Acne and its common consequence, post-acne, are a fairly acute and common dermatological problem. The term “acne” refers to acne or inflammation of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, which is accompanied by the formation of numerous pimples of different sizes and types. Most often, this disease occurs in adolescents, lasts for years and is difficult to treat. Although it can also develop in adulthood, including after 30-35 years.
According to the latest data, more or less 85% of people suffer from acne, and in 15-30% of cases the disease is severe and requires complex, long-term complex treatment. Acne affects those areas of the skin where sebaceous glands are most concentrated. Therefore, very often it affects the face, which causes serious psychological complexes. But acne can also occur on other parts of the body, in particular the back. At the same time, one of the common complications of the disease is post-acne, i.e. persistent changes in the skin in the form of spots, and more often scars of different sizes, which are extremely difficult to deal with, but still possible.
Peculiarities of skin structure and acne development
Human skin is a heterogeneous tissue. It has 3 layers:
- The epidermis is the top layer of skin in contact with the environment. It, in turn, consists of several more layers, the top of which is called the horny or outer layer. It is formed by cells that have lost their nucleus and other organelles and have a strong cell membrane called corneocytes, which are dead keratinocytes.
- The dermis is the middle and most important layer of the skin, which is responsible for all its functioning. After all, it is in it that blood vessels and numerous nerve endings are concentrated. Moreover, it is in the dermis that fibroblast cells are responsible for the tone and youth of the skin, synthesizing collagen and elastin fibers. It also contains sebaceous, sweat glands and hair follicles.
- Hypodermis or subcutaneous fat is the lowest layer of skin, represented by loose connective tissue and fat cells called adipocytes. Its thickness directly depends on the area of the body, gender and nature of nutrition. Therefore, on the face, subcutaneous fat is poorly expressed, but on the hips, especially in women, it is well expressed.
From the point of view of considering the issue of the development of acne, dermatologists and dermatocosmetologists are most interested in the dermis, or rather the activity of the sebaceous glands and other appendages of the skin, i.e., sweat glands and hair. The sebaceous glands are responsible for the synthesis of sebum, also called sebum. It is necessary to retain moisture in the skin, protect it from ultraviolet rays and the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms, and also to bring antioxidants to the surface of the skin and prevent oxidative damage. The functioning of the sebaceous glands is regulated by hormones of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and adrenal cortex, the work of which is in direct relationship with the activity of other endocrine glands. Therefore, any changes in hormonal levels lead to the functioning of the sebaceous glands being disrupted in one direction or another.
It is to the sebaceous glands that we owe such an unwanted shine to the skin of the face in the so-called T-zone: on the forehead, nose and chin.
Often, hormonal fluctuations provoke more active production of sebum, which is called seborrhea. It is classified as a separate disease, the presence of which can be indicated by:
- enlarged skin pores, including the formation of comedones (popularly called blackheads);
- oily or dry flaking skin;
- rapid contamination of hair, which leads to the need to wash your hair much more often, including daily or even more often.
Hormonal disorders that provoke the development of seborrhea also lead to changes in the composition of sebum. As a result, the content of androgens (male sex hormones) increases and the amount of estrogens (female sex hormones), as well as linolenic acid, decreases. Sebaceous gland receptors are sensitive to androgens. Therefore, an increase in their number provokes more active production of sebum or sebum.
Both men and women produce both androgens and estrogens in their bodies, but in different quantities. Moreover, androgens are precursors of estrogens, i.e., the starting compounds for the synthesis of female sex hormones.
Linolenic acid is responsible for maintaining a slightly acidic environment on the skin, which is an effective prevention of the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into it. Therefore, when the content of this unsaturated organic acid in sebum decreases, it becomes alkalized. This leads to a decrease in the barrier properties of the skin and the creation of favorable conditions for the development and reproduction of various microorganisms on its surface and penetration from the inside of the skin.
Causes of acne development
Activation of sebum synthesis, changes in its composition, in particular a decrease in the concentration of linoleic acid, is the main reason for the development of inflammatory processes in the skin, i.e., the occurrence of acne.
In the course of research, it was found that acne is most often provoked by:
- anaerobic lipophilic corynebacteria, in particular Propionibacterium acnes;
- aerobic bacteria, including Staphylococcum epidermidis;
- lipophilic fungi Pityrosporum ovale et orbiculare.
The most dangerous from the point of view of acne development are Propionibacterium acnes. These microorganisms are capable of synthesizing a variety of enzymes, including lipase, which destroys the walls of hair follicles.
The main problem is that all these microorganisms are a component of the normal microflora of the skin of the face, i.e. they are constantly present on it and in the normal state of immunity, the activity of the endocrine glands, and metabolism, their number is strictly regulated and cannot cause harm or provoke the development of diseases. Therefore, acne can be a consequence of various disorders in the body, i.e., the influence of endogenous causes, including decreased immunity and hyperandrogenism, i.e., increased synthesis of androgens (testosterone and dihydrotestosterone). Therefore, the disease often occurs when:
- puberty;
- endocrine diseases, in particular diseases of the ovaries and testicles, adrenal glands, pituitary gland and hypothalamus;
- obesity;
- premenopause and menopause;
- hyperkeratosis;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- suffering from severe infectious diseases;
- long-term stress, chronic fatigue syndrome.
Often the tendency to develop acne is inherited.
But the reasons for the development of acne can also lie in the action of external causes, which include the negative influence of sunlight. This is due to the fact that with active exposure to ultraviolet radiation, the skin's immunity sharply decreases, i.e. its ability to suppress the growth and reproduction of microorganisms living on it. As a result, the bacteria and fungi listed above are able to multiply uncontrollably and form colonies around the sebaceous glands, as they feed on the secretion they produce - sebum.
Acne also often occurs in bodybuilders of both sexes. This is due to the fact that in order to achieve their goals, they are forced to eat high-calorie foods and often take anabolic steroids. Such drugs contain substances that are derivatives of testosterone. Therefore, their use for a long period of time leads to changes in hormonal levels and the development of seborrhea, and then acne. Such cases have even been identified as a separate form of acne - bodybuilding acne.
If women take anabolic steroids, in addition to acne, they may experience a decrease in voice tone, male-pattern hair growth, menstrual irregularities, even amenorrhea. But in both cases, bodybuilders risk decreased fertility.
Pathogenesis
In its development, the disease sequentially goes through a number of stages:
- excessive secretion of sebum;
- the occurrence of follicular hyperkeratosis, which consists of an increase in the thickness of the stratum corneum of the epithelium in the area of the mouths of the hair follicles, which leads to the formation of comedones;
- proliferation of microorganisms in clogged hair follicles, as they feed on the sebum produced;
- an inflammatory process that becomes the body’s reaction to the accumulation of metabolic products of microorganisms (can be observed on the surface of the skin or in its deep layers) and manifests itself in the formation of red papules, pustules, and nodules.
Often, as the duration of the disease increases, the number of inflammatory elements increases. In this, a direct role is played not only by blockage and damage by microorganisms to other sebaceous glands, but also by the rupture of their walls as a result of the accumulation of sebum and its distribution in the thickness of the skin.
All-season peeling.
These are peels that can be used at any time of the year without fear of hyperpigmentation.
Peeling Kemikum
The main feature of this peeling is the presence of ozonides, which release oxygen and neutralize the effects of acids. As a result, the skin is actively saturated with oxygen, the production of collagen and elastin is activated, resulting in a noticeable lifting effect.
Indications for using Kemikum peeling include:
- Pigmentation and hyperpigmentation
- Dry skin
- Unhealthy facial tone
- Wrinkles
- Acne and post-acne of any complexity
- Scars
- Stretch marks on the skin
Peeling is indicated for all ages and skin types, because, despite the deep impact, the peeling effect is very soft and gentle.
Peeling PRX T33
This is the most popular peeling today! Positive reviews do not stop appearing and all this is for a reason!
Its incredible effect is due to three main components: trichloroacetic acid, kojic acid and hydrogen peroxide.
As a result of PRX peeling you will receive:
- Deep cleansing of the skin at all levels
- Activation of collagen and elastin production
- Antibacterial action
- Lightening pigmentation
- Evens out skin tone and texture
- Eliminate signs of skin aging
- Saturation of cells with oxygen
- Lightening pigmentation
- Removing acne marks
- Fighting inflammation and rashes
- Launching regenerative functions
Peeling is suitable for all skin types and even sensitive ones. The main task of peeling is deep but gentle cleansing and healing of dermal cells at all levels.
Peeling ULTRACEUTICALS VitaPeel
The peeling of the Australian brand, known for its natural and super-healthy compositions, is based on lactic and salicylic acid, as well as highly concentrated vitamins A and C.
Ultraceuticals peeling solves a whole range of problems:
- Gently cleanses the upper layer of the dermis
- Eliminates signs of skin aging
- Improves skin tone and condition
- Lightens pigmentation
- Restores water balance
- Improves the protective functions of the dermis
Indications for peeling are problematic skin, the presence of hyperpigmentation and the first sign of skin breakdown.
Back to blog
Forms and symptoms
Acne can visually manifest itself in quite different ways and occur in mild, moderate and severe forms. Therefore, many patients may not even realize that they have this dermatological disease. Symptoms of acne may include:
- open and closed comedones;
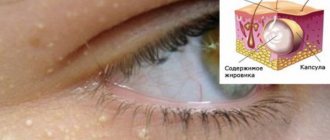
- milia - white dense acne, resembling grains, usually painless (most often located under the eyes and on the upper eyelids, less often on the forehead, cheeks, cheekbones);
- oily hair;
- papulopustular elements and nodes, which are often very painful;
- peeling of the skin or, conversely, the presence of an oily sheen.
Modern classification involves dividing all cases of acne into juvenile acne, adult acne, childhood acne, including newborns.
Depending on how acne manifests itself, there are 3 main forms:
- comedonal;
- papulopustular;
- conglobate.
At the same time, starting with the appearance of open and closed comedones, acne can eventually transform into a papulopustular rash, etc. Therefore, these forms are considered as stages of the disease. In mild forms of the disease, single comedones, papules and/or pustules are observed. In the moderate form, in addition to these single elements, single nodes are attached, while in the severe form, multiple papules and pustules, as well as conglobate nodes, are observed.
Comedonal form
This form is characterized by the formation of blackheads or comedones, which is considered as the first stage in the development of acne. Its signs can appear as early as 8-year-old children and initially consist of increased oiliness of the skin and hair. Over time, small comedones begin to form at the mouths of the sebaceous glands, which tend to transform into closed comedones. These are the same painless and non-inflamed blackheads that can appear as small bumps of normal skin color and with a white protruding tip of sebum.
Comedones often cannot resolve on their own, since the thickened walls of the mouths of the sebaceous glands prevent the arbitrary removal of accumulated secretions out. Since the sebaceous gland, despite the blockage of its duct, continues to function and produce new portions of sebum, its walls gradually stretch, and the pressure on them increases in direct proportion to the amount of accumulated sebum. This causes the formation of papules and pustules, i.e. the development of the papulopustular form of the disease.
Papulopustular form
This form is already characterized by the formation of papules and pustules against the background of the presence of open and closed comedones, as well as traces of resolved elements on the skin (post-acne), and their number directly depends on the severity of the disease. Papules are dense or soft formations that rise above the surface of the skin. At the same time, pustules mean formations rising above the surface of the skin with clearly visible white contents.
Often, with papulopustular acne, rashes are observed not only on the face, but also in the décolleté area, as well as on the back.
Acne conglobata
The conglobate form of acne is considered the most severe. It is characterized by the formation of large elements that rise greatly above the level of the skin and can reach large sizes and merge with each other. Conglobate acne is dense to the touch and very painful on palpation. They can form both on the face and on other parts of the body. But they are more often found on the back.
Conglobate acne can exist for months without opening. But if this does happen, long-term non-healing ulcers form in their place, leaving deep scars.
Types of post-acne
- Atrophic scars are the most common after acne. They resemble chickenpox scars - small indentations in the skin. They form when there is not enough collagen left in the affected area of the skin.
- Hypertrophic scars. These scars are most often found on the chest and back. They instead protrude above the surface of the skin and are caused by too much collagen after healing.
- Dark (stagnant) spots. After you have treated your acne, there may be too much pigment in that area of skin. In fact, these spots are not scars. Purple, red or brown - disappear within a few months if treated correctly.
Post-acne – a common consequence of acne
According to the latest data, acne resolves with the formation of post-acne in 40% of cases. This term refers to the occurrence of skin changes in places where the inflammatory process persists for a long time and the formation of the largest papules, pustules and nodules. Thus, post-acne may manifest itself:
- pigment spots - the result of squeezing out comedones, pustules and papules, as well as the action of sunlight, which led to a violation of pigment formation (most typical for patients with dark skin and late acne;
- stagnant or erythema spots - occur due to impaired microcirculation in the area of inflammation;
- enlarged pores – a consequence of prolonged stretching of the walls of the sebaceous glands by excess sebum;
- pathological scars (atrophic (chipped, round, square), normotrophic, hypertrophic, keloid) - the result of severe facial acne, leading to damage to the perifollicular part of the dermis;
- atheromas - large subcutaneous cysts of the sebaceous glands, completely filled with sebum;
- milia or millet - small round white pimples that arise against the background of disturbances in the keratinization process.
Therefore, post-acne can reduce the quality of life no less than acne directly affecting the face. At the same time, the likelihood of developing post-acne increases with:
- severe papulopustular and conglobate forms of acne;
- persistence of the inflammatory process for more than a year, which is usually observed in the absence of treatment or its improper implementation;
- presence of post-acne in close relatives;
- squeezing out comedones, pustules, papules or exposure to other traumatic factors on the facial skin.
In this case, post-acne becomes not only a pronounced cosmetic defect, but can also lead to the development of a number of complications, including dangerous ones:
- exacerbation of herpes infection;
- depigmentation;
- formation of new scars;
- allergic dermatitis;
- persistent erythema (redness of the skin);
- secondary infection, which can result in erysipelas.
The risk of developing post-acne complications increases with trauma to the facial skin and especially with squeezing out acne.
How to get rid of post-acne on your face at home?
Stagnant spots left by acne are most often removed in a beauty salon, but with the help of pharmacy cosmetics with active formulas aimed at intensive restoration and renewal of the epidermis, it is possible to significantly improve the condition of ex-problem skin at home.
How to remove post-acne using skincare products:
- Sebum-regulating products (washing gels, tonics and lotions) will help solve the problem of enlarged pores, keep them clean and prevent the occurrence of inflammatory processes and new rashes.
- Whitening creams and serums for daily care will help get rid of pigmentation.
- Homemade acid-based peels are effective for any manifestations of post-acne, even out skin tone and texture, and promote accelerated cell regeneration.
- Masks based on natural clay also help narrow pores, control sebum synthesis and prevent the emergence of new imperfections.
To lighten pigmentation, pay attention to creams and serums with components whose action is aimed at suppressing melanin synthesis: kojic acid, arbutin, glabridin, ascorbic acid, azelaic acid.
Alexander Prokofiev, medical expert of the La Roche-Posay brand
Diagnostics
If signs of acne occur, you should consult a dermatologist or dermatocosmetologist. The doctor will not only evaluate the number of elements, their nature, location and the presence of signs of post-acne, but will also clarify the patient’s dietary habits, whether close relatives have suffered from similar acne on the face, and a number of other points. In general, acne can be diagnosed and its severity determined at the first consultation, since the disease has a specific clinical picture.
But in order to choose the optimal treatment tactics, you need to accurately determine the cause of acne development and assess the general condition of the body. For these purposes, patients are prescribed:
- UAC;
- OAM;
- blood chemistry.
Identifying the cause of acne is extremely important, as it is a chronic disease. Therefore, in the absence of control, it can recur at any time when favorable conditions are created.
When diagnosing post-acne, the nature of facial skin changes, the presence of scars, their shape, depth, localization, and ability to smooth out when the skin is stretched are also assessed.
FROM COMEDONE TO SCAR
- first of all, comedones form (the sebaceous gland enlarges), blackheads
- they turn into pustules (pustules), which leave scars
- when squeezed out, the contents transfer to adjacent healthy areas of the skin
- collagen production is stimulated and scarring is formed
- new capillaries grow around (this gives redness) and age spots form
- Over time, the pigmentation becomes less bright,
- a visible scar remains: in the form of a dimple (crater-shaped) or convex.
Acne treatment
Patients should be prepared for the fact that treatment for acne on the face, like other parts of the body, will be quite lengthy. It is always comprehensive and selected for each patient individually. First of all, all patients are recommended to limit their time in the sun and use sunscreens with a high SPF factor, which will need to be thoroughly treated with the face a quarter of an hour before going outside on sunny days, including during the cold season. A diet must also be prescribed, which consists of excluding frankly harmful foods, fried and fatty foods. Otherwise, acne treatment tactics are largely determined depending on its degree.
So, in mild cases, only external therapy is usually prescribed. It consists in:
- regular mechanical facial cleansing performed by a qualified dermatocosmetologist in a medical facility, but in no case in a beauty salon or at home;
- a course of chemical peels, which can be salicylic or pyruvic, depending on the characteristics of the skin;
- the use of keratolytics, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory agents for external use, retinoids.
It is strictly forbidden to squeeze out comedones and inflammatory elements on your own, as this not only increases the risk of developing post-acne, but can also be complicated by the addition of a secondary infection and even the development of sepsis.
For moderate facial acne, in addition to the remedies described above, systemic therapy is prescribed, which consists of taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs, including oral contraceptives (for women). The choice of drugs directly depends on the diagnostic results and the detected diseases that caused the development of acne.
Sometimes treatment is supplemented with superficial cryotherapy, laser therapy, and darsonvalization.
In severe cases of the disease, drugs based on isotretinoin are prescribed. But since it can provoke a number of undesirable consequences, treatment with it is carried out under the constant supervision of a dermatologist. Also, while using this drug, women of childbearing age must be prescribed reliable contraception.
Often, patients additionally require the help of a psychologist, since acne and post-acne provoke the emergence of serious complexes and leave a serious imprint on the patient’s mental state, undermining his self-confidence, leading to depression and other undesirable consequences.
Deep peeling
This peeling works in all layers of the skin, starting from the superficial (removing it) and ending with the deep ones (regeneration processes are launched).
Yellow peeling
The basis of yellow peeling is retinoic acid, which can cope with complex problems such as scars on the skin. The peeling also contains other acids (kojic, phytic, azelaic) and vitamin C, which enhance the peeling effect.
Yellow peeling is aimed at:
- Skin cleansing
- Seboregulation
- Lightening pigmentation
- Removal of scars and stretch marks
- Elimination of acne and post-acne
- Smoothing out wrinkles
- Slowing down skin aging processes
- Increased skin tone
Yellow peeling is used for aging and problem skin, as well as for skin with severe pigmentation.
Post-acne treatment
Treatment of the consequences of acne or post-acne is a more complex task than directly eliminating the inflammatory process. Nevertheless, it is no less important, since various scars, age spots and other traces of inflammatory elements represent a serious cosmetic problem and sharply reduce the quality of life of patients.
Today there are several methods for correcting post-acne. The choice of specific ones is made based on the severity of the situation. These include:
- chemical peels;
- hardware procedures;
- injection therapy;
- surgery.
But for treatment to be effective, especially for moderate and severe post-acne, it must be comprehensive and combine different methods of influencing the skin of the face. At the same time, it is important not to rush, but to systematically work on eliminating post-acne, since after each procedure the skin needs restoration.
For deep scars, before starting correction, subcision may be required, i.e., destruction of the adhesions that connect it to the surrounding tissues.
Chemical peels
To eliminate post-acne in the form of stagnant spots and shallow square scars, chemical peels of varying depths of exposure using various acids are used. In other cases, they can only act as a component of complex therapy. This:
- superficial chemical peels (salicylic, glycolic, pyruvate, milk);
- medium (Jessner peel, trichloroacetic peel);
- deep (phenolic).
Today, deep chemical peels are performed extremely rarely for post-acne conditions, since they often provoke a large number of complications.
Each chemical peel has its own indications and contraindications, not to mention the specifics of its implementation. Therefore, the choice of a specific one is carried out strictly on an individual basis.
Hardware procedures
Hardware methods are considered one of the most effective in the treatment of facial post-acne. These include:
- Classic dermabrasion is a procedure that involves using special tips with an abrasive surface to remove the top layer of skin. But its implementation is associated with severe painful sensations, which often forces it to be performed under general anesthesia. Therefore, today this method is used extremely rarely.
- Microdermabrasion is an analogue of classical dermabrasion, but involves a smaller depth of impact. Therefore, it is effective only against stagnant spots, square scars with a depth of no more than 0.5 mm.
- Laser resurfacing is one of the most effective methods for treating post-acne, including round and square scars of varying depths.
Injection therapy
Modern injection procedures used to improve the appearance of the face during post-acne include:
- Needling is a cosmetic procedure, the essence of which is to carry out numerous micro-perforations of the skin with a special roller. It is equipped with many needles, the length of which does not exceed 2 mm. Needling is most effective for removing congestive spots and atrophic superficial scars.
- Plasmolifting is a medical procedure that involves introducing platelet mass separated from the patient’s own blood into the deep layers of the dermis.
- Mesotherapy is a well-known cosmetic procedure, the essence of which consists of numerous intradermal injections of individually selected mesopreparations, which include vitamins, enzymes, amino acids, nucleotides, organic acids and other biologically active compounds.
Surgery
Today, scar removal can be done through traditional surgery or laser destruction. Surgical methods are used extremely rarely and only in the most complex cases, in particular with large hypertrophic and keloid scars. But in the latter case, there is a risk of re-formation of the scar, since keloids tend to grow due to mechanical trauma. To reduce this risk, long-acting suspension corticosteroids are injected into the scar area. In other cases, injections of enzyme preparations, in particular longidase and collagenase, are indicated.
Thus, acne treatment, although it can be quite complex and lengthy, is still much simpler than the fight against post-acne. Therefore, it is important to contact a dermatologist as soon as possible if acne of any nature appears on the face. This will allow you to notice the onset of the development of the disease at the earliest stages and eliminate it even before unsightly scars, age spots, etc. form on the face. But even if time is lost, do not despair. The modern level of development of medicine makes it possible to effectively combat acne of any severity, as well as post-acne, improving the appearance of the face and returning the patient to an active social life.
5 1 vote
Article rating
The duration of resolution of inflammatory elements in acne correlates with the risk of scar formation. What aesthetic medicine methods will help avoid their formation, and which ones will help reduce post-acne marks?
One study found that 95% of patients experience some degree of scarring. According to other sources, resolution of acne elements with scar formation is 3.4–6.8 times more common in severe forms of the disease than in patients with milder forms of acne. In addition, it was found that in patients who did not receive adequate therapy in the first 3 years from the onset of the disease, scar deformities form 1.6–2.8 times more often.
The Global Alliance for Acne Treatment has proposed to combine the following phenomena under the term “post-acne”:
— cicatricial deformities formed during the resolution of acne rash elements; - post-inflammatory hyper- and depigmentation; - congestive erythema.
But if erythema and pigmentation disorders are temporary, then scar deformities remain forever.
There is still no clear answer to the question of what a scar is: a normal variant or a pathology. According to the classification proposed by A. E. Reznikova (1999), all types of scar deformities can be divided into two groups: normal (normotrophic and atrophic) and pathological (hypertrophic and keloid). This classification is based on the fact that the formation of normal scars occurs as a result of normal physiological protective reactions of the body in response to skin damage, while pathological scars are formed when these processes are disrupted.
Atrophic acne scars
The most common occurrence of atrophic scars can be observed, but hypertrophic and keloid scars also occur. However, the severity of scars does not correlate with the severity of the disease. The development of hypertrophic and keloid scars is observed in 10–20% of cases. Their formation is associated with insufficient activity of MMPs. They are localized mainly on the skin of the back and chest, rarely on the face. Keloid scars can develop spontaneously or long after injury.
Atrophic scars occur in 80–90% of cases and are formed more often on the face, less often on the body. According to modern concepts of scar pathogenesis, the evolution of inflammatory elements of acne resulting in an atrophic or hypertrophic scar is associated with an imbalance of metalproteinases MMPs (MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-9, MMP-13, proMMP-1, proMMP-9), responsible for the architecture of the extracellular matrix and their tissue inhibitors TIMPs.
Post-acne scars are formed with the participation of peptidoglycan of the cell wall of P. acnes, which, through gene expression of the synthesis of proMMP-2, enhances the degradation of the extracellular matrix.
Atrophic acne scars.
M-shaped (Rolling) scars, 4-6 mm Stretched, sunken scars with sloping edges, giving the skin a wavy appearance.
V-shaped (Ice pick) scars, < 2 mm Sharp, deep, sunken scars, wide at the surface and tapering towards the base.
U-shaped (Boxcar) scars, 0.1-4 mm Superficial or deep, wide both at the surface and at the base, round or oval in shape with clear edges.
Forms of atrophic post-acne scars
There are various forms of atrophic post-acne scars: V-shaped (Icepick), M-shaped (Rolling), U-shaped (Boxcar). But since in clinical practice, as a rule, a combination of the listed types of scars is encountered, differential diagnosis between them becomes very difficult. In this regard, in 2006, D. Goodman et al. The Global Qualitative Classification of Acne Scars was presented (Table 1). This scale is quite simple and convenient for use in clinical practice, which allows you to more accurately determine treatment tactics and evaluate the results obtained.
Despite the high risk of developing scars due to acne, at the moment, modern standards of acne treatment do not indicate measures to prevent the development of post-acne scars. Although the need for preventive treatment simultaneously with the main one or as soon as possible after its completion is beyond doubt. To determine the tactics of preventive measures for the development of scar deformities, it is necessary to take into account the predictors of their development.
In this regard, the early start of acne therapy, adequate to the severity of the disease, an integrated approach to solving problems, joint work of related specialists, the right attitude of the patient, a sufficient degree of compliance in most cases are the key to a positive treatment result and preventing the evolution of acne elements with an outcome in scar.
Treatment of scars must be carried out using a properly selected method, for the selection of which an accurate differential diagnosis of the scar is important. And if it is usually not difficult to distinguish a normotrophic scar from a hypertrophic one, then the differences between a hypertrophic and a keloid scar are not always obvious.
Table 1. Global qualitative classification of acne scars proposed by D. Goodman and Baron (2006)
severity level of damage clinical manifestations points 1 Macular Erythematous, hyper- or hypopigmented flat scars that do not change the texture of the skin, but affect its color. 1 2 Weak Weakly expressed atrophic or hypertrophic scars, not visible at a distance of 50 cm or more, easily masked with cosmetics, on the chin in men - with the shadow of hair growing after shaving, in extrafacial localization - with naturally growing hair. 2 3 Average Moderate atrophic or hypertrophic scars, clearly visible at a distance of 50 cm or more, poorly masked by cosmetics, the shadow of hair growing after shaving or naturally growing hair in extrafacial localization; When the skin is stretched, atrophic scars on the face are smoothed out. 3 4 Pronounced Pronounced atrophic or hypertrophic scars, clearly visible at a distance of more than 50 cm, poorly masked by cosmetics, the shadow of hair growing after shaving or naturally growing hair in extrafacial localization; When the skin is stretched, atrophic scars do not smooth out. 4 For the differential diagnosis of hypertrophic and keloid scars, anamnestic data are of greatest importance. The development of a hypertrophic scar occurs within 6–10 months after injury, while keloid scars can occur spontaneously or several years after injury (Table 2). In patients with keloid scars, there is an increase in deep skin sensitivity; subjective itching in the area of the lesion may be bothersome. Subjective sensations of patients with hypertrophic scars are usually absent.
Additional methods for preventing scars include the use of methods aimed at improving tissue trophism, these include cryomassage, vacuum massage, electrophoresis, phonophoresis, microcurrent therapy, and magnetic thermal therapy.
Table 2. Differential diagnosis of normal and pathological scar deformities
normotrophic scars
hypertrophic scars
keloid scars
Formation 7–10 days after injury
Formation within 6–10 months after injury
Formation several months, years after injury or spontaneously
No family predisposition
Family history
Without subjective feelings
Increased deep skin sensitivity, itching
The localization of the scar corresponds to the area of injury
The scar extends beyond the injury At the same level with the surrounding skin or retracted Rise above the skin level
Spontaneously flatten
Possible flattening over a long period of time Do not flatten over the years Never ulcerate May ulcerate
Very rarely ulcerate
Normal skin color or hypopigmented Predominantly red, hypo- or hyperpigmented
How to get rid of atrophic scars? In choosing one or another method for correcting an already formed post-acne scar, the presence of inflammatory elements simultaneously with post-acne elements is of great importance, which significantly reduces the range of possible treatment methods. The main treatment of such patients should be supplemented with the use of laser techniques that are also effective against inflammatory elements of acne (PDL, Nd:YAG laser, diode laser with a wavelength of 1320 nm).
Provided there are no inflammatory elements, the World Acne Alliance for the correction of post-acne scars has approved certain types of skin resurfacing, surgical excision of an atrophic scar, the use of dermal fillers and deep peels.
Methods for correcting post-acne scars
Chemical peels When correcting more superficial scars and dyschromia, it is recommended to use mid-superficial and mid-level peels with 70% glycolic acid, 30% salicylic acid, 20–35 TCA or 40–70% pyruvic acid [3]. Due to its high efficiency, the technique of targeted application of deep TCA peeling (CROSS technique) has become widespread, especially in the correction of V- and U-shaped scars. A study by N. Khunger et al. noted an improvement of more than 50% in 93.3% of patients after 4 peeling treatments at a 2-week interval.
Surgical method A universal method for correcting deep atrophic scars are surgical techniques, which are recommended to be combined with one of the skin resurfacing techniques. Thus, in one of the studies on the effectiveness of the method for correcting M-shaped post-acne scars using surgical subcision and 100% TCA peeling in patients with phototypes III and IV (Fitzpatrick), it was revealed that the subcision method is more effective, causing fewer side effects. However, further reduction in the depth of the scar defect appears to be more pronounced with subsequent use of TSA.
A method for correcting M-shaped post-acne scars using surgical subcision.
Mechanical skin resurfacing The use of mechanical dermabrasion (resurfacing of atrophic scars) is justified in the presence of a large number of post-acne scars located close to each other. However, due to the fact that this method is very traumatic, painful for the patient, requiring long-term rehabilitation, with a high risk of developing side effects in the form of pathological scars and dyschromia, its use is very limited. Microdermabrasion is a more gentle method, but its effectiveness in correcting deep scars is less pronounced.
Similar to microdermabrasion is the method of needling using mesoscooters. According to some data, this method, by stimulating the synthesis of type I collagen, is more effective than IPL systems.
Intradermal stimulation of scar tissue (Skinbiogeting) This method is used exclusively for atrophic scars and involves separating the bottom of the scar from the underlying tissue. Technically, this technique is carried out with a simple needle with an injection of novocaine under the scar or with a special thread.
Mechanical separation of the scar from the underlying tissue causes aseptic inflammation due to injury with subsequent activation of fibroblasts. The resulting defect is filled with connective tissue, as a result of which the bottom of the scar thickens and, as a result, the depth of the defect decreases.
Dermal fillers Correction of scar deformities using dermal fillers (filling atrophic scars) has a large number of limitations: use only on atrophic U-shaped scars with a low density of scar tissue. In addition, depending on the chosen material, it has a short duration of effect – 3–12 months. The advantages of the technique are good patient tolerance and low risk of complications. Stabilized hyaluronic acid, collagen (animal or synthetic origin), and adipose tissue are used as fillers.
Mesotherapy The mesotherapy method is used for all types of post-acne scars. Vitamins and biologically active preparations that improve tissue microcirculation are used.
The use of this method is justified in combination with various types of resurfacing (peelings, dermabrasion, laser resurfacing) and in the early stages of scar formation.
Electrophoresis Electrophoresis with lidase is used only on hypertrophic and keloid post-acne scars in the early stages of their formation. 2 courses of 10 procedures are carried out daily or every other day. The break between courses is 1–2 weeks. The use of lidase is aimed at destroying the extracellular matrix, more precisely its polysaccharide component. Providing a “loosening” effect, it promotes the penetration of other medicinal substances. Since collagen is another important component of the extracellular matrix, the use of collagenase, especially in later stages of scar formation, is also pathogenetically justified. Electrophoresis with collagenase is carried out according to a similar scheme. It is possible to combine this method with electrophoresis of prednisolone or dexamethasone, since corticosteroids reduce the activity of fibroblasts, block enzymes involved in collagen synthesis, and also reduce the permeability of the vascular wall, which leads to inhibition of the growth of scar tissue.
Ultrasound therapy This method is based on the use of ultrasonic vibrations with a frequency above 16 kHz. Ultrasound has a defibrosing, anti-inflammatory effect on biological tissue and leads to acceleration of local blood circulation. It has been proven that new collagen and elastin fibers formed under the influence of ultrasound have greater elasticity.
When using low power - from 0.4 to 0.8 W - ultrasound has a stimulating effect on trophic processes in tissues. Such stimulation is indicated for the treatment of fresh scars. The course consists of 14–20 procedures with an interval of 2–3 weeks.
With increasing power, heat generation increases, and the defibrosing effect of ultrasound increases, which is necessary for the correction of old scars. The defibrosing, softening effect of scars is achieved in the range of 0.8–2 W/cm2. A regime of continuous generation of ultrasonic waves per zone for 3–5 minutes is recommended for a course of 10–15 procedures every other day.
Laser therapy Atrophic acne scars are also removed using laser therapy. As before, the gold standard in the correction of post-acne scars using laser techniques is the ablative method of CO2 laser correction. As observations show, this technique allows one to achieve clinically significant results (50–81%) after the first procedure. However, due to the fact that the CO2 laser generates high-density energy, has low selectivity to water, and creates additional zones of thermal tissue damage, the risk of side effects is quite high. Erbium laser resurfacing is a less traumatic ablative method due to its high affinity for water molecules. However, to achieve an effect comparable to a CO2 laser, several procedures are necessary.
The emergence of a new method of exposing the skin to a laser beam, fractional photothermolysis, has made it possible to reduce the trauma of ablative techniques; in addition, it has become possible to increase the depth of penetration of the laser beam with minimal trauma to the epidermis.
A feature of fractional lasers is that the radiation used when influencing biological tissue does not arrive in a continuous stream (as, for example, with broadband lasers), but pointwise, forming scattered multiple microthermal treatment zones 70–150 microns in diameter and 380–1600 microns in depth, around which intact tissue is preserved. This effect is due to a microlens matrix installed at the output of the light beam, while a high radiation density is provided in the focal spots (about 200 J/cm2).
Due to the fact that the total surface area of the lesion is only 15–20%, epidermal reepithelialization occurs quite quickly, with minimal risk of side effects.
Conclusion Thus, despite the wide range of methods for correcting post-acne scar deformities, the search for a method that provides a solution to all problems of treatment and prevention of scars has not yet been completed. Further observations may help to select the most optimal parameters for working with such patients, achieving good therapeutic and aesthetic results while reducing the risk of adverse events.
Larisa Kruglova, MD, PhD, Head. Department, Professor, Natalya Korchazhkina, Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor of the Federal State Budgetary Institution of Further Professional Education "Central State Medical Academy" of the Administration of the President of the Russian Federation; Polina Kolcheva, dermatologist, cosmetologist, Moscow Scientific and Practical Center for Dermatovenereology and Cosmetology, Moscow
WHY CLIENTS CHOOSE TELOS BEAUTY PROF
- The Expert Cosmetology Clinic has valued its impeccable reputation since 2009!
- Our doctors have developed proprietary programs to effectively solve even complex problems.
- We attach great importance to your safety and compliance with sanitary standards.
- We carefully select our staff; procedures are performed only by cosmetologists.
- We use original drugs and equipment to ensure that the procedure is as safe as possible.
- We have our own parking, no need to waste time looking for a space on neighboring streets.
- Thousands of grateful clients confidently recommend us to their family and friends because they TRUST US!
Call the Telos Beauty Prof clinic by phone or
Getting rid of post-acne is not an easy task, but only an integrated approach allows the doctor to get the desired result!
If you still have questions about how to get rid of acne or post-acne, what treatment methods to choose, fill out the feedback form. The administrator will contact you within 10 minutes.
EXPERT COSMETOLOGY CLINIC TELOS BEAUTY PROF - WE KNOW HOW TO MAKE YOU BEAUTIFUL AND KEEP YOU NATURAL!