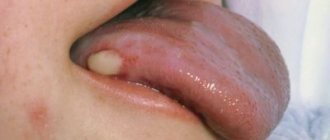
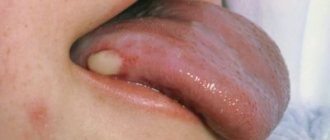
Choroidal melanoma is a malignant pigmented tumor of the choroid of the eye (choroid). This tumor is one of the most common intraocular neoplasms. Choroidal melanoma is the main cause of mortality and disability in cancer patients with damage to the organ of vision. The disease can be practically asymptomatic, but at the same time has a high tendency to metastasize, so the problem of identifying it in the initial stages is extremely relevant.
- Etiological factors
- Clinical picture
- Stages of development of choroidal melanoma
- Types of eye melanoma
- Diagnostics
- Treatment options for choroidal melanoma
- Prevention and follow-up
- Prognosis for life with choroidal melanoma
Etiological factors
Most cases of choroidal melanoma are sporadic, that is, caused by one or another mutation of the melanocytic precursor cell, which can give rise to a pathological tumor clone. In addition, there is an assumption about the hereditary cause of this disease. The influence of such a typical provoking factor for skin melanoma as increased insolation for this tumor is also not excluded.
Elderly people are at risk (the average age of tumor manifestation is 60 years). Men get sick a little more often. Those with fair skin and hair, nevi and freckles are prone to developing choroidal melanoma.
Useful video
Causes of birthmarks on the choroid of the eye. Effective treatment of this type of nevus.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2100
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 4 ratings, average: 3.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Clinical picture
Patient complaints depend on the size and location of choroidal melanoma, as well as on the presence of accompanying complications, which include: secondary retinal detachment, the appearance of degenerative processes in the retina, and clouding of the lens.
At the initial appointment with an ophthalmologist, a decrease in visual acuity, the appearance of blind spots (scotomas) in front of the eye, and hemianopsia (loss of half the visual field) are usually determined. In case of late treatment, patients complain of pain in the eye (secondary glaucoma), dilation of the vascular network. Also, a pigment spot (extraocular growth of a neoplasm) can be detected on the sclera.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Stages of development of choroidal melanoma
According to the international classification, there are 4 stages of development of this tumor. Criteria for the prevalence of the tumor process:
- T1 - melanoma size 10 mm or less, thickness - 2.5 mm or less.
- T2 - the size of the neoplasm is 10–16 mm, the greatest thickness is 2.5–10 mm.
- T3 - measuring 16 mm and/or thickness more than 10 mm without spreading beyond the eyeball.
- T4 - the largest tumor size is 16 mm and/or thickness more than 10 mm with extension beyond the eyeball.
There are also 4 clinical stages of choroidal melanoma. Each of them is characterized by certain symptoms of the disease:
- The first, so-called “quiet eye” stage, is characterized by the absence of significant clinical manifestations and complaints. Retinal clouding may be present, and visual field defects may also be detected.
- The second stage is characterized by the appearance of pain in the eyes, inflammation, redness of the eyeball, and swelling of the eyelids.
- At the third stage, choroidal melanoma extends beyond the boundaries of the eyeball, exophthalmos is formed, and the sclera loses its integrity.
- The fourth stage is accompanied by generalization of the process. The patient's general condition is deteriorating. Patients complain of severe pain, body weight decreases, and intoxication increases. Metastases of melanoma appear in internal organs: liver, lungs, bones. Damage to one or another organ provokes the appearance of corresponding symptoms. A further decrease in visual acuity, a feeling of veil or fog before the eyes may be detected. These manifestations are caused by bleeding into the vitreous body and clouding of the lens.
Symptoms of the second and third stages of choroidal melanoma are pronounced when the tumor is located in the central or paracentral part of the fundus. Peripheral localization of the tumor is characterized by a long absence of subjective sensations. In this case, melanoma is detected either by chance or at the stage of tumor disintegration and its secondary manifestations.
Causes
A mole can appear in infants, adults and the elderly. In this case, the ocular nevus can be localized on the iris, on the white or on the cornea. In some cases, the mole is not visible and can only be detected using an ophthalmological microscope.
As a rule, a birthmark is visible from the side. It has a darker pigment composition. Therefore, the nevus is very noticeable in people with light eyes. To understand why it is dangerous, you need to understand the reasons for the formation:
Congenital feature
Then the pupil and white will have a nevus from the first days of the child’s life. In newborns, this spot is often small in size. But over time, the eye changes color and it grows. Moreover, its increase is very intense.
| Congenital nevus does not pose a threat to vision. It does not interfere with visual function and does not affect the functioning of capillaries. |
Acquired nevus
In this case, the mole appears throughout life. And this can happen at any moment. After all, the conjunctiva and the eye are exposed to different influences throughout life. Moreover, such effects can be directed not only directly to the conjunctival region. This is caused by severe stress, hormonal changes, pregnancy, and so on. In any of the above cases, there is a possibility of a birthmark appearing on the eye.
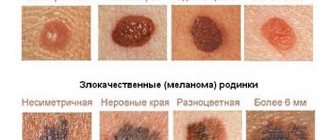
Types of eye melanoma
A classification of choroidal melanoma based on morphological characteristics has been developed. Depending on the cellular structure, the following types of this tumor are distinguished:
- Spindle cell.
- Epithelioid.
- Mixed (mixed melanoma).
- Fascicular.
- Necrotic.
This classification has certain disadvantages, since necrotizing choroidal melanoma is determined clinically, but it is impossible to determine its cellular identity due to extensive necrosis. Fusiform and fascicular types have a similar prognosis. In this regard, it is currently customary to distinguish only 2 types morphologically: spindle cell and epithelioid. The mixed form occupies an intermediate position. Its prognosis depends on the predominance of certain cells. Epithelioid cell melanoma of the choroid is considered to have the least favorable prognosis.
Interpretation of a mole on the eyelid
A nevus is not only an accumulation of pigment on the skin, it tells about a person’s character and future. The formation on the eyelids is noticeable to outsiders, so it is possible to determine what kind of personality a person is. If the mole is on the lower eyelid, the signs are as follows:
- He has an explosive temperament and gets irritated for any reason.
- There is no ease in making decisions regarding an important life issue.
- They need positive emotions.
- In stressful situations, they lose balance, panic, and become nervous.
- They have a good memory and choose an intellectual profession.
- They are capable of writing poetry and music, but they do not translate their plans into reality, because inspiration disappears.
- Realists in life, sensibly assess life situations.
- When making decisions, they prefer to derive material benefits.
- A mole on a woman’s right eyelid speaks of her daydreaming and inconstancy in love relationships. Due to the variety of life partners, people get married late.
- Does not have a strong opinion and quickly changes his point of view.
What a mole on the eyelid of a man’s left eye means will be explained by the following interpretation: he can easily leave his family to change his place of residence. Often life develops in such a way that a bad reputation is acquired. They do not strive to improve their financial situation through work, and as a result they end up in prison. A woman with a nevus on her left eye prefers career growth rather than starting a family or having children. Receives two or three degrees in order to achieve a high position in the professional field.
A nevus located on the upper eyelids indicates that a person has extraordinary intellectual abilities, high energy potential, and intuition. Differs in the makings of a manager or boss. Thanks to the charge of energy, they cannot stop in a timely manner when doing things. They develop themselves, strive for success and fame. There are cases when a person with pigment formation on the eyelids predicts the future. They lead people, promote their ideas, are good organizers and leaders.
If the nevus is located close to the eyelashes, this indicates a happy family life, a successful marriage. In a family, a person shows care, love, and attention. Raising children does not bother them; they invest all their strength in their offspring. Ready to make compromises. Throughout the marriage they are faithful and devoted to their chosen one.
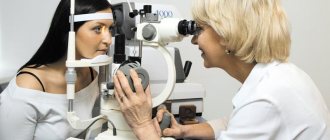
Diagnostics
Considering the clinical features of choroidal melanoma, its diagnosis, especially in the initial stages, presents certain difficulties. In addition to the analysis of patient complaints and clinical and anamnestic data, the results of the following instrumental studies are taken into account:
- Biomicroscopy.
- Ophthalmoscopy.
- Ultrasound examination of the eye.
- Diaphanoscopy, etc.
Choroidal melanoma is a neoplasm with a high risk of metastases. Therefore, when examining a patient, it is also necessary to use methods for diagnosing metastatic foci: ultrasound of the abdominal organs and lymph nodes, lung radiography, CT, MRI.
Treatment options for choroidal melanoma
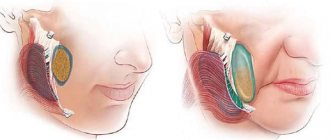
There are organ-preserving methods of treating this tumor and a surgical method without preserving the eye. In cases where it is not possible to save the eye, enucleation is performed - isolated removal of the eyeball or exenteration - excision of the entire contents of the orbital cavity along with the eyeball.
Indications for enucleation:
- The tumor is of significant size.
- Spread of melanoma to the optic disc.
- Complete absence of visual function.
- Extrabulbar tumor growth.
- Secondary glaucoma.
After removal of the eyeball, an internal prosthesis is implanted and subsequent external prosthetics is performed. These measures not only allow you to achieve a good cosmetic result, but also prevent facial deformation.
Organ-preserving methods of treating choroidal melanoma include:
- Radiation therapy. Depending on the method of delivering radiation, radiation therapy for this disease is carried out by contact or remote methods. Contact radiation, or brachytherapy, is the implantation of radioactive elements near the site of melanoma.
Indications for brachytherapy:
- No signs of decay.
The diameter of the neoplasm is up to 15 mm.
- The distance from the optic disc is at least 2 times the diameter of the disc itself.
- Laser coagulation in combination with thermotherapy. Transpupillary thermotherapy is a type of laser treatment for melanoma using deep local hyperthermia. The method is based on the possibility of deep penetration of infrared radiation through chorioretinal tissue. Transpapillary thermotherapy is an effective independent treatment for small choroidal melanomas (up to 4 mm in diameter).
- Cryodestruction. This method is based on extreme cooling of small melanoma lesions to −78 °C.
Brachytherapy is the most effective method of organ-preserving treatment for choroidal melanoma. Its use can reduce the likelihood of tumor metastases.
As part of systemic treatment, immune therapy is important. Also, when providing care to patients with choroidal melanoma in the later stages, the features of its metastasis are taken into account. This tumor is characterized by isolated liver damage by metastases. In such cases, chemoembolization of this organ is successfully used.
Such a common method of treating skin melanoma as targeted therapy is not used for choroidal melanoma, since this type of tumor does not have specific BRAF mutations.
How to remove a mole near the eye using a laser
No special preparation is required for the procedure. In one session it is possible to completely get rid of one or more tumors. The skin is pre-treated with an antiseptic. To prevent the patient from experiencing discomfort, he is injected with an anesthetic substance. Special glasses are used to protect the eyes. If the mole is located on the eyelid itself, during laser technology the eyeball is covered with a soft shield that reliably protects it from external influences.
Next, using the device, the doctor acts on the tumor in a targeted manner. During the procedure, the doctor is able to control the penetration of the laser beam deep into the epidermis (healthy nearby tissues are not injured). Thanks to its sterilizing properties, it is possible to avoid infection or inflammation in the treated areas. After the procedure, a small depression remains, which completely levels out within 10 days.
Prognosis for life with choroidal melanoma
Life expectancy for this type of cancer depends on the location and size of the tumor, the patient’s age, the morphology of the tumor, the treatment performed and other features. The five-year survival rate in the initial stages of choroidal melanoma after the use of organ-preserving radical methods is 93%, and the ten-year survival rate is 89%. In later stages, when liver metastases are detected, the median survival is only 4-6 months. For patients with metastatic disease to other organs, the one-year survival rate is 76%.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Symptoms of nevi
The main sign is that the stain is noticeable to others and to the person himself. The nevus can be located around the entire perimeter of the eye, this does not play any role.
The only symptom of a birthmark is a change in corneal pigmentation or protein. The appearance of small spots and clusters in the form of bubbles indicates the initial stage of the nevus. If such formation causes concern, you should contact an ophthalmologist and undergo an examination. It is impossible to be sure in any other way what type of nevus it is.