- Initial appointment with a dermatologist
1200 ₽ - Calling a dermatologist to your home
4000 ₽
The disease occurs as a result of weak immunity. After recovery in patients, the body is able to produce antibodies to the pathology. Pityriasis rosea is an infectious disease. Rashes form on the skin, they are curable if therapy is prescribed in a timely manner.
Women are susceptible to deprivation much more often than men; it occurs in children aged 10 years. Pregnant women are susceptible to pathology as a result of hormonal changes. The peak of the disease occurs in the off-season, with weakened immunity.
Clinic specialists treat the disease. They will identify the causes, conduct research and prescribe therapy.
Varieties of pityriasis rosea
- Typical form. It is formed from the mother's plaque.
- Antitypical shape. There is no redness, but vesicles and blisters appear on the body. Itching appears and spreads to the face; this is not typical for a typical pathology. A rash is observed, small bubbles form, which merge into one whole, the size is 10 cm.
The flaky atypical form has several stages:
- itching on the skin, small rashes;
- the formation of papules that have a rough, fine-grained surface;
- Whole lesions are observed, they are noticeable among uninfected areas of the skin.
Symptoms of lichen
What symptoms indicate that you have contracted lichen planus? It should be noted that lichen affects not only the skin of the body, but also mucous membranes, nails and even human hair. As a rule, any type of this disease begins with the appearance of the following symptoms:
- minimal increase in body temperature;
- the appearance of chills, mild headache, and sometimes nausea;
- later the temperature rises, and itching appears in certain places (face and body, less often - limbs);
- after a few hours, bubbles will appear at the site of redness, which soon burst and only a crust remains.
Symptoms of pityriasis rosea
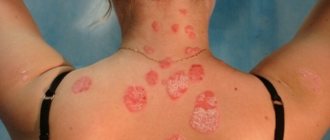
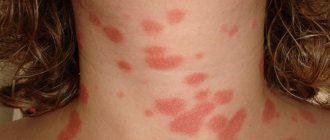
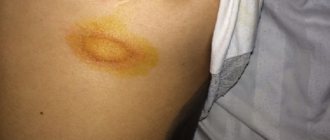
The patient has a large pink spot. Its diameter is 20 mm or more. After a few days, the plaque becomes pale and yellow in color. The skin begins to peel off in the infected area. After the formation of spots, 3-5 days later they are observed on the body, arms, their diameter is 1 cm. The spots are pink, round or cylindrical in shape. The rashes begin to dry out and scales appear in the form of folds.
The patient's health worsens. Weakness, fever, headache, drowsiness, myalgia, redness of the throat, and poor appetite are observed. Based on the symptoms, pityriasis can be mistaken for an allergy. In this case, self-medication will lead to a deterioration in the patient’s health. The symptoms of the pathology are similar to other dermatological diseases.
The spots cover the back, thighs, arms and cause itching. They form within 3 weeks, then slowly disappear. The total duration of the pathology is up to 2 months. Dermatologists at the medical clinic treat patients with severe and initial forms of the disease.
Pityriasis rosea - symptoms and treatment
Classic form of the disease
Symptoms of the classic form of pityriasis rosea are:[4]
- The mother's plaque is a single large flat oval spot, 2 to 5 cm in size, pink or red in color with clear boundaries, covered with thin scales and larger scales along the periphery, which gives it a ring-shaped appearance. The most typical localization is the neck, torso, and less commonly, limbs. It is the initial symptom of the disease.
- “Christmas tree” - rashes in the form of small (from 0.5 to 2 cm) numerous scaly papules and plaques of an oblong oval shape of pink color with a “collar” of gray scales located along the lines of Langer’s skin tension, which gives them when localized in the chest or back area looks like tree branches. This rash occurs several days (less often weeks) after the appearance of the maternal plaque.
- Itching is not a mandatory symptom of the disease and occurs in about a quarter of patients.
Atypical forms of the disease
Atypical variants of pityriasis rosea occur in approximately 20% of cases.[5] The uncharacteristic nature is manifested in the morphology of the elements of the rash, its size and location.[4] Some authors believe that children with atopic dermatitis are more predisposed to atypical variants of pityriasis rosea than adults.
Vesicular pityriasis rosea is a generalized rash of vesicles (vesicles) with a diameter of 2-6 mm, often forming “rosettes” and accompanied by severe itching. It is most common in children and adolescents and can be localized to the scalp, palms, and soles.[6]
Hemorrhagic pityriasis rosea is characterized by a purpuric eruption that occurs on the skin and, quite often, on the oral mucosa.[7]
Urticarial pityriasis rosea presents as blistering lesions, making it similar to hives. This type of disease is accompanied by intense itching.[7]
Papular pityriasis rosea is a rare form of the disease that is more common in young children and pregnant women. It manifests itself as rashes of several small papules measuring 1-2 mm, which may be present along with classic spots and plaques.[8]
Pityriasis rosea, similar to erythema multiforme - with this type of disease, along with the classic symptoms, target-shaped lesions are noted.[9]
Follicular pityriasis rosea is characterized by a rash of follicular papules grouped into round plaques. They often occur alongside classic lesions.[7]
Giant Darier's pityriasis rosea presents as very large plaques ranging from 5 cm to 7 cm, with individual lesions reaching the size of the patient's palm.[11]
Vidal's ring-shaped ring-shaped rosacea is localized primarily in the axillary and groin areas and is characterized by large ring-shaped rashes.[12]
Hypopigmented pityriasis rosea most often occurs in dark-skinned and dark-skinned people and presents as hypopigmented scaly plaques with a typical localization.[7]
Lichen rosea inversus is characterized by rashes in the folds - axillary and groin areas, elbow and popliteal fossae.[3]
Acral rosacea presents as a typical rash on the extremities—the forearm, wrist, palm, calf, and sole.[14]
Unilateral pityriasis rosea is an extremely rare variant that occurs in both children and adults. In this form, the rashes are located on one side of the body.[15]
Blaschkoid pityriasis rosea is characterized by lesions along Blaschko's lines (pattern-shaped pigmentation).[16]
Oral lesions in pityriasis rosea occur in 16% of patients in the form of erosions, bullous or hemorrhagic eruptions, but they are usually asymptomatic.[17]
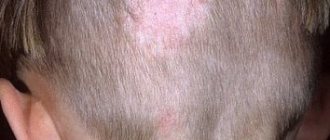
Asbestos pink lichen is a very rare form of the disease, presented in the form of plaques in the scalp area, covered with thick, dense gray scales. Clinically it mimics pityriasis amiantacea.[18]
Decapitated pityriasis rosea - rashes of only secondary small elements occur without the previous appearance of a maternal plaque. Occurs predominantly in children.[7]
Recurrent pityriasis rosea
Recurrence of pityriasis rosea occurs in 1-3% of patients.[19] Frequent relapses are considered a very rare occurrence. However, there are case reports with more than two episodes. The exact etiology is not known, but a possible cause is the reactivation of herpes viruses (varicella zoster, Epstein-Barr, types six and seven).[20]
Diagnosis of pityriasis rosea
The doctor will perform a diagnosis. At the first examination, he identifies the presence of a maternal plaque and determines the extent of the spread of rashes on the surface of the skin. Rarely, the pathology is similar to measles, eczema, rubella. The rash is similar to syphilis and is one of the signs of the disease.
Research is needed to confirm the disease. A urine and blood test will be required. If syphilis is suspected, a Wasserman test is performed. Also, a scraping is taken from the infected dermis and an examination is performed under a Wood's lamp. Diagnosing the disease in its early stages is difficult because maternal plaque is similar to other diseases. Doctors have extensive experience in treating pityriasis and will quickly identify it.
Diagnosis is prescribed by a dermatologist. Research is required to detect antibodies to the virus in a patient.
Treatment of lichen in adults
The diagnosis of lichen planus is made by a dermatologist; only in some cases additional tests are necessary. If the diagnosis is made incorrectly, then treatment can bring a negative result, which can lead to the transition of the disease to the chronic stage.
Treatment of lichen planus should be comprehensive. Only a doctor can select a remedy that will help to cope with the disease as much as possible, taking into account the stage of infection and its extent within certain areas of the body.
Differential diagnosis of pityriasis rosea with other diseases
The disease is differentiated from psoriasis, parapsoriasis, seborrheic eczema, syphilis, trichophytosis. The pathology differs from seborrheic eczema by the maternal plaque, the location of rashes that are not characteristic of eczema. Among other things, with seborrheic eczema the scales are often greasy.
Unlike psoriasis, lichen is spotty; it does not appear on the feet, hair, or hands. Difficult diagnosis is observed in the first stage of the disease.
There is a similarity between the disease and parapsoriasis; the spots may be similar. However, peeling and identical spots are not characteristic of lichen.
Lichen differs from syphilitic roseola in its brightness and the presence of peeling, since this is rarely found with syphilis.
Treatment of pityriasis rosea
To eliminate the disease, the dermatologist prescribes ointments, creams and tablets. These include:
- Acyclovir. It is used to inhibit pathogens. Experts advise applying cream or ointment every 4 hours. You can take the medicine in tablets.
- Flucinar. Reduces the formation of allergies, used for external use.
- Sinaflan. The medicine is an antihistamine, it is prescribed when lichen appears in children from 3 years of age and in adults. It is not recommended to use it for more than 7 days.
- Lokoid. Helps with allergies for women and when breastfeeding.
- Lorinden. Restores immunity, renews sleep, speeds up the healing process.
- Salicylic and zinc ointments. They have an antiseptic effect, prevent new skin rashes, and the spots dry out very quickly.
Dermatologists prescribe antiviral and antihistamine medications for therapy. If the pathology appears as a result of infection, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. Hormonal medications are prescribed in severe cases, if the disease is complicated by other chronic diseases.
For prolonged lichen, patients are prescribed antiviral drugs, it is recommended to treat stains with salicylic alcohol, as well as the use of ointments.
For symptoms of intoxication, the doctor prescribes activated charcoal as an auxiliary medicine.
The doctor prescribes antihistamines during therapy. These include Claritin, Tavegil, Loratadine, Suprastin. Taking medications is possible only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Why should you contact our clinic?
Dermatologists of the highest category
Experienced dermatologists in Moscow. Experience of specialists from 15 years.
Modern equipment
Modern equipment from the world's best manufacturers.
Expert class equipment
Ultrasound is performed using expert-class equipment manufactured by General Electric, SONY, Mindray.
Tests and ultrasound on the day of treatment
Tests, x-rays, ultrasound with interpretation, dressings on the day of treatment in Moscow.
Consultations for adults and children
A network of dermatological clinics in Moscow. Clinics near the metro.
Experienced doctors
Our experienced doctors with over 15 years of experience. Candidates of Medical Sciences.
Methods of treating the disease
With uncomplicated pityriasis rosea, the patient needs to change his lifestyle:
- avoid skin irritation in the rash area;
- use a soft washcloth when bathing, and it is better to reduce the water procedures themselves to a minimum;
- follow a hypoallergenic diet;
- exclude the use of cosmetics for the skin;
- Do not wear synthetics and woolen items until recovery.
In case of a protracted process and complications, the doctor may prescribe:
- antiviral agents;
- local antibacterial agents - ointments (in case of infection);
- treating stains with salicylic alcohol.
After healing, the skin on the affected area may darken or become lighter, but will soon return to normal.
In case of incorrect treatment:
- using products that irritate the skin;
- improper bathing;
- with hyperhidrosis;
- the presence of allergies - rashes can persist for a long time and cover the entire body.
Therefore, it is important not to self-medicate. The diagnosis of pityriasis rosea must be confirmed by a dermatovenerologist.
Prevention of pityriasis rosea
- regular walks;
- reduce consumption of fatty foods and foods containing dyes;
- include multivitamins in your diet only on the recommendation of a dermatologist;
- change bed linen and clothes regularly;
- Perform water procedures regularly;
- undergo preventive examinations;
- avoid stress;
- Do not use hard washcloths that irritate the skin.
The diet should be balanced; our doctors will recommend that the patient monitor the amount of carbohydrates and proteins. It is better to include fermented milk products, cereals, bread, and lean beef in the menu. Vegetables and berries are useful for treating the disease.
Complication of pityriasis rosea
Relapses do not occur very often, but in some cases there are complications. These include folliculitis, eczema, osteofolliculitis and others. Re-infection can occur as a result of wearing uncomfortable clothes, not following therapy, or in people who suffer from allergies.
Secondary disease is typical on skin that is subject to stretching: thighs, groin, forearms. Infection appears in the sweat glands or on the skin of the face. If you notice the appearance of lichen, immediately contact a specialist. Timely treatment will avoid negative consequences.
Carefully! Ringworm (microsporia)
What is microsporia?
Microsporia (ringworm) is a fungal disease caused by various types of fungi of the genus Microsporum, which affects the skin or hair.
Microsporia is the most common fungal infection, not counting foot fungus. The disease occurs everywhere. Microsporia is very contagious. Children get sick more often.
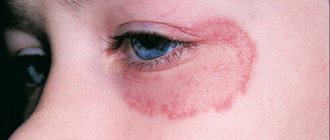
With microsporia of smooth skin, at the site of penetration of the fungal pathogen, a swollen spot appears, pale pink in color with clear boundaries in the form of a raised ridge of bright red color, i.e. the lesion has the appearance of a ring or oval. Most often these lesions are located on the skin of the face, neck, forearms and shoulders. Moderate itching may be bothersome.
With microsporia of the skin of the scalp, foci of microsporia of the skin of the scalp are located mainly on the crown, in the parietal and temporal regions. Usually these are 1-2 large lesions from 2 to 5 cm with rounded outlines and clear boundaries. Along the periphery of large lesions there may be screenings - small lesions with a diameter of 0.5-1.5 cm. At the beginning of the disease, a peeling area forms at the site of the lesion. After a week, scalp hair is affected, becoming brittle, breaking off 4-6 mm above the skin level and looking as if it had been trimmed (hence the second name for the disease, “ringworm”). Mostly children aged 5-12 years are affected.
How do children become infected?
The main source of the disease is cats (usually kittens), less often dogs. Microsporia of stray cats and dogs is especially common. The causative agent of microsporia, the fungus microsporum, is stable in the external environment, in hair, in skin flakes, wool that fall into sandboxes, contained in sand or dust of basements, entrances with irregular cleaning, and retains the ability to become infected for several years. But the main route of infection is direct contact with sick cats and dogs, when children stroke them, pick them up, caress them, or play with them.
You can also become infected through household items - combs, underwear, etc. When animals become ill, areas of baldness are located on the face, ears, paws, most often on the front ones. Often, apparently healthy cats can be carriers of the fungus, and then microsporia can be detected using fluorescent light; the examination can be done at a veterinary station where sick animals need to be treated.
The latent period of the disease in people is from 5-7 days to 5-6 weeks (this is the time from the fungus getting on the skin until the first signs of the disease appear).
How to prevent infection with microsporia?
Several rules must be followed:
- exclude contact with stray animals;
- Ensure that children thoroughly wash their hands with soap after playing outside or after playing with animals; Do not play with stray or strange animals under any circumstances;
- contact a veterinary station for examination and registration of your new pet;
- do not throw cats or dogs outside, which will lead to diseases that primarily infect children;
- monitor the cleanliness of children’s skin, hair, and nails;
- do not use other people’s hats, combs, towels, or clothes;
- wash your hair with hot water and detergent immediately after cutting your hair at the hairdresser.
Note! If microsporia is suspected, preparation for the study is the basis for a high-quality test result: Before the study, the patient must exclude:
- use of antifungal drugs (solutions, creams, ointments);
- taking systemic antimycotics;
- use of cosmetics;
- treating the affected area with soap.
Remember that in case of such a disease, you need to see a dermatovenerologist (at a convenient address for you)!
Consultative and diagnostic departments of the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution "SOKVD"
Main body:
Address: Samara, st. Venceka 35
Telephone
Consultative and diagnostic department No. 1 (KDO No. 1)
Address: st. Kirov Avenue, 242,
telephone
Consultative and diagnostic department No. 2 (KDO No. 2)
Address: st. Revolutionary, 138,
telephone
Consultative and diagnostic department No. 3 (KDO No. 3)
Address: st. N. Panova, 8,
phone:8
Consultative and diagnostic department of the city. Novokuibyshevsk
Address: st. Chernyshevsky, 1 "A",
phone: 8 (846) 35-6-84-93
Consultative and diagnostic department of the city. Chapaevsk
Address: st. Lenina, 5,
phone:8(846)39-2-23-45.
GBUZ SO "Togliatti KVD"
Address: Tolyatti, Avtozavodskoe highway, 7;
Phone: 8-8482-22-64-14
Clinical and diagnostic department of the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution SO "TKVD" Zhigulevsk
Address: Zhigulevsk, Pervomaiskaya st., 10,
Phone: 8-848-62-2-11-47
GBUZ SO "Syzran KVD"
Address: Syzran, Internationalnaya str., 13
Phone: 8-8464-98-15-02
Residents of rural areas (according to the territorial principle) - go to the dermatovenerological office of the Central Regional Hospital.
Pityriasis rosea in children
Pityriasis is diagnosed in children over 5 years of age. The dermatologist prescribes antihistamines and multivitamins to patients, which restore the immune system. For children under 2 years of age, the doctor prescribes antiseptics and zinc ointment.
Children with weak immunity are susceptible to pathology in the fall and spring. The disease is diagnosed more often in girls, less often in boys. Rashes are rare in infants. The reason is overheating or hypothermia of the baby.
Causes of skin disease:
- allergic reactions to foods or fabrics;
- intestinal disorder;
- depression, emotional turmoil;
- insect bites.
The specialist will recommend medications to speed up recovery. The disease period is up to 2 months. To destroy microorganisms, it is necessary to take antibiotics, and for allergies - antihistamines. At high temperatures, the doctor prescribes antipyretic tablets.
Pityriasis rosea during pregnancy
The appearance of pityriasis is frequent with hormonal changes in the patient’s body or with a reaction to any foods. The pathology can be dangerous for the health of mother and baby, but it causes discomfort, itching and spots appear. The cause of the disease is weak immunity.
During lactation, women are not prescribed hormonal or antiviral drugs. When itching occurs, the dermatologist prescribes antihistamines, taking into account the woman’s condition. Ointments containing zinc are prescribed as external agents.
In pregnant women in the early stages, lichen has a negative effect on the fetus, since the disease is infectious. The child will not be able to become infected, but there is a possibility of miscarriage or the birth may be premature. Patients who are up to 15 weeks pregnant are susceptible to infection.
If lichen appears, you should consult a doctor. He will prescribe antihistamines in case of swelling, antibiotics if the disease causes complications. He will also prescribe vitamins C, A, B. Sedatives will need to be taken if there is a risk to the fetus. Taking medications on your own is not recommended, as this may have a negative effect on the child.