Causes of tinea versicolor
The content of the article
Ringworm affects middle-aged people. Medicine identifies the causes that lead to the appearance of this disease in humans. These include:
- Predisposition to fungal skin diseases.
- Disruptions in the course of physiological processes in the epidermis.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Lack of a good night's sleep.
- Lack of rest.
- Time zone change.
- Excessive hygiene, using antiseptics.
- Improper functioning of the human immune system.
- Frequent bathing in salt water.
- Lack or excess of vitamins.
- Wearing clothes made of synthetic materials.
- Improper functioning of the lymphatic drainage system.
- Long-term use of steroid hormones.
- Nervous system problems.
- Hormone imbalance.
- Lack of hygiene measures in public places.
Tinea versicolor
Pityriasis versicolor (pityriasis versicolor) is a long-term fungal disease affecting the epidermis, which is manifested by the appearance on the skin of pigmented spots of various shades: yellow, pink, brown, and characteristic pityriasis-like peeling. There are no signs of inflammation. Pityriasis versicolor is diagnosed using the Balzer iodine test, fluorescence examination and microscopy of exfoliating scales. Treatment is carried out with antifungal ointments and solutions. Pityriasis versicolor of a common form requires general antimycotic therapy.
Causes of pityriasis versicolor
• The causative agents are the fungi Malassezia furfur, Pityrpsporum orbiculare and Pityrosporum ovale, and these species differ in their ability to transform into one another; • Infection occurs only in isolated cases with close and prolonged contact with a patient; • At the same time, the likelihood of developing pityriasis versicolor is largely determined by predisposing factors.
Factors that create a favorable background in the body for the development of pityriasis versicolor are:
• Weakening of the immune system; • Increased sweating; • Endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, Itsenko-Cushing's syndrome, obesity); • Changes in the chemical composition of sweat; • Vegetative-vascular dystonia; • Violation of the skin barrier function with frequent use of antibacterial gels and soaps; • stressful effects on the skin (excessive tanning, solarium, etc.).
Symptoms of pityriasis versicolor
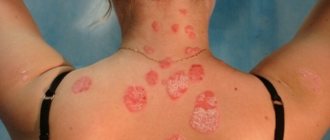
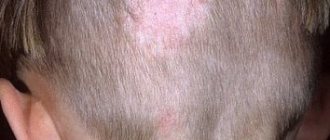
Most often, pityriasis versicolor appears on the skin of the back and chest. Less commonly, the neck, sides of the torso and abdomen are affected. In children and adolescents, spots can be localized on the skin of the extremities, in the armpits and on the scalp. There is no symmetry.
A patient with pityriasis versicolor, as a rule, does not notice any subjective sensations. In some cases, slight itching is observed on the affected skin areas. The occurrence of pain, burning or other unpleasant sensations indicates a secondary infection of the skin with bacterial flora.
Pityriasis versicolor has a long-term (several years) course. In the absence of systematic therapy after treatment, relapses of the disease may occur. Pityriasis versicolor often heals with exposure to sunlight. Areas previously affected by lichen do not tan and remain white against the background of tanned skin (pseudo-leukoderma).
Diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor
Pityriasis versicolor is often immediately diagnosed at a consultation with a dermatologist during examination and dermatoscopy of areas of skin with discoloration. To confirm the diagnosis, a Balzer iodine test is performed, which consists of applying a 5% alcohol solution of iodine to the skin. Due to the looseness of the affected areas of the epidermis, the skin in these areas absorbs iodine better and is colored more intensely than in healthy areas. With the same success, you can use solutions of aniline dyes for testing: brilliant green, iodine, fucarcin. The presence of Beignet's symptom or the “shavings phenomenon” is also determined: peeling of the skin when it is lightly scraped off on the surface of pityriasis versicolor spots.
It is also necessary to distinguish pityriasis versicolor from syphilitic roseola, and areas of pseudoleukoderma from syphilitic leucoderma. Syphilitic roseola does not peel off, has a pink color, and disappears when pressed. Syphilitic leucoderma in its appearance resembles a lace mesh, and not confluent spots of reduced pigmentation. To differentiate pityriasis versicolor from syphilitic manifestations, the patient may be prescribed the following tests: microscopy of a scraping for Treponema pallidum, PCR diagnosis of syphilis, or RPR test.
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis until the manifestations of pityriasis versicolor completely disappear. Local antifungal agents are used: 5% salicylic ointment, 3-5% salicylic alcohol, 5-10% sulfuric ointment, 3-5% resorcinol alcohol, terbinafine, bifonazole, clotrimazole, cycloperox, terbinafine, naftifine, etc. Common pityriasis versicolor or its relapsing course is an indication for general antifungal treatment. It is carried out by ingesting antifungal drugs such as itraconazole, ketoconazole.
Prevention
Prevention of recurrence of pityriasis versicolor includes a repeated course of antifungal treatment, regular water treatments and therapy for hyperhidrosis. To prevent infection of the patient's loved ones, the patient's clothes and linen are disinfected. People who are in constant contact with the patient are examined using a fluorescent lamp.
Treatment and tests are ANONYMOUS!
Method of infection
Mushrooms can come into contact with the skin of a healthy person, but with strong immunity, the body uses protective functions and the disease does not occur.
Main routes of transmission:
- Skin contact with the carrier.
- In public places: shower, fitting room.
- Use of a person’s personal belongings: towel, washcloth.
When infected with this microorganism, symptoms do not appear for 2 weeks to several months. They may not appear at all unless a situation arises when the immune system weakens.
How is pityriasis versicolor transmitted?
Pityriasis versicolor is transmitted through household contact, but this is rare: the disease is not very contagious. The causative agent of pityriasis versicolor, a fungus from the genus Malassezia, is present on the skin of most people, but does not penetrate the epithelium and does not lead to the appearance of a rash. However, under the influence of various factors, yeast transforms into a pathogenic form and begins to destroy skin cells. This process can be triggered by various factors: from excessive sweating to endocrine disorders.
Despite the low contagiousness of this type of lichen, patients are advised to adhere to some recommendations:
- do not share bed linen or towels;
- do not wear other people's clothes;
- do not visit baths, saunas, public swimming pools.
You should also take special care to disinfect the patient’s underwear, clothing and hats: wash at high temperatures (possibly boiling), iron with a hot iron, use steam treatment.
Recommendations
During treatment, hygiene rules must be observed. Wash clothes and bedding in high temperature water. Iron clothes on both sides. Clean the premises thoroughly and every day. Change the washcloth frequently and disinfect it.
- Stye: causes, symptoms and treatment
Ringworm on the face - types, causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention. 115 photos and videos of disease manifestations
Ringworm on the leg - 125 photos of what lichen looks like, common lesions and video tips on choosing a treatment method
You cannot be in the sun; the spots become light and differ from healthy skin. During treatment, the diet should be complete with a sufficient amount of vitamins, vegetables and fresh herbs, and include cereals and dairy products.
A healthy lifestyle, rest and good sleep during the treatment process will help you heal quickly. When treating hair, it is better to use detergents with ketoconazole.
2. Causes of the disease
Pityriasis versicolor is caused by the fungi Malassezia furfur and Pityrpsporum orbiculare.
Their habitat is the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
The causative agent of pityriasis versicolor is conditionally pathogenic, that is, it is transmitted from person to person, but does not cause the disease itself in everyone. The likelihood of infection and the onset of the disease increases by a number of factors - external and internal:
- increased sweating and oily skin;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- high blood sugar;
- treatment with corticosteroids;
- decreased immunity;
- hormonal disorders;
- chronic diseases;
- solar radiation;
- hygiene violations;
- stress and metabolic disorders.
It has been noted that the disease affects mainly people of the middle age group. Children under 7 years of age practically do not get pityriasis versicolor.
Visit our Dermatology page
How to treat lichen on the face
Treatment of any type of lichen on the face involves both getting rid of the cause of the disease and the symptoms.
General measures for the treatment of all types of lichen can be considered:
- antifungal and antiviral drugs;
- antibiotics (erythromycin, penicillin, ampicillin, gentomycin, tetracycline);
- vitamins (groups B, A, D, C and E);
- antiallergic (tablets - tavegil, suprastin, loratadine, diazolin);
- hormonal (ointments - flucinar, lorinden, sinalar, prednisolone, betamethasone, polcortolone, oxycort).
Private treatment methods are presented in the table:
| Disease | Drug and method of administration |
| Shearing superficial | If eyelashes and eyebrows are affected, they need to be plucked. Then an alcohol solution of 0.2% brilliant green (brilliant green) is carefully distributed along the edge of the eyelid. Then an ointment, cream or spray is applied, the main component of which is intraconazole (orungal, itracon) and terbinafine (lamisil, exifin) (for a month and a half). In complicated cases, griseofulvin is prescribed in tablets at the rate of 22 mg per kilogram of body weight. |
| Pink | Here you need acyclovir (200 mg 5 times a day), which is taken orally for 5 days (all except one-year-old children). Salicylic ointment is effective for treating lesions (twice a day). A combination of sulfur ointment and pharmaceutical birch tar, a teaspoon of each (morning and evening), will relieve inflammation. |
| Red flat | Absolutely necessary: hormonal ointments applied two to three times a day (reaferon), vascular preparations (tablets - xanthinol, trental), sedatives in tablets (diazepam), regenerating (solcoseryl ointment), exfoliating (belosalik), antibiotics. Physiotherapy has a positive effect: laser, magnetic and PUVA therapy. |
| Pityriasis | Shampoos for washing the body and face - sulsen and nizoral - with simultaneous intake of fluconazole capsules (three times a day), ointments with zinc and salicylic acid are remarkably helpful. |
| Weeping | In this case, lichen is of particular importance in relieving allergy symptoms with the help of intravenous administration of saline. solution with calcium and magnesium preparations, taking activated carbon tablets. In addition, the following are suitable: baths with sea salt and medicinal mud; cryotherapy; paraffin wraps; medicinal teas and herbal baths; laser treatment. |
| girdling | Acyclovir or famciclovir is used according to the instructions (both in injections and tablets) for a week. Be sure to take painkillers - analgin, ibuprofen. |
| Psoriasis | Cytostatics (cyclosporine) and drugs containing vitamin A - retinol, (isotretinoin), anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, antiallergic ointments (flumethasone, triamcinolone) are taken. Diet and physical therapy are of great importance. |
Symptoms in humans
Typical symptoms of pityriasis versicolor in humans are (see photo):
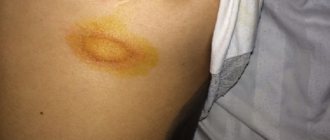
- The appearance of pink spots with a yellowish color;
- A gradual change in their color to brown pigmentation, localized in typical places (primarily the décolleté area);
- Slight fine-plate peeling of rashes that appear on the skin;
- Intermittent itching of the spots, which is not very intense;
- The skin does not tan in the place where the rash is localized. This is explained by the functional inferiority of melanocytes - skin cells that produce pigment.
To determine if you actually have sunburn, visit a dermatologist. The doctor will check your skin with a lamp - the fungus has luminescent properties. If the skin glows pink or greenish-blue, a dermatologist will diagnose lichen.
In humans, the symptoms of pityriasis versicolor, in the form of itching and burning, are often not expressed. If the doctor suspects the presence of a fungal pathogen, he will send the patient for analysis of keratinized skin flakes.
Effect on pregnancy
Tinea versicolor often appears in pregnant women due to hormonal changes, but the disease cannot harm either the expectant mother or the child.
Treatment of pathology during the period of bearing a baby becomes problematic, because many drugs intended for local application or oral administration are prohibited, which is the main inconvenience.
The expectant mother should understand that treatment may take an indefinite period, so you should listen to the doctor’s recommendations and not make independent attempts to eliminate the disease.
Is it possible to cure pityriasis versicolor permanently?
If you follow medical recommendations, pityriasis versicolor responds well to treatment: the rash completely disappears in 2-3 weeks. But the infection tends to become chronic: in this case, relapses occur every time sweating increases, for example, in the warm season, when traveling on vacation, or during intense physical activity.
To avoid this, you must:
- consult a dermatologist at the first signs of the disease. At the initial stage, pityriasis versicolor can be easily confused with other skin infections: tinea versicolor, seborrheic dermatitis, eczema, vitiligo, and so on. Each disease requires specific treatment, which is why it is so important to recognize the disease as early as possible;
- refuse self-medication. Uncontrolled use of medications and the use of “folk remedies” will not only not lead to a cure, but can also aggravate the course of the infection;
- follow your doctor's recommendations. This applies to both the use of prescribed medications and personal hygiene.
In this case, the patient can quickly recover from pityriasis versicolor and avoid its relapse.
3. Signs and diagnosis of the disease
, asymmetrical spots up to 5 cm in size appear
, which merge over time, forming quite large foci. The edges are usually jagged and the color is yellow, pink, brown or white. Sun exposure often changes the color of the spots. Pityriasis-like peeling occurs on the surface, although inflammatory processes are rare. If papules and pustules appear, then most likely this is a consequence of other skin infections superimposing on the affected areas.
Foci of lichen are usually located on the back, neck, abdomen and shoulders, in the groin area.
If the head is affected, the hair in these places does not change at all. Sometimes pityriasis versicolor causes itchy skin.
It is used to examine foci of affected skin.
Wood's lamp, microscopic analysis, Balser's iodine test.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Can pityriasis versicolor be cured with iodine?
Iodine-containing products are used in the diagnosis of lichen versicolor. Yeast colonies are sensitive to iodine, causing them to absorb it to a much greater extent than surrounding healthy skin. Therefore, if you apply an iodine solution to the epidermis, the affected areas will be much darker.
But many patients believe that iodine is suitable not only for diagnosis, but also for self-treatment of pityriasis. An alcohol solution of iodine is a popular antiseptic that is often used to disinfect the skin. Fungi from the genus Malassezia, which cause tinea versicolor, are sensitive to it and are partially killed upon contact with this substance, but it is impossible to completely destroy them with iodine.
In addition, an alcohol solution of iodine greatly dries already damaged skin, which can lead to various complications of dermatosis.
As a result of self-medication:
- the disease drags on - recovery does not occur, and the rash spreads to new areas of the body;
- the likelihood of relapse increases - after the rash disappears, it appears again when the immune system is weakened and is chronic;
- new symptoms are added to the symptoms of the disease: tightness and dryness of the skin treated with iodine, itching may occur.
Pityriasis versicolor can be cured with antifungal medications prescribed by a dermatologist. Special creams and ointments affect only colonies of the pathogen and do not affect healthy epithelium. Also, many products contain care components that additionally moisturize the skin, accelerate its regeneration and promote the resumption of melanin synthesis.
Drug therapy
How to treat lichen versicolor on the body is best known to a dermatologist, so at the first suspicion you should make an appointment with him. Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis; the patient does not need a sick leave. If test results indicate impaired glucose tolerance, he is prescribed a low-carbohydrate diet. The patient should give up sweets, sugary drinks, some fruits, white bread and pastries, and consume potatoes, corn and white rice sparingly.
Treatment of tinea versicolor in humans is carried out:
- Keratolytic drugs that disrupt the connections between horny scales. This accelerates the renewal of the upper layers of skin, releasing the pathogen.
- Antimycotic agents that disrupt the life cycle of the fungus and prevent the spread of mycelium.
An antifungal cream or spray should be applied to affected areas twice a day for seven days. Typically, such a course of treatment completely eliminates the manifestations of the disease. Its disadvantage is that antifungal drugs are highly toxic.
An alternative treatment regimen includes the use of a keratolytic and natural antifungal drug to treat the damaged epidermis. An excellent remedy is a two percent alcohol solution of salicylic acid. After applying it, the affected areas should be lubricated with iodine or Fukortsin.
A mixture of salicylic acid, alcohol and resorcinol has a good therapeutic effect. Prescriptions are filled in state pharmacies. Boric acid in a 4% solution, which penetrates deeply into damaged tissues, prevents the growth of mycelium. But it cannot be used to treat children and pregnant women due to toxic effects.
Treatment using the Demyanovich method includes treating the skin with one of the following drugs:
- benzyl benzoate (20% solution);
- sulfur-salicylic ointment (10% solution);
- sodium hyposulfite (60% solution).
After them, the foci of the disease should be lubricated with a 6% solution of hydrochloric acid, which has a pronounced antifungal effect.
When widespread skin lesions or persistent recurrent course of the disease occur, the doctor prescribes two-week systemic treatment with Intraconazole tablets. If effectiveness is low, therapy can be repeated after a 14-day break
This drug should be used with caution in patients with liver disease