Oncologist compulsory medical insurance
Ivanova
Marina Viktorovna
5 years experience
Oncologist (CHI)
Make an appointment
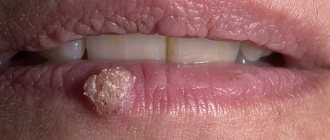
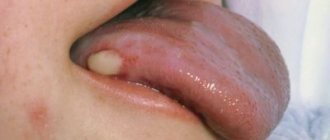
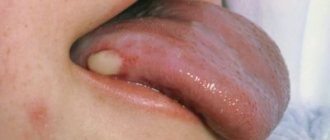
Tongue cancer is formed from malignantly modified epithelium covering the surface of the organ. Clinical manifestations of the disease include compactions, papillomatous growths, and ulcers on the surface. This is not the most common type of cancer, accounting for about 3% of all cancer cases. Tumors of the tongue are characterized by a fairly high degree of aggressiveness, growth and spread of metastases.
Kinds
Depending on the location of the tumor, cancer of the root of the tongue (about 20%), the body of the tongue (up to 70%), and the lower surface and base (about 10%) are distinguished. Based on the nature of growth, the following forms are distinguished:
- ulcerative, which is characterized by rapid decay of malignant cells with the formation of a bleeding ulcer;
- papillary, developing in the form of a growth on a broad base or on a thin stalk;
- infiltrative, penetrating into the thickness of the tissue and not having clearly defined boundaries.
According to histological type, up to 95% of neoplasms are squamous cell carcinoma. Other types of cells (adenocarcinomas, lymphoepitheliomas, etc.) are extremely rare.
Symptoms
Patients often ignore the initial signs of tongue cancer, since in the first stages the tumor remains painless and does not cause concern. Small growths, reddish or whitish spots appear on the surface of the organ, which are often mistaken for normal plaque. Small lumps may form that do not interfere with speech function and eating. Further development:
- ulcers that do not heal for a long time;
- enlarged lymph nodes under the jaw and on the neck;
- increased salivation;
- feeling of numbness in the tongue;
- voice change;
- speech disorders associated with deterioration of the movement of the tongue and lower jaw;
- pain in the tongue, sometimes radiating to the throat, neck, temples or ear;
- unpleasant odor caused by tissue decay.
The patient gets tired faster, his performance deteriorates, his body weight decreases for no apparent reason, and he suffers from attacks of nausea. With the appearance of metastases, the listed symptoms are supplemented by manifestations characteristic of other affected organs.
Cost of hemangiomas removal
| Laser tumor removal | Prices, rub. |
| Laser removal of papillomas, single warts - Cat. I. difficulties | 1200 |
| Laser removal of papillomas, multiple warts - Cat. I. difficulties | 350 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. II. difficulties | 700 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. III. difficulties | 1500 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - IV category. difficulties | 3000 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. V. difficulties | 4500 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. VI. difficulties | 6100 |
| CO2 Laser callus removal (per unit) | 6100 |
| Removal of atheroma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. I. difficulties | 6 900 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Category II. difficulties | 9 400 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. III. difficulties | 16 900 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - IV category. difficulties | 22 400 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. V. difficulties | 33 400 |
Sign up for laser removal of tongue hemangioma
- Full name
- Telephone
Causes and risk factors
The immediate cause of tongue cancer is a malignant modification of cells that stop responding to protein signals, lose their original function and begin to reproduce uncontrollably. The mechanism that triggers this process has not yet been sufficiently studied, however, long-term observations have made it possible to identify negative factors that increase the risk of tumor development:
- smoking tobacco and drinking strong alcoholic beverages;
- long-term mechanical injury to the tongue from an incorrectly made denture or a sharp fragment of a tooth;
- regular consumption of too hot or overly spicy foods, scalding drinks;
- chronic inflammation of oral tissues;
- precancerous conditions that remain untreated - leukoplakia, Bowen's disease, papillomavirus.
Men get sick several times more often than women. The majority of cases are in the age group over 40 years.
Prevention
- Quitting bad habits (smoking, alcohol).
- Elimination of tongue injury (high-quality treatment of fillings after their installation, correct selection and correct installation of dentures, timely treatment of dental chips).
- Regular oral hygiene, including professional.
- Timely detection of precancerous diseases of the tongue ( leukoplakia , dyskeratosis , papillomatosis ).
- Diet rich in vitamins . It has been proven that vitamin A and β-carotene are important in the prevention of neoplasms. With a deficiency of carotenoids, there is a risk of squamous cell carcinoma .
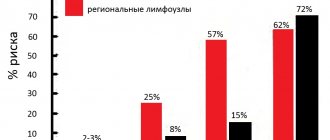
Stages
According to the generally accepted classification, tongue oncology has four stages, differing in the degree of spread of pathological tissue.
- The size of the affected area does not exceed 2 centimeters, the process has not spread to the lymph nodes and other organs.
- The tumor grows and grows into muscle tissue, but does not exceed 4 centimeters in size. Lymph nodes and other organs are not affected.
- The tumor spreads within the tongue and exceeds 4 centimeters in size, or can be of any size with metastasis to one regional lymph node.
- The malignant process spreads to most of the tissues of the oral cavity, metastases penetrate into distant lymph nodes and organs - liver, lungs, brain, bone tissue.
Diagnostics
When disturbing symptoms appear, tongue cancer is determined without alternative by visual examination only in advanced cases of the disease. As a rule, the patient first turns to the dentist, who refers him for a consultation with an oncologist. To make a final diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental studies are prescribed.
- Bacterioscopic analysis. A smear taken from the surface of the tumor is examined using a microscope to exclude bacterial inflammation of the tissue.
- Blood test for tumor markers.
- Biopsy. Using a hollow needle, a sample of pathological tissue is taken for examination.
- Histological analysis. The biopsy is dissected and examined under a microscope to determine the type of tumor based on the tissue structure.
- Cytological analysis. Using a microscope, the structure of the cells that make up the tumor is studied.
- Ultrasound of the head and throat. Allows you to determine how deeply the tumor has grown into the body of the tongue and surrounding tissues.
- Ultrasound of the liver. Necessary if distant metastases are suspected.
- Radiography. The most accessible study for the initial assessment of the prevalence of a neoplasm.
- CT scan of the facial skeleton and brain. The resulting images reveal metastases that have penetrated into the facial bones of the skull, meninges and tissues.
Attention!
You can receive free medical care at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) under the program of State guarantees of compulsory medical insurance (Compulsory health insurance) and high-tech medical care.
To find out more, please call +7, or you can read more details here...
Treatment
The treatment strategy depends on the stage of tumor development and the spread of the cancer process to other tissues. The most commonly used combination of several basic methods.
- Surgery. For a tumor whose size has not reached 4 centimeters, as a rule, it is limited to the removal of malignant tissue of the tongue and affected lymph nodes, if any. If the malignant process has spread to surrounding organs, surgical treatment is combined with other methods.
- Radiation therapy. Dosed hard radiation is used as the main method for some types of tumors that have not reached a large size. When malignant tissue grows, radiation precedes surgery to reduce the size of the tumor. After the intervention, radiation therapy is prescribed to destroy the remaining cancer cells and avoid relapse. In case of inoperable cancer of the tongue with metastases to distant organs and large-scale damage to surrounding tissues, radiation can prolong the patient’s life.
- Chemotherapy. Drugs that destroy cancer cells or inhibit their growth are usually used in combination with radiation therapy as a palliative treatment for inoperable patients, as well as before and after surgery. Polychemotherapy is most effective for the treatment of poorly differentiated tumors and metastases to distant organs.
- Targeted therapy. Targeted drugs do not destroy the tumor. By blocking a certain type of protein, they prevent cell division and the further development of the malignant process. They are used only after molecular genetic analysis confirms the presence of the desired type of proteins.
Observation
After treatment, you need to undergo regular examinations, their frequency depends on how many years have passed since entering remission.
- In the 1st year - every 1-3 months.
- In the 2nd year - every 2-6 months.
- In 3-5 years - every 4-8 months.
- In the 6th year and thereafter – annually.
The following manipulations and examinations are carried out as control tests:
- medical instrumental examination of the oral cavity, peripheral lymph nodes;
- examination by a dentist if radiation therapy was performed in the oral cavity;
- endoscopic examination of the pharynx and oral cavity;
- for patients who have previously smoked - MRI (CT) of the soft tissues of the neck with contrast, CT of the chest and abdominal cavity with contrast. If necessary, PET with glucose, osteoscintigraphy.
Diagnosis and treatment of tongue cancer in Moscow
If you find external signs of tongue cancer, contact the Medicina clinic for prompt and high-quality diagnosis. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, qualified oncologists provide treatment in accordance with the protocols of the world's leading clinics. The examination is carried out using the most modern diagnostic equipment available at the moment. For treatment and the subsequent rehabilitation period, we offer comfortable wards in the inpatient department, where patients receive professional care and high-quality medical service.
Our specialists
- Kiani Ali
Candidate of Medical Sciences, laser medicine specialist, dermatocosmetologist.
Sign up
- Stepanova Inna Igorevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, maxillofacial surgeon, specialist in laser medicine.
Sign up
- Fedotova Marina Andreevna
Surgeon, dermatocosmetologist, laser medicine specialist
Sign up
- Popovkin Pavel Sergeevich
Surgeon, oncologist, laser medicine specialist.
Sign up
Questions and answers
Is there a cure for tongue cancer?
Treatment of a tumor will be most successful if it is detected at an early stage of the disease. As the cancer process spreads to other organs, the effectiveness of treatment decreases, however, even in the most advanced cases, oncologists strive to prolong the patient’s life as much as possible.
How to determine tongue cancer?
It is impossible to independently determine that a spot or growth that appears on the tongue is a cancerous tumor. A histological analysis of the tissue is necessary to confirm or refute the suspicion of tongue cancer. If there are any suspicious signs, you must contact a qualified oncologist and undergo a special examination.
How long do people live with tongue cancer?
According to medical statistics, with timely detection and treatment of tongue cancer, patients live from 5 to 15 years. In the absence of medical care, the patient’s life expectancy does not exceed one and a half years.
Attention! You can cure this disease for free and receive medical care at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) under the State Guarantees program of Compulsory Medical Insurance (Compulsory Medical Insurance) and High-Tech Medical Care. To find out more, please call +7(495) 775-73-60, or on the VMP page for compulsory medical insurance