atypical cells are scattered throughout the thickness of the stratified mature dermal epidermis.
Lymphomatoid papulosis
Lymphomatoid papulosis (LIP) refers to chronic primary lymphoproliferative skin diseases with histological signs of CD30+ lymphoma and a recurrent course (repeated eruptions of papular elements) that resolve spontaneously.
The incidence of LiP in the world varies between 1.2-1.9 cases/100 thousand population, occurs more often in men (1.5:1), occurs in all age categories (the age of onset of the disease is on average 35-45 years) . The course of LiP in most cases is chronic and benign, however, patients with LiP have a high risk of complications in the form of the development of secondary cutaneous/nodal lymphoproliferative diseases ( mycosis fungoides , Hodgkin's lymphoma , cutaneous large cell anaplastic lymphoma ). The frequency of development of such LiP-associated lymphomas, according to various authors, is 10-25% and can occur both simultaneously with it and after its onset, less often - precede it. There are several histological variants of LiP (types A, B, C and D), each of which is characterized by the presence of specific types of cells, but the course and prognosis do not differ.
How to treat papules and pustules
Now that we have found out what papules and pustules are, the question arises whether they need to be treated. In this case, everything depends on their number and frequency of occurrence. If they are isolated and rarely appear on the face and body, for example, due to hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle, then there is no need to worry. You can simply choose suitable care cosmetics from a cosmetologist and cleanse your face efficiently. But if there are a lot of rashes, they can merge together and form spots; papules and pustules should be treated by a dermatologist.
Treatment of acne, papules and pustules is complex.
Lifestyle adjustments and adherence to doctor's recommendations are required. A non-hormonal ointment is used as a local remedy, which does not cause withdrawal effects in the future. Before treatment, the doctor will prescribe tests for hormones, the content of certain vitamins and a general blood test. This way you can choose an individual treatment plan. June 23, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
Classification
The classification of papules is based on a number of characterological characteristics.
According to the depth of placement, they are distinguished:
- Superficial papules (epidermal). Changes are noted only in the epidermis (flat papules with a diameter of up to 5 mm - flat warts without pain).
- Deep papules (epidermal-dermal) changes are noted between the layers of the epidermis and dermis. When pressed, there is a painful sensation and dermal (changes within the dermis).
By papules size:
- miliary (1–2 mm in diameter, cone-shaped);
- lenticular (size – 5–10 mm, have a rounded flat shape);
- nummular papules (reach a size of up to 2 cm, form independently or as a result of the fusion of small papules);
- plaques (diameter more than 20 mm, formed as a result of fusion.
The nature:
- non-inflammatory papules are formed due to increased proliferation of epidermal/dermal cells.
- inflammatory papules are formed as a result of local dilation of blood vessels, as well as cells of the immune system, the immigration of which is caused by inducers of inflammation.
Causes
Bowenoid papulosis . The disease is caused by activation of HPV types 33, 31, 18 and 16, less commonly types 35,39,48,51-54. It is transmitted predominantly through sexual contact, autoinoculation is possible, and infection of a newborn from the mother is extremely rare. The incubation period varies from 2 months to many years.
Lymphomatoid papulosis . The specific cause of lymphomatoid papulosis is currently unknown. There is an assumption that LiP is a manifestation of the immune response to antigens unknown to science, which have relatively little immunogenicity. Another assumption is a viral etiology (herpes virus type 6, human T-lymphotropic virus, Epstein-Barr virus). The disease can also be provoked by prolonged exposure to allergens on the human body, which form a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction and contribute to the development of a dysregulatory effect.
Symptoms
Bowenoid papulosis
The disease manifests itself in the anogenital area of multiple papules with a diameter of about 2-3 mm of brown, red or flesh color, which in the later stages can merge into plaques. There are several types of bowenous papules: erythematous macules (pigmented papules), lichenoid (lichenoid), leukoplakia-like (milky gray/white). Visually, lichenoid papules are similar to a warty formation with an intense red-brown color. Fused papules form plaques, which stand out sharply against the background of healthy areas of the skin and have a transparent milky color.
At the same time, pigmented round papules are localized mainly on the body of the penis, less often on the pubis, and lichenoid papules are usually localized on the glans penis. Papulosis in women manifests itself predominantly as pigmented papules, and the most common localization is the clitoris and labia minora/major. With extragenital localization, round papules may appear on the pubis and penis, as well as the scrotum in men; in women they more often appear in the perineum, inguinal folds, and perianal area. From time to time, patients may complain of mild itching in the area where the papulosis elements are located, and with inflammation, pain. Below are photos of bowenoid papulosis in women.
Lymphomatoid papulosis
It is benign and has a chronic course. The disease manifests itself with asymptomatic rashes (papules) mainly on the skin with a diameter of 2 to 30 mm in quantities ranging from several pieces to several hundred. Most often, lesions are localized on the trunk/limbs, less often on the scalp and face. Elements of the rash appear in waves, tend to group, are capable of self-resolution, the development of hemorrhages, ulceration/necrosis and repeated rashes. As hyperkeratosis , scales appear.
The life cycle of rash elements is 2-8 weeks. Papules can become covered with hemorrhagic crusts, scratching is possible, and a secondary infection often occurs. Elements of the rash can involute independently at any stage. As a rule, the resolution process begins from the center of the papule and ends with the formation of an atrophic scar, which is accompanied by hyper/hypopigmentation. The patient's general condition does not suffer; in rare cases, itching and prodromal phenomena are possible.
Acne
Acne is a disease in which papules, pustules, and comedones appear on the face and body (several follicles are affected at once). The inflammation is widespread, often the pimples are painful to touch, and as soon as one goes away, others appear. If a person has only comedones - white and blackheads, then we are talking about a non-inflammatory type of acne. And if there are papules and pustules, cysts, this is an inflammatory type. Pustules on the face should not be pressed, this will only worsen the situation; the contents may not break out, but subcutaneously.
It is worth saying that papules and pustules can appear not only as part of acne, for example, papular dermatosis with sterile papules is sometimes found, that is, P. Acnes is not detected in them, but acne is still the most common cause. Papular rashes also occur with psoriasis.
Tests and diagnostics
The diagnosis of bowenoid papulosis is made on the basis of examination, patient complaints, acetotest and cytological and histological examination data. To identify the type of papillomavirus, a PRC study is performed. Differential diagnosis is carried out with syphilitic papules , lichen planus , Queyre's erythroplasia , genital warts , angiokeratomas , warts , epidermoid cysts .
The diagnosis of CD30+ LiP is established by assessing the characteristic clinical picture and immunophenotypic/histological examination of biopsies obtained from skin lesions.
Diagnosis of syphilis
Syphilis is easily diagnosed at the primary or secondary stage in the presence of rashes and papules on the surface of the skin.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a tumor biopsy or microscopy may be prescribed.
This will allow the rash to be identified.
To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory tests are prescribed - PCR and ELISA.
They will also be repeated as control tests after treatment.
List of sources
- Dermatovenerology. National leadership. Ed. Yu. K. Skripkina, Yu. S. Butova, O. L. Ivanova. – M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2011. – 1024 p.
- Chernyshov P.V. Pearly penile papules//Ukrainian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, Cosmetology. – 2011 – No. 3 (42). pp. 100-103
- Lezvinskaya E.M., Vavilov A.M. Lymphoproliferative tumors of the skin. Guide for doctors. M.: Practical medicine; 2010: 134-92.
- Olisova O.Yu., Savelyeva S.V., Sitnikova E.V., Kabaeva T.I. Modern view of lymphomatoid papulosis. Russian Journal of Skin and Venereal Diseases. 2000; 6:8-11.
- Vasiliev M.M. Modern aspects of papillomavirus infection of the urogenital tract (Clinic, diagnosis, treatment) / M.M. Vasiliev, I.I. Bogatyreva, L.K. Kotova [and others] - TsNIKVI Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation Moscow. — 2004 — 158 p.