How to treat herpes?
It is impossible to completely destroy a virus that has entered the body. But it is quite possible to suppress its activity so much that it does not bother you. In modern medicine, an integrated approach is used for this. The best results are obtained by combination therapy, which involves the use of antiviral drugs (they are available in the form of drugs for internal use and in the form of external agents), as well as drugs that strengthen the immune system. In some cases, the patient is additionally prescribed local analgesics and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Many people are interested in whether it is possible to burn herpes with alcohol? Alas, this method does not affect the virus, but only damages the mucous membranes, so it is better to use special ointments.
What remedies are usually prescribed for herpes on the lips? The table shows a list of the most common medications used to treat the virus.
| Name, dosage form | Description |
| Acyclovir (aka Zovirax). Available in the form of tablets, cream, eye ointments, injection solutions. | An inexpensive antiviral drug that stops the replication of the virus. Addressed to adults and children over 3 years old. Not recommended for use during pregnancy. Antiviral ointment |
| Valacyclovir (aka Valtrex) Available in the form of 500 mg tablets. | One of the best drugs for herpes. It differs from Acyclovir in the method of delivery of the active ingredient. Suppresses the activity of the virus and reduces symptoms. When taking the drug, the risk of infection through contact with other people is reduced. Treatment of herpes in 3 days |
| Famciclovir (aka Famvir) Available in the form of tablets 125, 250 and 500 mg. | Just like Acyclovir and Valtrex, it blocks the replication of the virus. Helps in the treatment of simple virus and the virus that causes chickenpox. Famciclovir is effective against viruses resistant to Acyclovir. Famciclovir |
| Panavir Available in the form of a solution for intravenous injection, as well as in the form of a gel and suppositories (suppositories). | Antiviral, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory drug of plant origin. Increases the body's resistance to infections and has an antipyretic effect. |
| Docosanol (aka Erazaban) Available in the form of a cream for external use. | Has an antiviral effect. Intended for use in adults and children over 12 years of age. Pregnant women are prescribed with caution. |
| Proteflazid Available in the form of drops. | Antiviral agent for systemic use. Intended for the treatment of herpes simplex in children and adults. Used in pediatric practice (including in children under 1 year). |
| Flavoside Available in the form of syrup. | Effective in the treatment of herpes simplex, as well as in the treatment and prevention of influenza. Used in pediatric practice (including in children under 1 year). |
The presented list of drugs is far from complete - the doctor, depending on the characteristics of a particular patient, may recommend other drugs. For example, in some cases antibiotics cannot be avoided (if there is a risk of contracting other infections).
Is there any prevention against herpes?
To resist the virus, you need a strong immune system. Therefore, those who suffer from frequent colds on the lips need to pay attention to their immune system. Take care of a healthy, balanced diet, do not forget about sports, maintain a normal daily schedule (first of all, ensure that you get adequate sleep) and try to get rid of bad habits (smoking, etc.).
It is important to practice basic hygiene, including regular hand washing. It is recommended to use personal hygiene products. During infectious epidemics, it is advisable to avoid staying in crowded places if possible.
To reduce the risk of genital herpes, you should use condoms.
Symptoms of different types of herpes
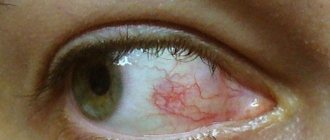
A “sleeping” virus may not bother its host for years. But if for some reason the virus enters the active phase, it is easy to recognize - by its characteristic rashes. The “classic” visual sign of herpes is itchy, watery blisters that can appear in different places - on the face and on the body.
There are several types of herpes virus - they differ in their manifestations. Most often in medical practice, diagnoses such as HSV-1 and HSV-2 are encountered - this is the abbreviated name for herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2.
Cold sores and chicken pox are related diseases caused by herpes. Several types of the virus can “coexist” in one person.
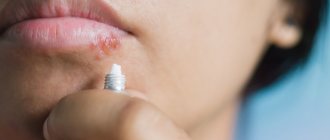
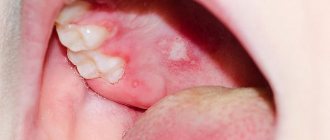
| Many people call this pathology a “cold on the lips,” although the “classic” cold and herpes are different things. We are talking about the herpes simplex virus type 1, which usually “attacks” the lips and nasolabial triangle. Externally, the disease manifests itself in the form of rashes. They represent one or a whole cluster of bubbles with liquid contents. When asked whether there can be a fever with herpes, the answer is positive: many patients complain of fever, headaches and general weakness. Among doctors, there is another name for pathology: when you see a diagnosis such as oral or labial herpes in your medical record, know that we are talking about the herpes simplex virus type 1. Herpes on the lip is usually very itchy |
| The second type of herpes simplex is accompanied by the development of genital (genital) infections. The disease in most cases is asymptomatic or, as with labial herpes, is accompanied by the appearance of blisters (ulcers), but only in the area of the external genitalia. Other signs of HSV-2 are fever, body aches, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes in the genitals. Most often, the disease is transmitted sexually, but infection can also occur from a person with labial herpes. |
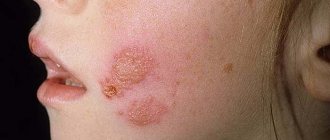
| Virus type 3, also known as the herpes zoster virus, is the culprit of chickenpox. To become infected, it is enough to enter into a conversation with a sick person (transmission occurs through airborne droplets). Having had chickenpox, a person remains a carrier of this virus for the rest of his life. In case of relapse, there is a risk of developing herpes zoster. This disease is characterized by the appearance of itchy rashes throughout the body, as well as fever. Chicken pox |
| Herpes type 4 causes such a serious infectious disease as mononucleosis. This disease is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes and fever; the patient complains of a sore throat and general weakness. The liver and spleen are also affected. |
| Herpes type 5 provokes the development of cytomegalovirus. The disease manifests itself differently, depending on which organ is affected. A runny nose, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, inflammatory diseases of the genital organs - all this can be a sign of pathology. |
| In addition to those described above, there are also types 6, 7 and 8 herpes. Scientists are now studying these viruses. |
How does herpes simplex develop?
- It all starts with itching and/or tingling in the place where herpes develops - as we have already found out, most often this is the area of the nasolabial triangle. The skin turns red and begins to itch.
- Next, the stage of inflammation begins. Swelling appears in the affected area and a small, painful pimple appears - a blister containing clear liquid. Over time, this liquid becomes cloudy. A small pimple(s) gradually increases in size.
- The blisters burst 3–5 days after the onset of the disease. A liquid flows from them, containing an uncountable number of viral particles. During this period, contact with a sick person should be stopped, since the risk of infection is very high. At the site of the rash, ulcers with a purulent crust (scabs) form. When the scab is damaged, bleeding begins.
A natural question for every patient is, how many days does it take for herpes to go away? This usually takes about 10 days. If symptoms do not disappear during this time, you should see a doctor, since herpes can signal the presence of other diseases.
Herpes ointment
Varicella zoster virus
The Varicella Zoster virus (herpes type 3) causes the following diseases:
1. Varicella (chickenpox) , which is characterized by:
- blistering rash on the skin of the trunk, limbs, scalp, mucous membranes;
- symptoms of intoxication;
- fever.
2. Herpes zoster , which manifests itself:
- blistering grouped rashes;
- neuralgia in certain skin segments innervated by sensory nerves (usually along the intercostal nerves, along the trigeminal nerve).
The rash with herpes zoster is accompanied by severe pain with moderate symptoms of intoxication.
Cytomegalovirus infection
An infectious disease that is caused by cytomegalovirus (CMV) and is characterized by a variety of clinical forms (from asymptomatic to severe generalized with damage to many organs) and course (acute or chronic). CMV transmission factors can be almost all biological substrates and human secretions that contain the virus: blood, saliva, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, vaginal secretions, sperm, amniotic fluid, breast milk. Potential sources of infection are organs and tissues in transplantology, as well as blood and its products in transfusiology. Routes of transmission of CMV infection: airborne, sexual, vertical and parenteral.
There are congenital and acquired forms of CMV infection. Congenital CMV infection. During antenatal infection of the fetus, infection occurs predominantly transplacentally. During intrapartum infection, CMV enters the body through aspiration of infected amniotic fluid or secretions from the mother's birth canal.
In older children, acquired CMV infection occurs in a subclinical form in 99% of cases. The most common manifestation of this form of CMV infection in children over one year of age is mononucleosis-like syndrome. As a rule, a clinical picture of acute respiratory disease is observed in the form of pharyngitis, laryngitis, and bronchitis.
Infections caused by the sixth, seventh and eighth types of herpes viruses Type six herpes viruses (HHV-6) can cause erythematous and roseolous rashes (sudden exanthema), lesions of the central nervous system and bone marrow in immunocompromised children. Herpesvirus type seven (HHV-7) causes neonatal exanthema
For the diagnosis of herpes infection, cytological, immunofluorescent, serological and PCR methods are valuable. Virological testing for herpes infection reveals complement-fixing antibodies to HSV-1 or -2 in the mother's blood, fetal cord blood and amniotic fluid. PCR method. The material for testing for herpes is blood, throat swabs, the contents of blisters, ulcers, and urine.
The study of specific antibodies of various subclasses: IgM, IgG1-2, IgG3 and IgG4 to herpes viruses is important. The detection in the blood serum of children of specific immunoglobulins M, IgG3, IgG1-2 in a titer > 1:20, viral antigen and specific immune complexes with antigen indicates the severity of the infectious process (active phase), and the determination of only specific IgG4 is regarded as the latent phase of infection or carriage of maternal antibodies.