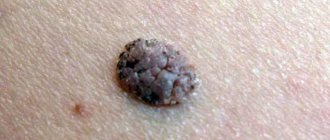
What are nevi
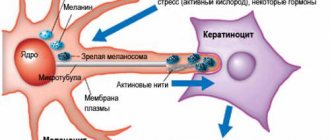
They are a formation consisting of melanocytes. The surface of the mole is smooth and dark in color. There are up to 40 such formations on the body of the average person. Some moles appear on the baby's body immediately after birth. Others are formed during growing up. Nevi can change their appearance and color. Most changes occur during adolescence during puberty. Also, degeneration in a nevus can begin when a person is exposed to direct sunlight for a long time. Ultraviolet radiation in large quantities has a negative effect on the skin. According to statistics, the more time a person spends in the sun, the more moles there are on his body.
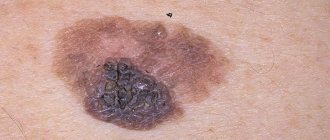
The changes concern not only color, but also appearance. An ordinary mole can become flabby and soft, or, on the contrary, develop into a dense and colorless formation. There are a large number of different types of nevi. The main danger of such formations, when exposed to certain factors, is that they can degenerate into malignant ones. Particularly dangerous are complex moles, as well as large formations. They must be constantly monitored by the attending physician in order to prevent a dangerous transformation.
Symptoms of nevi
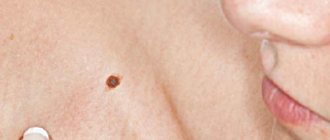
Nevi look like spots or nodules on the skin. Some of them are barely noticeable, others have a rich brown (melanocytic or pigmented) or red (vascular nevi) color.
As a rule, nevi do not cause any discomfort and are not felt.
Nevi can change their appearance and increase throughout life. It is important to correctly assess these changes; such manifestations can not only be a variant of the norm, but also serve as one of the signs of malignant skin formations.
Types of nevi
There are moles on every person's body. Most often they do not pose any danger. If the quantity exceeds 50 pieces, it is advisable to visit a doctor. Such patients are at risk for developing melanoma. Particularly alarming should be asymmetrical formations with an uneven surface, which have a non-standard color, more than 6 mm in diameter, and began to form on the body already in adulthood.
Congenital
This category includes formations with which a person is immediately born. Congenital nevi vary in shape, color and size. In some cases, the mole may occupy a large part of the child's body. Such neoplasms are cause for concern as they often degenerate into cancerous tumors.
Regular
The category of common moles consists of formations that have a symmetrical shape, uniform color and smooth surface. Most often the color is brown or pinkish. There are no foreign inclusions on the surface. Also, such moles can have a dome shape.
Atypical
Moles with non-standard size and appearance. There are few of them on the body, several times less than ordinary moles. The main danger of such neoplasms is that under certain factors they can degenerate into melanoma. Another feature of such formations is that they have an uneven color, uneven edges, and the nevus itself is asymmetrical. For people with atypical moles, it is important to control their number on the body; the more formations, the higher the risk of melanoma. Constant monitoring by the attending physician and completion of the necessary studies is required.
Blue
Neoplasms are divided into two categories: they can appear on the body already in the womb or develop during a person’s lifetime. They got their name due to their bluish color. But this category also includes nevi, the color of which varies from light gray to black. Most often, formations characteristic of the skin of Mongoloids; in other races they develop in extreme cases.
Miescher's nevi
Formations are brown or flesh-colored. The most common place for moles to appear is in the neck and face. The surface is hard, dome-shaped, but smooth, without foreign inclusions. Hair often grows on the nevus.
Nevi of Unna
In appearance they are similar to the moles from the previous description. Features include their appearance: they resemble raspberries. The color of the new growth is brown.
Meyerson's nevus
It is not difficult to determine the problem around such a mole, a rash with red papules begins to develop and spread. In some patients, eczema in the area is not registered. Another feature of Meyerson nevi predominantly develops in men over the age of 30 years. Women are much less susceptible to this problem.
Nevi halo
They got their name due to the atmospheric phenomenon of the same name. A pale whitish ring begins to appear and develop around the mole. Such education does not last until the end of life, even if nothing is done with it. First the ring changes its color to pink, and then disappears. In some cases, new haloes may appear around the tumor throughout the patient's life.
Spitz nevi
Moles are slightly raised above the skin and have a dome shape. The formation itself is pinkish in color; it is acquired and appears on the skin of patients at a young age. Color may be different. The surface of the nevus is often damaged and begins to bleed. As a result, doctors often confuse such moles with malignant ones, referring the patient for histological examination.
Reed's nevi
The color of the formations varies; they can be black or dark brown (closer to a black tint). Mostly develop in women. The peculiarity of the neoplasm is that it increases in size very quickly, which is why it causes concern among doctors. In fact, such moles are mostly harmless and rarely develop into cancer.
Agminated
They are several moles at once, which are concentrated on a small area of the skin. The peculiarity of formation is that all nevi are not the same. Some may be more, some may be less. Also, among flat formations, dome-shaped ones, etc., may appear.
Only the main types of moles are listed above. In fact, there are a huge number of such neoplasms on the skin. To determine what type of mole a particular mole on the body of a patient seeking medical help belongs to, doctors perform dermatoscopy.
Types of warty nevus
There are localized forms of nevus manifestation or systemic (verrucous).
Localized - most moles are found in this form.
Signs of its manifestation:
- The diameter of the neoplasm does not exceed 1 cm.
- elements appear separately or are located so close that they can merge
- localization zone is clearly limited
- the keratinized surface of the nevus often has cracks
- moles are dark brown or maroon in color. In very rare cases, nevi are light brown or light pink in color.
- the area affected by moles is often devoid of hair
Systemic form of the disease - the incidence of pathology is approximately 20% of cases.
A distinctive feature of a nevus is the presence of a “garland” of neoplasms.
Such elements are located at close distances relative to each other and “stretch” along the surface of the skin along the entire body.
This form of nevus has a number of features:
- the elements spread along large vessels, and they can also be in different places of the body
- The surface layer of moles may differ in shade. Elements may have different color intensities
- the length of one garland can reach up to 20 cm.
- When feeling the moles, it is noted that they have a dense structure
- the surface of each mole is lumpy and tortuous. As a person ages, these symptoms become more pronounced.
Each type of warty mole can be frequently injured.
Papillomatous nevus
There are a large number of neoplasms found on the human body. Not all of them are moles. Thus, warts, condylomas, papillomas and other formations may appear. When making a final diagnosis, the whole difficulty lies in the fact that the listed types of neoplasms are often no different in appearance from ordinary nevi. The most problematic is considered to be papillomatous nevus. In appearance, it is no different from ordinary papilloma caused by HPV. But when conducting research, it turns out that this is a bumpy mole of a convex type. The mole is benign, there is no risk of degeneration into cancer. The surface has a flesh-colored, brownish or light brown tint. Dark moles of this type are extremely rare.
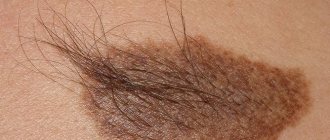
A characteristic feature of such moles is the presence of hair on the surface. They mainly appear on the head or neck; they can develop in other parts of the body, but in very extreme cases.
The appearance is not tied to a specific age period. They develop in both teenagers and old people. The mole grows over time, sometimes it increases in size so much that it begins to cause discomfort to the wearer. If the nevus is located on the head, it can be easily damaged when combing the hair. This leads to the onset of inflammatory processes that affect nearby tissues.
The nevus is harmless; its removal is generally carried out only for cosmetic purposes. The greatest discomfort for people is caused by moles on the face, which are visible to everyone around them. Before deciding to undergo a tumor excision procedure, it is important to consult a dermatologist. Only after all the studies have been carried out will the specific type of nevus be established, and the likelihood of the problem degenerating will be assessed. It is almost impossible to independently determine what exactly appears on your body.
Indications for removal may also be permanent damage to the surface of the nevus. Most often, several methods are used to combat education:
- Laser treatment of the area;
- Freezing and subsequent destruction;
- Radio wave exposure;
- Using electric current;
- Surgical intervention.
If the formation appears on the face, laser therapy is most often chosen.
Publications in the media
Nevi (moles, birthmarks) are hamartoma-like malformations of the skin that can develop both from elements of the epidermis and the dermis itself (connective tissue, vascular elements or melanocytes). Nevi are pigmented formations that usually protrude above the surface of the skin. Almost every person has moles; they can be congenital or occur throughout life, especially during puberty, in women during pregnancy, and hormonal dysfunctions. The clinical picture is characterized by extreme diversity in the number, size, morphological type and degree of pigmentation of individual elements - spots, nodules, plaques - up to subtotal damage to the skin with the so-called giant nevi. Large congenital nevi are considered to be elements >20 cm or occupying 2.5% of the body surface; they are considered a risk factor for malignancy.
• Epidermal nevi (warty or mole-like) are most often found at birth, although they can also develop in childhood (very rarely in adults). Externally they may be similar to papillomas (viral origin), but are usually represented by large linear plaques or an array of small papules. Epidermal nevi are often asymptomatic. Malignization is rare, with the exception of nevi of the sebaceous glands (basal cell carcinoma occurs in 5% of cases). Histologically they are characterized by acanthosis and hyperkeratosis. Nevus of the sebaceous glands is also characterized by the presence of a large number of sebaceous and apocrine glands. Cellular atypia is not observed. Treatment is mainly for cosmetic purposes. Preventive removal of sebaceous gland nevus is performed due to clinical manifestations (hair does not grow on it), and not the danger of malignancy.
• Dermal nevi •• Connective tissue nevi are predominantly congenital and are often represented by dense, single papules and flesh-colored plaques. The number of hair follicles in them can be significant (“pigskin”). This variant of nevi is idiopathic and is not associated with other diseases, with the exception of “shagreen skin” in tuberous sclerosis. Histologically, they consist of dense conglomerates of collagen and elastic fibers. Prognostically safe and removed solely for cosmetic reasons •• Vascular nevi (hemangiomas) are vascular formations lined with endothelium, mainly capillary, but cavernous structures can also occur, especially in large nevi. Three clinical types are considered typical: strawberry nevus, cherry nevus and cavernous hemangioma. Strawberry nevus and cavernous hemangiomas more often undergo spontaneous regression, while cherry nevus continues to grow throughout life. Surgical treatment is carried out for cosmetic reasons, for functional disorders (localized in the conjunctival area, lips) or thrombosis of the cherry nevus (due to suspicion of malignancy) •• Melanocytic nevi are of the greatest clinical importance, given the need for differential diagnosis with melanoma •• Pathohistology. Nevus cells are located in the form of nested clusters of various sizes and configurations in the dermis, subepidermally and between cell complexes. Sometimes the accumulations become diffuse and are located very close to the epidermis along the basement membrane, and atrophic changes in the epidermis are noted. The cells are large, of various shapes and sizes, with a clearly visible nucleus, sometimes several hyperchromatic nuclei, arranged in the form of “rosettes” or lumpy clusters. In some elements, the shape of the cells is spindle-shaped, which makes the nevus resemble a neurofibroma. Pigment content may vary. In “young” nevi, the stromal component is weakly expressed; over time, the connective tissue stroma begins to predominate; such a nevus is considered “fibroepithelial.” Localization of nevus cells among basal keratinocytes and in the zone of the basement membrane without its disruption is characteristic of a border nevus, and in combination with the intradermal component - of a mixed nevus.
Clinical types of nevi • Basal cell nevus - a hereditary disease (109400, 601309, BCNS gene, 9q22.3, Â) - characterized by (usually benign) skin lesions of the eyelids, nose, cheeks, neck, upper jaw, looks like a flesh-colored papule, without signs erosion, histologically does not differ from basal cell carcinoma. • Verrucous nevus is a skin-colored (or darker) lesion of the epidermis similar to a wart, often linear, appearing at birth or in early childhood; can be of different sizes and localization, single or multiple “verrucous nevus. • Hairy nevus is a mole covered with a large amount of growing hair. • Giant pigmented nevus is a large congenital, with pronounced hair growth, pigmented nevus with a predominant localization on the lower extremities “pigmented hairy nevus” .
• A blue nevus is a wide-based papule or plaque of varying shades of gray-blue color. Histologically, clusters of process melanocytes with a high pigment content are found in the dermis, located parallel to the epidermis, which determines the optical effect of blueness when incident rays of the visible spectrum “Jadassohn-Tische nevus”. • Intradermal nevus - a nevus with localization of nests of melanocytes in the dermis, and not at the border between the epidermis and dermis. • Ito nevus - pigmentation of the skin area innervated by the lateral branches of the supraclavicular nerve and the lateral cutaneous nerve of the shoulder; nevus cells lying randomly in the dermis.
• Strawberry nevus - a small vascular nevus similar in size, shape and color to strawberries - a bright red solitary formation of spongy density. It is observed in 3% of newborns and often spontaneously obliterates by 6-7 years of age. « cavernous hemangioma « cavernoma « cavernous hemangioma. • Unilateral nevus is a congenital linear nevus, which is located along the nerve either on one side of the body or on part of a limb also on one side linear nevus. • Ota nevus (oculodermal melanosis) - skin pigmentation in the area of innervation of the trigeminal nerve and conjunctiva of the eye in the form of bluish-gray spots; occurs in Asia, more often in women. The treatment is cosmetic. • Nevus dark blue orbital-maxillary .
• Borderline nevus - a nevus consisting of nests of nevus cells near the basal layer, the border of the epidermis and dermis, appears as a small, slightly raised, flat, non-hairy, pigmented (dark brown or black) tumor epidermal nevus. • Acquired nevus is a melanocytic nevus that is not detected at first after birth, but appears in childhood or in adults. • Flaming nevus ( port wine stain) is a large, vascularized nevus with a purple coloration, usually located on the head and neck. Unlike other vascular nevi, in this case there is no proliferation of a large number of vascular elements, but an expansion of the normal number of skin vessels. As the size of the vessels progresses, protrusion appears and the color of the nevus changes from pink to purple-red. See also Sturge-Weber syndrome in the appendix to this article. • Sebaceous nevus (Jadassohn) - congenital hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands with papillary acanthosis of the epidermis. • With thick curly hair, nevi are congenital foci of growth of spirally twisted hair in the scalp “limited [symmetrical] allotrichia.
• Atypical nevus syndrome (ICD-10: D22 Melanoform nevus; *155600, #155601 [mutation of the CDKN2A cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A gene, OMIM 600160.0001]) is an inherited disease (Â)) of pronounced familial nature. Prevalence: in the USA up to 5% of the general population; in the late 90s, about 40 thousand familial cases and 4.6 million sporadic forms were registered. Synonym: dysplastic melanocytic nevus •• Clinical picture. Usually spotted elements, but there are papular, plaque-like elements with a central papule or micropapules, oval or irregular in shape, sometimes with processes, 5 mm in size or more, with a finely scalloped clear outline, of varying intensity of brown color (up to black), with an erythematous rim along the periphery •• Pathohistology. There are no generally accepted criteria for diagnosing dysplastic nevus. The architecture of a dysplastic nevus suggests uneven hyperplasia of the epidermal processes with hypertrophy of the terminal sections. Melanocyte cells of adjacent processes are often connected. Among epidermal melanocytes, a spectrum of cytological changes is observed: from moderate pleomorphism to obvious atypia. The pronounced degree of the latter can be interpreted as melanoma in situ. • Red-blue vesicular nevus syndrome (*112200, Â)). Blistering hemangiomas of the skin, especially the trunk and upper extremities, night pain, regional hyperhidrosis, bleeding gastrointestinal hemangiomas, angiomatous gigantism, cerebellar medulloblastoma.
• Mucosal spongy white nevus is a congenital keratosis of the mucous membranes, manifested by a thickened white spongy fold of the oral mucosa. • Vascular nevus - congenital uneven red coloring of the skin due to the proliferation of skin capillaries “vascular nevus” hemangioma. • Spitz nevus is a benign juvenile melanoma (see below Juvenile nevus). • Elastic Levandowski nevus - clusters of smooth or bumpy papules of ivory or flesh color, found symmetrically on the trunk and limbs “collagenous nevus”.
• Juvenile nevus •• Spindle cell and/or epithelioid cell nevus (juvenile melanoma, benign juvenile melanoma, Spitz nevus) is a benign melanocytic nevus, usually acquired, having a characteristic histological structure different from other types of melanocytic nevi. Initially it was believed that it occurs mainly in children, but it has now been shown that juvenile nevus is more common (up to 60%) in adults •• Clinical picture. Usually the exophytic formation is hemispherical, less often flat; dense elastic consistency, with clear boundaries; color - from light red to dark brown, sometimes black; the surface is smooth or papillomatous •• Pathohistology. According to its architectonics, a nevus can be borderline, mixed (most often), intradermal. According to the cellular composition, it can be spindle-shaped, epithelioid cellular, and more often mixed. The pigment content in melanocytes is variable. Characteristic is the presence of eosinophilic accumulations - fragments of the basement membrane (the so-called Camino bodies). Spindle-shaped melanocytes are elongated with an elongated nucleus and a large eosinophilic nucleolus. In the epidermis, melanocytes have long cytoplasmic processes and form large elliptical nests, the long axis of which is usually perpendicular to the skin surface. In the dermis, spindle cells are often located parallel to each other in the form of bundles or cords. Polygonal or round epithelioid cells with abundant fine-grained, reticulate or vacuolated cytoplasm. Giant multinucleated cells are often found.
Treatment is indicated for dysplastic, nodular and giant pigmented nevi due to their possible malignancy • Indications for excision of any pigmented formation •• Change in color, size, shape and consistency •• Pain syndrome •• Regional lymphadenopathy • Further therapy after excisional biopsy of a healthy area skin are prescribed based on the results of histological examination and localization of the formation.
ICD-10 • D22 Melanoform nevus • I78.1 Non-tumor nevus • Q82.5 Congenital non-tumor nevus
Application. Sturge-Weber syndrome (185300) is classified as phakomatoses, characterized by a triad: congenital cutaneous angioma (flaming nevus), usually along the trigeminal nerve, often unilateral; homolateral meningeal angioma with calcification and neurological signs; angiomas of the choroid, often with secondary glaucoma; in incomplete forms, any two or more signs are possible, sometimes with angiomas of a different localization “encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis” Sturge-Weber disease “nevoid amentia.”
Intradermal nevus
A type of ordinary nevi that have a dome-shaped shape. Such moles rarely appear in childhood, but they are extremely common in the adult population. Up to ten such formations can appear on the body at the same time. Such neoplasms got their name due to the fact that they are located under the upper layer of the epidermis. Often such moles are difficult to notice; they hardly stand out above the surface of the body, and their shade is close to the surrounding tissues.
Nevus can appear in almost any area. Favorite places for neoplasms are the upper part of the arms, eyelids, neck, face, etc. The maximum size of moles is up to 1 centimeter. When they appear in childhood, nevi are practically invisible, but with age they begin to darken and often acquire a convex shape. If the mole persists, then after 70 years it will gradually begin to discolor.
There are several reasons why intradermal nevi can form on the human body:
- Hereditary factors
. If the baby’s parents have more than 50 ordinary moles on their body, then the child’s nevi will also be multiple in nature. - Exposure to sunlight
. Ultraviolet radiation negatively affects the skin, causing damage. Moles often appear in place. People with too light skin are at risk. - Decreased immunity
. Most often, nevi begin to form against the background of reduced immunity, including after taking drugs that suppress the immune system.
Even ordinary moles that have a symmetrical appearance and do not increase in size are important to constantly monitor. It is better to have a checkup with a dermatologist at least once a year, this way you will be able to identify the problem at an early stage of its occurrence. It is worth planning a visit to a specialist outside of the schedule if the mole begins to grow, changes its shape, acquires a different shade, or begins to bleed.
A dermatologist may prescribe a procedure for excision of a mole if it causes cosmetic discomfort to the wearer, if there is a risk of the neoplasm degenerating into melanoma, if the surface of the nevus is constantly damaged during the day.
Characteristic manifestations of verrucous nevus
The neoplasms rise above the skin by 2 cm, but sometimes they can be higher.
Moles look like a cluster of a large number of papilloma-like growths, which are located very close to each other and can merge into a single whole.
The surface of the new growths is slightly rough and quite dense.
The color of verrucous nevus varies from flesh-colored to dark brown.
Growths can appear on any part of the skin surface.
Both single neoplasms and large numbers can be observed, including they can be fused and have an individual shape, size and color.
Verrucous nevus is characterized by the presence of elements on one side of the body (right or left).
When located on the extremities, the localization of neoplasms is noted in the area of large vessels and nerve bundles.
Keratotic nevus grows very slowly, possibly the growth of new elements.
An increase in the size of moles is more often observed in the longitudinal direction than in the transverse direction.
The presence of moles does not cause discomfort, they do not cause pain or itching, and do not interfere with any movements.
Their presence on the body has a pronounced cosmetic disadvantage, especially if they are located on open areas of the body or on the face.
Epidermal nevus
As the name implies, this category includes moles that are formed from the upper cells of the epidermis. Mostly, neoplasms appear on the child’s body after birth; the vast majority of such nevi also appear in the first year of the baby’s life. A distinctive feature of the neoplasm is that it remains unchanged in shape and size throughout a person’s life.
Epidermal nevi are divided into several types depending on the cells that make up them. The most unpredictable are considered to be formations that include not only keratinocytes, but also sweat gland cells. The formations have a yellow-orange tint; in 25% of cases they degenerate into malignant tumors.
Treatment of warty nevus
The basis of treatment for keratotic nevus is its removal using one of the most suitable methods.
The choice of method depends on the location of the warty nevus, its shape, and size.
The specialist decides which destruction method will be most effective.
To get rid of the manifestations of skin defects, the following techniques can be used:
- use of liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy)
- application of electric current (electrocoagulation)
- removal by radio waves (radiotherapy)
- destruction with a laser beam (laser therapy)
Non-pigmented moles
Most species are characterized by a color ranging from light pink to black. There are a few exceptions to the rule. So, sometimes a nevus may not have pigment. Such moles are easy to identify; they appear as a whitish or lightish spot with unclear boundaries and an irregular shape. Moles without pigment can only appear on the body of Europeans.
Moles without pigment are characterized by a small size of up to 2 centimeters. Basically, only the cosmetic side of the issue becomes an indication for removal. If a person often sunbathes, the nevus remains light in color and, as a result, stands out on the skin and attracts attention.
Diagnosis of keratotic nevus
Only a specialist can identify the presence of a warty nevus.
Based on external data and a conversation with the patient, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis.
For a more accurate diagnosis, laboratory tests will be required.
When examining a nevus, the doctor pays attention to the presence of the following features:
- coloring of moles
- size of tumors
- Locations of birthmarks
- shape of moles
- absence or presence of hair on the surface of the neoplasm
To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory tests are performed:
- oncocytology. A scraping is taken from the surface of the nevus. The disadvantage of the technique may be a traumatic factor, which can provoke the development of complications such as infection or degeneration into melanoma. Therefore, this study is prescribed for those patients whose moles have been traumatized;
- Lumenescence microscopy technique. Its essence is to apply a special composition to the neoplasm, after which the birthmark is examined under a microscope. This research method is considered to be the safest, since the nevus is not injured during the procedure;
- conducting a computed tomogram , which allows you to examine the internal structure of moles using x-rays;
- blood tests . The blood is examined for tumor markers - specific proteins that are produced when the body is prone to cancer;
- histology . A piece of tissue is taken for examination. The resulting biomaterial is subjected to histological examination for malignancy of the nevus. This technique is informative enough to confirm the development of a malignant process.
Borderline nevus
The formations got their name due to the fact that they often develop into malignant formations. It is important to constantly monitor such moles and contact a dermatologist if any changes are detected.
Such moles are hidden under the stratum corneum of the skin; they have a uniform brown color and clear boundaries. The following factors should cause concern in the patient and provoke a visit to a dermatologist:
- the mole begins to increase in size;
- changes its color, becomes darker or lighter;
- pigment spots of various types began to appear around the adjacent area;
- the mole has become dense, standing out above the surface of the skin;
- Soreness appeared in the mole, the surface was very itchy.
How to remove a warty nevus
Removal of a verrucous nevus is carried out using one of the following methods.
Surgical excision of moles is a classic method of ridding a patient of skin tumors.
After anesthesia and antiseptic treatment of the skin and surface of the nevus, it is cut out with a scalpel.
Then the wound is treated with a disinfectant and a sterile gauze bandage is applied.
This technique has negative aspects: infection of the wound surface and the formation of a postoperative scar are possible.
Removal of a nevus using radio wave radiation - this technique has many advantages:
- the ability to control the depth of exposure to radio waves, which avoids damage to healthy tissue around the tumor
- absence of bleeding due to their coagulation
- the procedure is painless
- the procedure is carried out very quickly
- radio waves can be used on any area of the skin
- There are no negative consequences after surgery
Laser therapy is one of the most common.
The laser beam can be used for keratotic moles on the scalp, as well as in the facial area.
Benefits of using laser:
- it is impossible for infection to penetrate at the site of exposure
- Coagulation of the wound eliminates the development of bleeding
- after removing the growth, a crust remains
- the risk of scarring is minimal
Removing nevus with liquid nitrogen: the use of low temperatures allows you to remove small tumors.
The procedure is painless.
Pain appears some time after exposure to nitrogen.
A disadvantage of the technique is also the need for repeated sessions, since the technique does not allow accurately calculating the time of exposure of the pathological tissue to nitrogen.
Electrocoagulation method - high frequency currents are used for treatment.
Before removal, the doctor administers local anesthesia.
As a result of exposure to electric current, a crust forms at the site of removal, which protects the wound from infection.
What to do with huge nevi
The overwhelming majority of nevi are small formations on the skin with a diameter of several millimeters, which are practically invisible to the naked eye. Exceptions are formations that exceed 20 centimeters in diameter. They are classified as huge. The mole can cover most of the arm, leg, back, etc. Such moles can appear on the body of representatives of any race. They develop in almost 2% of the population of our planet. The main danger of large nevi is that they often degenerate into malignant ones. Formations that appear in the area of the spinal column are considered extremely unstable. Moles that continue to rapidly increase in size and also change their color should cause concern.
The most unpleasant huge nevi on the body of newborn children. As the child grows over time, it seems to parents that the mole is decreasing in size, but in fact it continues to grow, almost not keeping up with the whole body.
In 30% of cases, such nevi become melanoma. They should be under the supervision of a doctor. Rebirth can occur at absolutely any age. Removal of giant nevi is indicated. The most commonly used method is surgical excision. If the mole is located in a hard-to-reach place, the patient may be offered alternative treatment methods. Removal is also possible using laser therapy.
How are nevi treated in the Rassvet blade?
The doctor will examine the patient's skin completely to eliminate the risk of missing melanoma or other skin cancer. Suspicious formations are further studied using a device that allows you to examine the skin with 10 times magnification - a dermatoscope. The patient's chart describes nevi that require observation. The doctor will suggest surgical removal of suspicious nevi, followed by histological examination of the removed material (sent to an expert laboratory). Removal of nevi for aesthetic reasons can be performed at the request of the patient.
Recommendations of a dermatologist for patients with nevi:
- avoid excessive ultraviolet irradiation of the skin (tanning, sunbathing, solariums, ultraviolet drying of manicure and pedicure coatings); when staying outdoors for a long time, use a broad-spectrum photoprotective cream with SPF 30 or higher, clothing that covers the skin, a hat and glasses with an ultraviolet filter;
- try not to injure nevi when shaving, combing, changing clothes;
- undergo an annual preventive examination of nevi with a doctor;
- independently examine nevi according to the ABCDE rule;
- if there are a large number of nevi (50-100 or more), especially in combination with the presence of risk factors (sunburn, visits to a solarium, melanoma and skin cancer previously identified or in close relatives, the presence of atypical nevi), undergo a digital skin mapping procedure.
Author:
Kuzmina Tatyana Sergeevna dermatologist, Ph.D.
Nevi on the head
Such formations are most often removed precisely for cosmetic reasons. If a mole is located on the surface of the body, no matter what size it is, it can almost always be hidden under clothing. Nevi on the head cannot be hidden. Some patients believe that a mole emphasizes their individuality, others are sure that such a formation only spoils their beauty. As a result, patients often seek removal of even those nevi that will never become malignant.
Often, not only moles on the head are removed, but also tumors on the neck. The main danger of such moles is that they often rub against the surface of clothing and are eventually damaged, which increases the risk of degeneration. On the head, nevi also appear in the hair area. They are practically invisible to the naked eye and are often felt by the patient during hair washing and other procedures. The main danger of neoplasms is that they can be easily damaged during banal combing of hair. Nevi, which include cells of the sebaceous glands, also often appear on the scalp in the hairline area. They are characterized by the shape of a wart with no hair on the surface, as well as an irregular shape. Human papilloma viruses, as well as hereditary factors, can cause the appearance.
Most moles on the head appear at birth. The formation is examined and research is done to make a final diagnosis. In childhood, neoplasms are rarely removed, since they are not subject to degeneration during this period. It occurs most often during puberty. The removal method is selected depending on the size of the formation. If the nevus is small, you can get rid of it with laser therapy; to combat large formations, surgery will be required.
It is important to remember that at the moment there is no magic pill that could remove all dangerous moles from human skin that can become malignant. It is important to monitor the condition of nevi and pay attention to any changes.
Moles are successfully removed. It all depends on the size, qualifications of the medical specialist, as well as the location of the nevus.
Can a nevus turn into cancer?
A birthmark that forms in the upper layer of the skin poses a risk of degeneration.
Malignancy of a warty nevus can occur with repeated damage.
Please note the following changes:
- mole color change
- hair loss on a mole
- change in size towards larger tumors
- appearance of asymmetry
- presence of discharge from the nevus
- uneven edges
If at least one of the signs appears, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Treatment of nevus of Ota
A disease such as nevus of Ota does not cause physical discomfort. Nevus Ota is a cosmetic problem, due to which it is necessary to constantly use concealers, this is the only way to hide the presence of spots.
As a rule, modern dermatology does not perform surgical removal of nevus of Ota due to its specific localization and rare cases of malignancy.
Laser therapy provides the best cosmetic effect. The patient should regularly visit a dermatologist to avoid degeneration of nevus of Ota into a disease such as melanoma.
Malignant degeneration of nevus of Ota is characterized by a sharp increase in pigmentation and color change. In such situations, surgical intervention is required.
Diagnostics
Detection of nevi, as a rule, occurs accidentally during ophthalmoscopy of the fundus. For a final diagnosis, their dynamic observation with regular examinations of the fundus, including examinations with color filters, is necessary. Thus, a choroidal nevus becomes clearly visible in red light, and when examined in green light, the nevus “disappears.” At the same time, only changes in the layers of the retina, which are characteristic of a progressive nevus, remain visible. Ultrasound examination, in some cases, can sometimes reveal the protrusion of the formation. With fluorescein angiography (examination of the fundus vessels using a contrast agent - fluorescein), the presence of stationary nevi is indicated by the absence of changes in the vessels surrounding the choroid. With a progressive nevus, fluorescein angiography detects the leakage of fluorescein through the walls of the vessels adjacent to the nevus.
Why is a warty nevus dangerous?
This type of mole among other nevi is the safest.
A certain group of factors can contribute to its degeneration.
The possibility of infection due to injury to a mole can provoke the development of an inflammatory process.
If a keratotic nevus is localized on the head or in another area of increased risk of injury, they should be removed as quickly as possible after their formation.
In some cases, manifestations of a systemic warty neoplasm can serve as a sign of hydrocephalus and other lesions of the nervous system, as well as melanoma.
In this case, therapy should be carried out simultaneously by several specialists: oncologist, neurologist and dermatologist.
Preventive measures for warty nevus
Verrucous nevus can provoke the development of oncological pathology.
But with proper prevention it is possible to avoid complications.
Prevention of complications is as follows:
- eliminating the possibility of injury to neoplasms
- Seeing a doctor for excision of growths
- you need to forget forever about saunas and solariums. Even the use of sunscreen cosmetics cannot protect against the development of melanoma
- in hot weather, avoid going outside to prevent overheating of tumors
- stay indoors after 10 a.m. and before 4 p.m.
- If at least one of the signs of malignancy appears, immediately go to the doctor
- Regular visits to a specialist to monitor moles
Diagnosis - histopathological features of linear nevi
There is considerable variability in histopathological studies. The most common manifestations:
- hyperkeratosis;
- acanthosis;
- papillomatosis.
Some moles may exhibit acantholysis and dyskeratosis, resembling Darier's disease.
Sometimes you can find a picture of epidermolysis with hyperkeratosis, reminiscent of congenital bullous erythroderma ichthyosis. In these cases, mutations in the keratin 1 or 10 genes are found.
Diagnosis of nevus
Differential diagnosis
To make an accurate diagnosis, a dermatologist must conduct a series of tests, since the symptoms of linear moles are similar to those of other skin diseases.
At issue are:
- warty neurodermatitis
- characterized by lycosis and itching; - lichen planus papillary
- characterized by itching and its occurrence at a later age, determined by the presence of typical lesions of lichen planus in other places and histological examination; - lichen striata - characterized by inflammatory papular rashes and spontaneous resolution within a few months.