General information about the disease
Among all dermatological diseases, the share of psoriasis in adults is approximately 7-8%, in children under 16 years of age - 4%. Even newborns, more often females, are susceptible to it.
The disease is not contagious, but the theory of its viral origin has not yet been rejected.
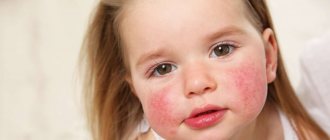
Psoriasis manifests itself equally at any age, but in childhood it often has uncharacteristic symptoms (atypical appearance), which can make diagnosis difficult. Thus, many dermatoses that affect the scalp and skin in the buttock area are similar to this disease. Source: Clinical guidelines “Psoriasis in children” Union of Pediatricians of Russia, 2016.
If at least one of the parents suffers from this disease, then the chance of its development in the child is 50%, if both - 60%. In the case of identical twins, if one of them is affected, the second will get sick with a 75% probability. Initially, psoriasis in a child appears in the groin area, lower back, rarely on the face, and later it is localized on the elbows, head, under the knees, spreads along the entire back, affects the armpits, and nails.
Almost half of all psoriasis sufferers acquired the disease in childhood. However, the first stage is often not detected due to the mildness of symptoms. Source: Benoit S., Hamm H. Childhood psoriasis // Clin. Dermatol. 2007. Vol. 25. P. 555–562.
The prognosis with early detection is good. In this case, local therapy is highly effective, followed by long-term remission (up to several years).
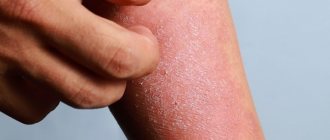
Complex therapy of psoriasis on the elbows using the line of dermatological products Losterin
"Losterin" is a line of dermatological drugs used for various skin diseases. For example, the classic Losterin cream can be used as a remedy for psoriasis on the elbows. It has a non-hormonal basis and contains soft components that have a non-aggressive effect on the lesions.
“Losterin” moisturizes the skin, fights inflammation, and also eliminates unpleasant symptoms such as itching and redness. The composition of the drug softens the skin and improves its regeneration processes.
Causes of psoriasis in children
Research continues all over the world to identify the causes of
this disease.
However, they have not yet been reliably established. The main theory is genetic predisposition
.
Scientists name the following as provoking factors:
- skin injury;
- lithium-containing medications;
- infectious diseases;
- metabolic disorders;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- stress;
- smoking and drinking alcohol (applies to adults and adolescents);
- weak immunity.
Normally, skin cells mature in 30 days, but with this disease – in 4-5. As a result, papules are formed. The same abnormalities are found in apparently healthy tissues, and not just in areas of rashes.
Prevention
Since the epidermis in this area is quite dry, regular care of the elbow area is required. To do this, you need to use a special cream with moisturizing properties.
You should also stop smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Strengthening the immune system plays an equally important role. For this purpose, experts recommend taking vitamin and mineral complexes, playing sports, and spending more time walking in the fresh air.
It is important to protect the skin from mechanical damage and not expose the body to frequent stress and psychological disorders.
At the first symptoms of an infectious disease, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor to provide timely medical care.
Symptoms of the disease
Psoriasis occurs in children in four stages: initial, progressive, stationary, regressive. Depending on this, the symptoms vary.
| Stage | Manifestations |
| Initial | Small rashes of a pinkish tint, the surface is smooth, shiny, hemispherical in shape. After some time, whitish or silver scales appear on them. |
| Progressive | The rashes grow and merge into conglomerates, the scales are located only in the center of the papules, along the edge of which there is a pink border. If the affected skin is injured, then after about a week a papule appears in this place, exactly repeating the shape of the injury (Koebner's symptom). |
| Stationary | New papules do not appear, old ones stop growing, peeling intensifies and spreads over the entire surface of the tubercle. |
| Regressive | Peeling decreases, papules become flatter in the center, gradually disappear, and in their place pigment spots or areas of skin devoid of pigmentation appear. |
Important! Psoriatic plaques have an extremely negative impact on the psychological state of children. Their peers focus on this, shy away for fear of getting infected, etc. Therefore, at the first signs, treatment should be started immediately.
As for babies, before two years of age, the first papules form in the folds of the skin, in the area where a diaper is worn. They differ from diaper dermatitis by their bright color and clear outline, with periodic mild itching.
After 10 years, children may develop psoriasis on the scalp, requiring treatment, which rarely happens at an earlier age.
Psoriatic arthritis often occurs, affecting the joints of the legs and arms. It begins with the onset of symptoms on the skin and develops approximately 10 years after the first rash.
In approximately 15% of cases, the disease affects the toenails and fingernails. Very often, the nail plates are the first to suffer, and skin rashes appear only years later.
Important! The disease has several forms and different symptoms. Any redness, peeling, or small swelling on the skin that does not go away within a week should be an alarm signal for parents. If you start treating your child in a timely manner, the process will not spread throughout the body.
Stages
Psoriasis occurs in several stages, periodically replacing each other.
Initial
The outer surface of the elbow area is covered with small papules. Outwardly, they resemble pimples with a random arrangement. After 14-21 days, the formations turn into voluminous plaques covered with scales. The dryness of the skin increases, the surface becomes rough.
Progressive
This stage is characterized by the formation of multiple large plaques. Patients complain of peeling and redness in the affected area. The boundaries of the rash are represented by a well-defined rim. At this stage, the disease transitions into a period of exacerbation.
Stationary
With a correctly selected scheme of therapeutic measures, the clinical picture becomes less pronounced, and the disease goes into a dormant state. The number of psoriatic rashes decreases, there are no new papules.
Regressive
This stage is accompanied by a decrease in the severity of symptoms, the number of plaques is noticeably reduced. The skin where the rash was previously localized is noticeably pigmented, but characteristic scales are absent in the affected areas, and the epidermis does not peel off.
Types of disease
Simple forms:
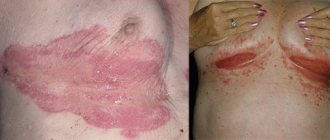
- ordinary, or plaque – areas of redness on the skin with clear boundaries and peeling;
- film - most often diagnosed in newborns, localized on the buttocks, difficult to diagnose because it is similar to diaper dermatitis and other skin ailments.
Heavy varieties:
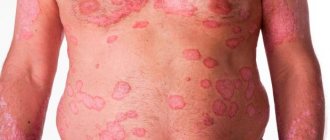
- psoriatic erythroderma - all skin turns red, joint pain, fever, blisters with pus may be observed;
- pustular - blisters filled with non-purulent fluid appear on the skin, causing fever if widespread;
- psoriatic arthritis - redness and blisters on the skin, asymmetric damage to the joints of the arms and legs.
Consequences
In the absence of therapeutic measures for a long time, the course of pathology on the elbows is complicated by the appearance of a number of diseases.
Psoriatic erythroderma may begin. In most cases, it occurs against the background of a sharp cessation or complete absence of treatment, frequent stressful situations, diseases of an infectious nature that occur in a severe form, and alcohol abuse.
Pustular generalized psoriasis poses a more serious health threat. This course of pathology is characterized by a massive combination of papules, as a result of which large lesions are formed, in the place of localization of which the skin exfoliates and pustular areas are formed.
Another complication is psoriatic arthritis. This is a pathological process that affects the joints, which is accompanied by swelling, severe pain and limited mobility.
Treatment of psoriasis
Therapy depends on the form of the disease, the person’s age, the presence of joint lesions, and previously used techniques. Severe forms often require treatment procedures in a hospital setting.
In each case, possible risks and potential benefits are assessed, especially when it comes to toxic drugs and hormonal drugs. Local treatment is most often used: moisturize the skin, soften it, relieve inflammation. Source: A.R. Umerova, I.P. Dorfman, V.V. Dumchenko, L.P. Makukhina Modern approaches to the treatment of psoriasis in children and adolescents // Russian Medical Journal, 2015, No. 19, p. 1156
In severe cases, systemic therapy may be prescribed. This is necessary when the disease significantly reduces the child’s quality of life. The consent of the child and parents must be obtained for such therapy, because it can lead to a number of side effects. Courses of treatment are usually short, each stage is carefully monitored by a doctor.
After 15 years and/or with extensive lesions, PUVA therapy is performed. The child uses a special drug containing psoralen externally or orally. After about 3 hours, his entire body or individual areas are irradiated with long-wave UV for several minutes. After several sessions every other day, formations on the skin decrease or disappear, peeling and itching are eliminated.
If other methods are ineffective, immunosuppressants are prescribed. However, they increase the risk of malignant tumors, so they are used rarely and under the strictest medical supervision.
Vitamins are prescribed together with any course of treatment: B12, ascorbic acid, A, B15, D2, pyridoxine. Only the doctor determines the dosage!
If the disease occurs in conjunction with a skin infection, antibiotics are prescribed.
Any treatment is usually long-term and is carried out to ensure that the disease is controlled and does not reduce the standard of living. Psoriasis cannot be completely eliminated.
Advantages of SM-Clinic
Our medical center employs some of the best pediatric dermatologists in the Northern capital. There is a modern diagnostic base, its own laboratory and hospital. Children are provided with a full range of services, comfort, absence of queues and attentive treatment are guaranteed.
Call to make an appointment.
Sources:
- Clinical guidelines “Psoriasis in children.” Union of Pediatricians of Russia, 2016
- Benoit S., Hamm H. Childhood psoriasis // Clin. Dermatol. 2007. Vol. 25. P. 555–562.
- A.R. Umerova, I.P. Dorfman, V.V. Dumchenko, L.P. Makukhina. Modern approaches to the treatment of psoriasis in children and adolescents // Russian Medical Journal, 2015, No. 19, p. 1156.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a dermatovenerologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1950 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Dermatoscopy 1 element | 700 rub. |
| Setting up functional tests | 190 rub. |
| Excision/removal of cutaneous/subcutaneous elements and formations (1 element) | 2550 rub. |
| Removal of milia of one unit using electrocoagulation | 350 rub. |