Primary syphilis: what you might not know about
From horror stories from Soviet propaganda, we know that syphilis is such a terrible disease in which the nose falls off. In addition to being properly intimidating, these ideas also had a downside. Like, if nothing hurts and your nose is still there, then it’s not syphilis... you can tolerate it.
Judging by the comments, including in my journal, many are still in such misconceptions to this day.
A little history
The science of syphilidology arose due to the enormous incidence of syphilis and its social significance. The experimental basis of syphilidology was often completely unethical experiments on people.
To understand how this terrible infection proceeds, healthy people were infected with syphilis (France, Russian Empire) or those infected were deliberately left without treatment (USA, Sweden, Norway). These absolutely inhumane experiments, however, brought a clear understanding of the stages of the infectious process and its patterns.
Onset of the disease. "Chancre"
Treponema pallidum, penetrating the body, spreads quite quickly through the lymphatic system and can enter any organs and tissues. However, the first manifestations of the disease should not be expected immediately, but after the incubation period, which averages one month. This period can vary from 9 to 90 days depending on many factors: taking antibiotics at this time, the presence of other diseases, alcohol or drug addiction; Also, the incubation period may change for those people who have encountered this infection more than once, etc.
You should know that syphilis infection can occur not only through sexual contact. And although there have been few such cases lately, they still occur.
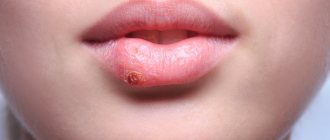
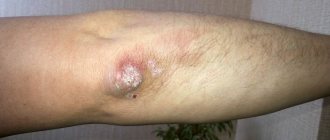
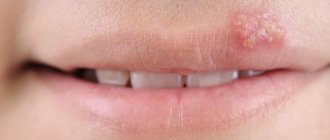
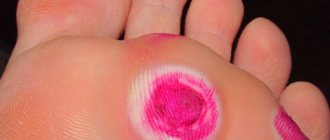
So, after about a month, primary syphiloma (hard chancre) forms exactly in the place where the treponema was introduced. Dermatologists have a saying: “Syphilis is the first to punish the organ that sinned.”
So if the lesion is still on the genitals, and not in some other place, the “everyday” version of infection looks doubtful, although it is not excluded (and who said that medicine is easy?).
A chancre is an ulcer or erosion that, depending on its location, can look different, but, as a rule, it has a regular, round shape and clearly defined boundaries. Actually, the term “chancre” is not entirely adequate; it is more correct to say “primary syphiloma.”
The hard base of syphiloma, which gives the name to the symptom, is not always pronounced, and only a doctor can distinguish a specific ulcer from others. In most cases, chancre is completely painless, which misleads those suffering. 8 out of 10 victims, proudly entering my office and showing skin lesions, refer to very, very violent sex, sports, tight trousers and use the word “rubbed”... I have to disappoint them and send them for tests. And, on the contrary, patients who come with huge round eyes and shouts “Doctor, I think I have syphilis - it hurts so much that I can’t walk” more often find solace in some other diagnosis.
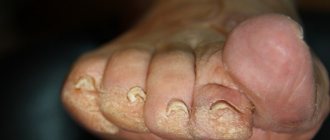
There are also atypical chancre. A chancre-felon (it is very painful), a chancre-amygdalitis (in the tonsils), a chancre-crack (in the folds of the skin, for example in the corner of the lips or the anus) and indurative edema, when the affected area swells, can develop on the fingers. But they are rare.
...And other symptoms
Other symptoms of infection include enlarged lymph nodes and lymphatic ducts. These appear as small, firm balls under the skin near the original lesion. If the primary lesion occurred on the genitals, then, accordingly, the lymph nodes will be enlarged in the groin area. The affected lymph nodes have a hard-elastic consistency, are not fused with the surrounding tissue, are not “hot”, and are painless.
The lymphatic duct may also be enlarged. It looks like a fairly dense, painless cord, reminiscent of a ballpoint pen refill that has gotten under the skin.
Attention! If you only have the last symptom, do not be alarmed, this may be a variant of the norm.
In general, the “troika” - primary syphiloma (chancroid), syphilitic lymphadenitis and syphilitic lymphangitis - makes up ALL the symptoms of primary syphilis. As you can see, syphilis already exists, but there are no falling noses yet, and not everyone will have them soon. But you need to be examined and treated, because there are no shameful diseases!
By the way, about analyzes
It is important to know that blood tests may be negative throughout the incubation period and as long as two weeks after the onset of symptoms. So if you took tests somewhere anonymously and you received a negative (good) result, but no one examined you, do not rush to rejoice. It’s better to have courage and go to a dermatovenerologist, because after the primary period (if left untreated), the secondary and tertiary periods may begin, and this is much worse.
But what about the USSR?
In the USSR there was syphilis. Both after the Civil War and after the Patriotic War. But really punitive Soviet venereology, grossly trampling on the rights of the sick in favor of the healthy, dealt with it. Only isolated cases remained, so students at that time had to see the above-described symptoms only on dummies. However, perestroika put everything in its place, now there is enough syphilis, and, of course, it is better to prevent it (read the article “
Prevention of sexually transmitted infections
"), than treatment.
If you are interested in what the secondary and tertiary periods of this disease look like (this is where the horror-horrors accumulate), what latent syphilis is, how this infection affects the nervous system and internal organs, and how dangerous this disease is for pregnant women, write questions in the comments, and I will try to answer them in the next article.
Leonid Shchebotansky
Photo istockphoto.com
Differential diagnosis
Syphilis is a disease very similar to a large number of other diseases, especially when skin rashes appear as a secondary disease. Therefore, sometimes even experienced doctors are confused in the diagnosis.
Table No. 1. Differential diagnosis of syphilitic rashes and similar diseases:
| Differential diagnosis | Differences between another disease and skin manifestations of secondary syphilis |
| Syphilitic roseola and measles | The skin manifestations are very similar, but measles is accompanied by fever, symptoms of intoxication, rhinitis, attacks of nausea and vomiting. |
| Papular syphilide and psoriasis | With psoriasis, the rashes have a chronic course with frequent exacerbations. Papules tend to grow peripherally and unite. Damage to the nail plates is observed. |
| Vesicular syphilide and vesicular lichen | The rash is accompanied by itching, burning and pain. The rash appears after swelling and inflammation of the skin. |
| Syphilitic leukoderma and vitiligo | Rashes of various shapes and ivory colors tend to grow peripherally and unite. |
| Diffuse syphilitic alopecia and favus of the scalp | Spots appear followed by transformation into a dry round element of a yellow hue. Prone to hair spreading and atrophy. |
Description of the disease
Ways of transmission of infection:
- The sexual tract occurs during any type of sexual intercourse (including anal, oral) due to the fact that the highest concentration of Treponema pallidum is determined in the discharge of syphilitic chancre, sperm, and vaginal secretions. When any of the listed liquids come into contact with the mucous membrane of the genital organs, oral cavity, or rectum, there is a high risk of transmission of infection from a person affected by syphilis to a healthy person.
- The contact-household route is implemented many times less frequently than the sexual route, but its role in the transmission of infection cannot be excluded. If there is a syphilitic chancre in the human oral cavity, treponemes can be transmitted through kissing, using shared utensils or cigarettes. If the chancre is on the surface of the body or genitals, then transmission through clothing, bedding, and towels is possible.
- Transfusion route – transmission of infection through blood transfusion. At the moment, this route is extremely rare, due to the fact that all blood at transfusion stations undergoes multiple, thorough testing for various sources of infection.
- The transplant route is the transmission of infection during organ transplantation. Also very rare due to the above reasons.
- The vertical route is transmission from mother to fetus both during the intrauterine development of the child and during childbirth.
- A professional path arises for people who work with blood, body secretions, whose profession is associated with injury to the surface of the skin (doctors, laboratory assistants, tattoo artists).
Syphilis occurs in stages and, in the absence of proper treatment, can last for decades. Each stage has a specific symptom complex.
Prevention
Disease prevention measures:
- Due to the fact that the main route of transmission of syphilis is sexual, the most important aspect of prevention is avoiding sexual contact with infected people.
- There is also preventive treatment that is given to pregnant women who have previously had syphilis; newborns whose mothers have not received a full course of treatment for syphilis.
- Also, special therapy is prescribed for people who have had sexual or personal contact with an infected person, if no more than 60 days have passed since the contact.
Differences between ecthyma in syphilis and normal
Common ecthyma has a staphylococcal or streptococcal etiology.
Rarely it is caused by gonococcus.
With simple ecthyma, a bubble or pustular element is formed.
The morphological element appears only against the background of infiltration.
It dries out quite quickly.
A crust forms.
After it leaves, an ulcer forms, the bottom of which bleeds and is covered with plaque.
Ecthyma heals in 2-3 weeks.
In some cases, it can heal without forming an ulcer.
Main localization:
- hips
- gluteal region
- shins
- hands
The main difference between ordinary ecthyma is that there is no infiltrate around the ulcer.
The crust covers the ulcerative defect completely, not partially.
Because ordinary ecthyma does not have a tendency to infiltrative growth.
Frequently asked questions to the doctor
Rash on the penis
Good afternoon, I discovered a red rash on the head of my penis. Tell me, could it be syphilis?
Hello, rashes on the head with syphilis are one of the first symptoms of the disease, but this does not mean that the diagnosis has been confirmed. Also, the cause may be other pathogens or an allergic reaction to hygiene products or underwear. It is better for you to consult a doctor and take all the necessary tests.
Rubbers and gums: flow features
The rubber layer in the bones eats away, which leads to fractures. The affected liver increases in size, which simulates various hypertrophies, subsequent scarring leads to cirrhosis. On the skin, gummas appear as subcutaneous nodes, which eventually open, forming an ulcer. The ulcers, decomposing, increase in size, then, over time, clean off and heal, leaving a scar. Rarely, gummous nodes are not opened; in such cases, they can resolve without leaving scars on the skin. Without proper treatment, gummas can affect tissue for years, penetrating deeper, involving muscles, periosteum, bones and joints. If the mucous membrane of the nose or palate is affected, gummas can deform them to the point of impaired breathing and disfigurement of the nose. Gummous formations usually affect the nasal septum, which stimulates the secretion of mucous masses. As a result, a dry crust forms, but if it is peeled off, there will be bleeding. Changing the shape of the nose occurs when the nasal bones are rejected. The soft palate becomes deformed and collapses due to the same processes. Damage to the aorta leads to an aneurysm, which can lead to atrophy. Pressure from the sternum and adjacent parts of the ribs on the aorta often provokes hemorrhage, leading to death. Damage to organs at this stage of syphilis leads to various types of disorders, often incompatible with life.
How does infection occur?
Among syphilidologists, there is an opinion that syphilis infection occurs exclusively through the “entry gate” (tears, wounds, scratches on the mucous membrane or skin), however, spirochetes can infect the body, penetrating even through minor injuries. Therefore, the skin and mucous membranes do not prevent the source of syphilis from entering the body.
Since the source of syphilis infection is its carrier, infection often occurs through interaction with it. For syphilis, the typical methods of infection are: sexual, household, blood transfusion, occupational and transplacental. At birth, a child can become infected with syphilis from the mother while passing through the birth canal. Breastfeeding also carries risks. Milk is infected even when patients have hidden symptoms of syphilis; it affects the child’s body from the first feeding. There is no innate immunity to syphilis. Almost any type of infection leads to the development of syphilis and damage to all vital systems of the body.
The difference between acne due to syphilis and chickenpox
Smallpox syphilide is most easily confused with chickenpox.
This disease is diagnosed mainly in childhood.
In adults it is more severe.
The difference is a pronounced intoxication syndrome.
It occurs 2-3 days before acne appears.
Severe hyperthermia, cephalalgia, myasthenia gravis, and sore throat are noted.
There are many foci of rashes, and they are located in groups.
While with syphilis there are few of them, and they are single.
Another feature of chickenpox is the extremely rapid transformation of morphological elements.
The entire cycle can take only 8 hours.
First, pink spots form.
From them papules are formed.
They turn into bubbles.
They usually contain completely clear liquid.
Unlike syphilis, in which the contents of the vesicles are often purulent.
With chickenpox, there is severe itching of the skin.
Treatment of syphilitic rash
Treatment of syphilitic rashes during all periods of the disease is not carried out separately, since it is only a separate symptom of the disease. Along with it, the entire body is affected and complex therapy for the disease is required.
To treat the disease, antibacterial agents from the penicillin series are used; if they are intolerant, other antibiotics from the group of macrolides, tetracyclines and cephalosporins are prescribed. The schematic prescription of drugs will depend on the stage of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
Treponema pallidum is most sensitive to penicillin-containing drugs that are administered by injection.
Table No. 2. Treatment at all stages of syphilis:
| Stage of syphilis | Features of treatment |
| First | Therapy at the first stage is carried out using water-soluble penicillins. Drugs in this group are most active against the causative agent of syphilis. Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting, since the drugs require frequent injections to maintain the required therapeutic concentration. The penicillin group is the drugs of choice, not only because of its high efficiency, but also because of its availability. The price of medicines is much lower than similar ones. Medicines:
|
| Second | Treatment of the second stage does not differ significantly from the treatment of primary syphilis; penicillin drugs are also prescribed. If they are intolerant, an alternative replacement is selected from the group of macrolides, tetracyclines and cephalosporins. Replacement drugs:
|
| Third | Therapy of the third stage is complicated by pathological lesions of the body, so treatment is prescribed based on the degree of damage to the body and the patient’s condition. As with the first two stages, the main thing is to take antibacterial drugs, but according to a specific regimen prescribed by the doctor. Further, complex treatment includes taking bismuth-based drugs and medications for the symptomatic treatment of damaged organs. |
Important. The instructions for bismuth preparations prohibit the use of the drug by patients with renal and liver failure.
The video in this article is about skin lesions caused by secondary syphilis.