The herpesvirus family includes about 100 viruses, and 8 are pathogenic for humans. Many people are familiar with the types that cause herpes infection, such as herpes virus type 1 and herpes virus type 2 . According to the International Classification of Diseases, herpes diseases from the herpes virus type 2 are classified as sexually transmitted infections, since it has been scientifically proven that infection with this type of virus occurs during sexual intercourse. However, in recent years, cases of genital herpes from type 1 virus and, conversely, lesions of the mucous membranes of the nose and oral cavity caused by type 2 herpes have become increasingly common. Scientists attribute this to the increased frequency of oral-genital contacts, which are very popular among young people.
Statistics
According to WHO, acute respiratory viral infections, including influenza, are inferior in frequency of infection to the herpes virus. Diseases caused by herpes virus types 1 and 2 have not been recorded in our country before. The incidence of other types of herpesvirus infections was officially recorded. For example, in Russia and the CIS countries, about 22 million people annually suffer from acute herpesvirus diseases, including chicken pox, infectious mononucleosis and cytomegalovirus infection. Due to the fact that genital herpes has become increasingly common among Russians, the appearance of a chronic form of infection with the presence of a greater number of exacerbations has become more frequent and the quality of life of patients has significantly decreased, its mandatory registration was introduced. According to some data, the number of registered cases of active infection caused by type 2 herpes virus among residents of Russia remains no more than 15% of the real incidence of the disease.
Prevention
Particular importance in preventing exacerbations is given to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. A rational, healthy diet, moderate physical activity, treatment of all infections, concomitant pathologies, elimination of stress and hypothermia are necessary.
When rashes appear, no special measures are taken; it is important to provide the patient with separate dishes and hygiene items, and avoid close contact and kissing until complete recovery. For HSV type 2, the use of condoms is important.
Taking medications for herpes or vaccination can reduce the risk of exacerbations. Source: Prospects for vaccine prevention of herpes simplex. Isakov V.A., Isakov D.V. Bulletin of Hematology No. 3, 2022. p. 4-10.
Sources:
- Features of herpes viruses. Peradze Kh.D., Sukhoruk A.A. Pediatrician, 2010. p. 78-80
- Viruses of the herpes family and immunity. Kharlamova F.S., Egorova N.Yu., Guseva L.N., Guseva N.A., Novosad E.V., Chernova E.V., Uchaikin V.F. Children's infections, 2006. p. 3-10
- Prospects for vaccine prevention of herpes simplex. Isakov V.A., Isakov D.V. Bulletin of Hematology No. 3, 2022. p. 4-10
- Approaches to immunotherapy for recurrent herpes simplex. Shulzhenko A.E., Zuikova I.N. Science of life and health, 2014. p. 130-131
- Modern prospects for the treatment of genital herpes. Khryanin A.A., Reshetnikov O.V. Medical Council, 2022. p. 80-84
- Some information about the morphology of herpes viruses and their properties. Lutsenko M.T., Gorikov I.N. Bulletin of physiology and pathology of breathing No. 38, 2010. p. 74-77
Features of the herpes virus
Once in the body, the herpes virus remains there forever. The infectious agent penetrates the mucous membranes and then invades the nerve cells. At the same time, it can either hide in ganglia and phagocytes, or become active, that is, begin to multiply and infect tissues and organs. The immune system reacts to viral particles that come out of cells. And it does not recognize dormant or latent viruses. As a rule, the pathogen is activated when the immune system is weakened, which can be caused by factors such as ARVI, poisoning, nervous stress, abuse of strong drinks, chronic fatigue and others. In addition, herpes infection provokes a decrease in the body's resistance to various diseases. Herpes virus type 2 and type 1 can cause immunosuppression. For example, often with herpes infection there is a decrease in the activity of the process of capturing and absorbing foreign particles. At the same time, on the one hand, the herpes virus worsens due to the appearance of provoking factors, and on the other hand, it opens the way for pathogenic bacterial and other viral agents into the body.
Herpes type 6 in adults
Herpes virus type 6 is referred to as HHV-6 or HHV-6. This is the common name for the human herpes virus of two subtypes homologous to each other. In adults, the HCH-6A subtype is active as one of the provocateurs of the development of multiple sclerosis.
Multiple sclerosis is a multifactorial autoimmune disease with a predominant lesion of the central nervous system, which is diagnosed in people 20 years of age and older, and very rarely in other age groups.
The most important facts about herpes virus type 6:
- The presence of this particular type of herpes virus in the etiopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis has been proven;
- The clinical picture of MS is chronic inflammation of nerve tissues, including the myelin layer of the brain - demyelination, which is accompanied by degenerative processes in nerve tissues;
- Without treatment, multiple sclerosis inevitably leads to disability, social and psychological isolation of the patient.
There are four types of multiple sclerosis:
- Primary progressive multiple sclerosis. The patient’s condition is characterized by a steady deterioration, a short-term subsidence of the process is possible, and then a rapid relapse;
- Secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Characteristic periods of exacerbation after the first wave of the disease;
- Remitting-progressive multiple sclerosis (Latin remitto - weaken). At a certain point, the signs of the disease disappear, and then there is a sharp return and increase in symptoms;
- Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. It is characterized by periods of disappearance and recovery of symptoms; a long-term stable condition of the patient is observed without visible signs of deterioration in well-being.
Symptoms of herpes type 6
Early symptoms of multiple sclerosis:
- Fatigue, depression;
- Unsteadiness of gait, poor coordination of movements;
- Change in sensitivity (temperature, vibration and tactile).
The main symptoms of MS, which characterize significant changes in the body, in addition to early signs that usually persist and worsen:
- Cognitive disorders, rapid mood swings;
- Visual disturbances (defocus in the form of double vision, decreased visual acuity);
- Difficulties with articulation when speaking (unusual pronunciation of words);
- Dysphagia (impaired swallowing);
- Spasms and cramps;
- Deterioration of sensitivity (lack of pain response);
- Fecal and urinary incontinence, constipation and diarrhea;
- Erectile disfunction.
The nature and degree of manifestation of symptoms of multiple sclerosis are varied, which is associated with the unpredictability of areas of damage to nervous tissue.
Treatment of herpes type 6
For the treatment of multiple sclerosis the following is used:
- Corticosteroids (methylprednisolone, dexamethasone and others);
- Antioxidants, antiplatelet agents, angioprotectors;
- Proteolysis inhibitors;
- Plasmapheresis with drugs;
- Immunomodulators, for example Copaxone;
- Stimulators of interferon production (Betaferon, Rebif, Avonesk);
- Immunoglobulins intravenously, for example, Sandoglobin.
Drugs from other groups may be indicated, depending on the stage and form of the disease. Symptomatic therapy and medical and social rehabilitation of patients with multiple sclerosis prevents the development of complications.
Characteristic symptoms
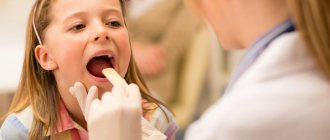
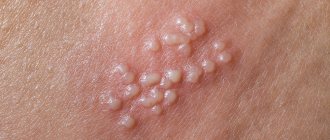
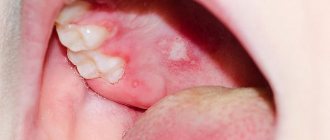
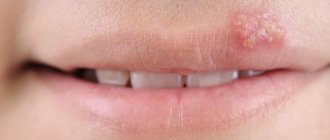
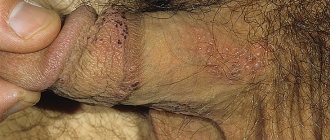
Herpes virus type 2 in the acute phase is characterized by itching and redness of the skin and mucous membranes of the external genitalia, in particular the vagina, penis, scrotum, urethra, anus and inner gluteal and femoral surfaces are affected. Then bubbles filled with liquid appear in these places. After some time, they burst with the formation of a painful wound surface, and then become covered with a crust. During the first infection, general weakness, malaise and low-grade fever often occur. These flu-like symptoms may be accompanied by enlarged inguinal lymph nodes. With recurrent herpesvirus infection, a wave-like course is observed - periods of exacerbation are replaced by periods of relative health (remission).
Exacerbation of herpes
The first relapse of a herpes infection may have pronounced symptoms. As other exacerbations occur, the tendency to pain in the affected area and the frequency of rashes becomes less, the duration of the inflammatory process is shortened. However, in many patients no blisters or crusts form, and relapse is preceded by tingling and burning in the genital area. In some cases, relapses of type 2 herpes virus may be accompanied by difficulty urinating and a small amount of discharge from the genital tract. And for some, repeated episodes of the disease are asymptomatic. The activity of herpes infection directly depends on the state of the immune system. For some, exacerbations may occur 1–2 times throughout their lives, while for others every 3 months, six months, or a year (with frequent weakening of defenses).
Causes
The main cause of the disease is infection with one of the types of viruses listed above. However, clinical signs of herpes do not appear in all people infected with viruses. This largely depends on immunological reactivity and the influence of provoking factors. These include the following influences:
- frequent and prolonged overwork of the body;
- systemic hypothermia or overheating, excess UV radiation;
- physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- insomnia, sleep problems;
- sudden changes in climate, region of residence, time zone;
- colds, decreased immune defense.
The severity of manifestations and the form of the disease depend on age, general condition of the body, and associated factors.
Complications of herpes virus infection
Infection or exacerbation of the herpes virus type 2 poses a risk to reproductive health. During pregnancy, primary infection or recurrence can cause miscarriage, the formation of malformations in the fetus and can lead to stillbirth. An active infection without clinical manifestations most often provokes a risk of infection in a child. In addition, when the brain is damaged, the herpes virus can become an initiating factor for Alzheimer's disease. In the presence of long-term recurrent genital herpes, the likelihood of developing cervical and prostate cancer increases.
Herpes Simplex Virus 1/2, DNA [real-time PCR]
A study to identify the causative agent of herpes viral infection types 1 and 2 (Herpes Simplex Virus 1/2), during which the genetic material (DNA) of the simplex virus is determined using the real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method herpes in a sample obtained from the urogenital tract.
Synonyms Russian
Herpes virus, herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2), determination of herpes by DNA.
English synonyms
Herpes Simplex Virus, Type 1 and Type 2, HSV-1 or HSV-2 IgM or IgG, HSV-1, HSV-2, HHV1, HHV2.
Research method
Real-time polymerase chain reaction.
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Urogenital smear, first portion of morning urine, urogenital smear with prostate secretion, ejaculate, rectal smear.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Women are recommended to take a urogenital smear or urine before menstruation or 2 days after its end.
- Men should not urinate for 3 hours before submitting a urogenital smear or urine test.
General information about the study
The PCR method can detect even a small amount of viral particles in biological material. It allows you to identify herpes viruses regardless of the period of infection, even during the period when antibodies in the blood have not yet formed.
The most common are types 1 and 2 of herpes. Both are contagious and contribute to the appearance of small bubbles (vesicles) on the mucous membranes, which burst, forming open wounds. With HSV-1, blisters appear around the mouth and in the oral cavity, while HSV-2 usually affects areas around the genital area.
The herpes simplex virus can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact when there are vesicles on the skin, and sometimes even when there are no visible lesions on it. HSV-2 is often classified as a sexually transmitted disease, but infection with HSV-1 herpes can also occur, for example, through oral sex. According to WHO, from 50% to 80% of the adult population of developed countries are infected with type 1 herpes and about 20% with type 2. Because the symptoms of type 2 are subtle, 90% of those infected with it may be unaware of their infection.
In the case of primary infection, painful blisters usually form at the site of infection after two weeks, which usually resolve after four weeks. They appear on the genitals, around the anus, on the buttocks or thighs, after which they can burst. You may also experience flu-like symptoms, such as chills and sore throat.
However, blisters with herpes do not always form. Sometimes symptoms of the disease are so mild that they go unnoticed or are mistaken for something else, such as insect bites or allergies. After the infection enters the body and spreads, the herpes virus remains in a latent form. With stress or other diseases that lead to a decrease in immunity, it can become active again. In most cases, herpes simplex is not dangerous to health, but it can cause serious illnesses: neonatal herpes (if a child becomes infected during childbirth from a mother infected with genital herpes) and encephalitis. They can lead to serious incurable neurological diseases and even death. The following factors increase the risk of contracting herpes:
- diseases that suppress the immune system (for example, HIV/AIDS),
- organ transplantation.
Currently, a cure for herpes is not possible, however, there are antiviral drugs that suppress its spread, and also shorten the duration of the acute phase of the viral infection and mitigate the symptoms of the disease.
What is the research used for?
- To detect herpes viral infection of the genital organs in men and women and monitor its treatment.
- To test a woman for herpes before and during pregnancy (if there is a risk of infection).
When is the study scheduled?
If necessary, confirm or deny the fact of genital herpes infection.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: negative.
Positive result
- The body is infected with a virus. The result is indicated in crosses depending on the amount of genetic material identified during the study.
| « » | 2 copies of DNA |
| « » | 102-103 copies of DNA |
| « » | 103-104 copies of DNA |
| « » | 104-105 copies of DNA |
| « » | >105 copies of DNA |
Negative result
- Most often, there is no infection of the genitals with the herpes virus.
What can influence the result?
- Antiviral therapy can reduce the amount of virus in epithelial cells, however, due to the high sensitivity of the PCR method, this rarely leads to false negative results.
- Errors at the stage of taking biological material, when a sufficient number of virus-infected cells do not enter the sample for research, can lead to false negative indicators.
Important Notes
- Herpes is most dangerous for newborns who are infected from their mother, and for patients with weakened immune systems.
- Herpes increases the risk of contracting HIV infection. Moreover, it can make HIV-infected patients even more infectious by increasing the amount of immunodeficiency virus in their blood.
- The herpes simplex virus in combination with the papilloma virus increases the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Also recommended
- Herpes Simplex Virus 1/2, IgM
- Herpes Simplex Virus 1/2, IgG, titer
- Herpes Simplex Virus 1/2, DNA [real-time PCR]
- Herpes Simplex Virus 1/2, immunofluorescence
- Human Papillomavirus of high carcinogenic risk (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59), DNA genotyping [real-time PCR]
Who orders the study?
Gynecologist, urologist, dermatologist, infectious disease specialist, pediatrician.
Medication measures
The main tasks in the treatment of herpetic infection:
– blockade of herpesvirus reproduction;
– achieving improved overall well-being;
– correction of immunity.
To treat herpesvirus infection in acute forms and reactivation of the disease, antiviral drugs and symptomatic therapy are used. Treatment measures include the administration of virostatics and interferons (for example, VIFERON® ). In severe forms of herpes infection, intravenous immunoglobulin is used. Monitoring the maintenance of remission is recommended to be carried out once every 3 months, in the absence of relapse within a year - once every 12 months. especially when planning pregnancy or during pregnancy in women with frequent recurrences
Based on materials:
1. “Herpesvirus infection: epidemiology, clinical picture, diagnosis, prevention and treatment”, Methodological recommendations, Karazhas N.V., Malyshev N.A., Rybalkina T.N., Kalugina M.Yu., Boshyan R.E., Kisteneva L.B., Cheshik S.G., Mazankova L.N., Vyzhlova E.N.
2. “Viferon: therapy for viral infections”, I.V. Nesterova.
Materials were prepared by employees based on open information sources
Loading...
Take other surveys
Diagnosis of HSV and other forms of infection
A preliminary diagnosis can be made based on the typical manifestations of the infection, but a number of herpes tests can confirm the presence of the virus. Laboratory methods for detecting herpes infection include:
- general clinical blood test: the size of erythrocytes, the level of leukocytes are assessed (leukopenia is typical), against the background of a secondary infection, an increase in leukocytes is possible (neutrophilic leukocytosis), ESR is accelerated or normal.
- urine test - changes are possible in case of damage to the kidneys or urinary tract; in other locations, the analysis will be within normal limits;
- blood biochemistry does not have significant deviations; in severe forms, an increase in ALT and AST enzymes is possible;
- ELISA blood test - determines an increase in the titer of IgG antibodies, which indicates infection with the virus. With a fresh infection, IgM antibodies also appear;
- carrying out PCR to detect the DNA of the virus itself in the blood, contents of vesicles or other biological fluids.