Causes of papillomas, their types and location
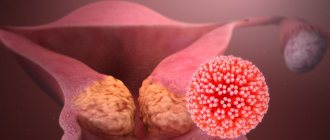
The cause of skin papillomas is the human papillomavirus (HPV). Science knows more than 150 types of HPV, they are divided into three groups:
- Non-oncogenic papillomaviruses - types 1, 2, 3, 5.
- Papillomaviruses of low oncogenic risk (6, 11, 42, 43, 44).
- Papillomaviruses of high oncogenic risk (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 51, etc.).
Viruses of the last two groups, with varying degrees of probability, can cause the development of malignant neoplasms.
Depending on the type of HPV, papillomas are divided into the following types: ordinary papillomas - also known as vulgar warts, filamentous growths, flat papillomas, genital papillomas - also known as condylomas, plantar warts, juvenile warts and papillomatosis.
The most common are vulgar, filiform and genital papillomas.
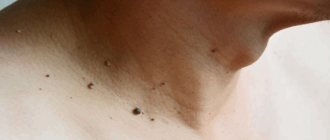
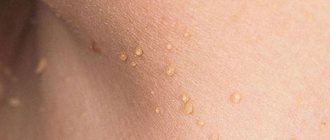
- Thread-like forms of papillomas are more common in people aged 40+ and are localized in areas with thin skin - on the chest, armpits, neck, etc.
- Vulgar warts most often “attack” the skin of the feet, palms, fingers and toes, but can appear on any other parts of the body. Often recur in conditions of decreased immunity.
- Condylomas appear only on the mucous membranes. They can affect the glans penis, foreskin, vagina, and labia minora.
- Plantar warts appear on the rough skin of the feet and on the balls of the toes.
- Papillomatosis is a generalized form of the disease, manifested by the formation of growths throughout the body.
Complex conditions are a consequence of untreated papillomas
- Local epithelial hyperplasia . Consequence of infection with papillomavirus types 13, 32. The affected area looks like a rash of papillary neoplasms on the tongue and along the edges of the lips. Papillomas can merge with each other, forming a clearly visible area.
- Precancerous conditions and cancer -
many forms of the human papillomavirus cause the development of neoplasms prone to malignant degeneration. It is in this regard that early diagnosis and detection of papillomavirus makes it possible to detect and remove oncological tumors of the cervix and other organs in the early stages of their development.
How does HPV infection occur?
The mechanism of transmission of the virus is contact; the source of infection is the patient or the virus carrier. HPV can be released not only from growths on the skin, but also circulate in the blood, saliva and urine. In this case, infection can occur in 4 main ways:
- through contact and everyday life;
- sexually;
- during childbirth from mother to child (which may be the cause of laryngeal papillomatosis);
- during autoinoculation (self-infection or dispersion of the pathogen from existing foci during combing, shaving, or using a hard washcloth).
The risk of HPV infection usually depends on the state of the human body’s immune system, viral load and the presence of microtraumas and other inflammations on the skin and mucous membranes.
Even when infected with the HPV virus, papillomas do not always form on the skin and mucous membranes. The virus is localized in the basal layer of the epithelium and can remain inactive for a long time. Only under certain conditions (weakening of the immune system, stress, exposure to unfavorable environmental factors) do the processes of its replication start, which leads to cell proliferation and the appearance of tumors.
What do condylomas look like?
The formation of growths in the intimate area is a common reason for girls to make an appointment with a gynecologist. Papillomas on the labia are small white growths. Vaginal papillomas can be of 2 types: exophytic and endophytic. The former are characterized by a papillary surface and a pointed shape; they are localized in the superficial layer. As a rule, they are provoked by HPV with a fairly low level of oncogenic activity. The latter are flat, they usually grow deep into the epithelial tissue and can cause pathologies in healthy tissue.
If such condylomas are not treated in time, the risk of developing cancer increases.
Indications for removal
The only way to treat already “formed” papillomas is to remove them. Indications for removal of tumors primarily include:
- Aesthetic problems. Papillomas are skin growths that are perceived as an aesthetic defect, especially when they are localized in open areas of the face and body.
- Papillomas can be constantly injured, cling to clothes, combs, etc. and due to this, quickly spread throughout the skin, soreness, inflammation, cracks and even bleeding may appear in the area of the tumors.
- Considering that some types of papillomaviruses have a high risk of oncogenicity, large papillomas (more than 6-10 mm) may be prone to degeneration, so timely removal of such tumors will prevent a serious illness in the patient.
How dangerous are papillomas on the body: why they need to be removed
Papillomas are harmless only in appearance. These neoplasms, in the absence of timely and adequate treatment, quickly spread throughout the body to healthy tissue. This process is called autoinaculation. The result of the proliferation of neoplasms is at least multiple warts.
Of course, warts - papillomas on the body - are very ugly, but this is not the only problem. A good dermatologist will tell you why papillomas on the body are dangerous - such neoplasms are susceptible to melanization - malignant degeneration of the tumor. How quickly the process will proceed and whether it will begin at all depends on the location of the papilloma and the type of HPV. Genital warts growing on the cervix are especially dangerous. The degeneration of such formations into cancer occurs in every second case.
The structures that form on the skin as a result of damage by the papilloma virus are usually not accompanied by pain, itching or burning, which often causes negligence on the part of the patient. But since papillomas almost always come into contact with clothing, there is a high risk of damage. The result will be severe bleeding, infection and the formation of unsightly scars on the skin. From all this follows the answer to the question of whether it is necessary to remove papillomas on the body - of course it is necessary!
Methods for removing papillomas
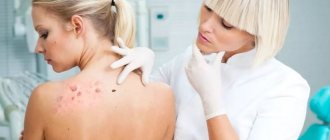
In our medical center, before removing a tumor, a dermatologist examines it and, if necessary, performs dermatoscopy in order to differentiate the type of papilloma and select the optimal method of removal.
It is possible to get rid of papillomas in our clinic without surgery using the destruction of formations using a laser, radio knife and plasma. Removal of papillomas with a laser, especially removal of papillomas on the face, is not carried out so often due to the high traumatic nature of the method and the possibility of hypopigmentation and scarring. Preference is given to radio wave destruction, as well as diathermocoagulation. These methods are highly effective and low traumatic.
- The radio wave method is one of the most effective and least traumatic ways to remove almost all types of papillomas. It is performed on the Surgitron DF-120 device (Ellman International Inc, USA). Removal of the tumor occurs due to local evaporation of cells under the influence of heat generated in the tissues in response to the penetration of radio frequency waves. The cells evaporate and the tissues move apart as if cut with a scalpel. In addition, instant coagulation of blood vessels occurs in the treatment area, so there is no bleeding and no damage to surrounding healthy tissue. In this aspect, laser removal of papillomas is significantly inferior to the radio wave method.
- Diathermocoagulation using the Plasmaskin device (Ultramed, Russia) is a non-contact effect on the affected tissue with a plasma beam. The high temperature of the plasma (up to 2000-2500 C) is combined with the bactericidal effect of an air flow containing a high concentration of ozone and has a virus-destructive effect, destroying HPV DNA, which prevents its spread.
The use of radio wave energy on the SURGITRON DF-120 device (Ellman International, Inc., USA) is the method of choice for removing most forms of papillomas, regardless of their location (face/body), and here’s why:
- Radical - no relapses;
- Rapid epithelization - healing;
- Atraumatic - no complications, no marks or scars remain on the skin;
- Painless - anesthesia is required only in cases of large tumor sizes.
- Complete safety of procedures.
During the destruction of papillomas, anesthesia is usually used. Application anesthesia with the application of lidocaine cream can be used, or infiltration anesthesia, when the site of papilloma localization is injected with an anesthetic solution (Ultracaine). The choice of pain relief method is determined by the size and location of the papilloma.
If the patient has no contraindications, removal of papillomas in Moscow in our clinic can be carried out on the day of treatment, immediately after an appointment and examination by our specialist. In this case, no additional tests are required.
In order to prevent relapses after removing a large number of tumors, our experts recommend taking immunomodulatory drugs. Immunomodulatory therapy is selected individually.
Local antiviral herbal remedies
Ammonium glycyrrhizinate
The active component of the drug, activated glycyrrhizic acid, is obtained from licorice root. It has a complex immunostimulating, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antipruritic effect. Glycyrrhizic acid interrupts the replication of a number of DNA and RNA viruses, including herpes simplex virus, human papillomavirus, and cytomegalovirus [5].
Indicated as a drug for the treatment of human papillomavirus infection and herpes simplex virus, including infection with oncogenic viruses. Available in the form of a spray, which is sprayed onto the mucous membranes and affected areas of the skin.
Vacation: without prescription.
+
It has a wide range of indications, including the prevention and treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis, discomfort in the genital area. Can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding; well tolerated.
Podophyllotoxin
The active component of podophyllin, a derivative of plant extracts isolated from the rhizomes with roots of Podophyllum thyroid - a plant of the barberry family. It has pronounced antitumor and antiviral properties and has a cytotoxic effect. When used externally, it cauterizes and mummifies condylomas. It is used as a drug for local treatment of human papillomavirus. Available in the form of a solution for the treatment of genital warts [8].
Release: by prescription.
+
Proven effect. According to research, a 0.5% solution of podophyllotoxin reduces the number of anogenital warts from 6.3 to 1.1, destroying about 70% of formations [8].
!
Care must be taken when using - contact with healthy skin can lead to ulceration. Local reactions during use, allergic reactions. The physician, when dispensing this antiviral drug for papillomas and condylomas, must draw the client’s attention to this feature and remind him that the drug should be stored out of the reach of children.
Tetrahydroxyglucopyranosylxanthene
Russian drug. The active component is isolated from the Alpine kopek plant or the yellow kopek plant.
According to the instructions, it has antiviral activity against HSV-1 and HSV-2, as well as cytomegalovirus and some other DNA-containing viruses. In addition, the drug presumably activates cellular and humoral immunity, inhibits the growth of a number of bacteria and pathogenic protozoa, including Trichomonas, and also has a moderate anti-inflammatory effect. Used in the form of an ointment as part of the combined treatment of acute and recurrent forms of herpes, including genital herpes [5].
Vacation: without prescription.
+
Favorable safety profile, the ability to be used as part of complex treatment.
Polysaccharides of Solanum tuberosum shoots
A Russian prescription drug, the active component is obtained from the shoots of tuberous nightshade. According to the instructions, it exhibits an antiviral effect against HSV-1 and HSV-2, promotes the induction of interferons and increases the immune response [5]. It should be noted that the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug have not been studied. Vaginal suppositories are used in complex therapy of genital herpes.
Vacation: without prescription.
+
High safety profile. Side effects are rare.
Desmodium canada herb extract
An antiviral drug for herpes of plant origin, created from a dry extract of the herb Desmodium canadensis. According to the instructions, it exhibits antiviral activity against herpes viruses and stimulates the production of interferon [5]. The ointment is indicated for use in acute and recurrent forms of herpes, including urogenital.
Vacation: without prescription.
+
High safety profile - no side effects identified.
Hyporamine extract
Russian development based on sea buckthorn leaf extract. According to the instructions, it is active against herpes simplex viruses, cytomegaloviruses and some others [5]. An ointment containing hyporamin extract is indicated for the treatment and prevention of episodes of herpes, including genital herpes.
Vacation: without prescription.
+
High safety profile; Possibility of use during pregnancy and lactation (after consultation with a doctor).
What will happen to the skin after papillomas are removed?
The next day after the procedure, a brown crust forms at the site of the removed tumor. Healing takes from 2 to 7 days, it all depends on the size of the removed papilloma. After healing, the crust will come off on its own. The main thing at this time is not to wet or injure this area.
After the procedure, the doctor gives some simple recommendations for further skin care.
In our clinic, it is carried out using modern equipment by highly qualified doctors, which allows us to solve problems of papillomas removal quickly, efficiently and safely. We use disposable consumables, which guarantees maximum patient safety.
Are there any special recommendations for skin care after the removal procedure?
We issue the following recommendations in the form of a reminder to our patients:
- During the first 24 hours, do not wet the removal site.
- Treat the wound with Fukortsin solution 2 times a day for 3-5 days or Baneocin powder.
- Men: do not shave in the area of removal for 3-4 days.
- Women: do not apply cream or decorative cosmetics to the removal area for 3-4 days.
- You cannot pick or remove the crust yourself!!! in order to reduce the likelihood of atrophic/keloid scars, hypo- and hyperpigmentation.
- In cases of removal of large tumors, after the crust is rejected, apply Levomekol ointment locally 1-2 times a day for a month.
- Before going outside, be sure to use sunscreen on the face and open areas of the body with an SPF of at least 50, especially on sunny days (to prevent pigmentation of the treated areas).